interface21 - web - ContextLoaderListener(Spring Web Application Context加载流程)
前言
最近打算花点时间好好看看spring的源码,然而现在Spring的源码经过迭代的版本太多了,比较庞大,看起来比较累,所以准备从最初的版本(interface21)开始入手,仅用于学习,理解其设计思想,后续慢慢研究其每次版本变更的内容。。。
先从interface21的一个典型web工程例子看起,宠物诊所 - petclinic,因为该工程基本涵盖了Spring的APO、IOC、JDBC、Web MVC、事务、国际化、主题切换、参数校验等主要功能。。。
继上一篇,了解完Log4jConfigListener(加载Log4j日志)的流程后,看看ContextLoaderListener(加载Spring Web Application Context)流程是如何的~~~~~~~
对应的web.xml配置
<listener>
<listener-class>com.interface21.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
执行时序图(看不清的话可以点击查看原图)
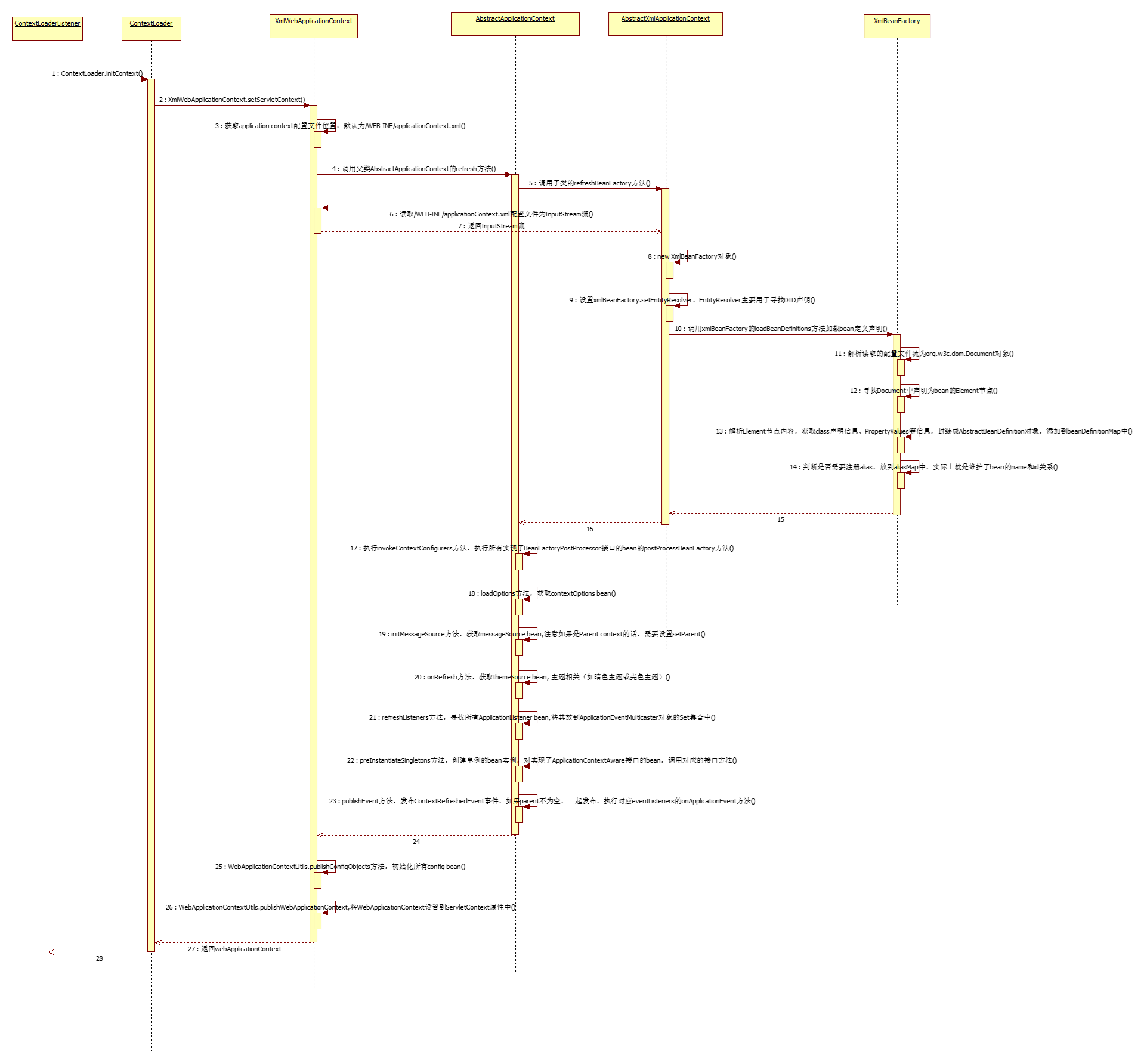
时序图中的各个步骤简要分析
执行的入口在ContextLoaderListener类的contextInitialized方法,由于ContextLoaderListener类实现了ServletContextListener接口,所以在Servlet容器(tomcat)启动时,会自动调用contextInitialized方法。
步骤描述:
- 进入ContextLoaderListener类的contextInitialized方法,该类只有一句代码,执行ContextLoader.initContext(event.getServletContext())方法;
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
ContextLoader.initContext(event.getServletContext());
} - 进入ContextLoader类的initContext方法,首先,从servletContext中获取contextClass参数,如果配置了该参数,则创建该实例对象,否则创建默认的XmlWebApplicationContext实例对象,接下来调用XmlWebApplicationContext的setServletContext方法;
public static WebApplicationContext initContext(ServletContext servletContext) throws ApplicationContextException {
servletContext.log("Loading root WebApplicationContext");
String contextClass = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM); // Now we must load the WebApplicationContext.
// It configures itself: all we need to do is construct the class with a no-arg
// constructor, and invoke setServletContext.
try {
Class clazz = (contextClass != null ? Class.forName(contextClass) : DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
logger.info("Loading root WebApplicationContext: using context class '" + clazz.getName() + "'"); if (!WebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Context class is no WebApplicationContext: " + contextClass);
} WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext = (WebApplicationContext) clazz.newInstance();
webApplicationContext.setServletContext(servletContext);
return webApplicationContext; } catch (ApplicationContextException ex) {
handleException("Failed to initialize application context", ex); } catch (BeansException ex) {
handleException("Failed to initialize beans in application context", ex); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
handleException("Failed to load config class '" + contextClass + "'", ex); } catch (InstantiationException ex) {
handleException("Failed to instantiate config class '" + contextClass + "': does it have a public no arg constructor?", ex); } catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
handleException("Illegal access while finding or instantiating config class '" + contextClass + "': does it have a public no arg constructor?", ex); } catch (Throwable ex) {
handleException("Unexpected error loading context configuration", ex);
} return null;
} - 进入XmlWebApplicationContext类的setServletContext方法,首先,调用initConfigLocation方法从servletContext中获取contextConfigLocation参数(Spring Application配置文件),如果没配置该参数,则默认获取/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml该文件;
public void setServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) throws ApplicationContextException {
