策略模式(Strategy
Strategy
无论什么程序,其目的都是解决问题。而为了解决问题,我们又需要编写特定的算法。使用Strategy模式可以整体地替换算法的实现部分。能够整体地替换算法,能让我们轻松地以不同的算法去解决同一个问题,这种模式就是Strategy模式。(整体替换算法)
理清职责
|名字|说明
|Hand表示猜拳游戏中的“手势”的类
|strategy|表示猜拳游戏中的策略的类
|Winningstrategy |表示“如果这局猜拳获胜,那么下一局也出一样的手势”这一策略的类表示“根据上一局的手势从概率上计算出下一局的手势从之前的猜拳结果计算下一局|
|Probstrategy出各种拳的概率”这一策略的类
|Player表示进行猜拳游戏的选手的类
|Main测试程序行为的类具体说明
- 比如C++ 的STL 的Sort 以及在Java中Arrays.sort()都是可以使用策略模式来根据情况构造解决办法的
- 如果使用Strategy模式,在程序运行中也可以切换ConcreteStrategy角色。例如,在内存容量少的运行环境中可以使用slowButLessMemoryStrategy(速度慢但省内存的策略),而在内存容量多的运行环境中则可以使用FastButMoreMemorystrategy(速度快但耗内存的策略)。
UML
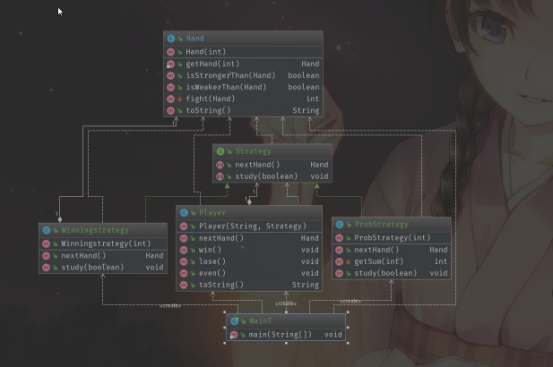
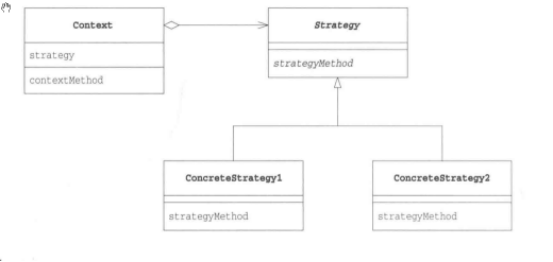
Code
- Hand:
public class Hand {// 石头private static final int HANDVALUE_GUU=0;// 剪刀private static final int HANDVALUE_GHO=1;// 布private static final int HANDVALUE_PAA=2;private static final Hand[] HANDS=new Hand[]{new Hand(HANDVALUE_GUU),new Hand(HANDVALUE_GHO),new Hand(HANDVALUE_PAA),};public static final String name[]={"石头","剪刀","布"};private int handvalue;public Hand(int handvalue) {this.handvalue = handvalue;}public static Hand getHand(int handvalue){return HANDS[handvalue];}// 胜利public boolean isStrongerThan(Hand hand){return fight(hand)==1;}// 战败public boolean isWeakerThan(Hand hand){return fight(hand)==-1;}/*** 计分: 平 0 胜1 负 -1* @param hand* @return*/private int fight(Hand hand) {if(this==hand){return 0;}else if((this.handvalue+1)% 3 ==hand.handvalue){return 1;}else{return -1;}}@Overridepublic String toString() {return name[this.handvalue];}}
- Player
public class Player {private String name;private Strategy strategy;private int wincount;private int losrcount;private int gamecount;public Player(String name, Strategy strategy) {this.name = name;this.strategy = strategy;}public Hand nextHand(){return strategy.nextHand();}/*** 分别是 胜利 负 平局*/public void win(){strategy.study(true);gamecount++;wincount++;}public void lose(){strategy.study(false);losrcount++;gamecount++;}public void even(){gamecount++;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Player{" +"wincount=" + wincount +", losrcount=" + losrcount +", gamecount=" + gamecount +'}';}}
- ProbStrategy
public class ProbStrategy implements Strategy {private Random random;public ProbStrategy(int seed) {this.random=new Random(seed);}private int pevHandValue=0;private int currentHandValue=0;private int [] [] history=new int[][]{{1,1,1},{1,1,1},{1,1,1}};/*** 如果该随机数在0至3(不含3)之间,那么出石头* 如果该随机数在3至8(不含8)之间,那么出剪刀* 如果该随机数在8至15(不含15)之间,那么出布* @return*/@Overridepublic Hand nextHand() {int