VGG19模型训练+读取
- VGG-19的介绍和训练这里不做说明,网上资源很多,而且相对比较简单.
- 本博文主要介绍VGG-19模型调用官方已经训练好的模型,进行测试使用.
VGG-19模型简单介绍
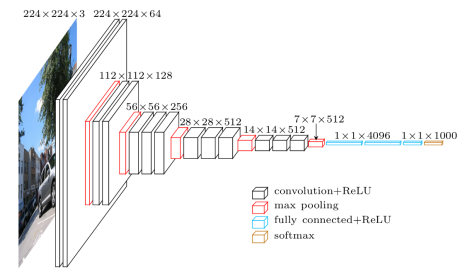
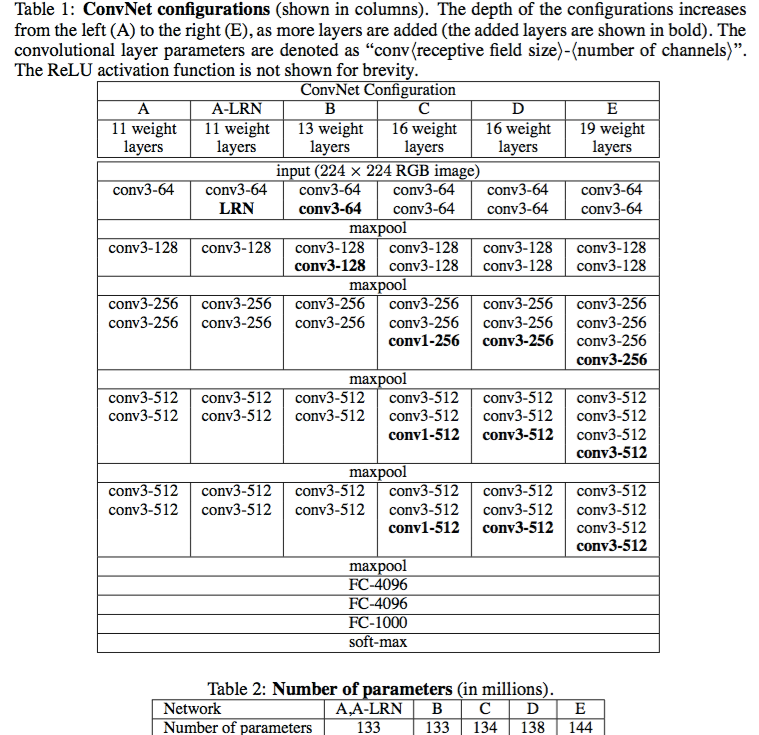
VGG-19模型文件介绍
这里是重难点,VGG-19模型存储的方式有点复杂
- 可以通过作者文档说明去查看
- 可以通过在线调试查看结构,对比模型得出结论
分析模型文件
首先我们通过scipy模块(当然你可以用其它方式入opencv / sklearn等)读取scipy.io.loadmat()文件
data = scipy.io.loadmat(data_path)
接下来使用Pycharm在线查看data数据结构:
- 总共有很多参数,我们只关心我们需要关注的,W和B在哪里就行了
- 注意这里还有一个mean(平均值),因为VGG使用了图像预处理方式是 input - mean,当然这种处理方式在现在看来不怎么好,但是现在我们用人家的模型,需要遵照人家的意思.
