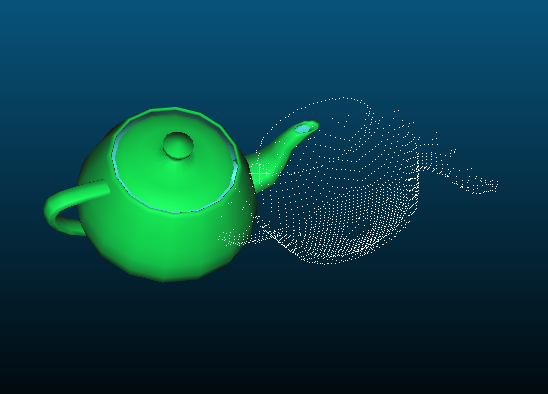
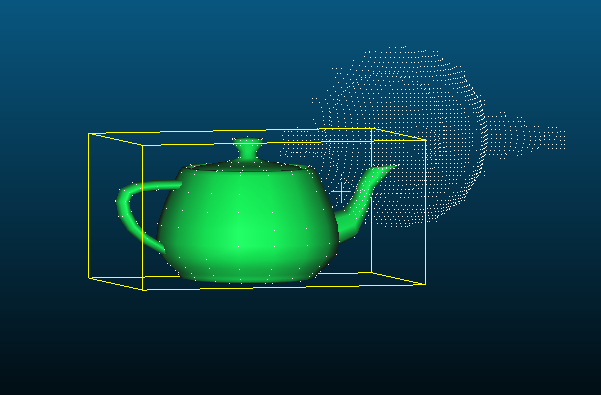
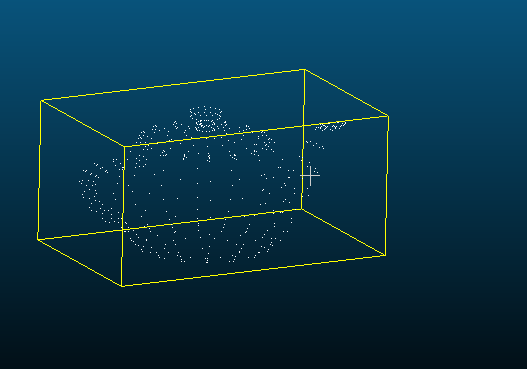
三维重建PCL:点云单侧面正射投影
终于把点云单侧面投影正射投影的代码写完了,为一个阶段,主要使用平面插值方法,且只以XOY平面作为的正射投影面。有些凑合的地方,待改进。
方法思路:使用Mesh模型,对每一个表面进行表面重建。借助OpenCV Mat类型对投影平面进行内点判断,对内点位置进行插值。
OpenCV cv::polylines 和lines 进行画图的时候都会出现问题,因此在某些时刻无法使用连通域查找的方法进行内点检测,应该重写line方法。
1.使用Mesh载入ply模型,和同步载入点云,也可以从mesh直接Copy点云。
pcl::PolygonMesh cloudMesh;
pcl::io::loadPolygonFileOBJ(ViewPath, cloudMesh);
pcl::fromPCLPointCloud2(cloudMesh.cloud, *cloud); ViewPath = "D:/DataSet/RGB_data/teapot.pcd";
pcl::io::savePCDFileASCII(ViewPath, *cloud);//一定要注意高和宽进行赋值 pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer Viewer;//pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer ViewerMesh;
Viewer.addPolygonMesh(cloudMesh); int FrameX = 1000;
int FrameY = 1000;
int FrameZ = 1000;
int Centroid = 0; int num = 12;
float gap = 3.141592653/num;
Eigen::Vector4f ViewPoint( 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1);//使用弧度 ViewPoint[0] = gap*i;
cv::Mat imgGray = viewEx->getCloudViewByEdge(
cloud, cloudView, cloudMesh, ViewPath, FrameX, FrameY, FrameZ, Centroid, ViewPoint);
2. 使用平面填充方法进行投影...