this.servletContext = servletContext;
this.configLocation = initConfigLocation();
logger.info("Using config location '" + this.configLocation + "'");
refresh(); if (this.namespace == null) {
// We're the root context
WebApplicationContextUtils.publishConfigObjects(this);
// Expose as a ServletContext object
WebApplicationContextUtils.publishWebApplicationContext(this);
}
} - 迎来了非常关键的一步操作,调用AbstractApplicationContext类的refresh()方法,该方法具体如下,每个阶段的英文注释已经比较清晰了,下面步骤也会做个详细描述:
public final void refresh() throws ApplicationContextException {
if (this.contextOptions != null && !this.contextOptions.isReloadable())
throw new ApplicationContextException("Forbidden to reload config"); this.startupTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); refreshBeanFactory(); if (getBeanDefinitionCount() == 0)
logger.warn("No beans defined in ApplicationContext [" + getDisplayName() + "]");
else
logger.info(getBeanDefinitionCount() + " beans defined in ApplicationContext [" + getDisplayName() + "]"); // invoke configurers that can override values in the bean definitions
invokeContextConfigurers(); // load options bean for this context
loadOptions(); // initialize message source for this context
initMessageSource(); // initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses
onRefresh(); // check for listener beans and register them
refreshListeners(); // instantiate singletons this late to allow them to access the message source
preInstantiateSingletons(); // last step: publish respective event
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
} - 首先,调用AbstractXmlApplicationContext类的refreshBeanFactory方法,该方法如下,具体完成的操作内容下面步骤会详细描述:
protected void refreshBeanFactory() throws ApplicationContextException {
String identifier = "application context with display name [" + getDisplayName() + "]";
InputStream is = null;
try {
// Supports remote as well as local URLs
is = getInputStreamForBeanFactory();
this.xmlBeanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(getParent());
this.xmlBeanFactory.setEntityResolver(new ResourceBaseEntityResolver(this));
this.xmlBeanFactory.loadBeanDefinitions(is);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("BeanFactory for application context: " + this.xmlBeanFactory);
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("IOException parsing XML document for " + identifier, ex);
} catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot load configuration: missing bean definition [" + ex.getBeanName() + "]", ex);
} catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot load configuration: problem instantiating or initializing beans", ex);
} finally {
try {
if (is != null)
is.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("IOException closing stream for XML document for " + identifier, ex);
}
}
} - 调用XmlWebApplicationContext类的getInputStreamForBeanFactory方法,读取阶段3获取到的配置文件为输入流InputStream
protected InputStream getInputStreamForBeanFactory() throws IOException {
InputStream in = getResourceAsStream(this.configLocation);
if (in == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException("Config location not found: " + this.configLocation);
}
return in;
} - 返回配置文件输入流InputStream
- 回到AbstractXmlApplicationContext的refreshBeanFactory方法,new出一个XmlBeanFactory对象
- 设置xmlBeanFactory.setEntityResolver,这里的EntityResolver主要用于寻找DTD声明
