spring路径通配符
在应用Spring的工程中,使用class path的方式加载配置文件应该是最常用的做法,然而对大部分人来说,刚开始使用Spring时,几乎都碰到过加载配置文件失败的情况,除了配置上的错误外,很多时候是因为配置文件的路径和程序中指定的加载路径不一致,从而导致配置文件找不到,或是加载了错误地方的配置文件。本文将就Spring如何从class path中加载配置文件做一些简要的分析。
classpath:与classpath*:的区别在于,前者只会从第一个classpath中加载,而后者会从所有的classpath中加载
如果要加载的资源,不在当前ClassLoader的路径里,那么用classpath:前缀是找不到的,这种情况下就需要使用classpath*:前缀
另一种情况下,在多个classpath中存在同名资源,都需要加载,那么用classpath:只会加载第一个,这种情况下也需要用classpath*:前缀
可想而知,用classpath*:需要遍历所有的classpath,所以加载速度是很慢的,因此,在规划的时候,应该尽可能规划好资源文件所在的路径,尽量避免使用classpath*
情形一:使用classpath加载且不含通配符
这是最简单的情形,Spring默认会使用当前线程的ClassLoader的getResource方法获取资源的URL,如果无法获得当前线程的ClassLoader,Spring将使用加载类org.springframework.util.ClassUtils的ClassLoader。
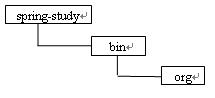
1.当工程目录结构如图所示:
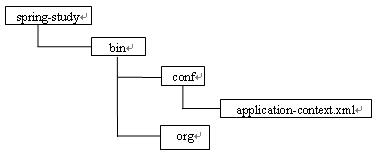
即配置文件放在bin目录中的conf文件夹里,这时使用
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("conf/application-context.xml");来创建ApplicationContext对象的话,Spring将加载bin/conf目录下的application-context.xml文件。Spring启动时的输出显示为:
Loading XML bean definitions from
class path resource [conf/application-context.xml]
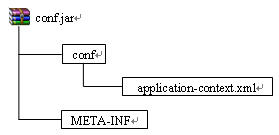
这时使用
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("conf/application-context.xml");来创建ApplicationContext对象的话,Spring将加载conf.jar文件中conf目录下的application-context.xml文件。Spring启动时的输出显示为:
Loading XML bean definitions from
class path resource [conf/application-context.xml]
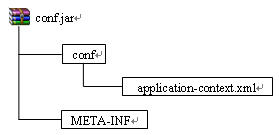
这时使用
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("conf/application-context.xml");来创建ApplicationContext对象的话,由于没有使用classpath*前缀,Spring只会加载一个application-context.xml文件。在eclipse中将会加载bin/conf目录下的application-context.xml文件,而jar包中的conf/application-context.xml并不会被加载,Spring启动时的输出显示为:
Loading XML bean definitions from
情形二:使用classpath加载,包含通配符
碰到通配符的情况时,Spring会通过使用路径中的非通配符部分先确定资源的大致位置,然后根据这个位置在确定具体的资源位置,结合下面给出的几种情况可以更好地理解Spring的这种工作方式

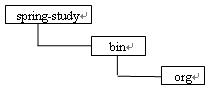
即配置文件放在bin目录中的conf文件夹里,这时使用
ApplicationContext context = new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("conf/**/*application-context.xml");
来创建ApplicationContext对象的话,Spring首先会通过路径中的非通配符部分即conf,先确定conf的路径,即bin/conf目录,然后从该目录下加载配置文件,由于使用了/**/的方式,表明要加载conf目录下包括各级子目录中的所有配置文件,因此bin/conf/application-context.xml文件和
bin/conf/admin/admin-application-context.xml都会被加载,Spring启动时的输出显示为:
Loading XML bean definitions from file
[D:\myworkspace\spring-study\bin\conf\admin\admin-application-context.xml]
Loading XML bean definitions from file
[D:\myworkspace\spring-study\bin\conf\application-context.xml]

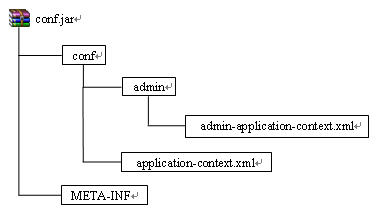
这时使用
ApplicationContext context = new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("conf/**/*application-context.xml");来创建ApplicationContext对象的话,Spring首先会通过路径中的非通配符部分即conf,先确定conf的路径,即conf.jar中的conf目录,然后从该目录下加载配置文件,由于使用了/**/的方式,表明要加载conf目录下包括各级子目录中的所有配置文件,因此conf/application-context.xml文件和
conf/admin/admin-application-context.xml都会被加载,Spring启动时的输出显示为:
Loading XML bean definitions from class path resource
[conf/admin/admin-application-context.xml]
Loading XML bean definitions from class path resource
[conf/application-context.xml]

