MySQL数据库2表的增删改查
一、数据表(文件):
什么是字段?
每个字段由若干按照某种界限划分的相同数据类型的数据项组成,这里指的数据表中的列,一列就是一个字段
1.1增
1.1.1列表的创建:
create table 表名(字段名 列约束 [可选的参数] , ### 记住加逗号
字段名 列约束 [可选的参数] , ### 记住加逗号
字段名 列约束 [可选的参数] ### 最后一行不加逗号
)charset=utf-8; ### 后面加分号
例子:
create table t1(
id int,
name char(5)
)charset=utf-8;
1.1.2增加数据:
insert into 表明 (列1,,列2) values (值1,'值2');
例子:insert into u1(id ,name) values(1,'guanghao');
inster into u2(id,name) values(1,'guanghao1');
插入多条记录
INSERT INTO 表名 VALUES
(值1,值2,值3…值n),
(值1,值2,值3…值n),
(值1,值2,值3…值n);
1.2查看表内数据
方式一
desc 表名
方式二
select 列1,列2 from 表名;(*代表查询所有的列)
例子:
mysql> select id,name from u1;
+------+-----------+
| id | name |
+------+-----------+
| 1 | guanghao |
| 1 | guanghao1 |
+------+-----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
例子2:
mysql> create table u2(
-> id int auto_increment primary key,
-> name char(10)
-> )charset=utf8;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.31 sec)
mysql> insert into u2(name) values('guanghao');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.05 sec)
mysql> select * from u2;
+----+----------+
| id | name |
+----+----------+
| 1 | guanghao |
+----+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
例子3(推荐使用这种方法):
mysql> create table u3(
-> name char(10) not null default 'xxx',
-> id int unsigned auto_increment primary key,
-> age int not null default 0
-> )charset=utf8;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.32 sec)
mysql> insert into u3(age) values (10);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.06 sec)
mysql> select * from u3;
+------+----+-----+
| name | id | age |
+------+----+-----+
| xxx | 1 | 10 |
+------+----+-----+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
1.3改
1.3.1修改表名
alter table 旧表名 rename 新表名;
mysql> alter table u6 rename hello;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.16 sec)
1.3.2增加字段
方式一
alter table 表名 add 字段名 列类型 [可选参数],add 字段名 列类型[可选参数];
这种方式添加的列默认添加到最后一列的后面。
mysql> alter table hello add name varchar(32) not null default '';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.80 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from hello;
+----+--------+------+
| id | gender | name |
+----+--------+------+
| 1 | female | |
| 2 | male | |
+----+--------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
方式二
alter table 表名 add 字段名 列类型 [可选参数] first;
添加到第一列的前面。
mysql> alter table hello add age int first;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.52 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from hello;
+------+----+--------+------+
| age | id | gender | name |
+------+----+--------+------+
| NULL | 1 | female | |
| NULL | 2 | male | |
+------+----+--------+------+
方式三
alter table 表名 add 字段名 列类型 [可选参数] after 字段名;
添加到某一列的后面。
mysql> alter table hello add age1 int not null default 0 after age;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.68 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from hello;
+------+------+----+--------+------+
| age | age1 | id | gender | name |
+------+------+----+--------+------+
| NULL | 0 | 1 | female | |
| NULL | 0 | 2 | male | |
+------+------+----+--------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
1.3.3删除字段
alter table 表名 drop 字段名 ;
mysql> alter table hello drop age;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (1.70 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from hello;
+------+----+--------+------+
| age1 | id | gender | name |
+------+----+--------+------+
| 0 | 1 | female | |
| 0 | 2 | male | |
+------+----+--------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
1.3.4修改字段
1.修改字段的数据类型
alter table 表名 modify 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件];
