python入门 -- 学习笔记4
习题38:列表的操作
当你看到像 mystuff.append('hello') 这样的代码时,你事实上已经在 Python 内部激发了一个连锁反应。以下是它的工作原理:
1. Python 看到你用到了 mystuff ,于是就去找到这个变量。也许它需要倒着检查看你有没有在哪里用 = 创建过这个变量,或者检查它是不是一个函数参数,或者看它是不是一个全局变量。不管哪种方式,它得先找到 mystuff 这个变量才行。
2. 一旦它找到了 mystuff ,就轮到处理句点 . (period) 这个操作符,而且开始查看 mystuff内部的一些变量了。由于 mystuff 是一个列表,Python 知道mystuff 支持一些函数。
3. 接下来轮到了处理 append 。Python 会将 “append” 和 mystuff 支持的所有函数的名称一一对比,如果确实其中有一个叫 append 的函数,那么 Python 就会去使用这个函数。
4. 接下来 Python 看到了括号 ( (parenthesis) 并且意识到, “噢,原来这应该是一个函数”,到了这里,它就正常会调用这个函数了,不过这里的函数还要多一个参数才行。
5. 这个额外的参数其实是…… mystuff! 我知道,很奇怪是不是?不过这就是 Python 的工作原理,所以还是记住这一点,就当它是正常的好了。真正发生的事情其实是append(mystuff, 'hello') ,不过你看到的只是 mystuff.append('hello')。
代码:
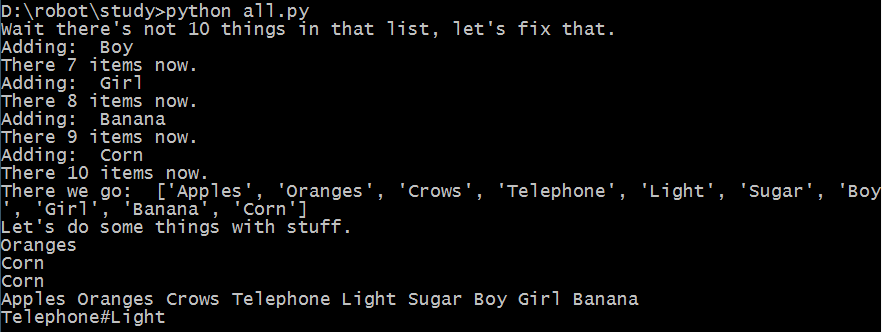
ten_things = "Apples Oranges Crows Telephone Light Sugar"
print "Wait there's not 10 things in that list, let's fix that."
stuff = ten_things.split(' ')
more_stuff = ["Day", "Night", "Song", "Frisbee", "Corn", "Banana", "Girl", "Boy"]
while len(stuff) != 10:
next_one = more_stuff.pop()
print "Adding: ", next_one
stuff.append(next_one)
print "There %d items now." % len(stuff)
print "There we go: ", stuff
print "Let's do some things with stuff."
print stuff[1]
print stuff[-1] # whoa! fancy
print stuff.pop()
print ' '.join(stuff) # what? cool!
print '#'.join(stuff[3:5]) # super stellar!
结果:
习题39:字典,可爱的字典
代码:
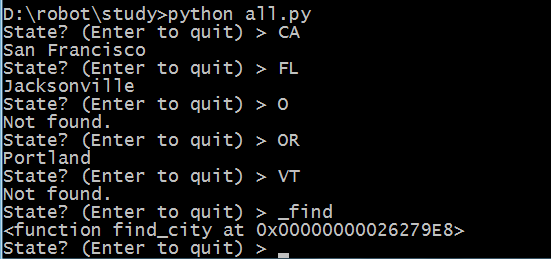
cities = {
'CA': 'San Francisco',
'MI': 'Detroit',
'FL': 'Jacksonville'
}
cities['NY'] = 'New York'
cities['OR'] = 'Portland'
def find_city(themap, state):
if state in themap:
return themap[state]
else:
return "Not found."
