<Effective C++>读书摘要--Resource Management<二>
<Item 15> Provide access to raw resources in resource-managing classes
1、You need a way to convert an object of the RAII class (in this case, tr1::shared_ptr) into the raw resource it contains (e.g., the underlying Investment*). There are two general ways to do it: explicit conversion and implicit conversion.
tr1::shared_ptr and auto_ptr both offer a get member function to perform an explicit conversion, i.e., to return (a copy of) the raw pointer inside the smart pointer object:
int days = daysHeld(pInv.get()); // fine, passes the raw pointer
// in pInv to daysHeld
Like virtually all smart pointer classes, TR1::shared_ptr and auto_ptr also overload the pointer dereferencing operators (operator-> and operator*), and this allows implicit conversion to the underlying raw pointers:
class Investment { // root class for a hierarchy
public: // of investment types
bool isTaxFree() const;
...
};
Investment* createInvestment(); // factory function
std::tr1::shared_ptr<Investment> // have tr1::shared_ptr
pi1(createInvestment()); // manage a resource
bool taxable1 = !(pi1->isTaxFree()); // access resource
// via operator->
...
std::auto_ptr<Investment> pi2(createInvestment()); // have auto_ptr
// manage a
// resource
bool taxable2 = !((*pi2).isTaxFree()); // access resource
// via operator*
...
2、The Font class could offer an explicit conversion function such as get:
class Font {
public:
...
FontHandle get() const { return f; } // explicit conversion function
...
};
Unfortunately, this would require that clients call get every time they want to communicate with the API:
void changeFontSize(FontHandle f, int newSize); // from the C API
Font f(getFont());
int newFontSize;
... changeFontSize(f.get(), newFontSize); // explicitly convert
// Font to FontHandle
Some programmers might find the need to explicitly request such conversions off-putting enough to avoid using the class. That, in turn, would increase the chances of leaking fonts, the very thing the Font class is designed to prevent.
The alternative is to have Font offer an implicit conversion function to its FontHandle:
class Font {
public:
...
operator FontHandle() const { return f; } // implicit conversion function
...
};
That makes calling into the C API easy and natural: 但是隐式转换可能会偷偷造成不想要的转换
Font f(getFont());
int newFontSize;
... changeFontSize(f, newFontSize); // implicitly convert Font
// to FontHandle
3、Often, an explicit conversion function like get is the preferable path, because it minimizes the chances of unintended type conversions. Sometime, however, the naturalness of use arising from implicit type conversions will tip the scales in that direction.但是一切以Item18为原则。Furthermore, some RAII classes combine true encapsulation of implementation with very loose encapsulation of the underlying resource. For example, tr1::shared_ptr encapsulates all its reference-counting machinery, but it still offers easy access to the raw pointer it contains. Like most well-designed classes, it hides what clients don't need to see, but it makes available those things that clients honestly need to access.
4、Things to Remember
APIs often require access to raw resources, so each RAII class should offer a way to get at the resource it manages.
Access may be via explicit conversion or implicit conversion. In general, explicit conversion is safer, but implicit conversion is more convenient for clients.
<Item 16>Use the same form in corresponding uses of new and delete.
5、When you employ a new expression (i.e., dynamic creation of an object via a use of new), two things happen. First, memory is allocated (via a function named operator new—see Items 49 and 51). Second, one or more constructors are called for that memory. When you employ a delete expression (i.e., use delete), two other things happen: one or more destructors are called for the memory, then the memory is deallocated (via a function named operator delete—see Item 51).
6、 In particular, the memory for an array usually includes the size of the array, thus making it easy for delete to know how many destructors to call. The memory for a single object lacks this information. This is just an example, of course. Compilers aren't required to implement things this way, though many do.
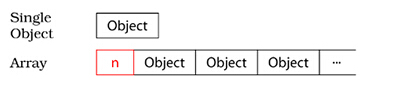
7、This is a particularly important rule to bear in mind when you are writing a class containing a pointer to dynamically allocated memory and also offering multiple constructors, because then you must be careful to use the same form of new in all the constructors to initialize the pointer member. If you don't, how will you know what form of delete to use in your destructor?
8、This rule is also noteworthy for the typedef-inclined, because it means that a typedef's author must document which form of delete should be employed when new is used to conjure up objects of the typedef type. For example, consider this typedef:
typedef std::string AddressLines[]; // a person's address has 4 lines,
// each of which is a string
Because AddressLines is an array, this use of new,
std::string *pal = new AddressLines; // note that "new AddressLines"
// returns a string*, just like
// "new string[4]" would
must be matched with the array form of delete:
delete pal; // undefined!
delete [] pal; // fine
delete 和delete []用错了的话,The result is undefined。使用string和vector来避免动态分配数组。
9、Things to Remember
If you use [] in a new expression, you must use [] in the corresponding delete expression. If you don't use [] in a new expression, you mustn't use [] in the corresponding delete expression.
