吴裕雄 python 机器学习-DMT(2)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8")
leafNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="0.8")
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-") def getNumLeafs(myTree):
numLeafs = 0
for i in myTree.keys():
firstStr = i
break
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':
numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])
else: numLeafs +=1
return numLeafs def getTreeDepth(myTree):
maxDepth = 0
for i in myTree.keys():
firstStr = i
break
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':
thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDict[key])
else: thisDepth = 1
if thisDepth > maxDepth: maxDepth = thisDepth
return maxDepth def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction',xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction',va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args ) def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString):
xMid = (parentPt[0]-cntrPt[0])/2.0 + cntrPt[0]
yMid = (parentPt[1]-cntrPt[1])/2.0 + cntrPt[1]
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30) def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):
numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree)
depth = getTreeDepth(myTree)
for i in myTree.keys():
firstStr = i
break
cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff)
plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode)
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0/plotTree.totalD
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':
plotTree(secondDict[key],cntrPt,str(key))
else:
plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalW
plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key))
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalD def createPlot(inTree):
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')
fig.clf()
axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[])
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops)
#createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False) #ticks for demo puropses
plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree))
plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree))
plotTree.xOff = -0.5/plotTree.totalW; plotTree.yOff = 1.0;
plotTree(inTree, (0.5,1.0), '')
plt.show() def retrieveTree(i):
listOfTrees =[{'no surfacing': {0: 'no', 1: {'flippers': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}}}},
{'no surfacing': {0: 'no', 1: {'flippers': {0: {'head': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}}, 1: 'no'}}}}
]
return listOfTrees[i] thisTree = retrieveTree(0)
createPlot(thisTree)
thisTree = retrieveTree(1)
createPlot(thisTree)

import numpy as np
import operator as op
from math import log def calcShannonEnt(dataSet):
labelCounts = {}
for featVec in dataSet:
currentLabel = featVec[-1]
if(currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys()):
labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0
labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1
shannonEnt = 0.0
rowNum = len(dataSet)
for key in labelCounts:
prob = float(labelCounts[key])/rowNum
shannonEnt -= prob * log(prob,2)
return shannonEnt def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value):
retDataSet = []
for featVec in dataSet:
if(featVec[axis] == value):
reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis]
reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:])
retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec)
return retDataSet def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet):
numFeatures = np.shape(dataSet)[1]-1
baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet)
bestInfoGain = 0.0
bestFeature = -1
for i in range(numFeatures):
featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featList)
newEntropy = 0.0
for value in uniqueVals:
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value)
prob = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet))
newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet)
infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy
if (infoGain > bestInfoGain):
bestInfoGain = infoGain
bestFeature = i
return bestFeature def majorityCnt(classList):
classCount={}
for vote in classList:
if(vote not in classCount.keys()):
classCount[vote] = 0
classCount[vote] += 1
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key=op.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
return sortedClassCount[0][0] def createTree(dataSet,labels):
classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet]
if(classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList)):
return classList[0]
if len(dataSet[0]) == 1:
return majorityCnt(classList)
bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet)
bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat]
myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}}
del(labels[bestFeat])
featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featValues)
for value in uniqueVals:
subLabels = labels[:]
myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, value),subLabels)
return myTree def classify(inputTree,featLabels,testVec):
for i in inputTree.keys():
firstStr = i
break
secondDict = inputTree[firstStr]
featIndex = featLabels.index(firstStr)
key = testVec[featIndex]
valueOfFeat = secondDict[key]
if isinstance(valueOfFeat, dict):
classLabel = classify(valueOfFeat, featLabels, testVec)