- 调用xmlBeanFactory的loadBeanDefinitions方法加载bean定义声明
- 进入xmlBeanFactory类的loadBeanDefinitions方法,解析读取的配置文件流InputStream为org.w3c.dom.Document对象,然后调用loadBeanDefinitions方法依次解析各个bean元素节点信息
public void loadBeanDefinitions(InputStream is) throws BeansException {
if (is == null)
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("InputStream cannot be null: expected an XML file", null); try {
logger.info("Loading XmlBeanFactory from InputStream [" + is + "]");
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
logger.debug("Using JAXP implementation [" + factory + "]");
factory.setValidating(true);
DocumentBuilder db = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
db.setErrorHandler(new BeansErrorHandler());
db.setEntityResolver(this.entityResolver != null ? this.entityResolver : new BeansDtdResolver());
Document doc = db.parse(is);
loadBeanDefinitions(doc);
} catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("ParserConfiguration exception parsing XML", ex);
} catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("XML document is invalid", ex);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("IOException parsing XML document", ex);
} finally {
try {
if (is != null)
is.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new FatalBeanException("IOException closing stream for XML document", ex);
}
}
} - 寻找Document中声明为bean的Element节点,依次解析
public void loadBeanDefinitions(Document doc) throws BeansException {
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();
logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");
NodeList nl = root.getElementsByTagName(BEAN_ELEMENT);
logger.debug("Found " + nl.getLength() + " <" + BEAN_ELEMENT + "> elements defining beans");
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node n = nl.item(i);
loadBeanDefinition((Element) n);
}
} - 解析Element节点内容,获取class声明信息、PropertyValues等信息,封装成AbstractBeanDefinition对象,添加到beanDefinitionMap中
private void loadBeanDefinition(Element el) throws BeansException {
// The DTD guarantees an id attribute is present
String id = el.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);
logger.debug("Parsing bean definition with id '" + id + "'"); // Create BeanDefinition now: we'll build up PropertyValues later
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition; PropertyValues pvs = getPropertyValueSubElements(el);
beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinition(el, id, pvs);
registerBeanDefinition(id, beanDefinition); String name = el.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
if (name != null && !"".equals(name)) {
// Automatically create this alias. Used for
// names that aren't legal in id attributes
registerAlias(id, name);
}
} - 判断是否需要注册alias,放到aliasMap中,实际上就是维护了bean的name和id关系
- 返回到AbstractXmlApplicationContext类refreshBeanFactory方法中
- 返回到AbstractApplicationContext类refresh方法中
- 执行AbstractApplicationContext的invokeContextConfigurers方法,实际上内部是执行所有实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的bean的postProcessBeanFactory方法
private void invokeContextConfigurers() {
String[] beanNames = getBeanDefinitionNames(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class);
for (int i = 0; i < beanNames.length; i++) {
String beanName = beanNames[i];
BeanFactoryPostProcessor configurer = (BeanFactoryPostProcessor) getBean(beanName);