mysql> alter table hello modify name char(10);
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.98 sec)
Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
2.修改字段名和数据类型
alter table 表名 change 旧字段名 新字段名 新数据类型 [完整性约束条件]
mysql> alter table hello change age1 age;
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near '' at line 1
#不能只改字段名而不指定数据类型,否则会报错
mysql> alter table hello change age1 age int not null default 1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from hello;
+-----+----+--------+------+
| age | id | gender | name |
+-----+----+--------+------+
| 0 | 1 | female | |
| 0 | 2 | male | |
+-----+----+--------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
1.4删除列表
删除表语法:drop table 表名;(注意慎用,线上禁止使用)
mysql> show tables;
+-----------------+
| Tables_in_test2 |
+-----------------+
| hello |
| t1 |
| t2 |
| t3 |
| t4 |
| t5 |
| t6 |
| t7 |
| u1 |
| u2 |
| u3 |
| u4 |
| u5 |
+-----------------+
13 rows in set (0.04 sec)
mysql> drop table u5;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.17 sec)
mysql> show tables;
+-----------------+
| Tables_in_test2 |
+-----------------+
| hello |
| t1 |
| t2 |
| t3 |
| t4 |
| t5 |
| t6 |
| t7 |
| u1 |
| u2 |
| u3 |
| u4 |
+-----------------+
12 rows in set (0.00 sec)
1.5查看库内列表及表结构
方式一
show tables;查看该数据库内所有的列表
方式二
show create table 表名;查看具体表结构的详细信息
mysql> show create table hello;
+-------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Table | Create Table |
+-------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| hello | CREATE TABLE `hello` (
`age` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1',
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`gender` enum('male','female') DEFAULT NULL,
`name` char(10) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 |
+-------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
1.6复制表结构
方式一
show create table 表名;查看具体表结构的详细信息然后手动复制过来,在创建新表。
方式二
create table 新表名 like 被复制的表名;需要强调的是,这里的复制仅仅是复制表的结构,而不复制表的内容,新表示一个空表。
mysql> create table hello1 like hello;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.32 sec)
mysql> show create table hello1;
+--------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Table | Create Table |
+--------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| hello1 | CREATE TABLE `hello1` (
`age` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1',
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`gender` enum('male','female') DEFAULT NULL,
`name` char(10) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 |
+--------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
二、列类型:(*********)
create table 表名(
字段名 列类型 unsigned [可选的参数], ### 记住加逗号
字段名 列类型 [可选的参数], ### 记住加逗号
字段名 列类型 [可选的参数] ### 最后一行不加逗号
)charset=utf8; #### 后面加分号
2.1数字
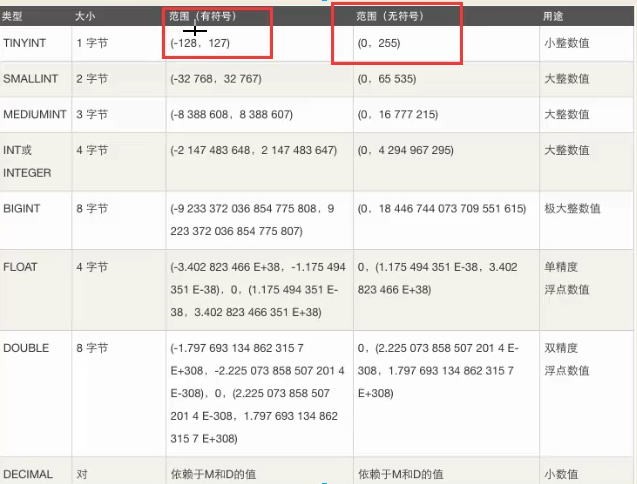
2.1.1整型
tinyint
smallint
int(*********)
mediumint
bigint
整数类型
取值范围
一个字节占8位,int占4个字节
在整数类型上加上
unsigned 代表不能取负数,不加是有符号的,且unsigned只适用于整型,且必须在数据类型前面。
数据类型前面。
根据应用场景:根据公司的业务场景,选择合适的类型。
2.1.2浮点型(*********)
float:一共只有四个字节,如果整数部分过长,则小数部分精确的位数会逐渐减少。
decimal:可以精确到设定的位数, decimal(m, d) m是数字总个数(负号不算),d是精确到小数点后多少位。
例子:
mysql> create table u4(
-> id int auto_increment primary key,
-> salary decimal(15,10),
-> num float
-> )charset=utf8;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.31 sec)
mysql> insert into u4(salary,num) alues(15000.12345678913579,15000.12345678913579);
Query OK, 1 row affected, 1 warning (0.15 sec)
mysql> select * from u4;
+----+------------------+---------+
| id | salary | num |
+----+------------------+---------+
| 1 | 15000.1234567891 | 15000.1 |
