[C++ Primer Plus] 第9章、内存模型和名称空间(一)程序清单
程序清单9.9(静态存储连续性、无链接性)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; const int Size=;
void strcount(const char *str){//const表示str指针不能修改指向的内容(不过可以指向另外一块内容)
static int total=;//static静态变量,首次初始化后,其值一直存在(即第二次调用strcount函数时,total的值不会再次初始化)
int count=;
cout<<"\""<<str<<"\" contains ";
while (*str++)//先判断*str是否为NULL,然后再str++
count++;
total+=count;
cout<<count<<" characters\n";
cout<<total<<" characters total!\n";
} void main() {
char in[Size];
char next;
cout<<"Enter a line:"<<endl;
cin.get(in,Size);//最多接收Size-1个字符+1个'\0'
while (cin) // ==while(!cin.fail()),即读入流成功
{
cin.get(next);
while(next!='\n') //若next不是换行符
cin.get(next);
strcount(in);
cout<<"Enter next line (empty line to quit):\n";
cin.get(in,Size);
}
cout<<"Bye!"<<endl;
system("pause");
}

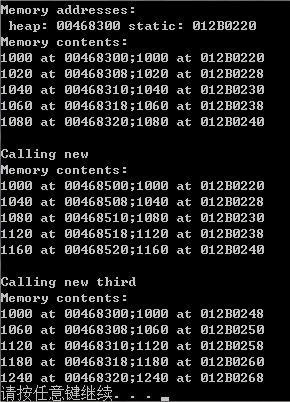
程序清单9.10(常规new和定位new运算符)
#include<iostream>
#include<new> //定位new运算符
using namespace std; const int BUF=;
const int N=;
char buff[BUF]; void main() {
double *p1,*p2;
int i;
cout<<"Calling"<<endl;
p1=new double[N];//常规new:p1是double指针
p2=new (buff) double[N];//定位new运算符:将数组p2放在了数组buff中
for (i = ; i < N; i++)
p2[i]=p1[i]=+20.0*i;
cout<<"Memory addresses:"<<endl<<" heap: "<<p1<<" static: "<<(void *)buff<<endl;//buffer是char指针,所以要使用(void *)对buffer进行强转,否则将显示字符串
cout<<"Memory contents:"<<endl;
for (i = ; i < N; i++)
{
cout<<p1[i]<<" at "<<&p1[i]<<";";
cout<<p2[i]<<" at "<<&p2[i]<<endl;
} cout<<"\nCalling new"<<endl;
double *p3,*p4;
p3=new double[N];
p4=new (buff) double[N];
for (i = ; i < N; i++)
p4[i]=p3[i]=+40.0*i;
cout<<"Memory contents:"<<endl;
for (i = ; i < N; i++)
{
cout<<p3[i]<<" at "<<&p3[i]<<";";
cout<<p4[i]<<" at "<<&p4[i]<<endl;
} cout<<"\nCalling new third"<<endl;
delete [] p1;
p1=new double [N];
p2=new (buff+N*sizeof(double)) double[N];
for (i = ; i < N; i++)
p2[i]=p1[i]=+60.0*i;
cout<<"Memory contents:"<<endl;
for (i = ; i < N; i++)
{
cout<<p1[i]<<" at "<<&p1[i]<<";";
cout<<p2[i]<<" at "<<&p2[i]<<endl;
}
//buff指定的内存是静态内存,所以不能delete
delete [] p1;
delete [] p3; system("pause");
}
程序清单9.11-13(名称空间示例)
namesp.h 头文件
#include<string>
namespace pers{ //包含Person结构的定义和两个函数原型
struct Person{
std::string fname;
std::string lname;
};
void getPerson(Person &);//引用
void showPerson(const Person &);
} namespace debts{ //定义Debt结构,用于存储人名和金额,使用using编译指令,让pers中的名称在debts空间也能使用
using namespace pers;
struct Debt{
Person name;
double amount;
};
void getDebt(Debt &);
void showDebt(const Debt &);
double sumDebts(const Debt ar[],int n);
}
namesp.cpp 函数定义
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include "namesp.h"//自己编写的头文件只能使用引号"",系统自带的头文件使用<>,不过""也能用 namespace pers{
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
void getPerson(Person &rp){
cout<<"Enter first name:";
cin>>rp.fname;
cout<<"Enter last name:";
cin>>rp.lname;
}
void showPerson(const Person &rp){
cout<<rp.lname<<","<<rp.fname;
}
} namespace debts{
void getDebt(Debt &rd){
getPerson(rd.name);
std::cout<<"Enter debt:";
std::cin>>rd.amount;
}
void showDebt(const Debt &rd){
showPerson(rd.name);
std::cout<<": $"<<rd.amount<<std::endl;
}
double sumDebts(const Debt ar[],int n){
double total=;
for (int i = ; i < n; i++)
total+=ar[i].amount;
return total;
}
}
main.cpp 主函数
#include<iostream>
#include "namesp.h"
using std::cout;
using std::endl; void other(){
using namespace debts;
Person dg={"Doodles","Glister"};
showPerson(dg);
cout<<endl;//因为showPerson没有换行
Debt zippy[];
int i;
for (i = ; i < ; i++)
getDebt(zippy[i]);
for (i = ; i < ; i++)
showDebt(zippy[i]);
cout<<"Total debt: $"<<sumDebts(zippy,)<<endl;
} void another(){
using pers::Person;
Person collector={"Milo","Rightshift"};
pers::showPerson(collector);
cout<<endl;
} void main(){
using debts::Debt;
using debts::showDebt;
Debt golf={{"Benny","Goatsniff"},120.0};
showDebt(golf);
other();
another();
system("pause");
}

[C++ Primer Plus] 第9章、内存模型和名称空间(一)程序清单的更多相关文章
- C++ primer plus读书笔记——第9章 内存模型和名称空间
第9章 内存模型和名称空间 1. 头文件常包含的内容: 函数原型. 使用#define或const定义的符号常量. 结构声明. 类声明. 模板声明. 内联函数. 2. 如果文件名被包含在尖括号中,则C ...
