07Mendel's First Law
Problem

Probability is the mathematical study of randomly occurring phenomena. We will model such a phenomenon with a random variable, which is simply a variable that can take a number of different distinct outcomes depending on the result of an underlying random process.
For example, say that we have a bag containing 3 red balls and 2 blue balls. If we let XX represent the random variable corresponding to the color of a drawn ball, then the probability of each of the two outcomes is given by Pr(X=red)=35Pr(X=red)=35 and Pr(X=blue)=25Pr(X=blue)=25.
Random variables can be combined to yield new random variables. Returning to the ball example, let YY model the color of a second ball drawn from the bag (without replacing the first ball). The probability of YY being red depends on whether the first ball was red or blue. To represent all outcomes of XX and YY, we therefore use a probability tree diagram. This branching diagram represents all possible individual probabilities for XX and YY, with outcomes at the endpoints ("leaves") of the tree. The probability of any outcome is given by the product of probabilities along the path from the beginning of the tree; see Figure 2 for an illustrative example.
An event is simply a collection of outcomes. Because outcomes are distinct, the probability of an event can be written as the sum of the probabilities of its constituent outcomes. For our colored ball example, let AA be the event "YY is blue." Pr(A)Pr(A) is equal to the sum of the probabilities of two different outcomes: Pr(X=blue and Y=blue)+Pr(X=red and Y=blue)Pr(X=blue and Y=blue)+Pr(X=red and Y=blue), or 310+110=25310+110=25 (see Figure 2 above).
Given: Three positive integers kk, mm, and nn, representing a population containing k+m+nk+m+n organisms: kk individuals are homozygous dominant for a factor, mm are heterozygous, and nn are homozygous recessive.
Return: The probability that two randomly selected mating organisms will produce an individual possessing a dominant allele (and thus displaying the dominant phenotype). Assume that any two organisms can mate.
Sample Dataset
2 2 2
Sample Output
0.78333 计算公式:
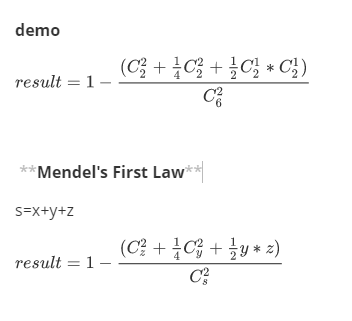
方法一:
def f(x, y, z):
s = x + y + z # the sum of population
c = s * (s - 1) / 2.0 # comb(2,s)
p = 1 - (z * (z - 1) / 2 + 0.25 * y * (y - 1) / 2 + y * z * 0.5) / c
return p print f(2, 2, 2)
方法二:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
### 7. Mendel's First Law ###
from scipy.misc import comb individuals = input('Number of individuals(k,m,n):')
[k, m, n] = map(int, individuals.split(','))
t = k + m + n rr = comb(n, 2) / comb(t, 2)
hh = comb(m, 2) / comb(t, 2)
hr = comb(n, 1) * comb(m, 1) / comb(t, 2) prob = 1 - (rr + hh * 1 / 4 + hr * 1 / 2) print (prob)
07Mendel's First Law的更多相关文章
- 齐夫定律, Zipf's law,Zipfian distribution
齐夫定律(英语:Zipf's law,IPA英语发音:/ˈzɪf/)是由哈佛大学的语言学家乔治·金斯利·齐夫(George Kingsley Zipf)于1949年发表的实验定律. 它可以表述为: 在 ...
- Conway's law(康威定律)
Mel Conway 康威在加利福尼亚理工学院获得物理学硕士学位,在凯斯西储大学获得数学博士学位.毕业之后,他参与了很多知名的软件项目,如 Pascal 编辑器.在他的职业生涯中,康威观察到一个现象 ...
- 加州大学伯克利分校Stat2.2x Probability 概率初步学习笔记: Section 3 The law of averages, and expected values
Stat2.2x Probability(概率)课程由加州大学伯克利分校(University of California, Berkeley)于2014年在edX平台讲授. PDF笔记下载(Acad ...
