045.Python线程队列
线程队列
1 基本语法和用法
- put 往线程队列里防止,超过队列长度,直接阻塞
- get 从队列中取值,如果获取不到,直接阻塞
- put_nowait: 如果放入的值超过队列长度,直接报错(linux)
- get_nowait: 如果获取的值已经没有了,直接报错
(1) queue 先进先出
from queue import Queue
q = Queue()
q.put(11)
q.put(22)
print(q.get())
print(q.get_nowait())
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
11
22
直接报错
from queue import Queue
q = Queue()
q.put(11)
q.put(22)
print(q.get())
print(q.get_nowait())
print(q.get_nowait())
执行

指定队列长度
from queue import Queue
q2 = Queue(2)
q2.put(33)
q2.put(44)
q2.put(55)
直接阻塞
使用put_nowait报错

LifoQueue 后进先出
数据结构中,栈队列的一种储存顺序
from queue import LifoQueue
lq = LifoQueue()
lq.put(55)
lq.put(66)
print(lq.get())
print(lq.get())
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
66
55
PriorityQueue 按照优先级顺序排列
- 默认按照数字大小排序,然后会按照ascii编码在从小到大排序
- 先写先排,后写后排
from queue import PriorityQueue
pq = PriorityQueue()
pq.put( (12,"John") )
pq.put( (6,"Jim") )
pq.put( (19,"Tom") )
pq.put( (8,"Lucy") ) print(pq.get())
print(pq.get())
print(pq.get())
print(pq.get())
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
(6, 'Jim')
(8, 'Lucy')
(12, 'John')
(19, 'Tom')
当数字一样 按照ascsi值
from queue import PriorityQueue
pq = PriorityQueue()
pq.put( (12,"John") )
pq.put( (6,"Jim") )
pq.put( (19,"Tom") )
pq.put( (19,"Lucy") ) print(pq.get())
print(pq.get())
print(pq.get())
print(pq.get())
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
(6, 'Jim')
(12, 'John')
(19, 'Lucy')
(19, 'Tom')
单独一个元素,必须放同一种类型
from queue import PriorityQueue
pq = PriorityQueue()
pg = PriorityQueue()
pg.put(13)
pg.put(18)
pg.put(3)
print(pg.get())
print(pg.get())
print(pg.get())
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
3
13
18
如果不同类型
from queue import PriorityQueue
pq = PriorityQueue()
pg = PriorityQueue()
pg.put(13)
pg.put(18)
pg.put(3)
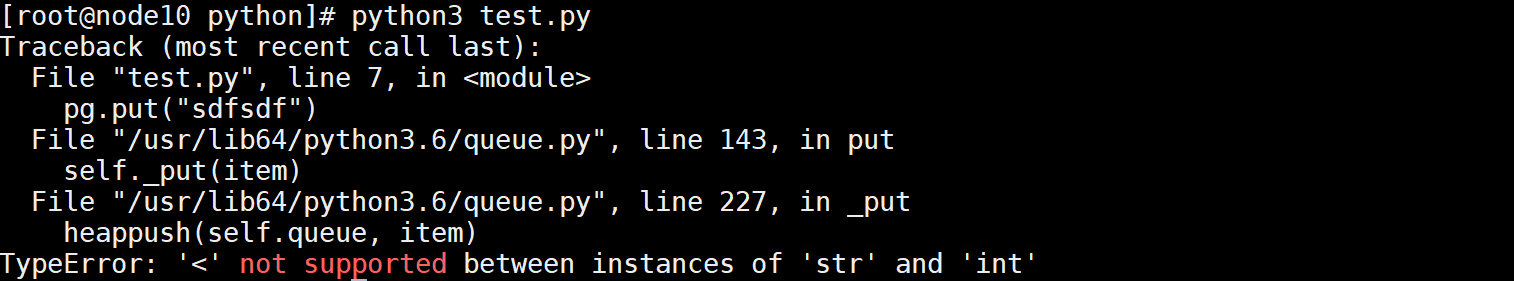
pg.put("sdfsdf")
print(pg.get())
print(pg.get())
print(pg.get())
执行
字符串类型
from queue import PriorityQueue
pg1 = PriorityQueue()
pg1.put("ab")
pg1.put("cc")
print(pg1.get())
print(pg1.get())
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
ab
cc
2 新版进程池,线程池
进程池 允许cpu并行
执行一个进程,如果使用了进程池,是要控制进程并行数量
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor,ThreadPoolExecutor
import os,time
def func(i):
print ("process:",i,os.getpid())
time.sleep(3)
print ("process:end")