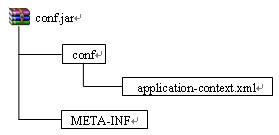
这时使用
ApplicationContext context = new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("conf/**/*application-context.xml");来创建ApplicationContext对象的话,Spring首先会通过路径中的非通配符部分即conf,先确定conf的路径,在eclipse中是bin/conf目录,然后从该目录下加载配置文件,由于使用了/**/的方式,表明要加载conf目录下包括各级子目录中的所有配置文件,因此bin/conf/application-context.xml文件和
bin/conf/admin/admin-application-context.xml都会被加载,但conf.jar文件中的配置文件并不会被加载,Spring启动时的输出显示为:
Loading XML bean definitions from file
[D:\myworkspace\spring-study\bin\conf\admin\admin-application-context.xml]
Loading XML bean definitions from file
情形三:使用classpath*前缀且不包含通配符
使用classpath*前缀可以获取所有与给定路径匹配的classpath资源,从而避免出现两个不同位置有相同名字的文件,Spring只加载其中一个的情况。

这时使用
ApplicationContext context = new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath*:conf/application-context.xml");来创建ApplicationContext对象的话, Spring将会加载bin目录下的application-context.xml文件和jar包里的application-context.xml文件,Spring启动时的输出显示为:
Loading XML bean definitions from URL
[file:/D:/myworkspace/spring-study/bin/conf/application-context.xml]
Loading XML bean definitions from URL
[jar:file:/D:/myworkspace/conf1.jar!/conf/application-context.xml]
情形四:使用classpath*前缀,包含通配符
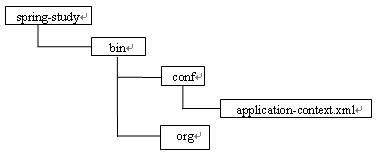
当工程目录结构如图所示:
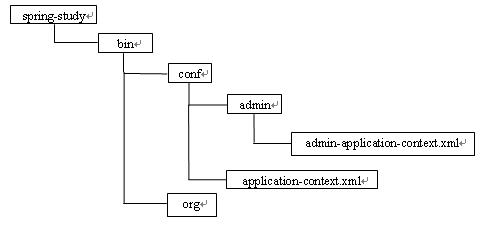

这时使用
ApplicationContext context = new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath*:conf/**/*application-context.xml");来创建ApplicationContext对象的话,Spring首先会通过路径中的非通配符部分即conf,先确定conf的路径,由于使用了classpaht*前缀,因此bin目录下的conf和jar包里的conf都会被加载,同时由于使用了/**/的方式,表明要加载conf目录下包括各级子目录中的所有配置文件,因此bin/conf/application-context.xml和
bin/conf/admin/admin-application-context.xml以及jar包中的
conf/application-context.xml和
conf/admin/admin-application-context.xml都会被加载,Spring启动时的输出显示为:
Loading XML bean definitions from file
[D:\myworkspace\spring-study\bin\conf\admin\admin-application-context.xml]
Loading XML bean definitions from file
[D:\myworkspace\spring-study\bin\conf\application-context.xml]
Loading XML bean definitions from URL
[jar:file:/D:/myworkspace/conf1.jar!/conf/admin/admin-application-context.xml]
Loading XML bean definitions from URL
[jar:file:/D:/myworkspace/conf1.jar!/conf/application-context.xml]
特别注意:

spring路径通配符的更多相关文章
- spring的路径通配符
Spring提供了强大的Ant模式通配符匹配,从同一个路径能匹配一批资源. Ant路径通配符支持"?"."*"."**",注意通配符匹配不包 ...
- spring 路径配置通配符是如何实现的
在spring的配置文件中.经常看见类似这样的配置路径: classpath:/com/module/**/*sql.xml 系统会根据配置路径自动加载符合路径规则的xml文件. Spring还提供了 ...
- spring3: 4.4 使用路径通配符加载Resource
4.4.1 使用路径通配符加载Resource 前面介绍的资源路径都是非常简单的一个路径匹配一个资源,Spring还提供了一种更强大的Ant模式通配符匹配,从能一个路径匹配一批资源. Ant路径通配 ...
- Java使用路径通配符加载Resource与profiles配置使用
序言 Spring提供了一种强大的Ant模式通配符匹配,能从一个路径匹配一批资源. Ant路径通配符 Ant路径通配符支持“?”.“*”.“**”,注意通配符匹配不包括目录分隔符“/”: “?”:匹配 ...
- Spring中通配符
一.加载路径中的通配符:?(匹配单个字符),*(匹配除/外任意字符).**/(匹配任意多个目录) classpath:app-Beans.xml 说明:无通配符,必须完全匹配 classpath: ...
- Spring中通配符问题
一.加载路径中的通配符 (1)?(匹配单个字符) (2)*(匹配除/外任意字符) (3)**/(匹配任意多个目录) 示例: (1)classpath:app-Beans.xml 说明:无通配符,必须完 ...
- Spring中通配符(转)
一.加载路径中的通配符:?(匹配单个字符),*(匹配除/外任意字符).**/(匹配任意多个目录) classpath:app-Beans.xml 说明:无通配符,必须完全匹配 classpath: ...
- Spring:通配符的匹配很全面, 但无法找到元素 XXXXX' 的声明
问题:配置Spring的时候容易发生如题的这样一个经常性的错误,错误如下(以context为例) org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefini ...
- Spring @CrossOrigin 通配符 解决跨域问题
@CrossOrigin 通配符 解决跨域问题 痛点: 对很多api接口需要 开放H5 Ajax跨域请求支持 由于环境多套域名不同,而CrossOrigin 原生只支持* 或者具体域名的跨域支持 所以 ...
随机推荐
- 开发中可能会用到的几个 jQuery 小提示和技巧(转)
今天,我们将分享一些很有用的技巧和窍门给 jQuery 开发人员.jQuery 是最好的 JavaScript 库之一,用于简化动画,事件处理,支持 Ajax 和 HTML 的客户端脚本.网络中有大量 ...
- win8 修改msconfig 里面的"引导高级选项" 最大内存后 BSOD的解决方案
最近由于本人的电脑一直非常卡,于11.4日通过win8任务管理器分析发现 Peer Name Resolution Protocol Peer Networking Grouping Peer Net ...
- MVC bundle(CSS或JS)
无论是有asp还是asp.net,还是php做网站经验的都知道当我们需要css或者js文件的时候我们需要在<head></head>标签中间导入我们需要的js或者css文件的路 ...
- 微信电脑版也能用公众号自定义菜单 微信1.2 for Windows发布
昨日,微信电脑版发布更新,版本为微信1.2 for Windows,最大的特色就是加入了保存聊天记录功能,可以使用公账号菜单,手机上收藏的表情也能在电脑版上发送,可以接收转账消息. 本次微信pc版更新 ...
- Mac下使用Apache TCPMon
Mac下使用Apache TCPMon 参考链接: TCPMon Tutorial Anyone know how to get TCPMON working on a mac? Apache TCP ...
- 编写更好的CSS
编写好的CSS代码能提升页面的渲染速度.本质上,一条规则都没有引擎解析的最快.MDN上将CSS选择符归拆分成四个主要类别,如下所示,性能依次降低. ID 规则 Class 规则 标签规则 通用规则 对 ...
- MapReduce数据流向分析
MR数据流向示意图 步骤 1 输入文件从HDFS流向Mapper节点.在一般情况下,map所需要的数据就存在本节点,这就是数据本地化计算的优势,但是往往集群中数据分布不均衡(1000台节点,数据冗余度 ...
- Chapter 4
1.Python中有四种函数:全局函数,局部函数,lambda函数,方法.其中全局函数与局部函数对比理解,局部函数就是定义在某函数之内的函数,否则就是全局函数,lambda函数就是表达式,方法就跟对象 ...
- 由浅入深了解Thrift之结果封装
一.thrift返回结果封装 Thrift文件添加版本号,方便对thrift的版本进行控制 服务与返回的数据类型分开定义 在项目中使用Thrift提供RPC服务时,很多情况下我们都会将返回的结果进行封 ...
- (转)单机上配置hadoop
哈哈,几天连续收到百度两次电话,均是利好消息,于是乎不知不觉的自己的工作效率也提高了,几天折腾了好久终于在单机上配置好了hadoop,然后也成功的运行了一个用例,耶耶耶耶耶耶. 转自:http://w ...