else:
classLabel = valueOfFeat
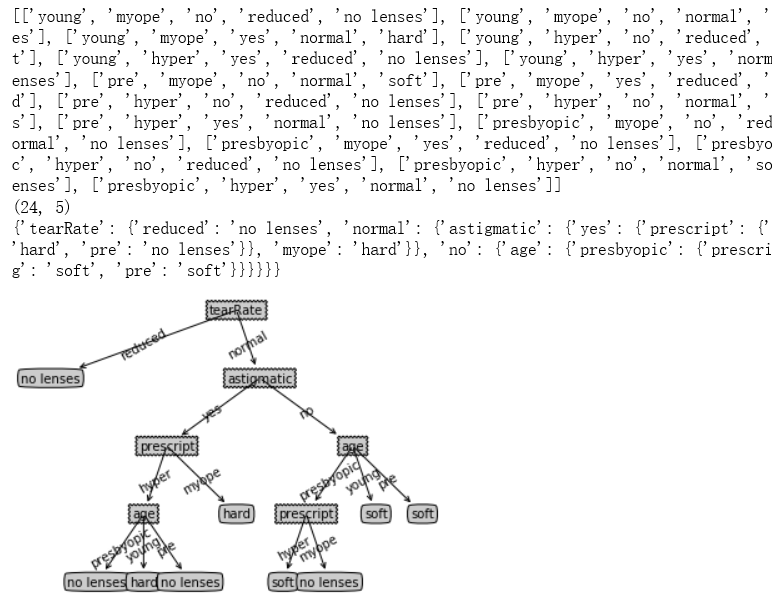
return classLabel data = open("D:\\LearningResource\\machinelearninginaction\\Ch03\\lenses.txt")
dataSet = [inst.strip().split("\t") for inst in data.readlines()]
print(dataSet)
print(np.shape(dataSet))
labels = ["age","prescript","astigmatic","tearRate"]
tree = createTree(dataSet,labels)
print(tree) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8")
leafNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="0.8")
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-") def getNumLeafs(myTree):
numLeafs = 0
for i in myTree.keys():
firstStr = i
break
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':
numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])
else: numLeafs +=1
return numLeafs def getTreeDepth(myTree):
maxDepth = 0
for i in myTree.keys():
firstStr = i
break
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':
thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDict[key])
else: thisDepth = 1
if thisDepth > maxDepth: maxDepth = thisDepth
return maxDepth def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction',xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction',va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args ) def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString):
xMid = (parentPt[0]-cntrPt[0])/2.0 + cntrPt[0]
yMid = (parentPt[1]-cntrPt[1])/2.0 + cntrPt[1]
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30) def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):
numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree)
depth = getTreeDepth(myTree)
for i in myTree.keys():
firstStr = i
break
cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff)
plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode)
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0/plotTree.totalD
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':
plotTree(secondDict[key],cntrPt,str(key))
else:
plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalW
plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key))
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalD def createPlot(inTree):
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')
fig.clf()
axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[])
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops)
#createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False) #ticks for demo puropses
plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree))
plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree))
plotTree.xOff = -0.5/plotTree.totalW; plotTree.yOff = 1.0;
plotTree(inTree, (0.5,1.0), '')
plt.show() createPlot(tree)
吴裕雄 python 机器学习-DMT(2)的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习-DMT(1)
import numpy as np import operator as op from math import log def createDataSet(): dataSet = [[1, 1, ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——分类决策树模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets from sklearn.model_s ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——回归决策树模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets from sklearn.model_s ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——线性判断分析LinearDiscriminantAnalysis
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib import cm from mpl_toolkits.mplot ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——逻辑回归
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib import cm from mpl_toolkits.mplot ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——ElasticNet回归
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib import cm from mpl_toolkits.mplot ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——Lasso回归
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets, linear_model from s ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——岭回归
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets, linear_model from s ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——线性回归模型
import numpy as np from sklearn import datasets,linear_model from sklearn.model_selection import tra ...
随机推荐
- Android获取文件夹下的所有子文件名称;
public static List<String> getFilesAllName(String path) { File file=new File(path); File[] fil ...
- Android最新版支付宝支付集成
上次集成支付宝支付已经很久了,今天写东西用到了支付宝支付,就大致写一下流程: 去蚂蚁金服下载最新版的Android&IOS端SDK 全部文档 -- 资源下载 -- App支付客户端 下载后解压 ...
- java第一次考试
这是我们开学的第一次Java课的考试,考的我有点害怕. 老师说这是给我们在正式上课之前提个醒,确实,我明白了我在学习方面还有多大的差距,确实,就如我高中同学所说的那样,没事就应该往机房跑了. 在上个学 ...
- Java并发知识整理
整理了一下前段时间学习Java并发的笔记,大约有40篇. 1. Java并发基础知识 并发基础(一) 线程介绍 并发基础(二) Thread类的API总结 并发基础(三) java线程优先级 并发基础 ...
- Call requires permission which may be rejected by user: code should explicitly check to see if permi
Call requires permission which may be rejected by user: code should explicitly check to see if permi ...
- c#上传文件并将word pdf转化成txt存储并将内容写入数据库
c#上传文件并将word pdf转化成txt存储并将内容写入数据库 using System; using System.Data; using System.Configuration; using ...
- 17.scrapy-splash安装-2
scrapy-splash是一个scrapy中支持的javascript渲染的工具. scrapy-splash安装分为两部分.一个是splash服务的安装,具体是通过docker,安装之后,会启动一 ...
- ADO.net 增删改查
ADO.net 一.定义:编程开发语言与数据库连接的一门语言技术 二.链接: 在vs中操作数据库需在开头进行链接 链接内容:using System.Data.SqlClient 三.引用数据库: 四 ...
- HTML5 元素超出部分滚动, 并隐藏滚动条
方法一, 利用 css 3 的新特性 -webkit-scrollbar, 但是这种方式不兼容 火狐 和 IE <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head ...
- redis点
(1)什么是redis? Redis 是一个基于内存的高性能key-value数据库. (有空再补充,有理解错误或不足欢迎指正) (2)Reids的特点 Redis本质上是一个Key-Value类型的 ...
