「SOL」NOI2016 Day1 解题报告
第一次打 NOI,还是先把以前的 NOI 题刷一遍吧?
# 目录
# A. 优秀的拆分 excellent
> Link 优秀的拆分 - LOJ
如果能对每个位置求出以它开头/结尾的形如 AA 的串的数量,那这个问题就非常简单了。
考虑如何对 AA 串计数。和另外一道题(忘了题目了)非常类似,那道题是回文串,将原串 \(kL\) 的位置设为关键点,任何长度为 \(2L\) 的回文串一定经过两个关键点。这道题则是任何 \(|A|=L\) 的 AA 串都会经过两个关键点。
用 SA 快速处理出两个前缀的 LCS 和两个后缀的 LCP。我们可以判断:
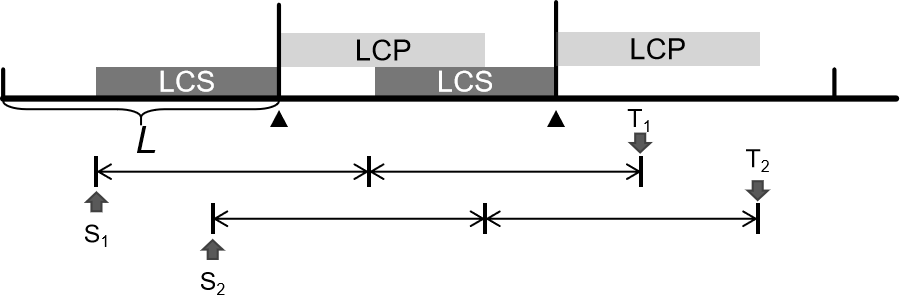
—— 以 \(S_1\) 到 \(S_2\) 这些位置开头存在长度为 \(2L\) 的 AA 串,以 \(T_1\) 到 \(T_2\) 这些位置结尾存在长度为 \(2L\) 的 AA 串。
差分计数即可。
# B. 网格 grid
> Link 网格 - LOJ
看来做的题比较多还是有好处。有一类题要求最小化操作数量,看起来非常复杂,但是通过一些人类智慧可以发现最大答案其实很小,即存在简单的合法构造方案。这样将问题转化为「判断是否存在答案为 \(x\) 的可行解」。
(称“跳蚤”为白格,“蛐蛐”为黑格)
同样的道理,分析这道题。首先不难发现无解的情况只有:
- 只有一个白格;
- 只有两个白格且相邻。
排除这两个情况,剩下的都有解。
可以用至多 \(4\) 次操作把一个白格围起来,因此答案至多为 \(4\)。远远不够,我们还发现可以利用一个极大白格连通块的边角处,一个白格连通块必定存在“角”这种只需要两次操作就可以围起来的格子,因此答案至多为 \(2\)。
换句话说,答案只能是 \(0,1,2\)。
答案是 \(0\) 可以直接判断连通性(关于建图之后再分析),那么就只剩下判断答案是 \(1\) 还是 \(2\)。
直观上感觉 \(2\) 比 \(1\) 难判断,的确如此。答案是 \(1\) 意味着只需要填一个格子就可以把原本的连通块割成多个……这不就是割点吗?