+----+------------------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into u4(num) values(3.1415926);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.10 sec)
mysql> select * from u4;
+----+------------------+---------+
| id | salary | num |
+----+------------------+---------+
| 1 | 15000.1234567891 | 15000.1 |
| 2 | NULL | 3.14159 |
+----+------------------+---------+
2.2字符串
char与varchar
char是定长的,无论插入的字符是多少个,永远固定占规定的长度;varchar是变长的,根据掺入的字符串长度计算所占的字节数,它所占的内存中有一个字节用来存储字符串的大小。
注意:如果在某些情况下不能确定数据的大小,建议使用varchar(255)。
char一般应用于固定长度的数据,如身份证、手机号、MD5加密之后的值。
| Value | CHAR(4) |
Storage Required | VARCHAR(4) |
Storage Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
'' |
' ' |
4 bytes | '' |
1 byte |
'ab' |
'ab ' |
4 bytes | 'ab' |
3 bytes |
'abcd' |
'abcd' |
4 bytes | 'abcd' |
5 bytes |
'abcdefgh' |
'abcd' |
4 bytes | 'abcd' |
5 bytes |
2.3时间日期类型
year精确到年
time只显示时分秒
date只显示到日期
datetime(*********)年月日时分秒(这个是最常用的,其他的时间类型基本不用)
timestamp时间戳
例子:
mysql> create table u5(d date,t time,dt datetime);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.46 sec)
mysql> insert into u5 values(now(),now(),now());#这里调用了new()函数
Query OK, 1 row affected, 1 warning (0.13 sec)
mysql> select * from u5;
+------------+----------+---------------------+
| d | t | dt |
+------------+----------+---------------------+
| 2019-10-29 | 15:08:42 | 2019-10-29 15:08:42 |
+------------+----------+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
2.4枚举ENUM
枚举就是限定输入该列的内容必修是已经对定好的几个选项中的一个,比如设定好性别一栏只能输入男或女。
ENUM对1-255个成员的枚举需要1个字节存储;对于255-65535个成员,需要2个字节存储;最多允许65535个成员,只能单选。
例子:
mysql> create table u6 (id int auto_increment primary key,
-> gender enum('male','female')
-> )charset utf8;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.44 sec)
mysql> insert into u6(gender) values ('female');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.07 sec)
mysql> insert into u6(gender) values('male');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.06 sec)
mysql> insert into u6(gender) values('123');
ERROR 1265 (01000): Data truncated for column 'gender' at row 1
三、操作表数据行
3.1增加表中的数据
语法 insert into 表名(列1,列2) values (值1,‘值2’);
值如果是字符串类型则需要加引号。
mysql> insert into hello(age,gender,name) values(18,'male','zgh');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.05 sec)
mysql> select * from hello;
+-----+----+--------+------+
| age | id | gender | name |
+-----+----+--------+------+
| 0 | 1 | female | |
| 0 | 2 | male | |
| 18 | 3 | male | zgh |
+-----+----+--------+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3.2 删除表中的数据
3.2.1删除表内具体的数据
delete from 表名 where 条件;
这里的条件可以是与或非和比较运算的组合。
mysql> delete from hello where id=1;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.14 sec)
mysql> delete from hello where id<=2 and id=3;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
3.2.2删除整个表所有的数据
1.delete from 表名;
mysql> delete from u4;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.06 sec)
mysql> show create table u4;
+-------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Table | Create Table |
+-------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| u4 | CREATE TABLE `u4` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`salary` decimal(15,10) DEFAULT NULL,
`num` float DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 |
+-------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from u4;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
2.truncate 表名;
mysql> select * from u4;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
mysql> truncate u3;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.32 sec)
mysql> select * from u3;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
delete 和truncate的区别:
1.delete之后,如果重新往表里插入数据,数据会从上一次主键自增加1开始(如果有某一列设置了自增加)而truncate则是从1开始。
如下例就是通过delete清空的列表由于id设置的自增加,所以,清空后再次插入新的数据,仍会接着之前的id创建新的id。
mysql> insert into u4(salary) values(10000);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.06 sec)
mysql> select * from u4;
+----+------------------+------+
| id | salary | num |
+----+------------------+------+
| 4 | 10000.0000000000 | NULL |
+----+------------------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
使用truncate清空列表
mysql> truncate u4;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.31 sec)
mysql> insert into u4(salary) values(10000);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.05 sec)
mysql> select * from u4;
+----+------------------+------+
| id | salary | num |
+----+------------------+------+
| 1 | 10000.0000000000 | NULL |
+----+------------------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
2.delete是一行一行删除的,truncate是全选删除;truncate删除的速度是高于delete。
3.3对列表中的某个值进行修改
update 表名 set 列名1=新值,列名2=新值 where 条件;
mysql> select *from u4;
+----+------------------+----------+
| id | salary | name |
+----+------------------+----------+
| 1 | 10000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 2 | 10000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 3 | 12000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 4 | 14000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 5 | 15000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 6 | 8000.0000000000 | xiaoming |
| 7 | 9000.0000000000 | xiaoming |
+----+------------------+----------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> update u4 set salary=10000 where name='xiaoming' and id=4;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
Rows matched: 0 Changed: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select *from u4;
+----+------------------+----------+
| id | salary | name |
+----+------------------+----------+
| 1 | 10000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 2 | 10000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 3 | 12000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 4 | 14000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 5 | 15000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 6 | 8000.0000000000 | xiaoming |
| 7 | 9000.0000000000 | xiaoming |
+----+------------------+----------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3.4查询表中的元素
3.4.1select 列1 ,列2 from表名;查询表中的指定列
3.4.2select * from 表名;*代表查询所有的列
3.4.3select * from 表名 where 条件;按条件查询
mysql> select *from u4;
+----+------------------+----------+
| id | salary | name |
+----+------------------+----------+
| 1 | 10000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 2 | 10000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 3 | 12000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 4 | 14000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 5 | 15000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 6 | 8000.0000000000 | xiaoming |
| 7 | 9000.0000000000 | xiaoming |
+----+------------------+----------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from u4 where id<5;
+----+------------------+------+
| id | salary | name |
+----+------------------+------+
| 1 | 10000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 2 | 10000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 3 | 12000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 4 | 14000.0000000000 | xxxx |
+----+------------------+------+
4 rows in set (0.02 sec)
3.4.4select * from 表名 where 列名 between 条件1 and 条件2;
取值范围是闭区间
mysql> select * from u4 where id between 1 and 4;
+----+------------------+------+
| id | salary | name |