return 6666
# 创建进程池对象,8是代表最大8个进程,ProcessPoolExecutor 后面的参数默认是cpu的最大逻辑处理器核心数.
p = ProcessPoolExecutor(8)
#异步触发进程,res 接收的是对象,这个对象可以通过result()来获取返回值
res = p.submit(func,1)
#获取进程任务的返回值
res2 = res.result()
#shutdown,等待所有子进程执行完毕之后,在向下执行,类似于join
p.shutdown() print("主进程执行完毕")
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
process: 1 42441
process:end
主进程执行完毕
执行多个进程,如果使用了进程池,是要控制进程并行数量
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor,ThreadPoolExecutor
import os,time
def func(i):
print ("process:",i,os.getpid())
time.sleep(3)
print ("process:end")
return 6666
# 创建进程池对象
p = ProcessPoolExecutor(8)
#异步触发进程,res 接收的是对象,这个对象可以通过result()来获取返回值
for i in range(12):
res = p.submit(func,i)
#获取进程任务的返回值
res2 = res.result()
#shutdown,等待所有子进程执行完毕之后,在向下执行,类似于join
p.shutdown() print("主进程执行完毕")
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
process: 0 42457
process: 1 42458
process: 2 42459
process: 3 42460
process: 4 42461
process: 5 42462
process: 6 42463
process: 7 42464
process:end
process:end
process:end
process: 8 42463
process: 9 42457
process: 10 42459
process:end
process: 11 42462
process:end
process:end
process:end
process:end
process:end
process:end
process:end
process:end
主进程执行完毕
3 线程池
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor,ThreadPoolExecutor
from threading import current_thread as cthread
import os,time
def func(i):
print("thread",i,cthread().ident)
time.sleep(3)
print("thread %s end %s"%(i)) #创建线程池。括号里面可以指定并发的线程数
tp = ThreadPoolExecutor(4)
for i in range(20):
tp.submit(func,i)
tp.shutdown()
print("主线程执行结束。。。")
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
thread 0 140712745903872
thread 1 140712737511168
thread 2 140712658073344
thread 3 140712649680640
thread 4 140712745903872
thread 5 140712658073344
thread 6 140712737511168
thread 7 140712649680640
thread 8 140712737511168
thread 9 140712658073344
thread 10 140712745903872
thread 11 140712649680640
thread 12 140712737511168
thread 13 140712745903872
thread 14 140712658073344
thread 15 140712649680640
thread 16 140712745903872
thread 17 140712737511168
thread 18 140712649680640
thread 19 140712658073344
主线程执行结束。。。
4 GIL锁
一个进程中的多条线程同一时间只能被一个cpu执行,不能实现并行操作.
想要解决:更换Jpython 或者 PyPy解释器
为什么加锁:
python是解释性语言,编译一行,就执行一行,不能提前规划系统资源,进行全局分配,根本原因是历史遗留问题.