configurer.postProcessBeanFactory(getBeanFactory());
}
} - 执行AbstractApplicationContext的loadOptions方法,获取contextOptions bean,首先,查看配置文件是否已经配置contextOptions bean,没有则自己创建一个new ContextOptions()对象,主要用于当应用运行时,是否可以重新加载该配置,如果配置成false的话,会在调用refresh方法时,抛出一个ApplicationContextException("Forbidden to reload config")异常;
private void loadOptions() {
try {
this.contextOptions = (ContextOptions) getBean(OPTIONS_BEAN_NAME);
} catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
logger.info("No options bean (\"" + OPTIONS_BEAN_NAME + "\") found: using default");
this.contextOptions = new ContextOptions();
}
} - 执行AbstractApplicationContext的initMessageSource方法,获取messageSource bean,首先,查看配置文件是否已经配置messageSource bean,没有则自己创建一个StaticMessageSource对象,注意如果Parent context不为null的话,需要设置Parent MessageSource
private void initMessageSource() {
try {
this.messageSource = (MessageSource) getBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME);
// set parent message source if applicable,
// and if the message source is defined in this context, not in a parent
if (this.parent != null && (this.messageSource instanceof NestingMessageSource) &&
Arrays.asList(getBeanDefinitionNames()).contains(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME)) {
((NestingMessageSource) this.messageSource).setParent(this.parent);
}
} catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
logger.info("No MessageSource found for [" + getDisplayName() + "]: using empty StaticMessageSource");
// use empty message source to be able to accept getMessage calls
this.messageSource = new StaticMessageSource();
}
} - 执行AbstractXmlUiApplicationContext的onRefresh方法,获取themeSource bean, 主题相关(如应用可配置暗色主题或亮色主题功能),同样,这里也首先查看配置文件是否已经配置themeSource bean,没有则自己创建一个ResourceBundleThemeSource对象,注意这里还需要根据判断条件设置Parent ThemeSource
protected void onRefresh() {
this.themeSource = UiApplicationContextUtils.initThemeSource(this);
}public static ThemeSource initThemeSource(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
ThemeSource themeSource;
try {
themeSource = (ThemeSource) applicationContext.getBean(THEME_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME);
// set parent theme source if applicable,
// and if the theme source is defined in this context, not in a parent
if (applicationContext.getParent() instanceof ThemeSource && themeSource instanceof NestingThemeSource &&
Arrays.asList(applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()).contains(THEME_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME)) {
((NestingThemeSource) themeSource).setParent((ThemeSource) applicationContext.getParent());
}
} catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
logger.info("No ThemeSource found for [" + applicationContext.getDisplayName() + "]: using ResourceBundleThemeSource");
themeSource = new ResourceBundleThemeSource();
}
return themeSource;
} - 执行AbstractApplicationContext的refreshListeners方法,寻找所有ApplicationListener bean,将其放到ApplicationEventMulticaster对象的Set集合中
private void refreshListeners() {
logger.info("Refreshing listeners");
List listeners = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfType(ApplicationListener.class, this);
logger.debug("Found " + listeners.size() + " listeners in bean factory");
for (int i = 0; i < listeners.size(); i++) {