bet=random.nextInt(getSum(currentHandValue));int handValue=0;if(bet<history[currentHandValue][0]){handValue=0;}else if(bet<(history[currentHandValue][0]+history[currentHandValue][1])){handValue=1;}else {handValue=2;}pevHandValue=currentHandValue;currentHandValue=handValue;return Hand.getHand(handValue);}private int getSum(int currentHandValue) {int sum=0;for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {sum+=history[currentHandValue][i];}return sum;}@Overridepublic void study(boolean win) {if(win){history[pevHandValue][currentHandValue]++;}else{history[pevHandValue][(currentHandValue+1)%3]++;history[pevHandValue][(currentHandValue+2)%3]++;}}}
- Strategy
public interface Strategy {/*** nextHand方法的作用是“获取下一局要出的手势”。调用该方法后,* 实现了strategy接口的类会绞尽脑汁想出下一局出什么手势。* @return*/Hand nextHand();/***study方法的作用是学习“上一局的手势是否获胜了”。* 如果在上一局中调用nextHand方法获胜了,就接着调用study(true);* 如果输了,就接着调用study(false)。这样,Strategy接口的实现类就会改变自己的内部状态,* 从而为下一次nextHand被调用时究竟是返回“石头”“剪刀”还是“布”提供判断依据。* @param win*/void study(boolean win);}
- Winningstrategy
public class Winningstrategy implements Strategy {private Random random;// 存储上一局状态private boolean won=false;private Hand preHand;/*** 有预见性的随机数种子* @param seed*/public Winningstrategy(int seed) {this.random =new Random(seed);}@Overridepublic Hand nextHand() {if (!won) {preHand= Hand.getHand(random.nextInt(3));}return preHand;}@Overridepublic void study(boolean win) {won=win;}}
- 测试
public class MainT {public static void main(String[] args) {Player tom = new Player("tom", new Winningstrategy(2));Player cat = new Player("cat", new ProbStrategy(3));for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {Hand hand = tom.nextHand();Hand hand1 = cat.nextHand();if(hand.isStrongerThan(hand1)){System.out.println("tom is win");tom.win();cat.lose();}else if(hand1.isStrongerThan(hand)){System.out.println("cat is win");cat.win();tom.lose();}else{System.out.println("Even----");cat.even();tom.even();}}System.out.println(tom);System.out.println(cat);}}
策略模式(Strategy的更多相关文章
- 设计模式(一):“穿越火线”中的“策略模式”(Strategy Pattern)
在前段时间呢陆陆续续的更新了一系列关于重构的文章.在重构我们既有的代码时,往往会用到设计模式.在之前重构系列的博客中,我们在重构时用到了“工厂模式”.“策略模式”.“状态模式”等.当然在重构时,有的地 ...
- 【转】设计模式 ( 十八 ) 策略模式Strategy(对象行为型)
设计模式 ( 十八 ) 策略模式Strategy(对象行为型) 1.概述 在软件开发中也常常遇到类似的情况,实现某一个功能有多种算法或者策略,我们可以根据环境或者条件的不同选择不同的算法或者策略来完成 ...
- 设计模式 ( 十八 ) 策略模式Strategy(对象行为型)
设计模式 ( 十八 ) 策略模式Strategy(对象行为型) 1.概述 在软件开发中也经常遇到类似的情况,实现某一个功能有多种算法或者策略,我们能够依据环境或者条件的不同选择不同的算法或者策略来完毕 ...
- 设计模式 - 策略模式(Strategy Pattern) 具体解释
策略模式(Strategy Pattern) 具体解释 本文地址: http://blog.csdn.net/caroline_wendy/article/details/26577879 本文版权全 ...