+----+------------------+------+
| 1 | 10000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 2 | 10000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 3 | 12000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 4 | 14000.0000000000 | xxxx |
+----+------------------+------+
4 rows in set (0.05 sec)
3.4.5避免重复查询distinct
mysql> select distinct salary from u4;
+------------------+
| salary |
+------------------+
| 10000.0000000000 |
| 12000.0000000000 |
| 14000.0000000000 |
| 15000.0000000000 |
| 8000.0000000000 |
| 9000.0000000000 |
+------------------+
6 rows in set (0.04 sec)
3.4.6四则运算查询(不要用,效率太低)
mysql> select id,salary*10 from u4;
+----+-------------------+
| id | salary*10 |
+----+-------------------+
| 1 | 100000.0000000000 |
| 2 | 100000.0000000000 |
| 3 | 120000.0000000000 |
| 4 | 140000.0000000000 |
| 5 | 150000.0000000000 |
| 6 | 80000.0000000000 |
| 7 | 90000.0000000000 |
+----+-------------------+
7 rows in set (0.03 sec)
3.4.7模糊查询like(效率也低)
以某个字符开头:
mysql> select * from u4 where name like 'x%';#这里的百分号指后面可以为任意字符
+----+------------------+----------+
| id | salary | name |
+----+------------------+----------+
| 1 | 10000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 2 | 10000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 3 | 12000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 4 | 14000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 5 | 15000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 6 | 8000.0000000000 | xiaoming |
| 7 | 9000.0000000000 | xiaoming |
+----+------------------+----------+
7 rows in set (0.02 sec)
以某个字符结尾:
mysql> select * from u4 where name like '%x';#这里的百分号指x前面可以为任意字符
+----+------------------+------+
| id | salary | name |
+----+------------------+------+
| 1 | 10000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 2 | 10000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 3 | 12000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 4 | 14000.0000000000 | xxxx |
| 5 | 15000.0000000000 | xxxx |
+----+------------------+------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
包含某个字符:
mysql> select * from u4 where name like '%a%';#这里的百分号指a前面后面可以为任意字符
+----+-----------------+----------+
| id | salary | name |
+----+-----------------+----------+
| 6 | 8000.0000000000 | xiaoming |
| 7 | 9000.0000000000 | xiaoming |
+----+-----------------+----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
四、特殊表(数据库用户的创建与修改)
特殊表 (mysql.user) => 用户管理
'''
# 操作前提:登录root用户
1.重要字段
Host | User | Password
2.新建用户
create user 用户名@主机名 identified by '密码'; # 正确
create user zero@localhost identified by 'zero';
注:insert into mysql.user(Host,User,Password) values("主机名","用户名",password("密码")); # 错误
3.设置用户权限
grant 权限们 on 数据库名.表名 to 用户名@主机名 [with grant option];
grant create on db1.* to zero@localhost with grant option;
注:权限有select,delete,update,insert,drop..., all代表所有权限
注:数据库名,表名可以用*替换,代表所有
注:设置权限时如果没有当前用户,会自动创建用户,提倡使用
重点: grant all on db1.* to owen@localhost identified by 'owen'; # (创建用户)设置权限
4.撤销权限
revoke 权限名 on 数据库名.表名 from 用户名@主机名;
revoke delete on db1.* from owen@localhost;
5.修改密码
set password for 用户名@主机名 = password('新密码');
set password for owen@localhost = password('123');
6.删除用户
drop user 用户名@主机名;
'''
MySQL数据库2表的增删改查的更多相关文章
- MySQL数据库之表的增删改查
目录 MySQL数据库之表的增删改查 1 引言 2 创建表 3 删除表 4 修改表 5 查看表 6 复制表 MySQL数据库之表的增删改查 1 引言 1.MySQL数据库中,数据库database就是 ...
- Mysql数据库和表的增删改查以及数据备份&恢复
数据库 查看所有数据库 show databases; 使用数据库 use 数据库名; 查看当前使用的数据库 select database(); 创建数据库 create database 数据库名 ...
- MySQL数据库 | 数据表的增删改查
MySQL数据的增删改查(crud) 本文结构 一.增加 create 二.修改 update 三.查询 retrieve(简单查询,下篇详细展开) 四.删除 delete 首先,创建简单的class ...