ApplicationListener listener = (ApplicationListener) listeners.get(i);
addListener(listener);
logger.info("Bean listener added: [" + listener + "]");
}
} - 执行AbstractApplicationContext的preInstantiateSingletons方法,创建单例的bean实例,创建bean对象是在调用getBean方法时创建的,具体创建逻辑在getSharedInstance方法里;另外,对实现了ApplicationContextAware接口的bean,会调用对应的接口setApplicationContext方法,这里涉及的细节比较多,后续有时间可以具体详细分析;
private void preInstantiateSingletons() {
logger.info("Configuring singleton beans in context");
String[] beanNames = getBeanDefinitionNames();
logger.debug("Found " + beanNames.length + " listeners in bean factory: names=[" +
StringUtils.arrayToDelimitedString(beanNames, ",") + "]");
for (int i = 0; i < beanNames.length; i++) {
String beanName = beanNames[i];
if (isSingleton(beanName)) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
Object bean = getBeanFactory().getBean(name);
configureManagedObject(name, bean);
return bean;
}private final synchronized Object getSharedInstance(String pname, Map newlyCreatedBeans) throws BeansException {
// Get rid of the dereference prefix if there is one
String name = transformedBeanName(pname); Object beanInstance = this.singletonCache.get(name);
if (beanInstance == null) {
logger.info("Creating shared instance of singleton bean '" + name + "'");
beanInstance = createBean(name, newlyCreatedBeans);
this.singletonCache.put(name, beanInstance);
} else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + name + "'");
} // Don't let calling code try to dereference the
// bean factory if the bean isn't a factory
if (isFactoryDereference(pname) && !(beanInstance instanceof FactoryBean)) {
throw new BeanIsNotAFactoryException(name, beanInstance);
} // Now we have the beanInstance, which may be a normal bean
// or a FactoryBean. If it's a FactoryBean, we use it to
// create a bean instance, unless the caller actually wants
// a reference to the factory.
if (beanInstance instanceof FactoryBean) {
if (!isFactoryDereference(pname)) {
// Configure and return new bean instance from factory
FactoryBean factory = (FactoryBean) beanInstance;
logger.debug("Bean with name '" + name + "' is a factory bean");
beanInstance = factory.getObject(); // Set pass-through properties
if (factory.getPropertyValues() != null) {
logger.debug("Applying pass-through properties to bean with name '" + name + "'");
new BeanWrapperImpl(beanInstance).setPropertyValues(factory.getPropertyValues());
}
// Initialization is really up to factory
//invokeInitializerIfNecessary(beanInstance);
} else {
// The user wants the factory itself
logger.debug("Calling code asked for BeanFactory instance for name '" + name + "'");
}
} // if we're dealing with a factory bean return beanInstance;
}private void configureManagedObject(String name, Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware &&
(!isSingleton(name) || !this.managedSingletons.contains(bean))) {
logger.debug("Setting application context on ApplicationContextAware object [" + bean + "]");
ApplicationContextAware aca = (ApplicationContextAware) bean;
aca.setApplicationContext(this);
this.managedSingletons.add(bean);
}
} - 执行AbstractApplicationContext的publishEvent方法,发布ContextRefreshedEvent事件,如果parent不为空,一起发布,内部的逻辑是执行对应eventListeners的onApplicationEvent方法
public final void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Publishing event in context [" + getDisplayName() + "]: " + event.toString());
