MySQLDemo2
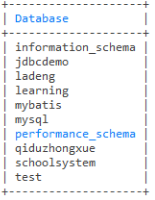
-- 查询所有数据库
show databases
-- 删除数据库
drop database a
-- use `数据库名称`; 表示使用此数据库
use mybatis
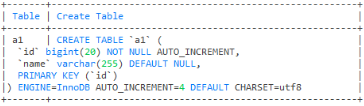
-- 查看表结构
show create table a1
-- 删除表
drop table a
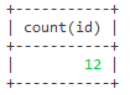
-- 查询表总共有多少条数据
select count(1) from user

select count(id) from user
-- 添加一条数据
insert into user (name,age) values ('蓝凤凰',19)
-- 添加多条数据
insert into user (name,age) values ('蓝凤凰',19),('蓝孔雀',20)
-- 这两个一起运行
insert into user (name,age) values ('曼联',21);
insert into user (name,age) values ('张倩',19);
-- 更新一条数据
update user set name = '阿紫',age =18 where id = 8
-- 更新多条数据
-- 这两个一起运行
update user set name = '小张',age = 19 where id = 9;
update user set name = '张三',age = 20 where id = 10;
-- 删除一条数据
delete from user where id = 1
-- 删除多条数据
delete from user where id in (2,3)
-- 这两个一起运行
delete from user where id = 5;
delete from user where id = 6;
-- 查询年龄在18到20之间
select * from user where age between 18 and 20
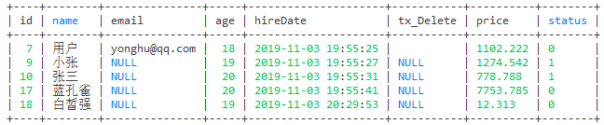
-- 查询年龄>= 18并且年龄<=20数据
select * from user where age >=18 and age <=20
-- 从id=10开始算总条数
select count(8) from user where id > 9