- Mysql数据库二:表的增删改查
----建表CREATE TABLE emp( id int PRIMARY key auto_increment, name char(10) , birthday DATE , salary FL ...
- MySQL数据库与表的增删改查
1.值库管理 1.1 查询所有值库 show databases; 1.2 创建一个值库 create database 值库名称 default character set 编码格式名称; 1.3 ...
- 使用JDBC分别利用Statement和PreparedStatement来对MySQL数据库进行简单的增删改查以及SQL注入的原理
一.MySQL数据库的下载及安装 https://www.mysql.com/ 点击DOWNLOADS,拉到页面底部,找到MySQL Community(GPL)Downloads,点击 选择下图中的 ...
- Python操作MySQL数据库完成简易的增删改查功能
说明:该篇博客是博主一字一码编写的,实属不易,请尊重原创,谢谢大家! 目录 一丶项目介绍 二丶效果展示 三丶数据准备 四丶代码实现 五丶完整代码 一丶项目介绍 1.叙述 博主闲暇之余花了10个小时写的 ...
- 在python中连接mysql数据库,并进行增删改查
数据库在开发过程中是最常见的,基本上在服务端的编程过程中都会使用到,mysql是较常见的一种数据库,这里介绍python如果连接到数据库中,并对数据库进行增删改查. 安装mysql的python扩展 ...
- python3.6 使用 pymysql 连接 Mysql 数据库及 简单的增删改查操作
1.通过 pip 安装 pymysql 进入 cmd 输入 pip install pymysql 回车等待安装完成: 安装完成后出现如图相关信息,表示安装成功. 2.测试连接 import ...
随机推荐
- 原生JS去重
方式一: function deleteRepetionChar(arr){ //先判断输入进来的是数组对象还是字符串 if( typeof arr == "object"){ v ...
- 阶段2 JavaWeb+黑马旅游网_15-Maven基础_第2节 maven的安装和仓库种类_05仓库的种类和彼此关系
maven工程里面放的是jar包的坐标. 启动项目的时候会根据jar包的坐标到仓库中找对应的坐标 maven的安装目录.conf/settings.xml文件 ${user.home}表示系统盘,用户 ...
- spotlight监控linux性能
linux性能监控有很多工具,spotlight只是其中一种 目录 1.安装spotlight 2.参数认识 1.安装spotlight spotlight不仅仅只是监控linux,还可以完成数据库以 ...
- oracle data guard --理论知识回顾02
继上一篇 管理影响物理standby的事件 1 创建表空间或数据文件初始化参数standby_file_management用来控制是否自动将primary数据库增加表空间或数据文件的改动,传播到st ...
- yum 下载rpm包 安装rpm包依赖关系
方法一:yumdownloader 工具 1.安装工具包 yum install yum-utils -y 2.下载一个RPM包 yumdownloader <package-name> ...
- Android:adb命令详解
什么是adb adb工具即Android Debug Bridge(安卓调试桥) tools.它就是一个命令行窗口,用于通过电脑端与模拟器或者真实设备交互
- awk结合数组统计
1.统计用户登录类型 #!/bin/bashdeclare -A shells (定义关联数组shells)while read ll (读取/etc/passwd,ll为变量) dotype= ...
- C语言实现单链表
大二学习数据结构和算法啦,因为之前用Java语言实现过,所以理解起来还是比较轻松,就是理解指针与结构体的运用.废话不多说,上代码! 初始化 typedef struct Node { int data ...
- 【css】子元素浮动到了父元素外,父元素没有随子元素自适应高度,如何解决?
正常情况 如果子元素没有设置浮动(float),父元素的高度会随着子元素高度的改变而改变的. 设置浮动以后 父元素的高度不会随着子元素的高度而变化. 例如:在一个ul中定义若干个li,并设置float ...
- eclipse sts 常规操作
项目:右键 refresh 右键 maven -> update project 重新remove add project 重启软件,电脑 1.项目冗余 Package Explorer ...
