C# 笔记——排序
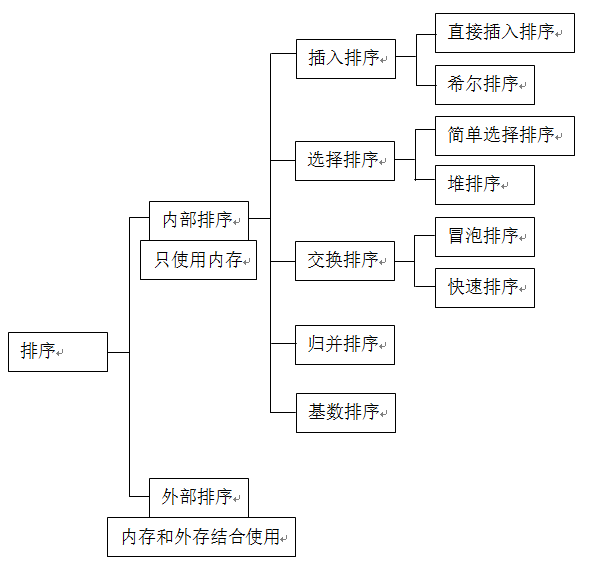
首先,一张图看懂8中排序之间的关系:
平均速度最快:快速排序
所需辅助空间最多:归并排序
所需辅助空间最少:堆排序
不稳定:快速排序,希尔排序,堆排序。
1. 直接插入排序
基本思想:在要排序的一组数中,假设前面(n-1)[n>=2] 个数已经是排好顺序的,现在要把第n个数插到前面的有序数中,使得这n个数也是排好顺序的。如此反复循环,直到全部排好顺序。
- for (int i = ; i < array.Length; i++)
- {
- if (array[i] > array[i - ])
- {
- int tmp = array[i];
- int j = ;
- for (j = i - ; j >= && tmp >array[j]; --j)
- {
- array[j + ] = array[j];
- }
- array[j + ] = tmp;
- }
- }
2.希尔排序(最小增量排序)
基本思想:算法先将要排序的一组数按某个增量d(n/2,n为要排序数的个数)分成若干组,每组中记录的下标相差d.对每组中全部元素进行直接插入排序,然后再用一个较小的增量(d/2)对它进行分组,在每组中再进行直接插入排序。当增量减到1时,进行直接插入排序后,排序完成。
- int length = array.Length;
- for (int h = length / ; h > ; h = h / )
- {
- for (int i = h; i < length; i++)
- {
- T temp = array[i];
- if (temp.CompareTo(array[i -h]) < )
- {
- for (int j = ; j < i; j += h)
- {
- if (temp.CompareTo(array[j]) < )
- {
- temp = array[j];
- array[j] = array[i];
- array[i] = temp;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
3. 简单选择排序
基本思想:在要排序的一组数中,选出最小的一个数与第一个位置的数交换;然后在剩下的数当中再找最小的与第二个位置的数交换,如此循环到倒数第二个数和最后一个数比较为止。
- for (int i = ; i < data.Length-; i++)
- {
- int min = data[i];
- int minIndex = i;
- for (int j = i+; j < data.Length; j++)
- {
- if (data[j] <min)
- {
- min = data[j];
- minIndex = j;
- }
- }
- if (minIndex != i)
- {
- int temp = data[i];
- data[i] = data[minIndex];
- data[minIndex] = temp;
- }
- }
4. 堆排序
基本思想:堆排序是一种树形选择排序,是对直接选择排序的有效改进。堆的定义如下:具有n个元素的序列(h1,h2,...,hn),当且仅当满足(hi>=h2i,hi>=2i+1)或(hi<=h2i,hi<=2i+1)(i=1,2,...,n/2)时称之为堆。在这里只讨论满足前者条件的堆。由堆的定义可以看出,堆顶元素(即第一个元素)必为最大项(大顶堆)。完全二叉树可以很直观地表示堆的结构。堆顶为根,其它为左子树、右子树。初始时把要排序的数的序列看作是一棵顺序存储的二叉树,调整它们的存储序,使之成为一个堆,这时堆的根节点的数最大。然后将根节点与堆的最后一个节点交换。然后对前面(n-1)个数重新调整使之成为堆。依此类推,直到只有两个节点的堆,并对它们作交换,最后得到有n个节点的有序序列。从算法描述来看,堆排序需要两个过程,一是建立堆,二是堆顶与堆的最后一个元素交换位置。所以堆排序有两个函数组成。一是建堆的渗透函数,二是反复调用渗透函数实现排序的函数。
- static void HeapAdjust(List<int> list,int parent,int length)
- {
- int temp=list[parent];//parent是索引
- int child = * parent + ;
- while (child < length)
- {
- if (child + < length && list[child] < list[child + ]) child++;
- if (temp >= list[child])
- break;
- list[parent] = list[child];
- parent = child;
- child = * parent + ;
- }
- list[parent] = temp;
- }
- public static List<int> HeapSort(List<int> list, int top)
- {
- List<int> topNode = new List<int>();
- for (int i = list.Count / - ; i >= ; i--)
