多线程实现之Java
关于Java线程的生命周期,请看下面这张图:
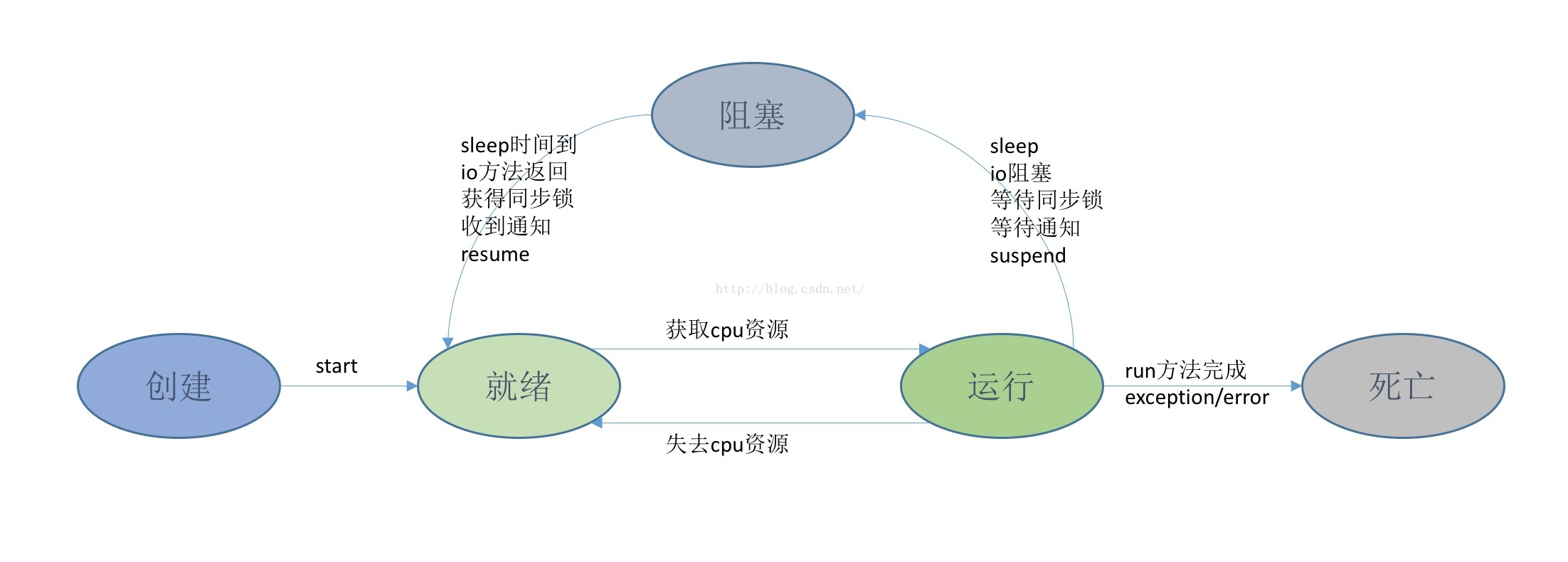
新建状态(New):当线程对象创建后,即进入了新建状态,如:Thread t = new MyThread();
就绪状态(Runnable):当调用线程对象的start()方法(t.start();),线程即进入就绪状态。处于就绪状态的线程,只是说明此线程已经做好了准备,随时等待CPU调度执行,并不是说执行了t.start()此线程立即就会执行;
运行状态(Running):当CPU开始调度处于就绪状态的线程时,此时线程才得以真正执行,即进入到运行状态。
阻塞状态(Blocked):处于运行状态中的线程由于某种原因,暂时放弃对CPU的使用权,停止执行,此时进入阻塞状态,直到其进入到就绪状态,才有机会再次被CPU调用以进入到运行状态。
阻塞状态有以下几种进入条件:
1.等待阻塞:运行状态中的线程执行wait()方法,使本线程进入到等待阻塞状态;
2.同步阻塞 -- 线程在获取synchronized同步锁失败(因为锁被其它线程所占用),它会进入同步阻塞状态;
3.其他阻塞 -- 通过调用线程的sleep()或join()或发出了I/O请求时,线程会进入到阻塞状态。当sleep()状态超时、join()等待线程终止或者超时、或者I/O处理完毕时,线程重新转入就绪状态。
4.调用线程的suspend方法主动挂起,不过这个方法目前不推荐使用。
出现上述几种条件对应的退出条件,阻塞状态会回到就绪状态,重新等待CPU调度执行。
阻塞状态需要再次进入就绪状态之后才能再次进入运行状态。
死亡状态(Dead):线程执行完了或者因异常退出了run()方法,该线程结束生命周期。
在java线程实现中,针对阻塞状态有做了一定的细分,分为了 BLOCKED ,WAITING,TIMED_WAITING 几种,分别对应等待 进入同步代码块,等待唤醒 ,有时间的等待唤醒几种。
具体枚举定义代码如下:
public enum State { NEW, RUNNABLE, BLOCKED, WAITING, TIMED_WAITING, TERMINATED; }Java线程实现几种方式
1.继承Thread类型,覆写run()方法,run方法里面实现自己需要的逻辑,new Thread()之后 线程进入创建状态,start()之后进入就绪状态,进入运行状态时机取决于系统CPU调度。
public class MyThread extends Thread{ public void run(){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } } //线程启动 new MyThread().start();2.实现Runnable接口,实现其run()方法,创建其实例,并通过该实例构造 Thread ,通过Thread来启动。
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } } //线程启动 Runnable runnable =new MyRunnable() ; new Thread(runnable).start(); 查看Thread类的run方法可以发现 其实现如下: public void run() { if (target != null) { target.run(); } }实际执行了我们传入Runnable对象的run方法。
3.jdk1.5之后又提供了另一种方式,通过实现Callable接口来创建线程,提供有返回值的call方法,来达到获得线程返回值的目的,外部线程可以通过future接口可以获得线程执行结果。
public class MyCallable implements Callable<String>{ @Override public String call() throws Exception { return "my name is MyCallable"; } }使用callable创建线程的启动方式稍微复杂,代码如下:
Callable<String> callable = new MyCallable(); FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<String>(callable); new Thread(futureTask).start(); System.out.println(futureTask.get());从上面可以看到callable和前两种实现方式的差别是Callable可以获得返回值。
除了我们手动创建FutureTask的方式启动以外,还可以通过jdk提供的并发执行器进行执行,不需要我们自己手动创建FutureTask对象来执行,代码如下:
Callable<String> callable = new MyCallable(); ExecutorService executorService =Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1); Future<String> future = executorService.submit(callable) ; System.out.println(future.get()); executorService.shutdown();执行器同样可以用来执行Runnable对象,代码类似,只是不能获得返回值。