//使用多边形填充的方法进行投影
//获取点云侧面投影
//输入:点云的点集、边集
cv::Mat CViewExtract::getCloudViewByEdge(
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloudView,
pcl::PolygonMesh &cloudMesh,
std::string ViewPath,
int FrameX, int FrameY, int FrameZ,
int Centroid,
Eigen::Vector4f &ViewPoint)
{
int BbxSize = FrameX;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloudTrans(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
this->viewTrans(cloud, cloudTrans, ViewPoint); //对点云进行侧面投影
std::vector<pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>> surfaces;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr surface(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>); //计算平面
genSurfaceFromVertices(cloudMesh.polygons, cloudTrans, surface);//由cloud替换cloudtrans,mesh只是一个索引
cv::Mat imgGray = getViewer(surface, cloudTrans, cloudView); return imgGray;
}
3. 子函数
视点变换
float CViewExtract::viewTrans(
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloudSrc,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloudTrans,
Eigen::Vector4f &AngleTrans)
{
//1. Trans the VIew...
float AngleA, AngleB, AngleC;//声明视角//初始化 作为原始角度
AngleA = AngleTrans[0];//49.0/pi;
AngleB = AngleTrans[1];//78.9/pi;
AngleC = AngleTrans[2];//34.8/pi; int size = cloudSrc->points.size();
cloudTrans->resize(0);
cloudTrans->reserve(size); //位姿识别角度变换矩阵/
Eigen::Matrix4f TransX, TransY, TransZ;
//初始化三个矩阵!变换!
TransX << 1, 0, 0, 0,
0, cos(AngleA), -sin(AngleA), 0,
0, sin(AngleA), cos(AngleA), 0,
0, 0, 0, 1;// TransY << cos(AngleB), 0, sin(AngleB), 0,
0, 1, 0, 0,
-sin(AngleB), 0, cos(AngleB), 0,
0, 0, 0, 1; TransZ << cos(AngleC), -sin(AngleC), 0, 0,
sin(AngleC), cos(AngleC), 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1; //点云模型角度变换
Eigen::Vector4f Centroid;
Centroid << 0, 0, 0, 0;
//pcl::compute3DCentroid(*cloudSrc, Centroid);
for (int idx = 0; idx < cloudSrc->points.size(); ++idx){ Eigen::Vector4f PointSrc, PointDest;//维数一致!
PointSrc[0] = cloudSrc->points[idx].x - Centroid[0];
PointSrc[1] = cloudSrc->points[idx].y - Centroid[1];
PointSrc[2] = cloudSrc->points[idx].z - Centroid[2];
//PointSrc[3] = 1;
PointDest = (TransX*(TransY*(TransZ*PointSrc)));//创建矩阵无效! //cloudSrc->points[idx].x = PointDest[0] + Centroid[0];
//cloudSrc->points[idx].y = PointDest[1] + Centroid[1];
//cloudSrc->points[idx].z = PointDest[2] + Centroid[2];
//cloudSrc->points[idx].rgb = cloudSrc->points[idx].rgb;
pcl::PointXYZ p;
p.x = PointDest[0] + Centroid[0];
p.y = PointDest[1] + Centroid[1];
p.z = PointDest[2] + Centroid[2];
//p.x *= 5; p.y *= 5; p.z *= 5;
cloudTrans->push_back(p);
//cloudTrans->points[idx].rgb = cloudSrc->points[idx].rgb;
} return 1.0;
}
重建表面
//仍然产生整数的空隙,应该把原始点云扩充到四个整数邻域//前N个为原始点云
int CViewExtract::genSurfaceFromVertices(std::vector< ::pcl::Vertices> &vertices,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr surfaces)
{
int size = vertices.size();
for ( int i = 0; i < size; ++i ){
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr
surface(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);//(&surfaces[i]);//
genSurfaceFromVertices( vertices[i], cloud, surface, i);