# ok pay attention!
cities['_find'] = find_city
while True:
print "State? (Enter to quit)",
state = raw_input("> ")
if not state: break
# this line is the most important ever! study!
city_found = cities['_find'](cities, state)
print city_found
结果:
习题40:模块、类、对象
Python 里边有这么一个通用的模式:
1. 拿一个类似 key=value 风格的数据容器
2. 通过 key 的名称获取其中的 value
对于字典来说,key 是一个字符串,获得值的语法是 [key] 。对于模块来说,key是函数或者变量的名
称,而语法是 .key
现在我有三种方法可以从某个东西里获取它的内容:
# dict style
mystuff['apples']
# module style
mystuff.apples()
print mystuff.tangerine
# class style
class MyStuff(object):
def __init__(self):
self.tangerine = "And now a thousand years between"
def apple(self):
print "I AM CLASSY APPLES!"
thing = MyStuff()
thing.apples()
print thing.tangerine
第一行代码就是“实例化”操作,这和调用函数很相似。然而,当你进行实例化操作时,Python 在背后做了一系列的工作,这里我针对上面的代码详细解释一下:
1. Python 看到了 MyStuff() 并且知道了它是你定义过的一个类。
2. Python 创建了一个空的对象,里边包含了你在类中用 def 创建的所有函数。
3. 然后 Python 回去检查你是不是在里边创建了一个 __init__ 魔法函数,如果你有创建,它就会调用这个函数,从而对你的空对象实现了初始化。
4. 在 MyStuff 中的 __init__ 函数里,我们有一个多余的函数叫做 self ,这就是 Python 为我们创建的空对象,而我可以对它进行类似模块、字典等的操作,为它设置一些变量进去。
5. 在这里,我把 self.tangerine 设成了一段歌词,这样我就初始化了该对象。
6. 最后 Python 将这个新建的对象赋给一个叫 thing 的变量,以供后面使用。
代码:
class Song(object):
def __init__(self, lyrics):
self.lyrics = lyrics
def sing_me_a_song(self):
for line in self.lyrics:
print line
happy_bday = Song(["Happy birthday to you",
"I don't want to get sued",
"So I'll stop right there"])
bulls_on_parade = Song(["They rally around the family",
"With pockets full of shells"])
happy_bday.sing_me_a_song()
bulls_on_parade.sing_me_a_song()
结果:

习题41:物以类聚
代码:
class TheThing(object):
def __init__(self):
self.number = 0
def some_function(self):
print "I got called."
def add_me_up(self, more):
self.number += more
return self.number
# two different things
a = TheThing()
b = TheThing()
a.some_function()
b.some_function()
print a.add_me_up(20)
print b.add_me_up(30)
print a.number
print b.number
# Study this. This is how you pass a variable
# from one class to another/ You will need this.
class TheMultiplier(object):
def __init__(self, base):
self.base = base
def do_it(self, m):
return m * self.base
x = TheMultiplier(a.number)
print x.do_it(b.number)
结果:

代码2:-- 尚未完全理解,后续通过其他文档加深理解
from sys import exit
from random import randint class Game(object): def __init__(self, start):
self.quips = [
"You died. You kinda suck at this.",
"Your mom would be proud. If she were smarter.",
"Such a luser.",
"I have a small puppy that's better at this."
]
self.start = start def play(self):
next = self.start while True:
print "\n--------"
room = getattr(self, next)
next = room() def death(self):
print self.quips[randint(0, len(self.quips)-1)]
exit(1) def central_corridor(self):
print "The Gothons of Planet Percal #25 have invaded your ship and destroyed"
print "your entire crew. You are the last surviving member and your last"
print "mission is to get the neutron destruct bomb from the Weapons Armory,"
print "put it in the bridge, and blow the ship up after getting into an "
print "escape pod."
print "\n"
print "You're running down the central corridor to the Weapons Armory when"
print "a Gothon jumps out, red scaly skin, dark grimy teeth, and evil clown costume"
print "flowing around his hate filled body. He's blocking the door to the"
print "Armory and about to pull a weapon to blast you." action = raw_input("> ") if action == "shoot!":
print "Quick on the draw you yank out your blaster and fire it at the Gothon."
print "His clown costume is flowing and moving around his body, which throws"
print "off your aim. Your laser hits his costume but misses him entirely. This"
print "completely ruins his brand new costume his mother bought him, which"
print "makes him fly into an insane rage and blast you repeatedly in the face until"
print "you are dead. Then he eats you."
return 'death' elif action == "dodge!":
print "Like a world class boxer you dodge, weave, slip and slide right"
print "as the Gothon's blaster cranks a laser past your head."
print "In the middle of your artful dodge your foot slips and you"
print "bang your head on the metal wall and pass out."