- 这里主要关注"layers"和"normalization"
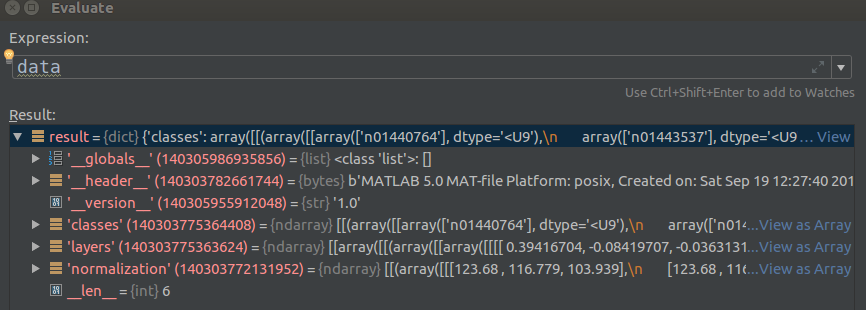
mean值查看
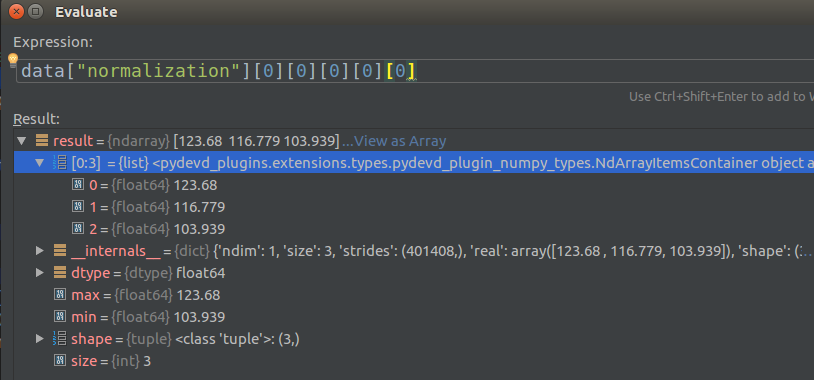
首先查看normalization的mean值:
- 注意我们使用的是RGB输入,且图像大小为224*224,也就是说图像是[1 * 224 * 224 *3]格式
- 那么我们的mean肯定就是[X,Y,Z]的格式,因为是RGB的平均值
这里使用笨方法,直接带入:
data["normalization"][0][0][0][0][0]
先看大概看一下数据结构,然后一个一个测试,因为在线调试,这样很快,比你精确的去找要快很多.
Weight和Bias查看
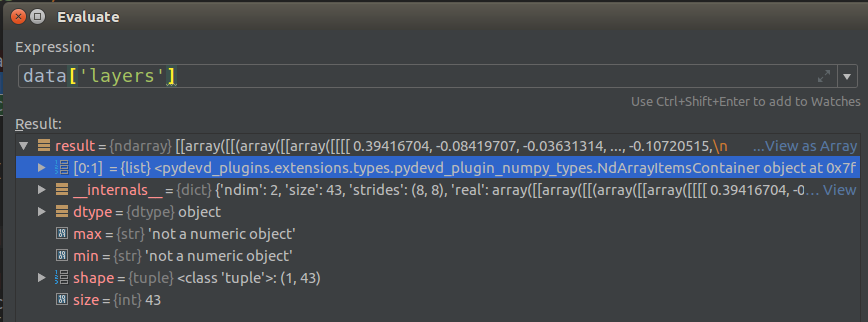
这里和mean查看方法不同,W和B得自习查看数据结构,因为太复杂了
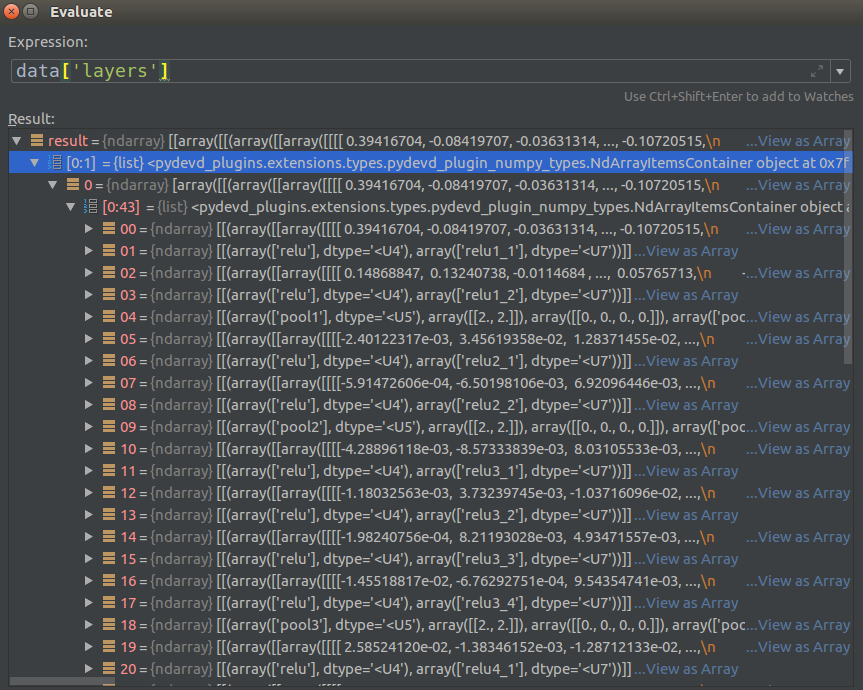
- 从下面的图看到存储的43个参数
- 注意里面的
Relu是没有数据的,因为Relu就是一个函数 - 注意
Pool的参数是固定的,因为大小为:[1,2,2,1],步长[1,2,2,1],这里可以自己写,也可以读取参数 WeightBias是存放在ReluPool中间的,而且两个值存在一起的.- 后期代码需要进一步处理,后面会说到.
- 再不明白的,自己画个VGG-19网络就知道了.
读取代码
mean = data["normalization"][0][0][0][0][0]
data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0])
读取模型
这里默认大家已经会CNN的基本操作了,代码不做详细说明
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
import scipy.io
import scipy.misc
from imagenet_classes import class_names
def _conv_layer(input,weight,bias):
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(input,weight,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding="SAME")
return tf.nn.bias_add(conv,bias)
def _pool_layer(input):
return tf.nn.max_pool(input,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME")
def preprocess(image,mean_pixel):
'''简单预处理,全部图片减去平均值'''
return image-mean_pixel
def unprocess(image,mean_pixel):
return image+mean_pixel
def imread(path):
return scipy.misc.imread(path)
def imsave(image,path):
img = np.clip(image,0,255).astype(np.int8)
scipy.misc.imsave(path,image)
def net(data_path,input_image,sess=None):
"""
读取VGG模型参数,搭建VGG网络
:param data_path: VGG模型文件位置
:param input_image: 输入测试图像
:return:
"""
layers = (
'conv1_1', 'conv1_2', 'pool1',
'conv2_1', 'conv2_2', 'pool2',
'conv3_1', 'conv3_2', 'conv3_3','conv3_4', 'pool3',
'conv4_1', 'conv4_2', 'conv4_3','conv4_4', 'pool4',
'conv5_1', 'conv5_2', 'conv5_3','conv5_4', 'pool5',
'fc1' , 'fc2' , 'fc3' ,
'softmax'
)
data = scipy.io.loadmat(data_path)
mean = data["normalization"][0][0][0][0][0]
input_image = np.array([preprocess(input_image, mean)]).astype(np.float32)#去除平均值
net = {}
current = input_image
net["src_image"] = tf.constant(current) # 存储数据
count = 0 #计数存储
for i in range(43):
if str(data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0])[:4] == ("relu"):
continue
if str(data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0])[:4] == ("pool"):
current = _pool_layer(current)
elif str(data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0]) == ("softmax"):
current = tf.nn.softmax(current)