for ( auto p : surface->points){
surfaces->points.push_back(p);
}
surface->clear();
}
return size;
}
//从表面获取点云,对单个面获取点云
int CViewExtract::genSurfaceFromVertices(const pcl::Vertices &vertice,
const pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr surface,
int idx)
{
int size = 0; int nV = vertice.vertices.size();
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr Votex(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
for (int i = 0; i < nV; ++i){
pcl::PointXYZ p(cloud->points[vertice.vertices[i]]);
Votex->points.push_back(p);
} int bx, by, bz;
std::vector<std::pair<float, float> > minmax(3);
//findMinMax( cloud, minmax );
MathCal::findMinMax(Votex, minmax);
bx = ceil(minmax[0].second - minmax[0].first);
by = ceil(minmax[1].second - minmax[1].first);
bz = ceil(minmax[2].second - minmax[2].first);
//bx *= 10; by *= 10; bz *= 10; //取平面上的点//以Z轴为正射方向
std::vector<cv::Point2f> vetexs(0);//生成顶点
int xmin = minmax[0].first;
int ymin = minmax[1].first;
int zmin = minmax[2].first;
for (int i = 0; i < vertice.vertices.size(); ++i){
int idx = vertice.vertices[i];
pcl::PointXYZ p = cloud->points[idx];
cv::Point2f p2 = cv::Point2f(p.x - xmin, p.y - ymin);
//p2.x *= 10;p2.y *= 10;
vetexs.push_back(p2);
} //生成图像//使用OpenCV画出对应二维图片
cv::Mat img = cv::Mat::zeros(by + 1, bx + 1, CV_8UC3);
cv::Mat _lableImg;
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point > > foreAreas;
//wishchin::findInliners2d( img, vetexs, _lableImg, foreAreas );
MathCal::findInliners2dNoCon(img, vetexs, _lableImg, foreAreas);
float zmean = 0;
if (foreAreas.size()>0)
{
size = foreAreas[0].size(); //获取平面方程//Ax + By + Cz + D
//std::vector<float> getPlaneParam(std::vector<cv::Point2f> vetexs);
std::vector<pcl::PointXYZ> VotexP;
for (int i = 0; i < vetexs.size(); ++i){
pcl::PointXYZ p(vetexs[i].x, vetexs[i].y, (cloud->points[vertice.vertices[i]].z - zmin));
VotexP.push_back(p);
zmean += cloud->points[vertice.vertices[i]].z;
}
zmean /= vetexs.size();
std::vector<float> abcd = MathCal::getPlaneParam(VotexP); //从平面上取点
surface->points.resize(0);
float x, y, z;//Mat xy的方向与 PCL是相反的!!!
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i){
x = foreAreas[0][i].x;
y = foreAreas[0][i].y;
//x = bx + 0 - x;
//y = by + 0 - y;
z = 0-(abcd[0] * x + abcd[1] * y + abcd[3]) / abcd[2];
pcl::PointXYZ p(x,y, z);
p.x += xmin; p.y += ymin; p.z += zmin;//移到原位
surface->points.push_back(p);
} surface->height = 1;
surface->width = size;
}
return size;
}
寻找多边形的内点
//寻找多边形的内点//取整数点//只能取凸多边形
//通过判断各个边的左边右边来进行计算//通过计算在多边形的内侧外侧计算-有点慢
//不使用连通域查找//
int MathCal::findInliners2dNoCon(cv::Mat &img, std::vector<cv::Point2f> &vetexs,
cv::Mat &_lableImg, std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point > > &foreAreas)
{
int size = 0; //获取多边形边集
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point2f>> edges(0);
if (vetexs.size() > 2)
{
std::vector<cv::Point2f> edge(0);
edge.push_back(cv::Point2f(vetexs[vetexs.size() - 1]));
edge.push_back(cv::Point2f(vetexs[0]));
edges.push_back(edge);
for (int i = 1; i < vetexs.size(); ++i)