- 《C++ Primer Plus》第9章 内存模型和名称空间 学习笔记
C++鼓励程序员在开发程序时使用多个文件.一种有效的组织策略是,使用头文件来定义用户类型,为操纵用户类型的函数提供函数原型,并将函数定义放在一个独立的源代码文件中.头文件和源代码文件一起定义和实现了用 ...
- 《C++ Primer Plus 6th》读书笔记 - 第九章 内存模型和名称空间
1. 单独编译 1.1 头文件中常包含的内容: 函数原型 使用#define或const定义的符号常量 结构声明 类声明 模板声明 内联声明 1.2 只需将源代码文件加入到项目中,而不用加入头文件.这 ...
- 《C++ Primer Plus》读书笔记之七—内存模型和名称空间
第九章 内存模型和名称空间 1.不要将函数定义或者变量声明放到头文件中. 2.头文件常包含的内容:函数原型.使用#define或者const定义的常量.结构声明.类声明.模板声明.内联函数. 3.避免 ...
- [C++ Primer Plus] 第8章、函数探幽(一)程序清单——内联、引用、格式化输入输出、模板、decltype
程序清单8.1(inline内联函数) #include<iostream> using namespace std; inline double square(double x) {// ...
- [C++ Primer Plus] 第4章、复合类型(一)程序清单——指针new和delete
程序清单4.1 #include<iostream> using namespace std; void main(){ ]; yams[]=; yams[]=; yams[]=; ]={ ...
- (8)C++ 内存模型与名称空间
一.单独编译 头文件 不要将函数定义或者变量声明放到头文件中,引入多个文件时可能会造成同一个函数定义多次 引入头文件 #include "文件名" File1.h #ifndef ...
- [C++ Primer Plus] 第9章、内存模型和名称空间(二)课后习题
一.复习题 2.using声明和using编译指令的区别 using声明: using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl; using编译指令:us ...
- C++ Primer Plus读书笔记(九)内存模型和名称空间
1.作用域和链接 int num3; static int num4; int main() { } void func1() { static int num1; int num2; } 上边的代码 ...
随机推荐
- Gym 101606 - A/B/C/D/E/F/G/H/I/J/K/L - (Undone)
链接:https://codeforces.com/gym/101606 A - Alien Sunset 暴力枚举小时即可. #include<bits/stdc++.h> using ...
- javascript 表达式
// for(表达式1;表达式2;表达式3){// 循环体语句;// }// 先执行表达式1,在执行2表达式,// 如果2表达式结果为false,退出循环 ...
- 转:三款免费好用的Gif录屏神器
原文链接:三款免费好用的Gif录屏神器 自己用了 ScreenToGif 版本2.14.1下载地址 原文内容: 三款免费好用的Gif录屏神器 2018年06月02日 18:52:21 独家雨 ...
- Java代码实现封装多级树结构对象
前言: 在开发中,我们经常见到,前端展示树状结构的,这时候就需要后端去封装一个多级树结构对象,前端根据这样结构的数据去渲染数据,这篇文章讲的是如何封装成多级树结构对象. 正文: 1.先封装个树结构的对 ...
- uboot - the bootloader of linux
[转载]https://blog.csdn.net/kernel_yx/article/details/53045424 最近一段时间一直在做uboot移植相关的工作,需要将uboot-2016-7移 ...
- YII - 打印 SQL
$query = Order::find()->select(['order_sys_id'])->where(['order_car_id'=>'AA','order_status ...
- 内网gitlab11.2升级至11.4.5
当前gitlab版本 宿主机是一台ubuntu 运行备份命令 sudo gitlab-rake gitlab:backup:create STRATEGY=copy 升级命令 sudo apt-get ...
- [LintCode] 77. Longest common subsequences_ Medium tag: Dynamic Programming
Given two strings, find the longest common subsequence (LCS). Example Example 1: Input: "ABCD&q ...
- 一个农民工混迹于 IT 行业多年后的泣血总结
一看题目,你心里一定闪出一个想法,这又是一篇软文吧,是不是,不想辩别了,自己判断吧哈哈.这是根据本人真实经历所写的一篇总结.假如你满足你的现状,这就是一篇软文,请立刻关闭此文章,继续你现在的生活. ...
- crypto++
CryptoPP库是一个C++书写的加密算法库,很棒. 在如今的抛却数字证书体系下,只关注公私钥对的情况下,我认为存粹的加解密算法库很有市场,虽然我以前觉得PolarSSL的加解密算法实现不错,但不影 ...