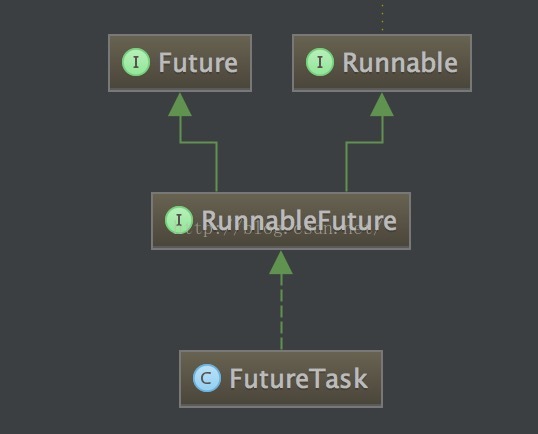
下面看看Callable如何做到返回线程执行结果的,首先我们看看FutureTask的类继承关系:
从上图可以很清晰的看到FutureTask实际也实现了Runnable接口 ,其run方法实现如下:
public void run() { if (state != NEW || !UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset, null, Thread.currentThread())) return; try { Callable<V> c = callable; if (c != null && state == NEW) { V result; boolean ran; try { result = c.call(); ran = true; } catch (Throwable ex) { result = null; ran = false; setException(ex); } if (ran) set(result); } } finally { // runner must be non-null until state is settled to // prevent concurrent calls to run() runner = null; // state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent // leaked interrupts int s = state; if (s >= INTERRUPTING) handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s); } }所以可以看出来Callable实际就是在Runnable进行了一层包装达到可以携带执行返回结果的目的。
所以总结下来,其实后两种实现都是在Thread基础上进行封装的,实际的执行都是靠Thread对象来执行的。
线程的start方法调用之后究竟会发生什么
首先我们看一下Thread类的start方法public synchronized void start() { /** * This method is not invoked for the main method thread or "system" * group threads created/set up by the VM. Any new functionality added * to this method in the future may have to also be added to the VM. * * A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW". */ if (threadStatus != 0) throw new IllegalThreadStateException(); /* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started * so that it can be added to the group's list of threads * and the group's unstarted count can be decremented. */ group.add(this); boolean started = false; try { start0(); started = true; } finally { try { if (!started) { group.threadStartFailed(this); } } catch (Throwable ignore) { /* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then it will be passed up the call stack */ } } }实际上是调用了本地方法start0()
本地方法,定义在Thread.c文件里面
static JNINativeMethod methods[] = { {"start0", "()V", (void *)&JVM_StartThread}, {"stop0", "(" OBJ ")V", (void *)&JVM_StopThread}, {"isAlive", "()Z", (void *)&JVM_IsThreadAlive}, {"suspend0", "()V", (void *)&JVM_SuspendThread}, {"resume0", "()V", (void *)&JVM_ResumeThread}, {"setPriority0", "(I)V", (void *)&JVM_SetThreadPriority}, {"yield", "()V", (void *)&JVM_Yield}, {"sleep", "(J)V", (void *)&JVM_Sleep}, {"currentThread", "()" THD, (void *)&JVM_CurrentThread}, {"countStackFrames", "()I", (void *)&JVM_CountStackFrames}, {"interrupt0", "()V", (void *)&JVM_Interrupt}, {"isInterrupted", "(Z)Z", (void *)&JVM_IsInterrupted}, {"holdsLock", "(" OBJ ")Z", (void *)&JVM_HoldsLock}, {"getThreads", "()[" THD, (void *)&JVM_GetAllThreads}, {"dumpThreads", "([" THD ")[[" STE, (void *)&JVM_DumpThreads}, };从上面的代码可以看出start0实际是调用了JVM_StartThread方法,我们找找JVM_StartThread方法的定义
static void thread_entry(JavaThread* thread, TRAPS) { HandleMark hm(THREAD); Handle obj(THREAD, thread->threadObj()); JavaValue result(T_VOID); JavaCalls::call_virtual(&result, obj, KlassHandle(THREAD, SystemDictionary::Thread_klass()), vmSymbols::run_method_name(), vmSymbols::void_method_signature(), THREAD); } JVM_ENTRY(void, JVM_StartThread(JNIEnv* env, jobject jthread)) JVMWrapper("JVM_StartThread"); JavaThread *native_thread = NULL; // We cannot hold the Threads_lock when we throw an exception, // due to rank ordering issues. Example: we might need to grab the // Heap_lock while we construct the exception. bool throw_illegal_thread_state = false; // We must release the Threads_lock before we can post a jvmti event // in Thread::start. { // Ensure that the C++ Thread and OSThread structures aren't freed before // we operate. MutexLocker mu(Threads_lock); // Since JDK 5 the java.lang.Thread threadStatus is used to prevent // re-starting an already started thread, so we should usually find // that the JavaThread is null. However for a JNI attached thread // there is a small window between the Thread object being created // (with its JavaThread set) and the update to its threadStatus, so we // have to check for this if (java_lang_Thread::thread(JNIHandles::resolve_non_null(jthread)) != NULL) { throw_illegal_thread_state = true; } else { // We could also check the stillborn flag to see if this thread was already stopped, but // for historical reasons we let the thread detect that itself when it starts running jlong size = java_lang_Thread::stackSize(JNIHandles::resolve_non_null(jthread)); // Allocate the C++ Thread structure and create the native thread. The // stack size retrieved from java is signed, but the constructor takes // size_t (an unsigned type), so avoid passing negative values which would // result in really large stacks. size_t sz = size > 0 ? (size_t) size : 0; <span