18_andriod常用布局&内容回顾

线性布局:


<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal" ><!-- 垂直 vertical--> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="第一个textView" /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="第一个textView"/> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="第一个textView" /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="第一个textView"/>
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="第一个textView"/> </LinearLayout>

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" ><!-- 垂直 vertical--> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="第一个textView" /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="第一个textView"/> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="第一个textView" /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="第一个textView"/>
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="第一个textView"/> </LinearLayout>
相对布局:所有的控件默认都是从左上角开始画的。安卓默认的布局就是相对布局。
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" > <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" /> </RelativeLayout>

相对布局它可以通过id来指定相互的位置。
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" > <TextView
android:id="@+id/textview1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview2"
android:layout_below="@id/textview1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" /> </RelativeLayout>

<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" > <TextView
android:id="@+id/textview1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview2"
android:layout_below="@id/textview1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="textview2" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview3"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/textview2"
android:layout_alignBottom="@id/textview2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" /> </RelativeLayout>
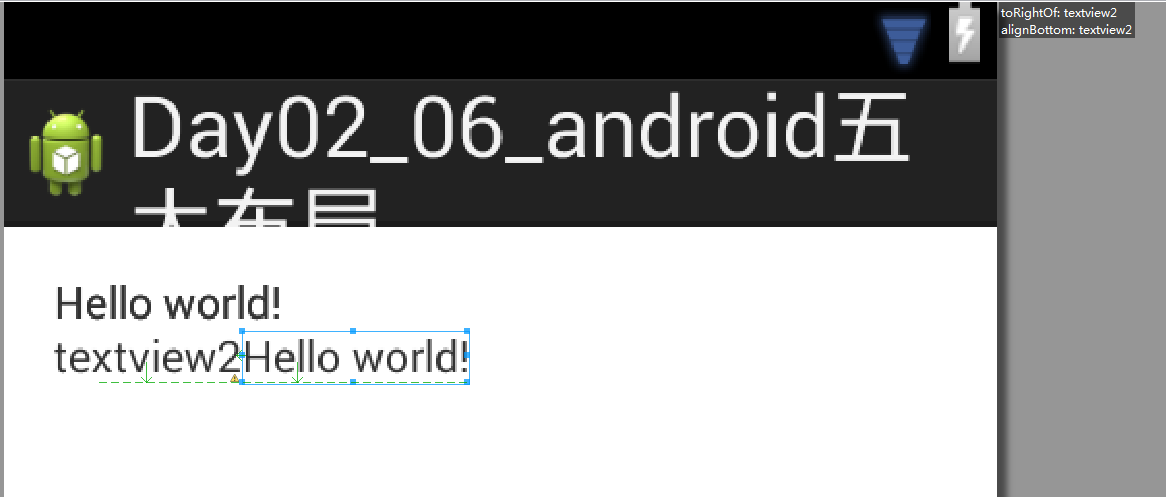
相对布局不仅可以指定控件之间相对的位置,咱们还可以针对父容器去挪一个位置。配置它在父容器的正中间。
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
所以相对来说相对布局它摆放控件的位置会更灵活。不但可以让它在每个控件之间指定相对的位置。可以写一个控件然后依照这个控件在它的前后左右上下去摆控件。也可以让它针对父容器放在父容器的上边下边左边右边中间,可以指定相互的这些位置。这个就是相对布局。
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" > <TextView
android:id="@+id/textview1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview2"
android:layout_below="@id/textview1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="textview2" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview3"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/textview2"
android:layout_alignBottom="@id/textview2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:text="@string/hello_world" /> </RelativeLayout>

帧布局/框架布局 也是从屏幕的左上角开始画。

android:layout_margin="10dp"可以指定外边距。
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|right"
android:layout_margin="100dp"
android:text="TextView" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|right"
android:layout_marginRight="100dp"
android:text="TextView" />
所以在framework框架布局里面除了用外边距和内边距的方式能够挪位置之外没有别的方法。只能通过android:layout_gravity在框架布局framework layout里面最终能够放的就是9个位置。最上面、中间、最下面的左中右。
开发当中用的比较多的是线性布局和相对布局,然后就是framework layout。
剩下两个不太常用。
table layout就类似于竖直方向的线性布局。


不指定<TableRow>默认占据着一整行.<TableRow>就是水平方向的线性布局.不指定<TableRow>就是竖直方向的线性布局.

最后一个是绝对布局。
AbsoluteLayout is deprecated
绝对布局是过时的了.绝对布局通过一个具体的坐标来确定控件的位置。随着安卓的设备发展的越来越快发展的越来越多,设备的尺寸千差万别。在这个设备上看的挺好换一个设备就跑偏了.换一个大的屏幕可能就偏的更厉害。所以绝对布局就被放弃掉了.
相对布局是用的最多的.接下来是线性布局.框架布局.表格布局.绝对布局已经不用了.