elif i == (37):
shape = int(np.prod(current.get_shape()[1:]))
current = tf.reshape(current, [-1, shape])
kernels, bias = data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0]
kernels = np.reshape(kernels,[-1,4096])
bias = bias.reshape(-1)
current = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(current,kernels),bias))
elif i == (39):
kernels, bias = data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0]
kernels = np.reshape(kernels,[4096,4096])
bias = bias.reshape(-1)
current = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(current,kernels),bias))
elif i == 41:
kernels, bias = data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0]
kernels = np.reshape(kernels, [4096, 1000])
bias = bias.reshape(-1)
current = tf.add(tf.matmul(current, kernels), bias)
else:
kernels,bias = data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0]
#注意VGG存储方式为[,]
#kernels = np.transpose(kernels,[1,0,2,3])
bias = bias.reshape(-1)#降低维度
current = tf.nn.relu(_conv_layer(current,kernels,bias))
net[layers[count]] = current #存储数据
count += 1
return net, mean
if __name__ == '__main__':
VGG_PATH = os.getcwd()+"/imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat"
input_image = scipy.misc.imread("234.jpeg")
input_image = scipy.misc.imresize(input_image,[224,224,3])
shape = (1, input_image.shape[0], input_image.shape[1], input_image.shape[2])
#image = tf.placeholder('float', shape=shape)
with tf.Session() as sess:
nets, mean_pixel, = net(VGG_PATH, input_image, sess=sess)
#print(sess.run(nets,feed_dict={image:input_image}))
nets = sess.run(nets)
'''
for key, values in nets.items():
if len(values.shape)<4:
continue
plt.figure(key)
plt.matshow(values[0, :, :, 0],)
plt.title(key)
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
'''
#打印概率最大的三个数据
net_sort = list(reversed(np.argsort(nets["softmax"]).reshape(-1).tolist()))
net_softmax = nets["softmax"].reshape(-1).tolist()
for i in range(3):
print(class_names[net_sort[i]],": ",net_softmax[net_sort[i]])
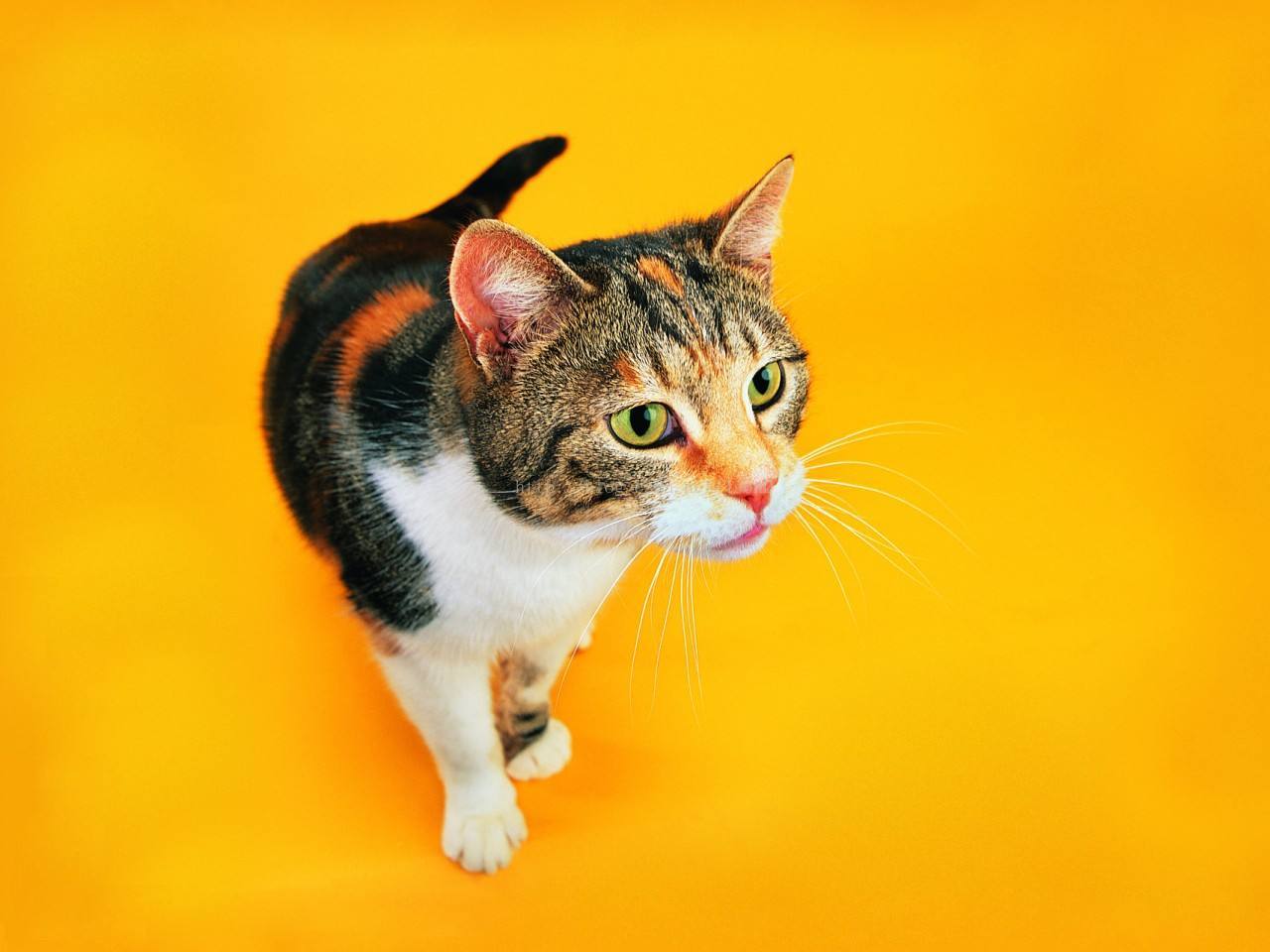
输入图片:

结果显示:
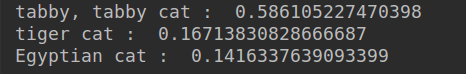
百度验证:
完整模型下载地址:
- 网盘老是被封,请留言邮箱发送
训练代码
以下是训练的代码:
这部分随便看看就好,比较简单~~主要看思想和细节!
########################################################################################
# Davi Frossard, 2016 #
# VGG16 implementation in TensorFlow #
# Details: #
# http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~frossard/post/vgg16/ #
# #
# Model from https://gist.github.com/ksimonyan/211839e770f7b538e2d8#file-readme-md #
# Weights from Caffe converted using https://github.com/ethereon/caffe-tensorflow #
########################################################################################