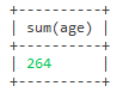
-- 查询age的总数
select sum(age) from user
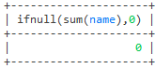
-- 这里查询名字没有总数就返回0
select ifnull(sum(name),0) from user
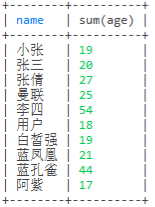
-- 这里是按照name分组去重,名字相同的就把age的值加起来
select name, sum(age) from user group by name;
-- 查询tx_delete判断是否删除
-- 第一种写法
select id,tx_delete,
case
when tx_delete = 0 then '未删除'
else '已删除'
end as delete_sc
from user
select id,tx_delete,
case
when tx_delete = 0 then '未删除'
when tx_delete = 1 then '已删除'
end as delete_sc
from user
select id,tx_delete,
case
when tx_delete = 0 then '未删除'
when tx_delete = 1 then '已删除'
else '' end as delete_sc
from user
-- 第二种写法
-- 这个随便怎么样都是已删除
select id,tx_delete,
case
when 0 then '未删除'
when 1 then '已删除'
end as delete_sc
from user
-- 这个添加过数据的就是未删除
select id,tx_delete,
case tx_delete
when 0 then '未删除'
else '已删除'
end as delete_sc
from user
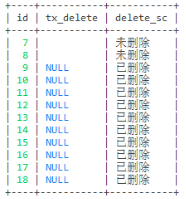
-- 第三种写法
select tx_delete, if(tx_delete = 0, '未删除', '已删除') as delete_sc from user
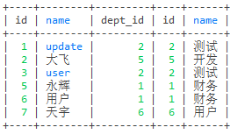
-- 左连接
select * from employee e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id
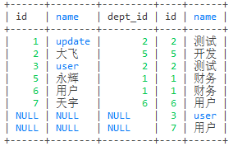
-- 右连接
select * from employee e right join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id
-- 内连接
select * from employee e join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id
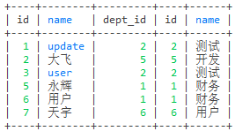
select * from employee e inner join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id
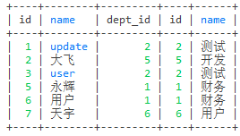
-- where连接
select * from employee e, dept d where e.dept_id = d.id
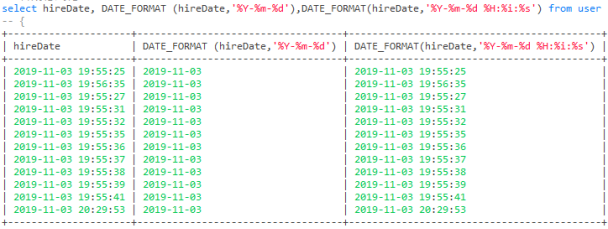
-- 日期格式化
| 格式 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| %a | 缩写星期名 |
| %b | 缩写月名 |
| %c | 月,数值 |
| %D | 带有英文前缀的月中的天 |
| %d | 月的天,数值(00-31) |
| %e | 月的天,数值(0-31) |
| %f | 微秒 |
| %H | 小时 (00-23) |
| %h | 小时 (01-12) |
| %I | 小时 (01-12) |
| %i | 分钟,数值(00-59) |
| %j | 年的天 (001-366) |
| %k | 小时 (0-23) |
| %l | 小时 (1-12) |
| %M | 月名 |
| %m | 月,数值(00-12) |
| %p | AM 或 PM |
| %r | 时间,12-小时(hh:mm:ss AM 或 PM) |
| %S | 秒(00-59) |
| %s | 秒(00-59) |
| %T | 时间, 24-小时 (hh:mm:ss) |
| %U | 周 (00-53) 星期日是一周的第一天 |
| %u | 周 (00-53) 星期一是一周的第一天 |
| %V | 周 (01-53) 星期日是一周的第一天,与 %X 使用 |
| %v | 周 (01-53) 星期一是一周的第一天,与 %x 使用 |
| %W | 星期名 |
| %w | 周的天 (0=星期日, 6=星期六) |
| %X | 年,其中的星期日是周的第一天,4 位,与 %V 使用 |
| %x | 年,其中的星期一是周的第一天,4 位,与 %v 使用 |
| %Y | 年,4 位 |
| %y | 年,2 位 |
-- 拼接字符串
-- concat_ws用法
-- 这个拼接的 '-' 都是在中间
select name,age, concat_ws ('-',name,age) from user
select name,age, concat_ws ('-',name,age,'%','=') from user
-- concat用法
-- 这个拼接的 '-' 这个符号放在哪个位置就在哪里
select name,age, concat(name,'-',age) from user
select name,age, concat(name,'-',age,'%','=') from user
-- 查询name相同的合并成一个name,id也查询出来
select name,group_concat(id) from user group by name
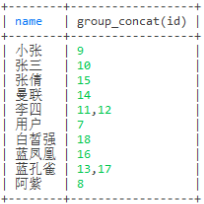
select name,group_concat(id order by id desc) from user group by name
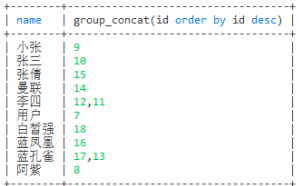
-- 分割
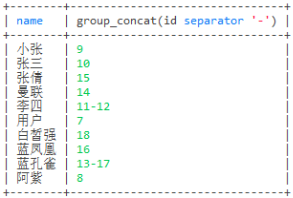
select name,group_concat(id separator '-') from user group by name
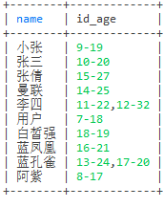
-- 查询name,id,age,id和age用 '-' 分割
select name,group_concat(concat_ws('-',id,age)) as id_age from user group by name
-- 保留两位小数
select name,price,round(price,2) from user
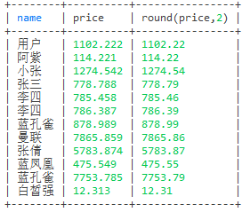
select round(111.245,2)
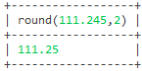
select round(123.1243/0,2)
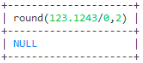
select round(0/1235.1545,2)
-- 去重
select distinct name,id from user
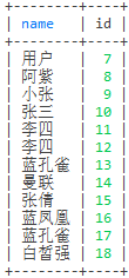
-- 去重来查询总数
select count(distinct name) from user
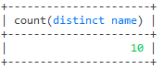
-- 模糊查询
select id,name from user where name like '蓝%'
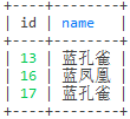
select id,name from user where name like '%孔%'

select id,name from user where name like '%雀'

-- 不查询id为7和8的信息
select id,name from user where not id in (7,8)
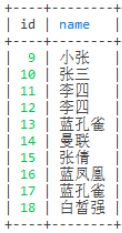
-- 只查询id为7和8的信息
select id,name from user where id in (7,8)
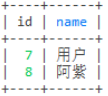
--这几个的优先级: where > group by > having > order by > limit
select e.dept_id,d.name from employee e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id
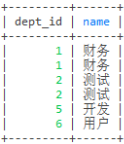
select count(1) c,d.name from employee e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id group by dept_id
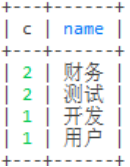
select count(1) c,d.name from employee e left join
dept d on e.dept_id = d.id
group by dept_id having c > 1 order by c desc
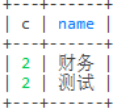
select count(1) c,d.name from employee e left join
dept d on e.dept_id = d.id where e.name!='天宇'
group by dept_id having c > 1 order by c desc limit 1

-- 根据status和age来统计 成年人已删除,成年人未删除,未成年人已删除,未成年人未删除的总数
select
ifNull(sum(case when status = 0 and age >= 18 then 1 else 0 end), 0) as '成年人未删除总数'
, ifNull(sum(case when status = 0 and age < 18 then 1 else 0 end), 0) as '未成年人未删除总数'
, ifNull(sum(case when status = 1 and age >= 18 then 1 else 0 end), 0) as '成年人已删除总数'
, ifNull(sum(case when status = 1 and age < 18 then 1 else 0 end), 0) as '未成年人已删除总数'
from user