style="color:#ff6666;">native_thread = new JavaThread(&thread_entry, sz);</span> // At this point it may be possible that no osthread was created for the // JavaThread due to lack of memory. Check for this situation and throw // an exception if necessary. Eventually we may want to change this so // that we only grab the lock if the thread was created successfully - // then we can also do this check and throw the exception in the // JavaThread constructor. if (native_thread->osthread() != NULL) { // Note: the current thread is not being used within "prepare". native_thread->prepare(jthread); } } } if (throw_illegal_thread_state) { THROW(vmSymbols::java_lang_IllegalThreadStateException()); } assert(native_thread != NULL, "Starting null thread?"); if (native_thread->osthread() == NULL) { // No one should hold a reference to the 'native_thread'. delete native_thread; if (JvmtiExport::should_post_resource_exhausted()) { JvmtiExport::post_resource_exhausted( JVMTI_RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED_OOM_ERROR | JVMTI_RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED_THREADS, "unable to create new native thread"); } THROW_MSG(vmSymbols::java_lang_OutOfMemoryError(), "unable to create new native thread"); } Thread::start(native_thread); JVM_END可以看到在JVM_StartThread方法里面创建了实际跟平台有关系的本地线程,线程函数是thread_entry ,thread_entry定义了实际调用vmSymbols::run_method_name()这个方法,这个方法实际就是定义运行run方法,在vmSymbols.hpp可以看到定义如下:本地线程最终执行run_method_name这个方法
template(run_method_name, "run")可以看到线程最终执行我们的Thread对象的run方法。
所以整个调用时序是 Thread.start -->JVM_StartThread -->thread_entry --> os本地线程(异步) --> Thread.run
总结
从上面我们知道java 线程是建立在系统本地线程之上的,通过Thread对象做了一层封装,封装了各个不同平台的细节,提供了统一的API ,Thread之上又做了 Runnable的回调和Callable的回调。
多线程实现之Java的更多相关文章
- 多线程包:java.util.concurrent,
Java1.5提供了一个非常高效实用的多线程包:java.util.concurrent,
- 多线程系列之 java多线程的个人理解(二)
前言:上一篇多线程系列之 java多线程的个人理解(一) 讲到了线程.进程.多线程的基本概念,以及多线程在java中的基本实现方式,本篇主要接着上一篇继续讲述多线程在实际项目中的应用以及遇到的诸多问题 ...
- 多线程系列之 Java多线程的个人理解(一)
前言:多线程常常是程序员面试时会被问到的问题之一,也会被面试官用来衡量应聘者的编程思维和能力的重要参考指标:无论是在工作中还是在应对面试时,多线程都是一个绕不过去的话题.本文重点围绕多线程,借助Jav ...
- Java网络多线程开发:java.io.EOFException
Java网络多线程开发:java.io.EOFException 在实现韩顺平Java的多用户即使通信系统实战项目中: 对于客户端线程的停止,老韩是向服务器端发送一个消息对象,提示服务器端进行资源释放 ...
- Java多线程编程核心技术---Java多线程技能
基本概念 进程是操作系统结构的基础,是一次程序的执行,是一个程序及其数据结构在处理机上顺序执行时所发生的活动,是程序在一个数据集合上运行的过程,是系统进行资源分配和调度的独立单位.线程可以理解成是在进 ...
