《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 8.27
7月底,又一个夏天,又一个火热的夏天,来到火炉城武汉,天天高温橙色预警,到今天已有二十多天。
先看看住的地方

下雨的时候是这样的

接着做题

代码:
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% Output Info about this m-file
fprintf('\n***********************************************************\n');
fprintf(' <DSP using MATLAB> Problem 8.27 \n\n'); banner();
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Fp = 100; % analog passband freq in Hz
Fs = 150; % analog stopband freq in Hz
fs = 1000; % sampling rate in Hz % -------------------------------
% ω = ΩT = 2πF/fs
% Digital Filter Specifications:
% -------------------------------
wp = 2*pi*Fp/fs; % digital passband freq in rad/sec
%wp = Fp;
ws = 2*pi*Fs/fs; % digital stopband freq in rad/sec
%ws = Fs;
Rp = 1.0; % passband ripple in dB
As = 30; % stopband attenuation in dB Ripple = 10 ^ (-Rp/20) % passband ripple in absolute
Attn = 10 ^ (-As/20) % stopband attenuation in absolute % Analog prototype specifications: Inverse Mapping for frequencies
T = 1/fs; % set T = 1
OmegaP = wp/T; % prototype passband freq
OmegaS = ws/T; % prototype stopband freq % Analog Butterworth Prototype Filter Calculation:
[cs, ds] = afd_butt(OmegaP, OmegaS, Rp, As); % Calculation of second-order sections:
fprintf('\n***** Cascade-form in s-plane: START *****\n');
[CS, BS, AS] = sdir2cas(cs, ds)
fprintf('\n***** Cascade-form in s-plane: END *****\n'); % Calculation of Frequency Response:
[db_s, mag_s, pha_s, ww_s] = freqs_m(cs, ds, 2*pi/T); % Calculation of Impulse Response:
[ha, x, t] = impulse(cs, ds); % Match-z Transformation:
%[b, a] = imp_invr(cs, ds, T) % digital Num and Deno coefficients of H(z)
[b, a] = mzt(cs, ds, T) % digital Num and Deno coefficients of H(z)
[C, B, A] = dir2par(b, a) % Calculation of Frequency Response:
[db, mag, pha, grd, ww] = freqz_m(b, a); %% -----------------------------------------------------------------
%% Plot
%% -----------------------------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.27 Analog Butterworth lowpass')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
M = 1.2; % Omega max subplot(2,2,1); plot(ww_s/pi*T, mag_s); grid on; axis([-1.5, 1.5, 0, 1.1]);
xlabel(' Analog frequency in k\pi units'); ylabel('|H|'); title('Magnitude in Absolute');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [-500, -300, 0, 200, 300, 1000]*T);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0, 0.0316, 0.5, 0.8913, 1]); subplot(2,2,2); plot(ww_s/pi*T, db_s); grid on; %axis([0, M, -50, 10]);
xlabel('Analog frequency in k\pi units'); ylabel('Decibels'); title('Magnitude in dB ');
%set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [-0.3, -0.2, 0, 0.2, 0.3, 1.0]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-65, -30, -1, 0]);
set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['65';'30';' 1';' 0']); subplot(2,2,3); plot(ww_s/pi*T, pha_s/pi); grid on; axis([-1.010, 1.010, -1.2, 1.2]);
xlabel('Analog frequency in k\pi nuits'); ylabel('radians'); title('Phase Response');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [-0.3, -0.2, 0, 0.2, 0.3, 1.0]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-1:0.5:1]); subplot(2,2,4); plot(t, ha); grid on; %axis([0, 30, -0.05, 0.25]);
xlabel('time in seconds'); ylabel('ha(t)'); title('Impulse Response'); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.27 Digital Butterworth lowpass')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
M = 2; % Omega max %% Note %%
%% Magnitude of H(z) * T
%% Note %%
subplot(2,2,1); plot(ww/pi, mag/fs); axis([0, M, 0, 1.1]); grid on;
xlabel(' frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('|H|'); title('Magnitude Response');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.2, 0.3, 1.0, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0, 0.0316, 0.5, 0.8913, 1]); subplot(2,2,2); plot(ww/pi, pha/pi); axis([0, M, -1.1, 1.1]); grid on;
xlabel('frequency in \pi nuits'); ylabel('radians in \pi units'); title('Phase Response');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.2, 0.3, 1.0, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-1:1:1]); subplot(2,2,3); plot(ww/pi, db); axis([0, M, -120, 10]); grid on;
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Decibels'); title('Magnitude in dB ');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.2, 0.3, 1.0, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-70, -30, -1, 0]);
set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['70';'30';' 1';' 0']); subplot(2,2,4); plot(ww/pi, grd); grid on; %axis([0, M, 0, 35]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Samples'); title('Group Delay');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.2, 0.3, 1.0, M]);
%set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0:5:35]); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.27 Pole-Zero Plot')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
zplane(b,a);
title(sprintf('Pole-Zero Plot'));
%pzplotz(b,a); % Calculation of Impulse Response:
%[hs, xs, ts] = impulse(c, d);
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.27 Imp & Freq Response')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
t = [0:0.001:0.07]; subplot(2,1,1); impulse(cs,ds,t); grid on; % Impulse response of the analog filter
axis([0, 0.07, -100, 250]);hold on n = [0:1:0.07/T]; hn = filter(b,a,impseq(0,0,0.07/T)); % Impulse response of the digital filter
stem(n*T,hn); xlabel('time in sec'); title (sprintf('Impulse Responses, T=%.3f',T));
hold off %n = [0:1:29];
%hz = impz(b, a, n); % Calculation of Frequency Response:
[dbs, mags, phas, wws] = freqs_m(cs, ds, 2*pi/T); % Analog frequency s-domain [dbz, magz, phaz, grdz, wwz] = freqz_m(b, a); % Digital z-domain %% -----------------------------------------------------------------
%% Plot
%% ----------------------------------------------------------------- M = 1/T; % Omega max subplot(2,1,2); plot(wws/(2*pi),mags*fs,'b', wwz/(2*pi)*fs,magz,'r'); grid on; xlabel('frequency in Hz'); title('Magnitude Responses'); ylabel('Magnitude'); text(1.4,.5,'Analog filter'); text(1.5,1.5,'Digital filter');
运行结果:
绝对指标