- {
- HeapAdjust(list, i, list.Count);//最大堆
- }
- for (int i = list.Count - ; i >= list.Count - top; i--)
- {
- int temp = list[];
- list[] = list[i];
- list[i] = temp;
- topNode.Add(temp);
- HeapAdjust(list, , i);
- }
- return topNode;
- }
5.冒泡排序
基本思想:在要排序的一组数中,对当前还未排好序的范围内的全部数,自上而下对相邻的两个数依次进行比较和调整,让较大的数往下沉,较小的往上冒。即:每当两相邻的数比较后发现它们的排序与排序要求相反时,就将它们互换。
- int[] numbers = { , , , , , , , , , }; //定义一个要排序的数组,这里可以随便写多少个数
- for (int i = ; i < numbers.Length - ; i++) //外层 循环比较遍数
- {
- for (int j = ; j < numbers.Length - - i; j++)
- {
- if (numbers[j] > numbers[j + ]) //两个数进行比较,如果大于就交换
- {
- int temp = numbers[j]; //temp 两个数交换时要有第三个数来过度
- numbers[j] = numbers[j + ];
- numbers[j + ] = temp;
- }
- }
- }
6.快速排序
基本思想:选择一个基准元素,通常选择第一个元素或者最后一个元素,通过一趟扫描,将待排序列分成两部分,一部分比基准元素小,一部分大于等于基准元素,此时基准元素在其排好序后的正确位置,然后再用同样的方法递归地排序划分的两部分。
- private static int QuickSort_Once(int[] _pnArray, int _pnLow, int _pnHigh)
- {
- int nPivot = _pnArray[_pnLow];
- int i = _pnLow, j = _pnHigh;
- while (i < j)
- {
- while (_pnArray[j] >= nPivot && i<j) j--;
- _pnArray[i] = _pnArray[j];
- while (_pnArray[i] <= nPivot && i<j) i++;
- _pnArray[j] = _pnArray[i];
- }
- _pnArray[i] = nPivot;
- return i;
- }
- private static void QuickSort(int[] _pnArray, int _pnLow, int _pnHigh)
- {
- if (_pnLow >= _pnHigh) return;
- int _nPivotIndex = QuickSort_Once(_pnArray, _pnLow, _pnHigh);
- QuickSort(_pnArray, _pnLow, _nPivotIndex-);
- QuickSort(_pnArray, _nPivotIndex + ,_pnHigh);
- }
7.归并排序
基本思想:归并(Merge)排序法是将两个(或两个以上)有序表合并成一个新的有序表,即把待排序序列分为若干个子序列,每个子序列是有序的。然后再把有序子序列合并为整体有序序列。
- //归并排序(目标数组,子表的起始位置,子表的终止位置)
- private static void MergeSortFunction(int[] array, int first, int last)
- {
- try
- {
- if (first < last) //子表的长度大于1,则进入下面的递归处理
- {
- int mid = (first + last) / ; //子表划分的位置
- MergeSortFunction(array, first, mid); //对划分出来的左侧子表进行递归划分
- MergeSortFunction(array, mid + , last); //对划分出来的右侧子表进行递归划分
- MergeSortCore(array, first, mid, last); //对左右子表进行有序的整合(归并排序的核心部分)
- }
- }
- catch (Exception ex)
- { }
- }
- //归并排序的核心部分:将两个有序的左右子表(以mid区分),合并成一个有序的表
- private static void MergeSortCore(int[] array, int first, int mid, int last)
- {
- try
- {
- int indexA = first; //左侧子表的起始位置
- int indexB = mid + ; //右侧子表的起始位置
- int[] temp = new int[last + ]; //声明数组(暂存左右子表的所有有序数列):长度等于左右子表的长度之和。
- int tempIndex = ;