18_andriod常用布局&内容回顾的更多相关文章
- rem自适应布局的回顾总结
使用rem实现自适应布局,应该算是当前移动前端的一大趋势,有些人对此还有点迷惑,搞不懂rem是如何实现自适应布局,如何根据设计稿来调整rem的值?rem布局如何用雪碧背景图片?rem一定要加载JS吗? ...
- python:页面布局 后台管理页面之常用布局
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
- WPF中的常用布局
一 写在开头1.1 写在开头评价一门技术的好坏得看具体的需求,没有哪门技术是面面俱到地好. 1.2 本文内容本文主要内容为WPF中的常用布局,大部分内容转载至https://blog.csdn.net ...
- Android开发工程师文集-Fragment,适配器,轮播图,ScrollView,Gallery 图片浏览器,Android常用布局样式
Android开发工程师文集-Fragment,适配器,轮播图,ScrollView,Gallery 图片浏览器,Android常用布局样式 Fragment FragmentManager frag ...
- ExtJs常用布局--layout详解(含实例)
序言: 笔者用的ExtJs版本:ext-3.2.0 ExtJs常见的布局方式有:border.form.absolute.column.accordion.table.fit.card.anchor ...
- WPF中的常用布局 栈的实现 一个关于素数的神奇性质 C# defualt关键字默认值用法 接口通俗理解 C# Json序列化和反序列化 ASP.NET CORE系列【五】webapi整理以及RESTful风格化
WPF中的常用布局 一 写在开头1.1 写在开头微软是一家伟大的公司.评价一门技术的好坏得看具体的需求,没有哪门技术是面面俱到地好,应该抛弃对微软和微软的技术的偏见. 1.2 本文内容本文主要内容 ...
- Android常用布局和控件
一.Android常用布局属性 1. LinearLayout的特有属性 android:orientation:设置布局排列方式 android:layout_weight:设置所占布局的权重 ...
- 基本数据类型-集合(set)_上周内容回顾(字符串_数字_列表_元组_字典_集合)
上周内容回顾 1.字符串 2.数字 除了布尔类型外,int.long.float和complex都可以使用的运算为:加.减.乘.除.整除.幂运算和取余 3.列表和元组 列表的内容可变,可以包含任意对象 ...
- 常用布局,div竖直居中
常用两列布局,多列布局和div竖直居中 body { margin:; padding:; } .w200 { width: 200px; } .mar-left200 { margin-left: ...
随机推荐
- Zookeeper启动Permission denied
Zookeeper 查询状态,出现如下问题: JMX enabled by default Using config: /usr/zookeeper/zookeeper-/bin/../conf/zo ...
- 每天一个Linux命令(22)find命令_命令详解
find命令的一些常用参数的常用实例和用时的注意事项. 实例: (1)-name参数: 1)[sunjimeng@localhost home]$ find ~ -name & ...
- [原创]java WEB学习笔记42:带标签体的自定义标签,带父标签的自定义标签,el中自定义函数,自定义标签的小结
本博客为原创:综合 尚硅谷(http://www.atguigu.com)的系统教程(深表感谢)和 网络上的现有资源(博客,文档,图书等),资源的出处我会标明 本博客的目的:①总结自己的学习过程,相当 ...
- Vue-Quill-Editor回显不显示空格的处理办法
我自己在用VUE做一个博客网站,查了一下好多人都在用Vue-Quill-Editor,于是我也把这个插件加入到我的程序里,可是后来却出现了个问题,如图: 简单的代码如下: <template&g ...
- Spark集群搭建(local、standalone、yarn)
Spark集群搭建 local本地模式 下载安装包解压即可使用,测试(2.2版本)./bin/spark-submit --class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkP ...
- ML2 Extension Manager
The extension manager for ML2 was introduced in Juno (more details can be found in the approvedspec) ...
- 模拟C#的事件处理和属性语法糖
1. [代码]SharpEvent.hpp /* * SharpEvent.hpp * * Created on: 2014-5-5 * Author: leoking * Copyr ...
- php数据结构课程---1、数据结构基础介绍(程序是什么)
php数据结构课程---1.数据结构基础介绍(程序是什么) 一.总结 一句话总结: 程序=数据结构+算法 设计好数据结构,程序就等于成功了一半. 数据结构是程序设计的基石. 1.数据的逻辑结构和物理结 ...
- 再次理解WCF以及其通信(附加一個編程小經驗)
一.概述 Windows Communication Foundation(WCF)是由微软发展的一组数据通信的应用程序开发接口,可以翻译为Windows通讯接口,它是.NET框架的一部分.由 .NE ...
- 1115. Counting Nodes in a BST (30)
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a binary tree which has the following propertie ...