- (原创)Java多线程作业题报java.lang.IllegalMonitorStateException解决
作业: 有一个水池,水池容量500L,一边为进水口,一边为出水口,要求进水放水不能同时进行,水池一旦满了不能继续注水,一旦空了,不能继续放水,进水速度5L/s,放水速度2L/s. 这是我学多线程时做的 ...
- 多线程并发之java内存模型JMM
多线程概念的引入是人类又一次有效压寨计算机的体现,而且这也是非常有必要的,因为一般运算过程中涉及到数据的读取,例如从磁盘.其他系统.数据库等,CPU的运算速度与数据读取速度有一个严重的不平衡,期间如果 ...
- 【java多线程系列】java中的volatile的内存语义
在java的多线程编程中,synchronized和volatile都扮演着重要的 角色,volatile是轻量级的synchronized,它在多处理器开发中保证了共享变量的可见性,可见性指的是当一 ...
- 【java多线程系列】java内存模型与指令重排序
在多线程编程中,需要处理两个最核心的问题,线程之间如何通信及线程之间如何同步,线程之间通信指的是线程之间通过何种机制交换信息,同步指的是如何控制不同线程之间操作发生的相对顺序.很多读者可能会说这还不简 ...
- java多线程的基础-java内存模型(JMM)
在并发编程中,需要处理两个关键问题:线程之间如何通信,以及线程之间如何同步.通信是指线程之间如何交换信息,在命令式编程中,线程之间的通信机制有两种:内存共享和消息传递. 同步是指程序中用于控 ...
随机推荐
- struts2.xml的配置问题
1.<package namespace="/"></package> namespace决定访问action的路径: 如果省略,将代表任意路径: 2.&l ...
- HTTP基本知识
1.TCP/IP 传输控制协议/因特网互联协议 (1)应用层:决定向用户提供应用服务时通信的活动(FTP.DNS和HTTP都属于该层). (2)传输层:提供处于网络连接中的两台计算机之间的数据传输(T ...
- ansible 批量安装zabbix agentd客户端
目录结构 # tree /etc/ansible/ /etc/ansible/ ├── ansible.cfg ├── hosts ├── roles │ └── zabbix-agentd │ ...
- 极其蛋疼的if else 中的break用法
主要原因是if不是循环语句 像这样的: while(...) { ==res) { break; } printf("A"); } 跳出的就是while循环.而不是if判断语句 补 ...
- (三)surging 微服务框架使用系列之我的第一个服务(审计日志)
前言:前面准备了那么久的准备工作,现在终于可以开始构建我们自己的服务了.这篇博客就让我们一起构建自己的第一个服务---审计日志. 首先我们先创建两个项目,一个控制台的服务启动项目,一个业务的实现项目. ...
- docker命令行学习
docker命令行学习 docker run docker run --help:老实说这条最管用了 docker run -it:交互模式,允许控制台输出 docker run -d:detach, ...
- C#基础(二)--之数据类型
在第一章我们了解了C#的输入.输出语句后,我这一节主要是介绍C#的基础知识,本节的内容也是后续章节的基础,好的开端等于成功的一半.在你阅读完本章后,你就有足够的C#知识编写简单的程序了.但还不能使用继 ...
- python 列表操作方法详解
列表是Python中最基本的数据结构,列表是最常用的Python数据类型,列表是一个数据的集合,集合内可以放任何数据类型,可对集合方便的增删改查操作.Python已经内置确定序列的长度以及确定最大和最 ...
- stat,fstat,lstat三者区别
fstat ,lstat,stat; 头文件:#include<sys/stat.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<unistd.h&g ...
- yii2 源码分析Action类分析 (六)
Action类是控制器的基类, <?php namespace yii\base; use Yii; /** * Action是所有控制器动作类的基类,它继承组件类 * * 动作提供了重用动作方 ...