可以暴力建出点、边数量都是 \(\mathcal O(nm)\) 的图通过部分数据。
我们只需要用到这张图的连通性以及可能的割点,显然图中有很多点是可以合并的:
- 合并点不会改变原图连通性;
- 如果两个点都不可能是割点,则可以合并,合并后的点不可能是原图的割点。
什么点可能是割点?必然是在周围(八联通)有一个黑格的白格。因此我们只需要把黑格周围的白格单独建点,其他的按行合并。如图:
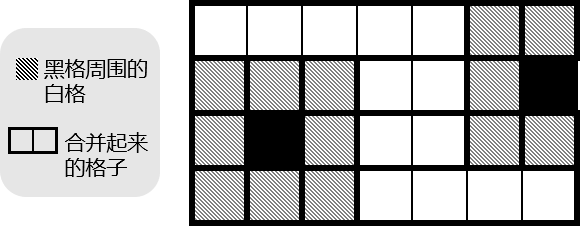
这样点数、边数都与黑格数量同阶,可以用 Tarjan 求割点判断答案,顺便还可以判断连通性。
# C. 循环之美 cyclic
久仰大名
结论
一个数 $A$ 是 $k$ 进制 $L$ 纯循环的充要条件是 $A\times k^L-A$ 是整数。
如果 $A$ 表示成最简分数 $\frac xy$,则上述条件等价于 $y\mid k^L-1$。则 $A$ 是 $k$ 进制纯循环小数当且仅当 $k^L\equiv1\pmod y$ 有 $L\gt 1$ 的解 $L$,运用某些数论知识(忘了,但是我记得住结论 awa)可以得到等价条件为 $k,y$ 互质。
于是我们可以知道答案为:
\]
看着就很莫比乌斯反演,但是我自己做的时候思路错了,不应该直接把两个条件都反演掉(只能做到 \(\mathcal O(n\sigma_0(k))\))……
UPD. 两个条件都反演掉也能做,将 \([(y,k)=1]\) 反演后设 \(t\mid (y,k)\),则 \(y\) 的可取值的数量为 \(\lfloor\tfrac m{\mathrm{lcm}(t,d)}\rfloor\),再对 lcm 进行反演:
\[\begin{aligned}
&\sum_{d=1}^n\mu(d)\lfloor\tfrac nd\rfloor\sum_{d\mid j}^{j\le m}[(j,k)=1]\\
=&\sum_d\mu(d)\lfloor\tfrac nd\rfloor\sum_{d\mid j}\sum_{t\mid k,t\mid j}\mu(t)\\
=&\sum_d\mu(d)\lfloor\tfrac nd\rfloor\sum_{t\mid k}\lfloor\tfrac m{\mathrm{lcm}(t,d)}\rfloor\\
\end{aligned}
\]枚举 \(t,d\) 的 GCD 为 \(p\):
\[\sum_d\mu(d)\lfloor\tfrac nd\rfloor\sum_{t\mid k}\sum_p\lfloor\tfrac {mp}{td}\rfloor\big[(t,d)=p\big]
\]再反演掉,第二行是转为枚举 \(r=qp\):
\[\begin{aligned}
&\sum_d\mu(d)\lfloor\tfrac nd\rfloor\sum_{t\mid k}\sum_p\lfloor\tfrac {mp}{td}\rfloor\sum_{q\mid\frac dp,q\mid\frac tp}\mu(q)\\
=&\sum_d\mu(d)\lfloor\tfrac nd\rfloor\sum_{t\mid k}\sum_{r\mid d,r\mid t}\sum_{p\mid r}\mu(\tfrac rp)\lfloor\tfrac{mp}{td}\rfloor
\end{aligned}
\]整理一下整除的关系:\(p\mid r\to r\mid t\to t\mid k\),还有 \(r\mid d\),简化一下式子,直接枚举 \((p,r,t)\):
\[\begin{aligned}
&\sum_{p\mid r\mid t\mid k}\mu(\tfrac rp)\sum_{r\mid d}^{d\le n}\mu(d)\lfloor\tfrac nd\rfloor\lfloor\tfrac {mp}{td}\rfloor
\end{aligned}
\]后边的那个求和可以写为
\[f(n,m,r)=\sum_{r\mid d}\mu(d)\lfloor\tfrac nd\rfloor\lfloor\tfrac md\rfloor
\]继续推式子:
\[\begin{aligned}
f(n,m,r)&=\sum_{d=1}^{\lfloor n/r\rfloor}\mu(dr)\lfloor\tfrac n{dr}\rfloor\lfloor\tfrac m{dr}\rfloor\\
&=\sum_{d=1}^{\lfloor n/r\rfloor}\mu(d)\mu(r)\big[(r,d)=1\big]\lfloor\tfrac n{dr}\rfloor\lfloor\tfrac m{dr}\rfloor\\
&=\mu(r)\sum_{t=1}^{\lfloor n/r\rfloor}\mu(t)\sum_{t\mid d}^{\lfloor n/r\rfloor}\mu(d)\lfloor\tfrac n{dr}\rfloor\lfloor\tfrac m{dr}\rfloor\\
&=\mu(r)\sum_{t=1}^{\lfloor n/r\rfloor}\mu(t)f(\lfloor \tfrac nr\rfloor,\lfloor \tfrac mr\rfloor, t)
\end{aligned}
\]当 \(r\neq1\) 时可以递归计算,只会递归 \(\mathcal O(\log n)\) 层,当 \(r=1\) 时
\[f(n,m,1)=\sum_{d=1}^n\mu(d)\lfloor\tfrac nd\rfloor\lfloor\tfrac md\rfloor
\]可以数论分块+杜教筛。
还是下面这个做法比较小清新……
直接上正解吧,两个条件中取较简单的一个反演 —— \(k\) 是常数,所以尝试反演 \([(y,k)=1]\):
&\sum_{d\mid k}\mu(d)\sum_{d\mid y}^{y\le m}\sum_{x=1}^n\big[(x,y)=1\big]\\
=&\sum_{d\mid k}\mu(d)\sum_{y=1}^{\lfloor m/d\rfloor}\sum_{x=1}^{n}\big[(x,d)=1\big]\big[(x,y)=1\big]
\end{aligned}
\]