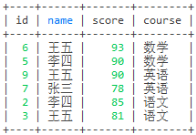
-- 查询科目前二的分数
select u1.* from user1 u1 where
(select count(1) from user1 u2 where u1.course = u2.course and u1.score < u2.score) < 2
order by u1.course, u1.score desc;
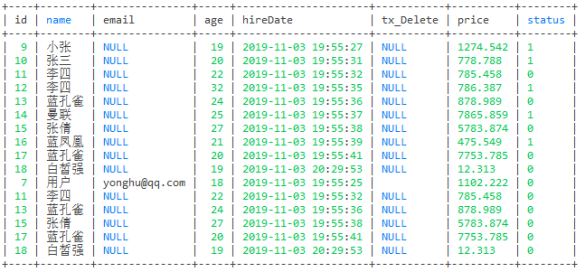
-- 这句代码的意思是不会去重
select * from user where age > 18 union all
select * from user where status = 0;
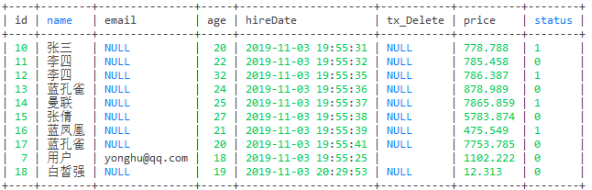
-- 这句代码的意思是会去重
select * from user where age > 19 union
select * from user where status = 0;
-- 这句代码的意思是可以把u1表中的数据拷贝多次去u2表中
insert into u2(name,age) select name,age from u1
-- 这句代码的意思是不可以把t1表中的数据拷贝多次去t2表中,拷贝多次会报错,只能拷贝一次
insert into t2 select * from t1
-- 这句代码的意思是把t1表的结构复制一份再创建一个表数据会过去,但是id自动递增不会设置
create table tt3 select * from t1;
-- 查询a1表设置进b1表中的数据
select * from a1
where exists (select 1 from b1 where a1.id = b1.aid)

-- 查询a1表没有设置进b1表中的数据
select * from a1
where not exists (select 1 from b1 where a1.id = b1.aid)
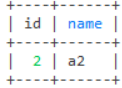
-- 查询a1表id为2的数据
select * from a1
where exists (select 1 from b1 where a1.id = 2)
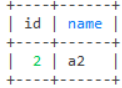
-- 查询b1表连接a1表中的数据
select * from a1
where exists (select 1 from b1 where b1.aid = 1)
MySQLDemo2的更多相关文章
随机推荐
- configparser 配置文件模块
#_author:star#date:2019/11/7# configparser 配置文件模块import configparserconfig=configparser.ConfigParser ...
- logger----->模块级别的函数
#_author:star#date:2019/11/6#logger----->模块级别的函数#文件与屏幕同时显示日志信息import logginglogger=logging.getLog ...
- Python-线程(1)
目录 什么是线程 进程与线程的区别 开启线程 为什么要使用线程 线程之间数据是共享的 什么是线程 线程与进程都是虚拟单位,目的是为了更好的描述某种事物 进程与线程的区别 进程:资源单位 线程:执行单位 ...
- php中$_REQUEST、 $_GET、 $_POST、 $_COOKIE 的关系和区别
看到REQUEST可以通吃GET .POST .COOKIE 后 感觉这个$_REQUEST太强大了是不是其他的几个超级变量就没有用了,下面对他们整体做个比较: 1.安全性 post>get 2 ...
- swoole是如何实现任务定时自动化调度的?
https://www.muzilong.cn/article/117 开发环境 环境:lnmp下进行试验. 框架:laravel5 问题描述 这几天做银行对帐接口时,踩了一个坑,具体需求大致描述一下 ...
- RasieException
RasieException是SEH API,SEH != 进内核,RasieException并不必然导致用户态内核态切换.事实上这个API被调用以后会首 先尝试在用户态进行处理,如果没有任何处理 ...
- Android之shape属性简介和使用
1.shape标签简介 shape的形状,默认为矩形,可以设置为矩形(rectangle).椭圆形(oval).线性形状(line).环形(ring) ! 设置形状: <shape xmln ...
- SpringMVC学习总结
SpringMVC部分重点组建介绍 前端处理器(DispatcherServlet):接受请求,响应结果,是SpringMVC的核心 处理映射器(HandlerMapping):根据URL去查找处理器 ...
- 关于Spring Cloud Feign的一些记录!
学习Spring Cloud Feign过程中,相关资料都会反复强调:微服务调用的话(@FeignClient) 客户端方法的返回值和服务端方法的返回值还有方法名之类的都是要求一致的! 关于方法名是 ...
- mybatis第二篇—参数绑定
不管我们在做数据库作业或者任务还是当时的仅靠jdbc来写一个管理系统的时候,sql语句需要一些参数,从而来实现模糊查询,精确查询,插入数据,更新数据和删除数据.这些参数,在mybatis里面,又该如何 ...