}
this.eventMulticaster.onApplicationEvent(event);
if (this.parent != null) {
parent.publishEvent(event);
}
} - 回到XmlWebApplicationContext类
- 执行WebApplicationContextUtils.publishConfigObjects方法,寻找所有config bean,将其设置到ServletContext的属性中
public static void publishConfigObjects(WebApplicationContext wac) throws ApplicationContextException {
logger.info("Configuring config objects");
String[] beanNames = wac.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (int i = 0; i < beanNames.length; i++) {
String name = beanNames[i];
if (name.startsWith(CONFIG_OBJECT_PREFIX)) {
// Strip prefix
String strippedName = name.substring(CONFIG_OBJECT_PREFIX.length());
try {
Object configObject = wac.getBean(name);
wac.getServletContext().setAttribute(strippedName, configObject);
logger.info("Config object with name [" + name + "] and class [" + configObject.getClass().getName() +
"] initialized and added to ServletConfig");
} catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Couldn't load config object with name '" + name + "': " + ex, ex);
}
}
}
} - 执行WebApplicationContextUtils.publishWebApplicationContext,将WebApplicationContext设置到ServletContext属性中
public static void publishWebApplicationContext(WebApplicationContext wac) {
// Set WebApplicationContext as an attribute in the ServletContext so
// other components in this web application can access it
ServletContext sc = wac.getServletContext();
if (sc == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("ServletContext can't be null in WebApplicationContext " + wac); sc.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE_NAME, wac);
logger.info(
"Loader initialized on server name "
+ wac.getServletContext().getServerInfo()
+ "; WebApplicationContext object is available in ServletContext with name '"
+ WebApplicationContext.WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE_NAME
+ "'");
} - 返回webApplicationContext到ContextLoader类
- ContextLoaderListener.contextInitialized方法执行结束
就这样,Spring Web Application Context加载完成了,是不是感觉也挺简单的,主要就是读取xml配置文件中bean的配置信息,创建bean实例放到一个map中维护,当然,中间还穿插了各种逻辑;
另外补充下,当Servlet容器销毁时,会调用ContextLoaderListener的contextDestroyed方法,最终是调用ContextLoader.closeContext(event.getServletContext(),执行一些资源销毁等操作,销毁工厂创建的bean对象,发布ContextClosedEvent事件等;
public void close() {
logger.info("Closing application context [" + getDisplayName() + "]");
// destroy all cached singletons in this context,
// invoking DisposableBean.destroy and/or "destroy-method"
getBeanFactory().destroySingletons();
// publish respective event
publishEvent(new ContextClosedEvent(this));
}
interface21代码参考
https://github.com/peterchenhdu/interface21
interface21 - web - ContextLoaderListener(Spring Web Application Context加载流程)的更多相关文章
- Spring Security拦截器加载流程分析--练气中期
写在前面 上回我们讲了spring security整合spring springmvc的流程,并且知道了spring security是通过过滤器链来进行认证授权操作的.今天我们来分析一下sprin ...
- Spring源码剖析2:Spring IOC容器的加载过程
spring ioc 容器的加载流程 1.目标:熟练使用spring,并分析其源码,了解其中的思想.这篇主要介绍spring ioc 容器的加载 2.前提条件:会使用debug 3.源码分析方法:In ...
- Spring源码剖析3:Spring IOC容器的加载过程
本文转自五月的仓颉 https://www.cnblogs.com/xrq730 本系列文章将整理到我在GitHub上的<Java面试指南>仓库,更多精彩内容请到我的仓库里查看 https ...
- 第8章—使用Spring Web Flow—Spring Web Flow的配置
Spring中配置Web Flow Spring Web Flow 是 Spring 的一个子项目,其最主要的目的是解决跨越多个请求的.用户与服务器之间的.有状态交互问题,比较适合任何比较复杂的.有状 ...