- HeadFirst设计模式读书笔记(1)-策略模式(Strategy Pattern)
策略模式(Strategy Pattern): 定义了了算法簇,分别封装起来,让它们之间可以相互替换,此模式让算法的变化独立于使用算法的客户端. 第一个设计原则:找出应用中可能需要变化之处,把他们独立 ...
- 乐在其中设计模式(C#) - 策略模式(Strategy Pattern)
原文:乐在其中设计模式(C#) - 策略模式(Strategy Pattern) [索引页][源码下载] 乐在其中设计模式(C#) - 策略模式(Strategy Pattern) 作者:webabc ...
- 反馈法学习设计模式(一)——策略模式Strategy Pattern
简介(Introduction) 之前学习Java8实战时,遇到一个很好的策略模式示例.便想着借着这个示例结合反馈式的方法来,学习策略设计模式,也以便后面反复琢磨学习. 首先我们通过练习,逐步写出符合 ...
- 策略模式 Strategy 政策Policy 行为型 设计模式(二十五)
策略模式 Strategy 与策略相关的常见词汇有:营销策略.折扣策略.教学策略.记忆策略.学习策略.... “策略”意味着分情况讨论,而不是一概而论 面对不同年龄段的人,面对不同的商品,必然将会 ...
- 策略模式-Strategy(Java实现)
策略模式-Strategy 在策略模式中,一个类(策略使用者)可以更改自己的执行策略. 比如以排序算法为例子, 多种排序算法都归属于排序算法, 但是实现的算法细节不同, 使用者可以很轻松地替换策略, ...
- [.net 面向对象程序设计深入](26)实战设计模式——策略模式 Strategy (行为型)
[.net 面向对象程序设计深入](26)实战设计模式——策略模式 Strategy (行为型) 1,策略模式定义 策略模式定义了一系列的算法,并将每一个算法封装起来,而且使它们还可以相互替换.策略模 ...
随机推荐
- noip退役赛
上下午 6 题一起考 自闭了 T1 小明要参加一场比赛,赛制给你一个表格 $p$ ,$p_{(i,j)}$ 表示他在第 $i$ 场比赛前如果输了 $j$ 场,他这一场赢的概率,他也可以故意输掉任意多场 ...
- PythonPath在Windows 下的设置
今天在调试Evernote SDK时, 遇到PythonPath的问题. 查了很多资料,有说用系统环境变量添加PythonPath, 有说在注册表中的PythonPath添加新Default字段, 但 ...
- NSDictionary 用法
//Dictionary //不可变 //字典里面:是以键值对存放的 //字典存放顺序是无序的 //字典里面:value可以重复,但key不能重复 //字典里面:key一般用字符串表示,value可用 ...
- Poj1159 Palindrome(动态规划DP求最大公共子序列LCS)
一.Description A palindrome is a symmetrical string, that is, a string read identically from left to ...
- 【转】Pro Android学习笔记(三十):Menu(1):了解Menu
目录(?)[-] 创建Menu MenuItem的属性itemId MenuItem的属性groupId MenuItem的属性orderId MenuItem的属性可选属性 Menu触发 onOpt ...
- C#的闭包
简单的理解:闭包变量是把局部变量的作用域扩展到回调函数,发生在匿名方法注册到委托上,而匿名方法中使用外部的局部变量 说什么都不如图示那么容易明白啊 先看C#的源码 class Program { st ...
- 4.JasperReports学习笔记4-查询数据库生成动态的报表(WEB)
转自:http://www.blogjava.net/vjame/archive/2013/10/12/404908.html 第一种方式: sql语句中定义查询条件,报表中定义接收参数 第二种方式: ...
- jquery 键盘事件的使用方法详解
转自:https://www.jb51.net/article/123579.htm jQuery处理键盘事件有三个函数,根据事件发生的顺序分别是: jquery 代码: 1. keydown(); ...
- 关于request的几个字段值
domain: localhost host: localhost:9000 url: /wechat/mynews action: WechatController.myNews path: /we ...
- tar压缩解压缩
Linux下的tar压缩解压缩命令详解tar -c: 建立压缩档案-x:解压-t:查看内容-r:向压缩归档文件末尾追加文件-u:更新原压缩包中的文件 这五个是独立的命令,压缩解压都要用到其中一个,可以 ...