程序分为两大类:
- 计算密集型程序,通过c语言改写python部分模块来实现
- io密集型程序,类似于python_web 运维,数据分析 都可以使用
线程池的返回值
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor,ThreadPoolExecutor
from threading import current_thread as cthread
import os,time
def func(i):
#获取当前线程号
print("thread",i,cthread().ident)
time.sleep(1)
#返回线程号,获取返回值,会加阻塞,无需shutdown
return cthread().ident #创建线程池。括号里面可以指定并发的线程数
tp = ThreadPoolExecutor(6)
lst = []
setvar = set()
for i in range(12):
#异步出发
res = tp.submit(func,i)
lst.append(res)
for i in lst:
#获取该进程对象的返回值
print (i.result())
#塞到集合里面,可以去重,验证
setvar.add(i.result())
#打印所有的线程号
print (setvar)
print("主线程执行结束。。。")
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
thread 0 140423614576384
thread 1 140423606183680
thread 2 140423597790976
thread 3 140423589398272
thread 4 140423581005568
thread 5 140423572612864
thread <Future at 0x7fb6f7ad4b70 state=running> 140423597790976
thread <Future at 0x7fb6f7ad4b70 state=running> 140423572612864
thread <Future at 0x7fb6f7ad4b70 state=running> 140423589398272
thread <Future at 0x7fb6f7ad4b70 state=running> 140423606183680
thread <Future at 0x7fb6f7ad4b70 state=running> 140423581005568
thread <Future at 0x7fb6f7ad4b70 state=finished returned int> 140423614576384
140423614576384
140423606183680
140423597790976
140423589398272
140423581005568
140423572612864
140423597790976
140423572612864
140423589398272
140423606183680
140423581005568
140423614576384
{140423614576384, 140423606183680, 140423581005568, 140423597790976, 140423589398272, 140423572612864}
主线程执行结束。。。
5 map返回迭代器
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor,ThreadPoolExecutor
import os,time
from threading import current_thread as cthread
def func(i):
time.sleep(0.2)
print("thread",i,cthread().ident)
print("thread .. end %s" % (i))
return "*" * i tp = ThreadPoolExecutor(5)
it = tp.map(func,range(20))
tp.shutdown()
print("<===>")
from collections import Iterator
res = isinstance(it,Iterator)
print(res)
print(list(it)) # "1234567"
# it = map(int,"1234567")
# print(list(it))
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
thread 0 140381751781120
thread .. end 0
thread 2 140381734995712
thread .. end 2
thread 1 140381743388416
thread .. end 1
thread 3 140381726603008
thread .. end 3
thread 4 140381718210304
thread .. end 4
thread 5 140381751781120
thread 6 140381734995712
thread .. end 5
thread .. end 6
thread 9 140381718210304
thread 8 140381726603008
thread .. end 8
thread 7 140381743388416
thread .. end 7
thread .. end 9
thread 14 140381718210304
thread .. end 14
thread 10 140381751781120
thread .. end 10
thread 11 140381734995712
thread .. end 11
thread 13 140381743388416
thread .. end 13
thread 12 140381726603008
thread .. end 12
thread 15 140381718210304
thread .. end 15
thread 19 140381726603008
thread .. end 19
thread 16 140381751781120
thread .. end 16
thread 18 140381743388416
thread .. end 18
thread 17 140381734995712
thread .. end 17
<===>
True
['', '*', '**', '***', '****', '*****', '******', '*******', '********', '*********', '**********', '***********', '************', '*************', '**************', '***************', '****************', '*****************', '******************', '*******************']
045.Python线程队列的更多相关文章
- python 线程队列PriorityQueue(优先队列)(37)
在 线程队列Queue / 线程队列LifoQueue 文章中分别介绍了先进先出队列Queue和先进后出队列LifoQueue,而今天给大家介绍的是最后一种:优先队列PriorityQueue,对队列 ...
- python 线程队列LifoQueue-LIFO(36)
在 python线程队列Queue-FIFO 文章中已经介绍了 先进先出队列Queue,而今天给大家介绍的是第二种:线程队列LifoQueue-LIFO,数据先进后出类型,两者有什么区别呢? 一.队 ...
- python线程队列Queue-FIFO(35)
之前的文章中讲解很多关于线程间通信的知识,比如:线程互斥锁lock,线程事件event,线程条件变量condition 等等,这些都是在开发中经常使用的内容,而今天继续给大家讲解一个更重要的知识点 — ...
- python 线程队列、线程池、全局解释器锁GIL
一.线程队列 队列特性:取一个值少一个,只能取一次,没有值的时候会阻塞,队列满了,也会阻塞 queue队列 :使用import queue,用法与进程Queue一样 queue is especial ...
- python线程+队列(queue)
---恢复内容开始--- python的线程学习 用处 pocpiliang脚本的编写 函数式:调用 _thread 模块中的start_new_thread()函数来产生新线程.语法如下: _thr ...