{
edge.resize(0);
edge.push_back(cv::Point2f(vetexs[i - 1]));
edge.push_back(cv::Point2f(vetexs[i]));
edges.push_back(edge);
}
}
//测试
//bool isIn =isInliner(cv::Point2f(2, 538), vetexs, edges);//true
//bool isIn = isInliner(cv::Point2f(476, 258), vetexs, edges);//false
//bool isIn = isInliner(cv::Point2f(704, 137), vetexs, edges);
//bool isIn = isInliner(cv::Point2f(6, 11), vetexs, edges); //取多边形的质心
//从质心开始查找连通域//需要提前染色 std::vector<cv::Point2d> inliners;
cv::Point2d seed(-1, -1);
bool findseed = false;
std::vector<cv::Point > foreArea;
for (int i = 0; i < img.rows; ++i)
{
unsigned char *ptrm = img.ptr<unsigned char>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < img.cols; ++j)
{
int c = *ptrm;
bool isIn = false;
isIn = isInliner(cv::Point2f(j, i), vetexs, edges); //!!!!!出现错误!待调试!//出现了两个方向都奇异的直角三角形
if (isIn){
seed.x = j;
seed.y = i;
foreArea.push_back(seed);
}
++ptrm;
}
}
if (foreArea.size()>0){
foreAreas.push_back(foreArea);
} size = foreAreas.size();
return size;
}
获取平面方程
//获取平面方程//Ax + By + Cz + D
std::vector<float> MathCal::getPlaneParam(const std::vector<pcl::PointXYZ> &votexs)
{
std::vector<float> abcd;
if (votexs.size() < 3){
return abcd;
}
else
{//取前三个点计算平面
float x1, x2, x3, y1, y2, y3, z1, z2, z3;
x1 = votexs[0].x; x2 = votexs[1].x; x3 = votexs[2].x;
y1 = votexs[0].y; y2 = votexs[1].y; y3 = votexs[2].y;
z1 = votexs[0].z; z2 = votexs[1].z; z3 = votexs[2].z;
float A = y1*(z2 - z3) + y2*(z3 - z1) + y3*(z1 - z2);
float B = z1*(x2 - x3) + z2*(x3 - x1) + z3*(x1 - x2);
float C = x1*(y2 - y3) + x2*(y3 - y1) + x3*(y1 - y2);
float D = -(x1*(y2*z3 - y3*z2) + x2*(y3*z1 - y1*z3) + x3*(y1*z2 - y2*z1));
abcd.push_back(A); abcd.push_back(B); abcd.push_back(C);
abcd.push_back(D);
} return abcd;
}
int MathCal::findMinMax(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud,
std::vector<std::pair<float, float> > &minmax)
{
float minX = 10000000;
float minY = 10000000;
float minZ = 10000000;
float maxX = -10000000;
float maxY = -10000000;
float maxZ = -10000000;
for (int i = 0; i < cloud->points.size(); ++i)
{
pcl::PointXYZ p(cloud->points[i]);
if (minX >p.x) minX = p.x;
if (minY > p.y) minY = p.y;
if (minZ > p.z) minZ = p.z;
if (maxX < p.x) maxX = p.x;
if (maxY < p.y) maxY = p.y;
if (maxZ < p.z) maxZ = p.z;
}
minmax.resize(0);
minmax.push_back(std::pair<float, float>(minX, maxX));
minmax.push_back(std::pair<float, float>(minY, maxY));
minmax.push_back(std::pair<float, float>(minZ, maxZ)); return 1;
}
//获取点云,直接从上一步获取
cv::Mat CViewExtract::getViewer(const pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr surface,
const pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloudView)
{
//获取大包围盒
int bx, by, bz;
std::vector<std::pair<float, float> > minmax(3);
MathCal::findMinMax(surface, minmax);
float xmin = minmax[0].first;
float ymin = minmax[1].first;
float zmin = minmax[2].first;
bx = ceil(minmax[0].second - minmax[0].first);
by = ceil(minmax[1].second - minmax[1].first);
bz = ceil(minmax[2].second - minmax[2].first);
std::vector<float> bbx;