- web.xml中配置启动时加载的servlet,load-on-starup
web.xml中配置启动时加载的servlet,load-on-starup 使用servlet来初始化配置文件数据: 在servlet的配置当中,<load-on-startup>1&l ...
- Spring Boot JPA 懒加载
最近在使用spring jpa 的过程中经常遇到懒加载的错误:"` org.hibernate.LazyInitializationException: could not initiali ...
- java面试记录二:spring加载流程、springmvc请求流程、spring事务失效、synchronized和volatile、JMM和JVM模型、二分查找的实现、垃圾收集器、控制台顺序打印ABC的三种线程实现
注:部分答案引用网络文章 简答题 1.Spring项目启动后的加载流程 (1)使用spring框架的web项目,在tomcat下,是根据web.xml来启动的.web.xml中负责配置启动spring ...
- Spring IoC BeanDefinition 的加载和注册
前言 本系列全部基于 Spring 5.2.2.BUILD-SNAPSHOT 版本.因为 Spring 整个体系太过于庞大,所以只会进行关键部分的源码解析. 本篇文章主要介绍 Spring IoC 容 ...
- 微服务架构 | *2.3 Spring Cloud 启动及加载配置文件源码分析(以 Nacos 为例)
目录 前言 1. Spring Cloud 什么时候加载配置文件 2. 准备 Environment 配置环境 2.1 配置 Environment 环境 SpringApplication.prep ...
随机推荐
- 二级接口ListableBeanFactory
package org.springframework.beans.factory; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation; import java.util. ...
- Hibernate Generic DAO的介绍安装和使用
java 的包挺多,比c#多 . jar包一个名,解压缩出来又出来又叫另一个名 .搜索起来,内容都分散的很 http://mvnrepository.com maven库搜索 com.googlec ...
- 现代编译原理--第六章(中间树 IR Tree 含源码)
(转载请表明出处 http://www.cnblogs.com/BlackWalnut/p/4559717.html ) 这一章,就虎书而言,理论知识点是及其少的,就介绍了为什么要有一个中间表示树 ...
- 设计模式学习心得<工厂方法 Factory Method>
概述 意图 业务代码中常常有构造对象的过程,它拥有大量的参数.并且有很多地方需要这对象. 简化对象构造过程. 主要解决 一个类在不同场景的频繁地创建,让不同对象的创建更有语义化,提高代码复用性. 何时 ...
- [SoapUI] 检查测试步骤的类型或者或者某种特定类型的步骤列表
SoapUI Groovy : Check if test step is of specific type, such as : Wsdl, Rest, Jdbc, HTTP, Groovy etc ...
- 《C#从现象到本质》读书笔记(四)第4章C#和面向对象
<C#从现象到本质>读书笔记第4章C#和面向对象 面向对象程序设计OOP 面向对象的三大特性是: 1)封装:类可以将它的成员私有化,只暴露它认为应当暴露给外界的成员.通过私有化成员,外界不 ...
- W7500P硬件TCP/IP+硬件物理层PHY+Cortex-M0处理器(48MHZ)
W7500P 硬件TCP/IP+硬件物理层PHY+Cortex-M0处理器(48MHZ) 硬件TCP/IP+硬件物理层PHY+Cortex-M0处理器(48MHZ) 如果您发现商品信息不准确,欢迎纠错 ...
- Win7 VS2015 NASM汇编语言环境配置
参考了以下两个博客文章 http://blog.csdn.net/x356982611/article/details/51260841 http://www.cnblogs.com/antonioz ...
- 从中央仓库下载所想要的jar包
中央仓库地址:https://mvnrepository.com/ 这边我搜索一个commons-logging包作为例子: 点击下面第二个绿色的comons-logging进入这个页面: 一.win ...
- 第一节 —— vue2.0 环境安装,工程化开发
vue的开发有两种,一种是直接的在script标签里引入vue.js文件即可,这样子引入的话个人感觉做小型的多页面会比较舒坦,一旦做大型一点的项目,还是离不开webpack. 所以另一种方法也就是基于 ...