print "You wake up shortly after only to die as the Gothon stomps on"
print "your head and eats you."
return 'death' elif action == "tell a joke":
print "Lucky for you they made you learn Gothon insults in the academy."
print "You tell the one Gothon joke you know:"
print "Lbhe zbgure vf fb sng, jura fur fvgf nebhaq gur ubhfr, fur fvgf nebhaq gur ubhfr."
print "The Gothon stops, tries not to laugh, then busts out laughing and can't move."
print "While he's laughing you run up and shoot him square in the head"
print "putting him down, then jump through the Weapon Armory door."
return 'laser_weapon_armory' else:
print "DOES NOT COMPUTE!"
return 'central_corridor' def laser_weapon_armory(self):
print "You do a dive roll into the Weapon Armory, crouch and scan the room"
print "for more Gothons that might be hiding. It's dead quiet, too quiet."
print "You stand up and run to the far side of the room and find the"
print "neutron bomb in its container. There's a keypad lock on the box"
print "and you need the code to get the bomb out. If you get the code"
print "wrong 10 times then the lock closes forever and you can't"
print "get the bomb. The code is 3 digits."
code = "%d%d%d" % (randint(1,9), randint(1,9), randint(1,9))
guess = raw_input("[keypad]> ")
guesses = 0 while guess != code and guesses < 10:
print "BZZZZEDDD!"
guesses += 1
guess = raw_input("[keypad]> ") if guess == code:
print "The container clicks open and the seal breaks, letting gas out."
print "You grab the neutron bomb and run as fast as you can to the"
print "bridge where you must place it in the right spot."
return 'the_bridge'
else:
print "The lock buzzes one last time and then you hear a sickening"
print "melting sound as the mechanism is fused together."
print "You decide to sit there, and finally the Gothons blow up the"
print "ship from their ship and you die."
return 'death' def the_bridge(self):
print "You burst onto the Bridge with the netron destruct bomb"
print "under your arm and surprise 5 Gothons who are trying to"
print "take control of the ship. Each of them has an even uglier"
print "clown costume than the last. They haven't pulled their"
print "weapons out yet, as they see the active bomb under your"
print "arm and don't want to set it off." action = raw_input("> ") if action == "throw the bomb":
print "In a panic you throw the bomb at the group of Gothons"
print "and make a leap for the door. Right as you drop it a"
print "Gothon shoots you right in the back killing you."
print "As you die you see another Gothon frantically try to disarm"
print "the bomb. You die knowing they will probably blow up when"
print "it goes off."
return 'death' elif action == "slowly place the bomb":
print "You point your blaster at the bomb under your arm"
print "and the Gothons put their hands up and start to sweat."
print "You inch backward to the door, open it, and then carefully"
print "place the bomb on the floor, pointing your blaster at it."
print "You then jump back through the door, punch the close button"
print "and blast the lock so the Gothons can't get out."
print "Now that the bomb is placed you run to the escape pod to"
print "get off this tin can."
return 'escape_pod'
else:
print "DOES NOT COMPUTE!"
return "the_bridge" def escape_pod(self):
print "You rush through the ship desperately trying to make it to"
print "the escape pod before the whole ship explodes. It seems like"
print "hardly any Gothons are on the ship, so your run is clear of"
print "interference. You get to the chamber with the escape pods, and"
print "now need to pick one to take. Some of them could be damaged"
print "but you don't have time to look. There's 5 pods, which one"
print "do you take?" good_pod = randint(1,5)
guess = raw_input("[pod #]> ") if int(guess) != good_pod:
print "You jump into pod %s and hit the eject button." % guess
print "The pod escapes out into the void of space, then"
print "implodes as the hull ruptures, crushing your body"
print "into jam jelly."
return 'death'
else:
print "You jump into pod %s and hit the eject button." % guess
print "The pod easily slides out into space heading to"
print "the planet below. As it flies to the planet, you look"
print "back and see your ship implode then explode like a"
print "bright star, taking out the Gothon ship at the same"
print "time. You won!"