bbx.push_back(bx); bbx.push_back(by); bbx.push_back(bz); //std::vector<bool > visibies(surface->points.size() );//直接重新生成点,不取浮点数
//生成图像//使用OpenCV画出对应灰度图片
cv::Mat img = cv::Mat::zeros(by + 1, bx + 1, CV_32FC1);
//for ( pcl::PointXYZ p: surface->points )
for (int i = 0; i < surface->points.size(); ++i)
{
pcl::PointXYZ p = surface->points[i];
int x = p.x - xmin;
int y = p.y - ymin; float z = p.z - zmin + 1;
//取最大Z//必须使用四邻域 int x1 = floor(x); int x2 = ceil(x); //if (x1 < 0) x1 = 0;
int y1 = floor(y); int y2 = ceil(y); //if (y1 < 0) y1 = 0;
MathCal::cutValue(x1, 0, img.cols - 1);
MathCal::cutValue(x2, 0, img.cols - 1);
MathCal::cutValue(y1, 0, img.rows - 1);
MathCal::cutValue(y2, 0, img.rows - 1);
if ( img.at<float>(y1, x1) < z) img.at<float>(y1, x1) = z;
if ( img.at<float>(y1, x2) < z) img.at<float>(y1, x2) = z;
if ( img.at<float>(y2, x2) < z) img.at<float>(y2, x2) = z;
if ( img.at<float>(y2, x1) < z) img.at<float>(y2, x1) = z;
} //补加原始点云的四邻域//原始点云已添加,不再重复补偿,原始点云已删除
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloudFourNear(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
for (int i = 0; i < cloud->points.size(); ++i)
{
pcl::PointXYZ p = cloud->points[i];
float x = p.x - xmin;
float y = p.y - ymin;
float z = p.z - zmin + 1;
int x1 = floor(x); int x2 = ceil(x); //if (x1<0) x1 = 0; if (x2<0) x2 = 0;
int y1 = floor(y); int y2 = ceil(y); //if (y1<0) y1 = 0; if (y2<0) y2 = 0;
MathCal::cutValue(x1, 0, img.cols - 1);
MathCal::cutValue(x2, 0, img.cols - 1);
MathCal::cutValue(y1, 0, img.rows - 1);
MathCal::cutValue(y2, 0, img.rows - 1);
//重复填充四邻域
//若未被填充,则填充
if ( 0.0001> img.at<float>(y1, x1) ) img.at<float>(y1, x1) = z;
if (0.0001> img.at<float>(y1, x2)) img.at<float>(y1, x2) = z;
if (0.0001> img.at<float>(y2, x2)) img.at<float>(y2, x2) = z;
if (0.0001> img.at<float>(y2, x1)) img.at<float>(y2, x1) = z; } cloudView->resize(0);
cv::Mat imgGray = cv::Mat::zeros(by + 1, bx + 1, CV_8UC1);
float x, y, z;
for (int i = 0; i < img.rows; ++i)
{
float *ptr = img.ptr<float>(i);
unsigned char *ptrg = imgGray.ptr<unsigned char>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < img.cols; ++j)
{
if (*ptr > 0)
{
x = j - xmin;
y = i - ymin;
z = *ptr - zmin-1;
cloudView->points.push_back(pcl::PointXYZ(x, y, z));
if (z < 0) z = 0;
if (z >255) z = 255;
*ptrg = (unsigned char)z;
}
++ptr;
++ptrg;
}
} cloudView->height = 1;
cloudView->width = cloudView->points.size(); //cv::flip(imgGray, imgGray, 2);
//cv::imshow("imgGray", imgGray);
//cv::waitKey(0); return imgGray;
}
void MathCal::cutValue(int &inv, const int start, const int end)
{
if (inv < start) inv = start;
if (inv > end) inv = end;
//return inv;
}
输出结果;
通过传入viewpoint输出不同的位姿可见面
三维重建PCL:点云单侧面正射投影的更多相关文章
- PCL点云库:ICP算法
ICP(Iterative Closest Point迭代最近点)算法是一种点集对点集配准方法.在VTK.PCL.MRPT.MeshLab等C++库或软件中都有实现,可以参见维基百科中的ICP Alg ...
- 恒天云单节点部署指南--OpenStack H版本虚拟机单节点部署解决方案
本帖是openstack单节点在虚拟机上部署的实践.想要玩玩和学习openstack的小伙伴都看过来,尤其是那些部署openstack失败的小伙伴.本帖可以让你先领略一下openstack的魅力.本I ...
- PCL中点云数据格式之间的转化
(1) 关于pcl::PCLPointCloud2::Ptr和pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>两中数据结构的区别 pcl::PointXYZ::PointXYZ ...
