理解 LinkedList
java -version :jdk 1.8.0_191
构造
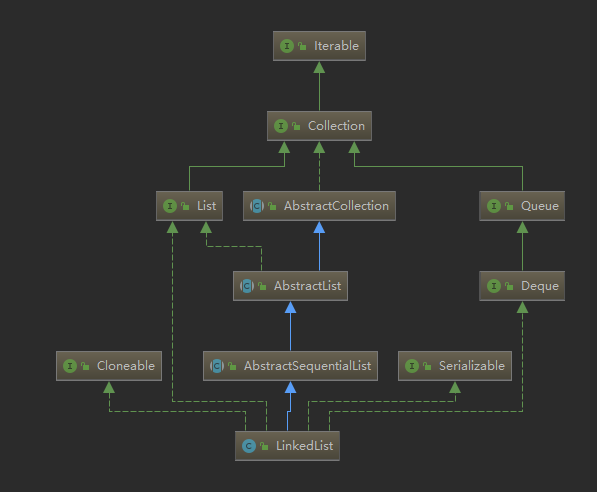
类内参数,方法
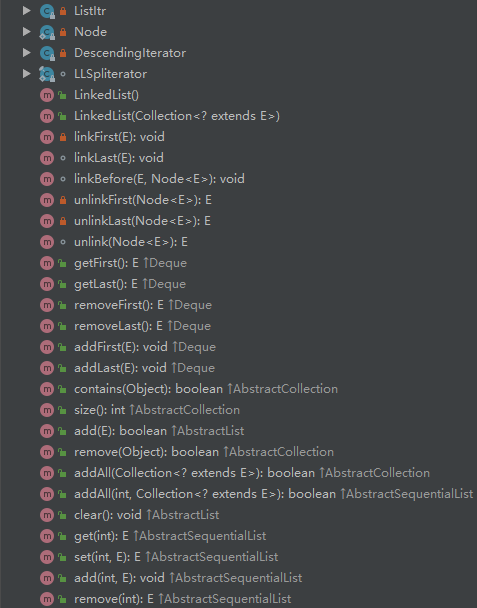
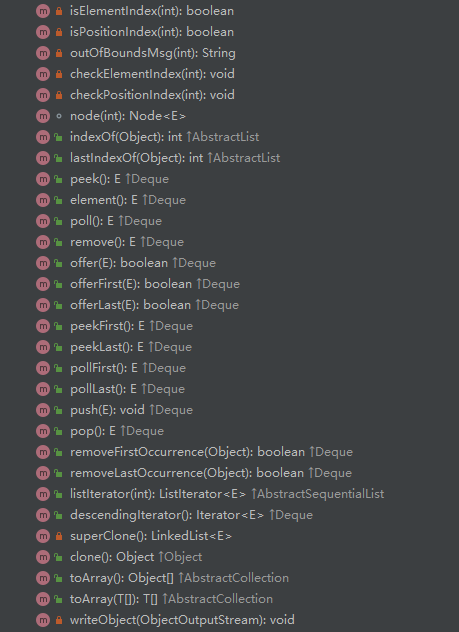
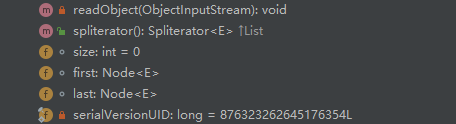
实现
基于双向链表实现。
插入时间复杂度 O(1)
查找时间复杂度 O(n)
删除时间复杂度 O(1)
修改时间复杂度 O(n)
链表不存在扩容的问题。
静态参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> first;
链表的第一个,不能被序列化
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> last;
链表的最后一个,不能被序列化
节点参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
private static class Node<E> {
//数据
E item;
//下一个节点
Node<E> next;
//上一个节点
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
add方法
public boolean add(E e)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
//插入到链表的尾端
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
public void add(int index, E element)
将 e 添加到指定位置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any
* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
//先判断是否会越界
checkPositionIndex(index);
//刚好是最后一个
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
get方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
for 循环遍历下标,找到对应的节点,根据下标的大小判断是从头遍历还是从尾部遍历
/**
* Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.
*/
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isEle 大专栏 理解 LinkedListmentIndex(index);
从头遍历
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
从尾部遍历
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
remove方法
循环遍历找到对应的节点,然后将上一个节点的next指向该节点的下一个节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If this list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* {@code i} such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>
* (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
序列化
LinkedList 和 ArrayList 一样,不能通过一般方式的序列化
序列化writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
/**
* Saves the state of this {@code LinkedList} instance to a stream
* (that is, serializes it).
*
* @serialData The size of the list (the number of elements it
* contains) is emitted (int), followed by all of its
* elements (each an Object) in the proper order.
*/
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out size
s.writeInt(size);
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
s.writeObject(x.item);
}
反序列化readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
/**
* Reconstitutes this {@code LinkedList} instance from a stream
* (that is, deserializes it).