- while (indexA <= mid && indexB <= last) //进行左右子表的遍历,如果其中有一个子表遍历完,则跳出循环
- {
- if (array[indexA] <= array[indexB]) //此时左子表的数 <= 右子表的数
- {
- temp[tempIndex++] = array[indexA++]; //将左子表的数放入暂存数组中,遍历左子表下标++
- }
- else//此时左子表的数 > 右子表的数
- {
- temp[tempIndex++] = array[indexB++]; //将右子表的数放入暂存数组中,遍历右子表下标++
- }
- }
- //有一侧子表遍历完后,跳出循环,将另外一侧子表剩下的数一次放入暂存数组中(有序)
- while (indexA <= mid)
- {
- temp[tempIndex++] = array[indexA++];
- }
- while (indexB <= last)
- {
- temp[tempIndex++] = array[indexB++];
- }
- //将暂存数组中有序的数列写入目标数组的制定位置,使进行归并的数组段有序
- tempIndex = ;
- for (int i = first; i <= last; i++)
- {
- array[i] = temp[tempIndex++];
- }
- }
- catch (Exception ex)
- { }
- }
8.基数排序
基本思想:将所有待比较数值(正整数)统一为同样的数位长度,数位较短的数前面补零。然后,从最低位开始,依次进行一次排序。这样从最低位排序一直到最高位排序完成以后,数列就变成一个有序序列。
- public static int[] RadixSort(int[] ArrayToSort, int digit)
- {
- //low to high digit
- for (int k = ; k <= digit; k++)
- {
- //temp array to store the sort result inside digit
- int[] tmpArray = new int[ArrayToSort.Length];
- //temp array for countingsort
- int[] tmpCountingSortArray = new int[]{,,,,,,,,,};
- //CountingSort
- for (int i = ; i < ArrayToSort.Length; i++)
- {
- //split the specified digit from the element
- int tmpSplitDigit = ArrayToSort[i]/(int)Math.Pow(,k-) - (ArrayToSort[i]/(int)Math.Pow(,k))*;
- tmpCountingSortArray[tmpSplitDigit] += ;
- }
- for (int m = ; m < ; m++)
- {
- tmpCountingSortArray[m] += tmpCountingSortArray[m - ];
- }
- //output the value to result
- for (int n = ArrayToSort.Length - ; n >= ; n--)
- {
- int tmpSplitDigit = ArrayToSort[n] / (int)Math.Pow(,k - ) - (ArrayToSort[n]/(int)Math.Pow(,k)) * ;
- tmpArray[tmpCountingSortArray[tmpSplitDigit]-] = ArrayToSort[n];
- tmpCountingSortArray[tmpSplitDigit] -= ;
- }
- //copy the digit-inside sort result to source array
- for (int p = ; p < ArrayToSort.Length; p++)
- {
- ArrayToSort[p] = tmpArray[p];
- }
- }
- return ArrayToSort;
- }
C# 笔记——排序的更多相关文章
- [笔记]ACM笔记 - 排序小技巧
Description 一个数组,要求先对前n个数字排序(以方便后续操作):又要求对前n+i个数字排序:又要求对前n+j - 前n+k个数字排序(i.j.k的大小远小于n,且i.j.k间没有大小关系) ...
- Java学习笔记——排序算法之快速排序
会当凌绝顶,一览众山小. --望岳 如果说有哪个排序算法不能不会,那就是快速排序(Quick Sort)了 快速排序简单而高效,是最适合学习的进阶排序算法. 直接上代码: public class Q ...
- Java学习笔记——排序算法之进阶排序(堆排序与分治并归排序)
春蚕到死丝方尽,蜡炬成灰泪始干 --无题 这里介绍两个比较难的算法: 1.堆排序 2.分治并归排序 先说堆. 这里请大家先自行了解完全二叉树的数据结构. 堆是完全二叉树.大顶堆是在堆中,任意双亲值都大 ...