注意到后面的式子和原问题很像,实际上令 \(f(n,m,k)\):
\]
则反演后的结果为:
\]
递归处理 \(d\gt1\) 的情况,直到 \(nm=0\) 答案为 \(0\);对于 \(d=1\) 即 \(k=1\) 直接计算:
\]
直接数论分块+杜教筛。
# 小结
A 题有一定思维难度,不过题目给的部分分比较生艹,\(\mathcal O(n^2)\) 给到了 95pts,如果没有时间想正解拿了 95pts 也差不多了。
B 题纯粹考实现,也就是建图那部分。只要把答案只有 \(-1,0,1,2\) 这一点想到,正解就呼之欲出了,只是看实现问题,预估将会是考场上用时最长的一道题。
C 题的结论可以靠感知(背结论 awa)+暴力验证,我是写了一个 BSGS 来验证了 \(500\) 范围内是正确的,然后就默认结论没有错。不管怎么莫比乌斯反演,至少能够得到一个 \(\mathcal O(n\sigma_0(k))\) 的可以直接暴力算的式子,然后线性筛 \(\le2\times10^7\) 的就可以得到 84pts,应该是比较好的成绩了。说起来,要敢开数组,只要不爆空间,虽然看起来 \(\mathcal O(n\sigma_o(k))\) 跑 \(n=2\times10^7\) 看起来很离谱,但是敢写就能过……
# 源代码
差点忘了
几份代码写的时间间隔比较长,中途还改了码风……
点击展开/折叠 excellent.cpp
/*Lucky_Glass*/
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 30005;
#define con(typ) const typ &
int n, ncas;
int elg2[N], cnts[N], cntt[N];
char str[N];
struct Sa {
int sa[N], rnk[N], nsa[N], nrnk[N], bin[N];
int hgt[N][20];
void clean(con(int) len) {
memset(bin, 0, sizeof bin);
for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++)
rnk[i] = nrnk[i] = 0;
}
void build(char *sstr, con(int) len) {
clean(len);
for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++) bin[sstr[i] - 'a' + 1]++;
for (int i = 1; i <= 26; i++) bin[i] += bin[i - 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++) sa[bin[sstr[i] - 'a' + 1]--] = i;
rnk[sa[1]] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= len; i++) {
rnk[sa[i]] = rnk[sa[i - 1]];
if ( sstr[sa[i]] != sstr[sa[i - 1]]) rnk[sa[i]]++;
}
#define ikey(i) ((i) > len ? 0 : rnk[i])
for (int l = 1; rnk[sa[len]] < len; l <<= 1) {
for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++) bin[rnk[sa[i]]] = i;
for (int i = len; i >= 1; i--)
if ( sa[i] > l )
nsa[bin[rnk[sa[i] - l]]--] = sa[i] - l;
for (int i = len - l + 1; i <= len; i++)
nsa[bin[rnk[i]]--] = i;
nrnk[nsa[1]] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= len; i++) {
nrnk[nsa[i]] = nrnk[nsa[i - 1]];
if ( ikey(nsa[i]) != ikey(nsa[i - 1])
|| ikey(nsa[i] + l) != ikey(nsa[i - 1] + l) )
nrnk[nsa[i]]++;
}
swap(rnk, nrnk), swap(sa, nsa);
}
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= len; i++) {
if ( j ) j--;
while ( rnk[i] < len && sstr[i + j] == sstr[sa[rnk[i] + 1] + j] ) j++;
hgt[rnk[i]][0] = j;
}
// for (int i = 1; i < len; i++)
// printf("%d%c", hgt[i][0], i == len - 1 ? '\n' : ' ');
for (int i = len; i; i--)
for (int j = 1; j < 20; j++)
if ( i + (1 << (j - 1)) <= len )
hgt[i][j] = min(hgt[i][j - 1], hgt[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1]);
else hgt[i][j] = hgt[i][j - 1];
}
int query(con(int) s, con(int) t) {
if ( s > n || t > n ) exit(-1);
int ss = rnk[s], tt = rnk[t];
if ( ss > tt ) swap(ss, tt);
tt--;
int l = elg2[tt - ss + 1];
return min(hgt[ss][l], hgt[tt - (1 << l) + 1][l]);
}
} tol, tor;
void init() {
elg2[1] = 0;