非归一化Butterworth模拟低通直接形式的系数
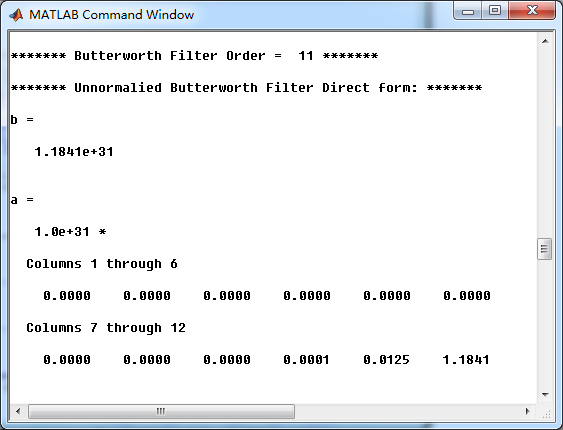
模拟低通串联形式的系数

开始Match-z方法,转变成数字低通
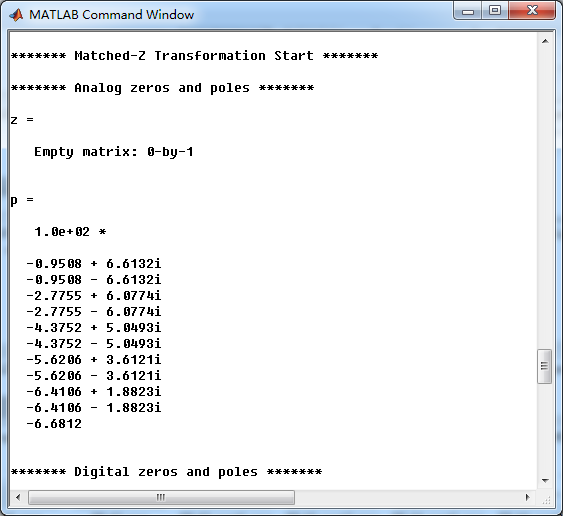

数字低通直接形式的系数

数字低通的并联形式的系数

模拟Butterworth低通的幅度谱、相位谱和脉冲响应

经过Match-z方法得到的数字Butterworth低通的幅度谱、相位谱和群延迟
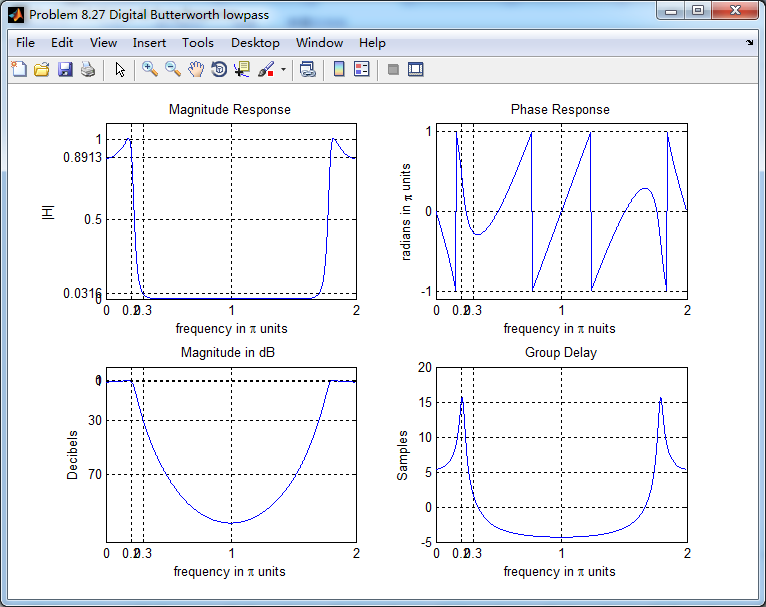
数字Butterworth低通的零极点图