<Item 17>Store newed objects in smart pointers in standalone statements.
10、C++的编译器相比java和C#给予更多语句执行顺序的自由度,exception可能打断正常的执行流程,导致资源泄露
int priority();
void processWidget(std::tr1::shared_ptr<Widget> pw, int priority);
processWidget(new Widget, priority()); //不会编译,没有定义好的隐式转换
processWidget(std::tr1::shared_ptr<Widget>(new Widget), priority());
Execute "new Widget".
Call priority.
Call the tr1::shared_ptr constructor.
可以修正如下
std::tr1::shared_ptr<Widget> pw(new Widget); // store newed object
// in a smart pointer in a
// standalone statement processWidget(pw, priority()); // this call won't leak
11、Things to Remember
Store newed objects in smart pointers in standalone statements. Failure to do this can lead to subtle resource leaks when exceptions are thrown.
<Effective C++>读书摘要--Resource Management<二>的更多相关文章
- <Effective C++>读书摘要--Resource Management<一>
1.除了内存资源以外,Other common resources include file descriptors, mutex locks, fonts and brushes in graphi ...
- <Effective C++>读书摘要--Implementations<二>
<Item29> Strive for exception-safe code. 1.如下面的代码 class PrettyMenu { public: ... void changeBa ...
- <Effective C++>读书摘要--Designs and Declarations<一>
<Item 18> Make interfaces easy to use correctly and hard to use incorrectly 1.That being the c ...
- <Effective C++>读书摘要--Inheritance and Object-Oriented Design<二>
<Item 36> Never redefine an inherited non-virtual function 1.如下代码通过不同指针调用同一个对象的同一个函数会产生不同的行为Th ...
- <Effective C++>读书摘要--Designs and Declarations<二>
<Item 20> Prefer pass-by-reference-to-const to pass-by-value 1.By default, C++ passes objects ...
- <Effective C++>读书摘要--Ctors、Dtors and Assignment Operators<二>
<Item 9> Never call virtual functions during construction or destruction 1.you shouldn't call ...
- <Effective C++>读书摘要--Templates and Generic Programming<一>
1.The initial motivation for C++ templates was straightforward: to make it possible to create type-s ...
- <Effective C++>读书摘要--Implementations<一>
1.For the most part, coming up with appropriate definitions for your classes (and class templates) a ...
- <Effective C++>读书摘要--Designs and Declarations<三>
<Item 22> Declare data members private 1.使数据成员private,保持了语法的一致性,client不会为访问一个数据成员是否需要使用括号进行函数调 ...
随机推荐
- mysql8.0.11的坑早知道
1.plugin caching_sha2_password could not be loaded 我在mac上用Sequel Pro连数据库的时候,会报出以上错误,这是应为8.0.11把身份认证插 ...
- Python 爬虫 (五)
# 头条街拍图片爬取 1 import re import requests from urllib import request import json import os i = 0 header ...
- Java Web开发后端常用技术汇总
技术名称及官网 Spring Framework Spring容器 http://projects.spring.io/spring-framework/ SpringMVC Spring MVC框架 ...
- verilog中参数传递与参数定义中#的作用(二)
一.module内部有效的定义 用parameter来定义一个标志符代表一个常量,称作符号常量,他可以提高程序的可读性和可维护性.parameter是参数型数据的关键字,在每一个赋值语句的右边都必须是 ...
- 韩国KT软件NB-IOT开发记录V150(2)FOTA差分包生成
1. 生成差分包
- Mac安装php和redis扩展
Mac上有特定的包管理工具homebrew,也叫brew,这里的php安装用的就是brew 1安装php brew install php@7.0. brw安装会自动管理依赖,所以不用你一个个先安装依 ...
- 怎样下载JDBC驱动
MySQL官网: https://www.mysql.com/ 请注意: 需要把mysql-connector-java-5.1.45-bin.jar放到C:\JMeter\apache-jmeter ...
- 第六阶段·数据库MySQL及NoSQL实践 第2章·Redis
01-Redis简介 02-Redis基本安装启动 03-Redis的配置文件基本使用 04-Redis安全管理 05-Redis安全持久化-RDB持久化 06-Redis安全持久化-AOF持久化 0 ...
- webservice调用天气
class WebServiceHelper { /// <summary> /// 动态调用WebService /// </summary> /// <param n ...
- 前端开发工程师 - 01.页面制作 - 第1章.Photoshop切图
第1章--Photoshop切图 工具.面板.视图 什么是切图? 1. 从设计稿(.psd)中切出网络素材,如按钮.图标.logo.背景图等 2. 编写代码,在代码中使用图片,生成静态页面 --给网页 ...