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++)
elg2[i] = elg2[i >> 1] + 1;
}
int matchR(con(int) s, con(int) t) {
if ( s > n || t > n ) return 0;
return tor.query(s, t);
}
int matchL(con(int) s, con(int) t) {
return tol.query(n - s + 1, n - t + 1);
}
int main() {
// freopen("input.in", "r", stdin);
init();
scanf("%d", &ncas);
while ( ncas-- ) {
scanf("%s", str + 1);
n = (int) strlen(str + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cntt[i] = cnts[i] = 0;
tor.build(str, n);
reverse(str + 1, str + 1 + n);
tol.build(str, n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = i; j + i <= n; j += i) {
int pl = matchL(j, j + i), pr = matchR(j + 1, j + i + 1);
pl = min(pl, i), pr = min(pr, i - 1);
int tmp = pr + pl - i + 1;
if ( tmp > 0 ) {
// printf("%d: start at [%d, %d]\n", i, i - pl + 1, i - pl + tmp);
// printf("%d: end at [%d, %d]\n", i, i - pl + 2 * i, i - pl - 1 + tmp + 2 * i);
cnts[j - pl + 1]++, cnts[j - pl + 1 + tmp]--;
cntt[j - pl + 2 * i]++, cntt[j - pl + tmp + 2 * i]--;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cnts[i] += cnts[i - 1], cntt[i] += cntt[i - 1];
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// printf("start at %d = %d\n", i, cnts[i]);
long long ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
ans += 1ll * cnts[i + 1] * cntt[i];
printf("%lld\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
点击展开/折叠 grid.cpp
/*Lucky_Glass*/
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int DIR[9][2] = {
{-1, -1}, {-1, 0}, {-1, 1},
{0, -1}, {0, 0}, {0, 1},
{1, -1}, {1, 0}, {1, 1}
};
inline int rin(int &r) {
int b = 1, c = getchar(); r = 0;
while ( c < '0' || '9' < c ) b = c == '-' ? -1 : b, c = getchar();
while ( '0' <= c && c <= '9' ) r = (r * 10) + (c ^ '0'), c = getchar();
return r *= b;
}
const int N = 1e5 + 10, NP = N * 20, NE = N * 80;
#define con(typ) const typ &
struct Graph {
int head[NP], to[NE], nxt[NE], ncnt, np;
void addEdge(con(int) u, con(int) v) {
int p = ++ncnt, q = ++ncnt;
to[p] = v, nxt[p] = head[u], head[u] = p;
to[q] = u, nxt[q] = head[v], head[v] = q;
}
inline int operator [] (con(int) u) const {return head[u];}
} gr;
struct SPNode {
int x, y, tag;
bool operator < (con(SPNode) p) const {
if ( x == p.x ) return y < p.y;
return x < p.x;
}
} nod[N * 9];
bool isans1;
int ncas, n, m, nc, nnod, itmp, ndfn;
int dfn[NP], low[NP];
bool ptag[NP];
int tmp[2][NP][3], ntmp[2];
pair<int, int> pos[N];
void dfs(con(int) u) {
bool iscut = false;
int cntson = 0;
dfn[u] = low[u] = ++ndfn;
for (int it = gr[u]; it; it = gr.nxt[it]) {
int v = gr.to[it];
if ( dfn[v] ) low[u] = min(low[u], dfn[v]);
else {
cntson++;
dfs(v);
low[u] = min(low[u], low[v]);
if ( low[v] >= dfn[u] )
if ( ptag[u] )
iscut = true;
}
}
if ( iscut )