模拟Butterworth低通、Match-z方法得到的数字Butterworth低通,二者的脉冲响应、幅度响应如下
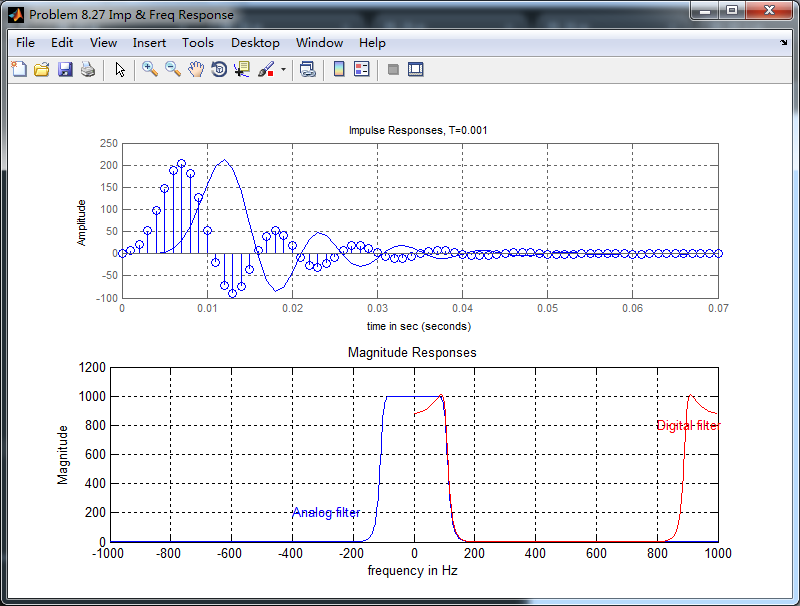
从上图可以看出,Match-z方法得到的数字低通,其脉冲响应与原模拟脉冲响应似乎有延迟的效果;其不像脉冲响应不变法那样,数字低通的
脉冲响应是相应模拟低通脉冲响应的采样序列,即保持了脉冲响应形式不变。
《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 8.27的更多相关文章
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.27
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 5.27
代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Outp ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.23
%% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output Info a ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.16
使用一种固定窗函数法设计带通滤波器. 代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.38
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.36
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.32
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.31
参照Example7.27,因为0.1π=2πf1 f1=0.05,0.9π=2πf2 f2=0.45 所以0.1π≤ω≤0.9π,0.05≤|H|≤0.45 代码: %% +++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.26
注意:高通的线性相位FIR滤波器,不能是第2类,所以其长度必须为奇数.这里取M=31,过渡带里采样值抄书上的. 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
随机推荐
- 转——调试寄存器 原理与使用:DR0-DR7
下面介绍的知识性信息来自intel IA-32手册(可以在intel的开发手册或者官方网站查到),提示和补充来自学习调试器实现时的总结. 希望能给你带去有用的信息. (DRx对应任意的一个调试寄存器. ...
- abstract类中method
一.abstract的method是否可同时是static,是否可同时是native,是否可同时是synchronized? 都不可以,因为abstract申明的方法是要求子类去实现的,abstrac ...
- 清空资源管理器访问过FTP的账号、密码
修改注册表,删除HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\FTP\Accounts下相对应的项即可,即为xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx项. 如下图所示:
- centos 下载并安装nodejs
安装方法1——直接部署 1.首先安装wget ,这个一般都有自带有的,可能已经在系统里安装好了的. yum install -y wget 如果已经安装了可以跳过该步 2.下载nodejs最新的tar ...
- [JZOJ6341] 【NOIP2019模拟2019.9.4】C
题目 题目大意 给你一颗带点权的树,后面有许多个询问\((u,v)\),问: \[\sum_{i=0}^{k-1}dist(u,d_i) \ or \ a_{d_i}\] \(d\)为\(u\)到\( ...
- 异或前缀和——cf1186C
很思维的题,b的1个数和c的1个数相差为偶数时,必定有偶数个不同 反之必定有奇数个不同 #include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> #incl ...
- 关于maven工程将model删除重建之后变为灰色的问题的解决
问题描述: IDEA中的maven工程中有时候将model或者子model建错,删除之后,子模块在maven在侧栏的maven projects中是灰色的,而且是并没有依赖父工程 在网上搜了搜解决办法 ...
- PAT甲级——A1115 Counting Nodes in a BST【30】
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a binary tree which has the following propertie ...
- 6_2.springboot2.x整合Druid和配置数据源监控
简介 Druid首先是一个数据库连接池.Druid是目前最好的数据库连接池,在功能.性能.扩展性方面,都超过其他数据库连接池,包括DBCP.C3P0.BoneCP.Proxool.JBoss Data ...
- ERROR 1839 (HY000): @@GLOBAL.GTID_PURGED can only be set when @@GLOBAL.GTID_MODE = ON
从cdb上dump一个库结构,准备与本地结构做对比(可以直接compare,但速度贼慢).使用dump脚本在本地创建的时候报错 -- 导出指定库的结构 shell> mysqldump -hxx ...