exit(0) a_game = Game("central_corridor")
a_game.play()
习题42:对象、类、以及从属关系
小方是一条泥鳅 -- 小方是一条鱼(鱼是“类”),小方是一条泥鳅(泥鳅是“类”,泥鳅是鱼类的一种,泥鳅继承鱼“类”),小方是一个对象。
---- 对象属于某个类,而某个类又属于另一个类
代码:
class Animal(object):
pass
class Dog(Animal):
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
class Cat(Animal):
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
class Person(object):
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
self.pet = None
class Employee(Person):
def __init__(self, name, salary):
super(Employee, self).__init__(name)
self.salary = salary
class Fish(object):
pass
class Salmon(Fish):
pass
class Halibut(Fish):
pass
rover = Dog("Rover")
satan = Cat("Satan")
mary = Person("Mary")
mary.pat = satan
frank = Employee("Frank", 120000)
frank.pet = rover
fliper = Fish()
crouse = Salmon()
harry = Halibut()
习题43:来自Percal 25 号行星的哥顿人(Gothons)
代码:-- 尚未完全理解,后续通过其他文档加深理解
from sys import exit
from random import randint def death():
quips = ["You died. You kinda suck at this.",
"Nice job, you died ...jackass.",
"Such a luser.",
"I have a small puppy that's better at this."] print quips[randint(0, len(quips)-1)]
exit(1) def central_corridor():
print "The Gothons of Planet Percal #25 have invaded your ship and destroyed"
print "your entire crew. You are the last surviving member and your last"
print "mission is to get the neutron destruct bomb from the Weapons Armory,"
print "put it in the bridge, and blow the ship up after getting into an "
print "escape pod."
print "\n"
print "You're running down the central corridor to the Weapons Armory when"
print "a Gothon jumps out, red scaly skin, dark grimy teeth, and evil clown costume"
print "flowing around his hate filled body. He's blocking the door to the"
print "Armory and about to pull a weapon to blast you." action = raw_input("> ") if action == "shoot!":
print "Quick on the draw you yank out your blaster and fire it at the Gothon."
print "His clown costume is flowing and moving around his body, which throws"
print "off your aim. Your laser hits his costume but misses him entirely. This"
print "completely ruins his brand new costume his mother bought him, which"
print "makes him fly into an insane rage and blast you repeatedly in the face until"
print "you are dead. Then he eats you."
return 'death' elif action == "dodge!":
print "Like a world class boxer you dodge, weave, slip and slide right"
print "as the Gothon's blaster cranks a laser past your head."
print "In the middle of your artful dodge your foot slips and you"
print "bang your head on the metal wall and pass out."
print "You wake up shortly after only to die as the Gothon stomps on"
print "your head and eats you."
return 'death' elif action == "tell a joke":
print "Lucky for you they made you learn Gothon insults in the academy."
print "You tell the one Gothon joke you know:"
print "Lbhe zbgure vf fb sng, jura fur fvgf nebhaq gur ubhfr, fur fvgf nebhaq gur ubhfr."
print "The Gothon stops, tries not to laugh, then busts out laughing and can't move."
print "While he's laughing you run up and shoot him square in the head"
print "putting him down, then jump through the Weapon Armory door."
return 'laser_weapon_armory' else:
print "DOES NOT COMPUTE!"
return 'central_corridor' def laser_weapon_armory():
print "You do a dive roll into the Weapon Armory, crouch and scan the room"
print "for more Gothons that might be hiding. It's dead quiet, too quiet."
print "You stand up and run to the far side of the room and find the"
print "neutron bomb in its container. There's a keypad lock on the box"
print "and you need the code to get the bomb out. If you get the code"
print "wrong 10 times then the lock closes forever and you can't"
print "get the bomb. The code is 3 digits."
code = "%d%d%d" % (randint(1,9), randint(1,9), randint(1,9))
guess = raw_input("[keypad]> ")
guesses = 0 while guess != code and guesses < 10:
print "BZZZZEDDD!"
guesses += 1
guess = raw_input("[keypad]> ") if guess == code:
print "The container clicks open and the seal breaks, letting gas out."
print "You grab the neutron bomb and run as fast as you can to the"
print "bridge where you must place it in the right spot."
return 'the_bridge'
else:
print "The lock buzzes one last time and then you hear a sickening"
print "melting sound as the mechanism is fused together."
print "You decide to sit there, and finally the Gothons blow up the"
print "ship from their ship and you die."