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in size
int size = s.readInt();
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
linkLast((E)s.readObject());
}
其他
LinkedList 和 ArrayList 一样,都不是线程安全的数据结构。
理解 LinkedList的更多相关文章
- 理解ArrayList与LinkedList的区别
一.先来看看ArrayList与LinkedList 在JDK中所在的位置 从图中可以看出,ArrayList与LinkedList都是List接口的实现类,因此都实现了List的所有未实现的方法,只 ...
- 深入理解ArrayList与LinkedList的区别
一.先来看看ArrayList与LinkedList 在JDK中所在的位置 从图中可以看出,ArrayList与LinkedList都是List接口的实现类,因此都实现了List的所有未实现的方法,只 ...
- 理解java容器底层原理--手动实现LinkedList
Node java 中的 LIinkedList 的数据结构是链表,而链表中每一个元素是节点. 我们先定义一下节点: package com.xzlf.collection; public class ...
- 容器--LinkedList
一.前言 上一篇我们介绍了List的重要实现之一ArrayList, 在大多数情况下,我们写代码时会直接使用到ArrayList,因为其在随机访问的优势是其它List无法比拟的.除了ArrayLis ...
- LinkedList源码分析
LinkedList也和ArrayList一样实现了List接口,但是它执行插入和删除操作时比ArrayList更加高效,因为它是基于链表的.基于链表也决定了它在随机访问方面要比ArrayList逊色 ...
- Java 集合深入理解(8):AbstractSequentialList
点击查看 Java 集合框架深入理解 系列, - ( ゜- ゜)つロ 乾杯~ 今天有点无聊,来学学 AbstractSequentialList 解解闷 吧! AbstractSequentialLi ...
- LinkedList源码浅析(jdk1.8)
LinkedList由双向链表实现的集合,因此可以从头或尾部双向循环遍历. LinkedList的操作都是对双向链表的操作,理解双向链表的数据结构就很容易理解LinkedList的实现. 双向链表由带 ...
- LinkedList 源码分析(JDK 1.8)
1.概述 LinkedList 是 Java 集合框架中一个重要的实现,其底层采用的双向链表结构.和 ArrayList 一样,LinkedList 也支持空值和重复值.由于 LinkedList 基 ...
- Java集合框架之二:LinkedList源码解析
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请注明出处,欢迎交流学习! LinkedList底层是通过双向循环链表来实现的,其结构如下图所示: 链表的组成元素我们称之为节点,节点由三部分组成:前一个节点的引用地 ...
随机推荐
- JS控制 input 输入字符限制全搜集
ENTER键可以让光标移到下一个输入框 <input onkeydown="if(event.keyCode==13)event.keyCode=9" > 只能是中文 ...
- 关于tomcat启动错误:At least one JAR was scanned for TLDs yet contained no TLDs
一.问题原因: 1.出现这个问题的原因就是Tomcat启动时会扫描大量jar包,如果含有不符合TLD规范的就会出现这个问题 2.以后基本上不会使用JSP作为视图层,所以我们可能根本不需要TLD这个东西 ...
- ZJNU 1138 - 小兔的棋盘——中级
二维图的动态规划因为不能穿越对角线,则选取对角线的一边dp即可选取对角线右下侧则x轴上每个点只能由其左侧的点走过去(只有1条)对角线上的点只能由对角线下方的点走过去其他点可以由左侧和下侧两种方式到达因 ...
- linux操作提示:“Can't open file for writing”或“operation not permitted”的解决办法
在linux上使用vi命令修改一个文件内容的时候,发现无法保存,每次写完使用":q!"命令可以正常退出但是使用":wq!"命令保存文件并退出时出现一下信息提示: ...
- python,openpyxl,读写excel文件
import openpyxl as oxl from openpyxl.utils import get_column_letter, column_index_from_string import ...
- bind() 方法
一. 定义和用法 bind() 方法为被选元素添加一个或多个事件处理程序,并规定事件发生时运行的函数. 语法: $(selector).bind(event,data,function) 举例:
- 查看linux系统安装的服务
如何查看linux系统安装了哪些服务呢,因不同版本的操作系统可能使用的命令不一样或者有些命令在某些操作系统不可用,现列举一些常用查看命令(基于我的linux版本). 我的操作系统版本如下: 1.ser ...
- 好久不见,Java设计模式
引子 设计模式是很多程序员总结出来的最佳实践.曾经在刚开始写项目的时候学习过设计模式,在开发过程中,也主动或者被动的使用过.现在写代码虽说不会特意明确在用哪种设计模式,但潜移默化的写出来公认的最佳实践 ...
- QLIKVIEW基础设置及初步了解
改变语言环境 开发工具条勾选出来 创建selection box 创建search box 编辑脚本 重加载数据 基本联动思路:table view tableview load FSUPPLIERI ...
- 学习python-20191217(1)-Python Flask高级编程开发鱼书_第04章_应用、蓝图与视图函数
视频01: flask框架:最上层是app,它就像一个插线板一样,比如可以插入蓝图,还可以插入其他各种flask插件. 每个蓝图又可以插入很多视图函数,并可指定静态文件夹和模板文件夹. 好的代码结构, ...