isans1 |= (u != 1 || cntson > 1);
}
void newTemp() {itmp ^= 1, ntmp[itmp] = 0;}
void setTemp(con(int) l, con(int) r, con(bool) tag) {
int p = ++gr.np;
if ( p >= NP ) exit(0);
dfn[p] = 0, gr.head[p] = 0;
ptag[p] = tag;
tmp[itmp][++ntmp[itmp]][0] = l, tmp[itmp][ntmp[itmp]][1] = r;
tmp[itmp][ntmp[itmp]][2] = p;
}
void arrangeTemp() {
for (int i = 1; i < ntmp[itmp]; i++)
if ( tmp[itmp][i][1] + 1 == tmp[itmp][i + 1][0] )
gr.addEdge(tmp[itmp][i][2], tmp[itmp][i + 1][2]);
if ( !ntmp[0] || !ntmp[1] ) return;
for (int i = 1, jl = 1, jr = 0; i <= ntmp[0]; i++) {
while ( jr < ntmp[1] && tmp[1][jr + 1][0] <= tmp[0][i][1] ) jr++;
while ( jl <= jr && tmp[1][jl][1] < tmp[0][i][0] ) jl++;
for (int j = jl; j <= jr; j++)
gr.addEdge(tmp[0][i][2], tmp[1][j][2]);
}
}
bool bf[N];
bool isNeg() {
if ( 1ll * n * m - nc > 2 ) return false;
if ( 1ll * n * m - nc <= 1 ) return true;
#define id(x, y) ((x) * m - m + (y))
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
bf[id(i, j)] = false;
for (int i = 1; i <= nc; i++)
bf[id(pos[i].first, pos[i].second)] = true;
const int DIR[4][2] = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
if ( !bf[id(i, j)] )
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int x = i + DIR[k][0], y = j + DIR[k][1];
if ( 1 <= x && x <= n && 1 <= y && y <= m && !bf[id(x, y)] )
return true;
}
return false;
#undef id
}
int main() {
rin(ncas);
while ( ncas-- ) {
ndfn = nnod = 0;
gr.np = gr.ncnt = 0;
itmp = 0;
isans1 = false;
//
rin(n), rin(m), rin(nc);
for (int i = 1; i <= nc; i++)
rin(pos[i].first), rin(pos[i].second);
if ( isNeg() ) {printf("-1\n"); continue;}
sort(pos + 1, pos + 1 + nc);
if ( m == 1 ) {
int cnti = 0;
if ( nc ) {
if ( pos[1].first > 1 ) cnti++;
for (int i = 2; i <= nc; i++)
if ( pos[i - 1].first + 1 <= pos[i].first - 1 )
cnti++;
if ( pos[nc].first < n ) cnti++;
} else cnti = 1;
if ( cnti > 1 ) printf("0\n");
else printf("1\n");
continue;
}
if ( n == 1 ) {
int cnti = 0;
if ( nc ) {
if ( pos[1].second > 1 ) cnti++;
for (int i = 2; i <= nc; i++)
if ( pos[i - 1].second + 1 <= pos[i].second - 1 )
cnti++;
if ( pos[nc].second < m ) cnti++;
} else cnti = 1;
if ( cnti > 1 ) printf("0\n");
else printf("1\n");
continue;
}
for (int i = 1, p, q; i <= nc; i++) {
p = pos[i].first, q = pos[i].second;
for (int k = 0; k < 9; k++) {
int x = p + DIR[k][0], y = q + DIR[k][1];
if ( 1 <= x && x <= n && 1 <= y && y <= m ) {
// cerr << "build " << x << ' ' << y << endl;
nod[++nnod].x = x, nod[nnod].y = y, nod[nnod].tag = k == 4;
}
}
}
//
sort(nod + 1, nod + 1 + nnod);
ntmp[0] = ntmp[1] = 0;
if ( nod[1].x > 1 ) newTemp(), setTemp(1, m, false);
int lasl = nod[1].x - 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= nnod; i++) {
if ( lasl < nod[i].x - 1 ) {
newTemp(), setTemp(1, m, false);