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from scipy.misc import imread, imresize
from imagenet_classes import class_names
class vgg16:
def __init__(self, imgs, weights=None, sess=None):
self.imgs = imgs
self.convlayers()
self.fc_layers()
self.probs = tf.nn.softmax(self.fc3l)
if weights is not None and sess is not None:
self.load_weights(weights, sess)
def convlayers(self):
self.parameters = []
# zero-mean input
with tf.name_scope('preprocess') as scope:
mean = tf.constant([123.68, 116.779, 103.939], dtype=tf.float32, shape=[1, 1, 1, 3], name='img_mean')
images = self.imgs-mean
# conv1_1
with tf.name_scope('conv1_1') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 3, 64], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[64], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv1_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv1_2
with tf.name_scope('conv1_2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 64, 64], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv1_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[64], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv1_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# pool1
self.pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv1_2,
ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME',
name='pool1')
# conv2_1
with tf.name_scope('conv2_1') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 64, 128], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.pool1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[128], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv2_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv2_2
with tf.name_scope('conv2_2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 128, 128], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv2_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[128], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv2_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# pool2
self.pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv2_2,
ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME',
name='pool2')
# conv3_1
with tf.name_scope('conv3_1') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 128, 256], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.pool2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv3_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv3_2
with tf.name_scope('conv3_2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 256], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv3_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv3_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv3_3
with tf.name_scope('conv3_3') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 256], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv3_2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv3_3 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# pool3
self.pool3 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv3_3,
ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME',
name='pool3')
# conv4_1
with tf.name_scope('conv4_1') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 512], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.pool3, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv4_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv4_2
with tf.name_scope('conv4_2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv4_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv4_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv4_3
with tf.name_scope('conv4_3') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv4_2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv4_3 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# pool4
self.pool4 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv4_3,
ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME',
name='pool4')
# conv5_1
with tf.name_scope('conv5_1') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.pool4, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv5_1 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv5_2
with tf.name_scope('conv5_2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv5_1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv5_2 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# conv5_3
with tf.name_scope('conv5_3') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 512, 512], dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(self.conv5_2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[512], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
out = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
self.conv5_3 = tf.nn.relu(out, name=scope)
self.parameters += [kernel, biases]
# pool5
self.pool5 = tf.nn.max_pool(self.conv5_3,
ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME',
name='pool4')
def fc_layers(self):
# fc1
with tf.name_scope('fc1') as scope:
shape = int(np.prod(self.pool5.get_shape()[1:]))