- 墨菲定律-Murphy's Law (转载)
墨菲定律 “墨菲定律”(Murphy's Law)亦称莫非定律.莫非定理.或摩菲定理,是西方世界常用的俚语. “墨菲定律”:事情往往会向你所想到的不好的方向发展,只要有这个可能性.比如你衣袋里有两把钥 ...
- BendFord's law's Chi square test
http://www.siam.org/students/siuro/vol1issue1/S01009.pdf bendford'law e=log10(1+l/n) o=freq of first ...
- 帕金森定律(Parkinson's Law)
帕金森定律(Parkinson's Law)是官僚主义或官僚主义现象的一种别称, 是由英国历史学家.政治学家西里尔·诺斯古德·帕金森(Cyril Northcote Parkinson)通过长期调查研 ...
- 默菲定律 [Murphy's Law]
一.关于默菲定律(Murphy's Law) “墨菲定律”.“帕金森定律”和“彼德原理”并称为二十世纪西方文化三大发现. “墨菲定律”的原话是这样说的:If there are two or mo ...
- 【分享】IT产业中的三大定理(一) —— 摩尔定理(Moore's Law)
科技行业流传着很多关于比尔·盖茨的故事,其中一个是他和通用汽车公司老板之间的对话.盖茨说,如果汽车工业能够像计算机领域一样发展,那么今天,买一辆汽车只需要 25 美元,一升汽油能跑四百公里.通用汽车老 ...
- 【分享】IT产业中的三大定理(二) —— 安迪&比尔定理 (Andy and Bill's Law)
摩尔定理给所有的计算机消费者带来一个希望,如果我今天嫌计算机太贵买不起,那么我等十八个月就可以用一半的价钱来买.要真是这样简单的话,计算机的销售量就上不去了.需要买计算机的人会多等几个月,已经有计算机 ...
随机推荐
- oracle 查版本号
oracle是强大的数据库,我们怎样看它的版本呢? 工具/原料 oracle 数据库, sqlplus 方法/步骤 首先进入sqlplus,cmd---plsql,登陆我们的用户,如:user/pas ...
- equals方法和==的区别
equals方法和==的区别 首先大家知道,String既可以作为一个对象来使用,又可以作为一个基本类型来使用.这里指的作为一个基本类型来使用只是指使用方法上的,比如String s = &quo ...
- oracle的热备份和冷备份
一.冷备份介绍: 冷备份数据库是将数据库关闭之后备份所有的关键性文件包括数据文件.控制文件.联机REDO LOG文件,将其拷贝到另外的位置.此外冷备份也可以包含对参数文件和口令文件的备份,但是这 ...
- 使用SafeViewFlipper避免ViewFlipper交替时Crash
使用SafeViewFlipper避免ViewFlipper交替时Crash 柳志超博客 » Program » Andriod » 使用SafeViewFlipper避免ViewFlipper交替时 ...
- C++ 构造函数_初始化列表
构造函数初始化列表以一个冒号开始,接着是以逗号分隔的数据成员列表,每个数据成员后面跟一个放在括号中的初始化式.例如: class Student { public: //构造函数初始化列表 Stude ...
- Spark系列(二) Spark Shell各种操作及详细说明
并行化scala集合(Parallelize) //加载数据1~10 val num=sc.parallelize(1 to 10) //每个数据项乘以2,注意 _*2记为一个函数(fun) val ...
- MTU&MSS
MTU是Maximum Transmission Unit的缩写,意为最大传输单元,通俗的理解就是在网络上传送的最大数据包,单位是字节. 以太网对数据帧的长度都有一个限制,其最大值为1500,这个特性 ...
- Asp.net 页面传值的方法
ASP.NET页面传值的方法 From:Refresh-air 在面试的时候,经常会遇到这样的问题,其实我们会对其中的几种方法比较熟悉,因为项目中经常使用.但是要全面的回答ASP.NET中页面传值的方 ...
- django-常用过滤器
django常用过滤器 add :字符串相加,数字相加,列表相加,如果失败,将会返回一个空字符串. default:提供一个默认值,在这个值被django认为是False的时候使用.比如:空字符串.N ...
- XE7 update1