- PCL点云库中的坐标系(CoordinateSystem)
博客转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33624918/article/details/80488590 引言 世上本没有坐标系,用的人多了,便定义了坐标系统用来定位.地理坐标 ...
- Windows下安装PCL点云库
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/u012337034/article/details/38270109 简介: 在Windows下安装PCL点云库的方法大概有两种: ...
- Windows 8 64位系统 在VS2010 32位软件上 搭建 PCL点云库 开发环境
Windows 8 64位系统 在VS2010 32位软件上 搭建 PCL点云库 开发环境 下载PCL For windows 软件包 到这个网站下载PCL-All-In-One Installer: ...
- PCL学习之:将超声数据按照PCL点云方式发布出去
前言:基于2D激光雷达的机器人,想让它跑自动导航,众所周知有2个比较明显的缺陷,1,那就是普通的激光雷达无法对玻璃或是镜面物体有反映; 2,机器人避障时只能对某一个平面的物体有反映,超过或者低于这个平 ...
- PCL点云特征描述与提取(1)
3D点云特征描述与提取是点云信息处理中最基础也是最关键的一部分,点云的识别.分割,重采样,配准曲面重建等处理大部分算法,都严重依赖特征描述与提取的结果.从尺度上来分,一般分为局部特征的描述和全局特征的 ...
- PCL—点云分割(最小割算法) 低层次点云处理
1.点云分割的精度 在之前的两个章节里介绍了基于采样一致的点云分割和基于临近搜索的点云分割算法.基于采样一致的点云分割算法显然是意识流的,它只能割出大概的点云(可能是杯子的一部分,但杯把儿肯定没分割出 ...
随机推荐
- cocos2d-x中绘制3D图形--3D ToolKit for cocos2dx实现原理
首先:了解具体情况请看这里:https://github.com/wantnon2/3DToolKit-for-cocos2dx 在看代码之前,最好还是先把项目git下来执行一下demoproject ...
- 何时、怎样开启 MySql 日志?
假如你是一名 web 开发者.假设你想调试你的应用或提升其性能的话,那你须要去參考各种日志文件.日志是開始故障排除最好的选择.就著名的 MySql 数据库server而言,你须要參考下面日志文件: 错 ...
- for in、for和EnumerateObjectsUsingBlock遍历的区别
1.对于集合中对象数很多的情况下,for in 的遍历速度非常之快,但小规模的遍历并不明显(还没普通for循环快) 2. 如果在for in 循环里,对这个数组进行了修改的话,无论是增,删,修改数组元 ...
- 【v2.x OGE-example 第三节 播放精灵动画】
1. 位置:Drawing_example --> SpriteAnimated 2. 类名:SpriteAnimated 3.利用AnimatedSprite动画精灵类能够实现多种多种动作. ...
- grep结合awk简单用法
一.grep简介: grep (缩写来自Globally search a Regular Expression and Print)是一种强大的文本搜索工具,它能使用正则表达式搜索文本,并把匹配的行 ...
- [计算机故障]excel无法存盘,总是自动重启恢复
同事的excel文档,无法保存.总是提示什么要发送错误报告.错误报告中的错误信息包含event type:BXE.这个文件大小约1M多.工作簿中包含表大约有30张,表名称为中文.我去看了看,其他电子表 ...
- JS重名解决方案
一个页面如果引用多个JS,或者像ASP.NET MVC,一个视图包含多个子视图,每个子视图有自己的JS,那么变量.函数的重名冲突机会将会大增. 如何解决? 这里有一个方案: 1.用类来封装子页的JS代 ...
- 稀疏表达是要求信号在该模型下的sparse code,只有少数的non-zero elements
为什么sparse representation比起其它成分分析方法(DFT,Wavelet)能得到更好的效果? - 知乎 https://www.zhihu.com/question/241241 ...
- POJ 2562:Primary Arithmetic
Primary Arithmetic Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 11135 Accepted: 40 ...
- POJ2208 Pyramids 四面体体积
POJ2208给定四面体六条棱(有序)的长度 求体积 显然用高中立体几何的方法就可以解决. 给出代码 #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> # ...