fc1w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([shape, 4096],
dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
fc1b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[4096], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
pool5_flat = tf.reshape(self.pool5, [-1, shape])
fc1l = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(pool5_flat, fc1w), fc1b)
self.fc1 = tf.nn.relu(fc1l)
self.parameters += [fc1w, fc1b]
# fc2
with tf.name_scope('fc2') as scope:
fc2w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4096, 4096],
dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
fc2b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[4096], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
fc2l = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(self.fc1, fc2w), fc2b)
self.fc2 = tf.nn.relu(fc2l)
self.parameters += [fc2w, fc2b]
# fc3
with tf.name_scope('fc3') as scope:
fc3w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4096, 1000],
dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
fc3b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[1000], dtype=tf.float32),
trainable=True, name='biases')
self.fc3l = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(self.fc2, fc3w), fc3b)
self.parameters += [fc3w, fc3b]
def load_weights(self, weight_file, sess):
weights = np.load(weight_file)
keys = sorted(weights.keys())
for i, k in enumerate(keys):
print i, k, np.shape(weights[k])
sess.run(self.parameters[i].assign(weights[k]))
if __name__ == '__main__':
sess = tf.Session()
imgs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 224, 224, 3])
vgg = vgg16(imgs, 'vgg16_weights.npz', sess)
img1 = imread('laska.png', mode='RGB')
img1 = imresize(img1, (224, 224))
prob = sess.run(vgg.probs, feed_dict={vgg.imgs: [img1]})[0]
preds = (np.argsort(prob)[::-1])[0:5]
for p in preds:
print class_names[p], prob[p]
参考资料
- https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~frossard/post/vgg16/
- http://x-algo.cn/index.php/2017/01/08/1471/
- https://blog.csdn.net/wyl1987527/article/details/68168115
VGG19模型训练+读取的更多相关文章
- tensorflow-Inception-v3模型训练自己的数据代码示例
一.声明 本代码非原创,源网址不详,仅做学习参考. 二.代码 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import glob # 返回一个包含有匹配文件/目录的数组 import os.pat ...
- 人脸检测及识别python实现系列(3)——为模型训练准备人脸数据
人脸检测及识别python实现系列(3)——为模型训练准备人脸数据 机器学习最本质的地方就是基于海量数据统计的学习,说白了,机器学习其实就是在模拟人类儿童的学习行为.举一个简单的例子,成年人并没有主动 ...
- 基于Python3.7和opencv的人脸识别(含数据收集,模型训练)
前言 第一次写博客,有点紧张和兴奋.废话不多说,直接进入正题.如果你渴望使你的电脑能够进行人脸识别:如果你不想了解什么c++.底层算法:如果你也不想买什么树莓派,安装什么几个G的opencv:如果你和 ...