- Java学习笔记——排序算法之希尔排序(Shell Sort)
落日楼头,断鸿声里,江南游子.把吴钩看了,栏杆拍遍,无人会,登临意. --水龙吟·登建康赏心亭 希尔算法是希尔(D.L.Shell)于1959年提出的一种排序算法.是第一个时间复杂度突破O(n²)的算 ...
- Java学习笔记——排序算法之简单排序
男儿何不带吴钩,收取关山五十州.请君暂上凌烟阁,若个书生万户侯? --南园十三首 三种排序法: 1.冒泡法 2.简单选择法 3.直接插入法 上代码: 1.冒泡排序 public class Bub ...
- STL学习笔记--排序算法
排序算法 C++ STL 的排序算法(Sorting algorithms)是一组将无序序列排列成有序序列的模板函数或与排序相关的模板函数,提供了排序.折半搜索.归并.集合操作.堆操作.最值求解.字典 ...
- DataTable学习笔记---排序细则、列隐藏
耽误了好几天,因为要做一个嵌入式的实验-android内核编译与裁剪,很久之前装的wubi不知道为什么运行出错了,然后看着当前的win7系统觉得有点讨厌了,也是因为快1年半没装机了,所以就重新装机了, ...
- C++面试笔记--排序
这里我们开始复习排序的一些面试题. 首先我们来看一下各个排序方法的时间复杂度和稳定性的比较,见下面表格: 排序法 平均时间 最差情形 稳定度 额外空间 备注 冒泡 O(n2) O(n2) 稳定 ...
- Java基础 TreeSet()来实现数组的【定制排序】 : Comparable接口(自然排序) 或者 Comparator接口 (定制排序)
笔记: //排序真麻烦!没有C++里的好用又方便!ORZ!ORZ!数组排序还还自己写个TreeSet()和( Comparable接口(自然排序) 或者 Comparator接口 (定制排序))imp ...
随机推荐
- 源码安装和yum安装的区别。
yum是将yum源中别人已经编译好的rpm包下载到本地,然后安装,不需要考虑依赖,主要是方便.源码安装没法人为的控制,安装的版本也很低. 源码安装需要自己编译,安装,编译过程中可以设置参数.可安装的版 ...
- IDEA中使用Docker: 图形化 or 命令行 ,你更稀罕那个??
Docker简介: Docker 是一个开源的应用容器引擎,让开发者可以打包他们的应用以及依赖包到一个可移植的容器中,然后发布到任何流行的 Linux 机器上,也可以实现虚拟化. 容器是完全使用沙箱机 ...
- bzoj1483: [HNOI2009]梦幻布丁(链表+启发式合并)
题目大意:一个序列,两种操作. ①把其中的一种数修改成另一种数 ②询问有多少段不同的数如1 2 2 1为3段(1 / 2 2 / 1). 昨晚的BC的C题和这题很类似,于是现学现写居然过了十分开心. ...
- mybatis 根据id批量删除的两种方法
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40010745/article/details/81032218 mybatis 根据id批量删除的两种方法 第一种,直接传递给mappe ...
- 【转载】Innodb共享表空间VS独立表空间
http://www.mysqlsupport.cn/innodb%E5%85%B1%E4%BA%AB%E8%A1%A8%E7%A9%BA%E9%97%B4vs%E7%8B%AC%E7%AB%8B%E ...
- 基于Bootstrap的遮罩层,带有加载提示
1.body中的html <div class="modal fade" id="loadingModal"> <div style=&quo ...
- C语言双链表遍历,插入,删除
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #define bzero(a, b) memse ...
- JQuery源码实现
技术提高篇--- 推荐--- 动脑学院--- http://www.toutiao.com/a6368703139592569089/
- php环境的安装
一.xampp的安装 1.下载xampp安装包. 2.next下一步傻瓜式的安装. 3.输入地址127.0.0.1进入如下页面. 二.LAMP环境的安装
- LightOJ 1137 - Expanding Rods 基础计算几何
http://www.lightoj.com/volume_showproblem.php?problem=1137 题意:一根长度为L的杆热膨胀为L',左端点到右端点间距离不变,且膨胀后的杆的弧为圆 ...