- python线程池ThreadPoolExecutor(上)(38)
在前面的文章中我们已经介绍了很多关于python线程相关的知识点,比如 线程互斥锁Lock / 线程事件Event / 线程条件变量Condition 等等,而今天给大家讲解的是 线程池ThreadP ...
- python全栈开发 * 线程队列 线程池 协程 * 180731
一.线程队列 队列:1.Queue 先进先出 自带锁 数据安全 from queue import Queue from multiprocessing import Queue (IPC队列)2.L ...
- Python之线程 3 - 信号量、事件、线程队列与concurrent.futures模块
一 信号量 二 事件 三 条件Condition 四 定时器(了解) 五 线程队列 六 标准模块-concurrent.futures 基本方法 ThreadPoolExecutor的简单使用 Pro ...
- Python进阶----异步同步,阻塞非阻塞,线程池(进程池)的异步+回调机制实行并发, 线程队列(Queue, LifoQueue,PriorityQueue), 事件Event,线程的三个状态(就绪,挂起,运行) ,***协程概念,yield模拟并发(有缺陷),Greenlet模块(手动切换),Gevent(协程并发)
Python进阶----异步同步,阻塞非阻塞,线程池(进程池)的异步+回调机制实行并发, 线程队列(Queue, LifoQueue,PriorityQueue), 事件Event,线程的三个状态(就 ...
随机推荐
- Qt信号槽源码剖析(二)
大家好,我是IT文艺男,来自一线大厂的一线程序员 上节视频给大家讲解了Qt信号槽的基本概念.元对象编译器.示例代码以及Qt宏:今天接着深入分析,进入Qt信号槽源码剖析系列的第二节视频. Qt信号槽的宏 ...
- 201871030140-朱婷婷 实验三 结对项目—《D{0-1}KP 实例数据集算法实验平台》项目报告
项目 内容 课程班级博客链接 2018级卓越班 这个作业要求链接 实验三 结对项目 我的课程学习目标 1.体验软件项目开发中的两人合作,练习结对编程:2.掌握GitHub协作开发程序的操作方法. 这个 ...
- 在nginx配置将请求转发到某个真实后端服务ip
一.打开nginx机器的nginx配置文件 命令: locate nginx.conf 会列出所有nginx.conf文件的地址, 一般咱们要用的nginx配置文件是/usr/local/nginx/ ...
- C/C++ 手工实现IAT导入表注入劫持
DLL注入有多种方式,今天介绍的这一种注入方式是通过修改导入表,增加一项导入DLL以及导入函数,我们知道当程序在被运行起来之前,其导入表中的导入DLL与导入函数会被递归读取加载到目标空间中,我们向导入 ...
- hdu4122 制作月饼完成订单的最小花费
题意: 有一个加工厂加工月饼的,这个工厂一共开业m小时,2000年1月1日0点是开业的第一个小时,每个小时加工月饼的价钱也不一样,然后每个月饼的保质期都是t天,因为要放在冰箱里保存,所以在 ...
- WindowsPE 第七章 资源表
资源表 在程序设计中,总会设计一些数据.这些数据可能是源代码内部需要用到的常量,菜单选项.界面描述等:也可能是源代码外部的,比如程序的图标文件.北京音乐文件.配置文件等,以上这些数据统称为资源.按照程 ...
- 学习Canvas绘图与动画基础 canvas入门(一)
一.创建canvas 1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head lang="en"> 4 <meta char ...
- Mybatis的初始化和结合Spring Framework后初始化的源码探究
带着下面的问题进行学习: (1)Mybatis 框架或 Spring Framework 框架对数据层 Mapper 接口做了代理,那是做了 JDK 动态代理还是 CGLIB 代理? (2)Mappe ...
- php 获取某数组中出现次数最多的值(重复最多的值)与出现的次数
1.$arr = array(7,7,8,9,10,10,10); $arr = array_count_values($arr); // 统计数组中所有值出现的次数 arsort($arr); ...
- Nginx如何配置Http、Https、WS、WSS?
写在前面 当今互联网领域,Nginx是使用最多的代理服务器之一,很多大厂在自己的业务系统中都是用了Nginx作为代理服务器.所以,我们有必要了解下Nginx对于Http.Https.WS.WSS的各项 ...