- Windows下mnist数据集caffemodel分类模型训练及测试
1. MNIST数据集介绍 MNIST是一个手写数字数据库,样本收集的是美国中学生手写样本,比较符合实际情况,大体上样本是这样的: MNIST数据库有以下特性: 包含了60000个训练样本集和1000 ...
- Python之TensorFlow的模型训练保存与加载-3
一.TensorFlow的模型保存和加载,使我们在训练和使用时的一种常用方式.我们把训练好的模型通过二次加载训练,或者独立加载模型训练.这基本上都是比较常用的方式. 二.模型的保存与加载类型有2种 1 ...
- 深度学习之加载VGG19模型分类识别
主要参考博客: https://blog.csdn.net/u011046017/article/details/80672597#%E8%AE%AD%E7%BB%83%E4%BB%A3%E7%A0% ...
- Keras入门(六)模型训练实时可视化
在北京做某个项目的时候,客户要求能够对数据进行训练.预测,同时能导出模型,还有在页面上显示训练的进度.前面的几个要求都不难实现,但在页面上显示训练进度当时笔者并没有实现. 本文将会分享如何在K ...
- 从软件开发到 AI 领域工程师:模型训练篇
前言 4 月热播的韩剧<王国>,不知道大家有没有看?我一集不落地看完了.王子元子出生时,正逢宫内僵尸作乱,元子也被咬了一口,但是由于大脑神经元尚未形成,寄生虫无法控制神经元,所以医女在做了 ...
- 轻量化模型训练加速的思考(Pytorch实现)
0. 引子 在训练轻量化模型时,经常发生的情况就是,明明 GPU 很闲,可速度就是上不去,用了多张卡并行也没有太大改善. 如果什么优化都不做,仅仅是使用nn.DataParallel这个模块,那么实测 ...
随机推荐
- 同时兼容ie8 与ie11
最近公司发文规定说程序要必须同时兼容ie8与ie11 下面是在修改程序时遇到的一些问题. 1:new Date 获取年的问题,在ie8及以下ie以下版本是可以用getYear()方法来获取年得到的数值 ...
- Visible Lattice Points SPOJ - VLATTICE 三维+莫比乌斯反演
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define ll long long using namespace std; ; int vis[maxn]; int mu[maxn ...
- P2257 莫比乌斯+整除分块
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define ll long long using namespace std; ; int vis[maxn]; int mu[maxn ...
- 安装Oracle数据库心得
学到Oracle数据库了,想在自己电脑上安装个Oracle数据库.在网上下载了一个Oracle18c版 下边是我安装Oracle18c版的数据库失败,后来在卸载过程中遇到的问题: 1.用Univers ...
- 试写foxit reader的ConvertToPDF功能的wrapper
相比于直接fuzzing大型程序本身,针对程序的某一特定功能写wrapper后再fuzzing则要高效的多.网上搜了下,仅有两篇关于foxit reader的wrapper文章,一个用python,另 ...
- linux下用ctrl+r快速搜索history命令
前提是,搜索已经使用的命令,否则是查不出来结果的. ctrl+r用途:反向搜索执行过的命令.(reverse-i-search) 1.任何目录下按住ctrl + r 2.输入历史命令中的字符串 ,比如 ...
- python 和python-m 的区别
首先在python自带的,help命令中,可以看到,官方的说明是:-m mod : run library module as a script (terminates option list) 意思 ...
- Actifio最新软件下载更新
提供最近2个版本的软件. https://pan.baidu.com/s/10KajjJTMAKIHkRsfg3-A5g
- 在<canvas>上绘制img(drawImage())时需要注意的事
<canvas>标签相当于是一个画布,css决定画布的样式(这块画布的背景颜色.大小等),脚本(一般使用JavaScript)就是画笔,我们可以在这个画布上绘制线条.形状.文字.图片等. ...
- Windows文本文件上传至linux显示乱码解决方法
iconv -f gbk -t UTF-8 显示异常文本名 -o 另存为文件名 iconv -f gbk -t UTF-8 rkgxdt_new.log -o new