return 'death' def the_bridge():
print "You burst onto the Bridge with the neutron destruct bomb"
print "under your arm and surprise 5 Gothons who are trying to"
print "take control of the ship. Each of them has an even uglier"
print "clown costume than the last. They haven't pulled their"
print "weapons out yet, as they see the active bomb under your"
print "arm and don't want to set it off." action = raw_input("> ") if action == "throw the bomb":
print "In a panic you throw the bomb at the group of Gothons"
print "and make a leap for the door. Right as you drop it a"
print "Gothon shoots you right in the back killing you."
print "As you die you see another Gothon frantically try to disarm"
print "the bomb. You die knowing they will probably blow up when"
print "it goes off."
return 'death' elif action == "slowly place the bomb":
print "You point your blaster at the bomb under your arm"
print "and the Gothons put their hands up and start to sweat."
print "You inch backward to the door, open it, and then carefully"
print "place the bomb on the floor, pointing your blaster at it."
print "You then jump back through the door, punch the close button"
print "and blast the lock so the Gothons can't get out."
print "Now that the bomb is placed you run to the escape pod to"
print "get off this tin can."
return 'escape_pod'
else:
print "DOES NOT COMPUTE!"
return "the_bridge" def escape_pod():
print "You rush through the ship desperately trying to make it to"
print "the escape pod before the whole ship explodes. It seems like"
print "hardly any Gothons are on the ship, so your run is clear of"
print "interference. You get to the chamber with the escape pods, and"
print "now need to pick one to take. Some of them could be damaged"
print "but you don't have time to look. There's 5 pods, which one"
print "do you take?" good_pod = randint(1,5)
guess = raw_input("[pod #]> ") if int(guess) != good_pod:
print "You jump into pod %s and hit the eject button." % guess
print "The pod escapes out into the void of space, then"
print "implodes as the hull ruptures, crushing your body"
print "into jam jelly."
return 'death'
else:
print "You jump into pod %s and hit the eject button." % guess
print "The pod easily slides out into space heading to"
print "the planet below. As it flies to the planet, you look"
print "back and see your ship implode then explode like a"
print "bright star, taking out the Gothon ship at the same"
print "time. You won!"
exit(0) ROOMS = {
'death': death,
'central_corridor': central_corridor,
'laser_weapon_armory': laser_weapon_armory,
'the_bridge': the_bridge,
'escape_pod': escape_pod
} def runner(map, start):
next = start while True:
room = map[next]
print "\n--------"
next = room() runner(ROOMS, 'central_corridor')
习题44:继承与合成
继承:指明一个类的大部分功能或全部功能,都是从一个父类中获得的
父类与子类的三种交互方式:
1、子类上的动作完全等同于父类上的动作
2、子类上的动作完全改写了父类上的动作
3、子类上的动作部分变更了父类上的动作
隐式继承:譬如在父类里定义了一个函数,但没有在子类中定义,会发生隐式继承
显式覆写:在子类中重新定义一个相同名称的函数,则不再继承父类中相同名称的函数
在运行前或运行后覆写:覆写的一个特例。若想在父类中定义的内容运行之前或之后再修改行为。首先先显式覆写,接着用Python的内置函数super来调用父类里的版本
代码:
class Parent(object):
def altered(self):
print "PARENT altered()"
class Child(Parent):
def altered(self):
print "CHILD, BEFORE PARENT altered()"
super(Child, self).altered()
print "CHILD, AFTER PARENT altered()"
dad = Parent()
son = Child()
dad.altered()
son.altered()
结果:

代码:--三种方式
class Parent(object):
def override(self):
print "PARENT override()"
def implicit(self):
print "PARENT implicit()"
def altered(self):
print "PARENT altered()"
class Child(Parent):
def override(self):
print "CHILD override()"
def altered(self):
print "CHILD, BEFORE PARENT altered()"
super(Child, self).altered()
print "CHILD, AFTER PARENT altered()"
dad = Parent()
son = Child()
dad.implicit()
son.implicit()
dad.override()
son.override()
dad.altered()
son.altered()
结果:

多重继承:同时继承多个类 super()和__init__搭配使用
合成:父类与子类的关系不再是“A是B”,而是“A里有B”
代码:
class Other(object):
def override(self):
print "OTHER override()"
def implicit(self):
print "OTHER implicit()"
def altered(self):
print "OTHER altered()"
class Child(object):
def __init__(self):
self.other = Other()
def implicit(self):
self.other.implicit()
def override(self):
print "CHILD override()"
def altered(self):
print "CHILD, BEFORE OTHER altered()"
self.other.altered()
print "CHILD, AFTER OTHER altered()"
son = Child()
son.implicit()
son.override()
son.altered()
结果:

python入门 -- 学习笔记4的更多相关文章
- Python入门学习笔记4:他人的博客及他人的学习思路
看其他人的学习笔记,可以保证自己不走弯路.并且一举两得,即学知识又学方法! 廖雪峰:https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/0014316089557264a6b348958 ...
- Python入门学习笔记
了解 一下Python中的基本语法,发现挺不适应的,例如变量经常想去指定类型或者if加个括号之类的.这是在MOOC中学习到的知识中一点简单的笔记. Python的变量和数据类型: 1.Python这种 ...
- python入门学习笔记(三)
10.函数 求绝对值的函数 abs(x) 也可以在交互式命令行通过 help(abs) 查看abs函数的帮助信息.调用 abs 函数:>>> abs(100)100>>& ...
- Python入门 学习笔记 (二)
今天学习了一些简单的语法规则,话不多说,开始了: 二.数据类型 常用数据类型中的整形和浮点型就不多说了. 1.字符串 ...
- python入门 -- 学习笔记1
学习资料:笨方法学Python 准备: 安装环境----请自行网络搜索(Windows安装很简单,和其他安装程序一样) 找一个自己习惯的编辑器(比如:sublime text 3) 创建一个专门的目录 ...
- Python入门 学习笔记 (一)
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lujianwenance/p/5939786.html 说到学习一门语言第一步就是先选定使用的工具(环境).因为本人是个小白,所以征求了一下同 ...
- python入门学习笔记(二)
6.6替换元素 7.tuple类型 7.1创建tuple 7.2创建单元素tuple 7.3"可变"的tuple 8.条件判断和循环 8.1,if语句 8.2,if... ...
- python入门学习笔记(一)
写在开头: A:python的交互式环境 ...
- python入门 -- 学习笔记3
习题21:函数可以返回东西 过程解析: 1.定义函数:如def add(形参)函数 2.调用函数: add(实参) 别忘记加() 3.在函数调用的时候将实参的值传给形参,代入到函数中进行计算,r ...
随机推荐
- 【转载】 pytorch笔记:06)requires_grad和volatile
原文地址: https://blog.csdn.net/jiangpeng59/article/details/80667335 作者:PJ-Javis 来源:CSDN --------------- ...
- linux sar命令详解
sar(System Activity Reporter系统活动情况报告)是目前 Linux 上最为全面的系统性能分析工具之一,可以从多方面对系统的活动进行报告,包括:文件的读写情况.系统调用的使用情 ...
- LeetCode - Unique Email Addresses
Every email consists of a local name and a domain name, separated by the @ sign. For example, in ali ...
- EBS获取code_combination_id(CCID)时段值自动被置为默认值的问题
EBS中在使用标准的API(FND_FLEX_EXT.GET_COMBINATION_ID 和 FND_FLEX_EXT.GET_CCID还有fnd_flex_keyval.validate_segs ...
- Python开发 基礎知識 (未完代補)
一.Python基本知識 1.Python屬高階語言,所編築的是字節碼 2.一般狀態statement 終止於換行,如需使用多數行編寫,可在行末加上 \,以表延續 但在 parentheses ( ) ...
- 菜鸟Vue学习笔记(二)
上一篇文章跟大家分享了Vue笔记上半部分,这篇文章接着跟大家分享.最近学习Vue越来越顺利了,今天接着学习,接着记录. 首先,来学习下常用的v-bind属性,它的作用是在属性中使用vue中定义的变量的 ...
- Android related
The build env. ensure that your computer’s BIOS is set up to support Intel’s virtualization extensio ...
- kvm报错集
虚拟机console窗口看到一些报错 也可以在终端使用dmesg命令查看 [17617.701174] kvm [17393]: vcpu0 unhandled rdmsr: 0x1ad [19053 ...
- zabbix图形化界面乱码(二)
中文字体乱码,解决办法: 1:从Windos下拷贝字体到服务器,C:\Windows\Fonts,有很多,看着喜欢的拷贝 2:然后在zabbix 服务端,进入到zabbix web的工作目 ...
- 计算:表中varchar类型的字段能容纳的最大字符数?
建表语句: CREATE TABLE `test2` ( `id` int unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `content` varchar(21842) NOT ...