arrangeTemp();
}
newTemp();
if ( nod[i].y > 1 ) setTemp(1, nod[i].y - 1, false);
int toi = i; while ( toi < nnod && nod[toi + 1].x == nod[i].x ) toi++;
for (int j = i; j <= toi; j++) {
int toj = j; bool itag = nod[j].tag;
while ( toj < toi && nod[toj + 1].y == nod[j].y )
itag |= nod[++toj].tag;
if ( !itag) setTemp(nod[j].y, nod[j].y, true);
if ( toj < toi && nod[j].y + 1 < nod[toj + 1].y )
setTemp(nod[j].y + 1, nod[toj + 1].y - 1, false);
j = toj;
}
if ( nod[toi].y < m ) setTemp(nod[toi].y + 1, m, false);
arrangeTemp();
lasl = nod[i].x, i = toi;
}
if ( lasl < n ) {
newTemp(), setTemp(1, m, false);
arrangeTemp();
}
dfs(1);
if ( ndfn < gr.np ) printf("0\n");
else if ( isans1 ) printf("1\n");
else printf("2\n");
}
return 0;
}
点击展开/折叠 cyclic.cpp
/*Lucky_Glass*/
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
typedef long long llong;
#define con(typ) const typ &
const int M = 1e6 + 10, HMOD = 1000793;
int dv[200], prm[M], mu[M], summu[M];
bool bok[M];
int ndv, nprm;
struct HashTable {
int head[HMOD], nxt[M << 1], val[M << 1], key[M << 1];
int ncnt;
int& operator [] (con(int) _key) {
for (int it = head[_key % HMOD]; it; it = nxt[it])
if ( key[it] == _key )
return val[it];
int p = ++ncnt;
key[p] = _key, nxt[p] = head[_key % HMOD], head[_key % HMOD] = p;
return val[p] = 2e9;
}
} htab;
void init(con(int) vk) {
mu[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < M; ++i) {
if ( !bok[i] ) mu[i] = -1, prm[++nprm] = i;
for (int j = 1; j <= nprm && 1ll * prm[j] * i < M; ++j) {
bok[i * prm[j]] = true;
if ( i % prm[j] == 0 ) break;
mu[i * prm[j]] = -mu[i];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < M; ++i) summu[i] = summu[i - 1] + mu[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= vk; ++i)
if ( vk % i == 0 && mu[i] )
dv[++ndv] = i;
}
int funSum(con(int) n) {
if ( n < M ) return summu[n];
int &ret = htab[n];
if ( ret != 2e9 ) return ret;
llong tmp = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
int ii = n / (n / i);
tmp -= (ii - i + 1ll) * funSum(n / i);
i = ii;
}
return ret = (int)tmp;
}
llong fun(con(int) n, con(int) m, con(int) vk) {
if ( !n || !m ) return 0ll;
llong ret = 0;
if ( vk == 1 ) {
int las = 0;
for (int i = 1, li = std::min(n, m); i <= li; ++i) {
int ii = std::min(n / (n / i), m / (m / i)), tmp = funSum(ii);
ret += 1ll * (n / i) * (m / i) * (tmp - las);
las = tmp;
i = ii;
}
return ret;
}
if ( vk < ndv ) {
for (int i = 1; i <= vk; ++i)
if ( vk % i == 0 && mu[i] )
ret += mu[i] * fun(m / i, n, i);
} else {
for (int i = 1; i <= ndv; ++i)
if ( vk % dv[i] == 0 )
ret += mu[dv[i]] * fun(m / dv[i], n, dv[i]);
}
return ret;
}
int main() {
int n, m, vk;
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &vk);
init(vk);
printf("%lld\n", fun(n, m, vk));
return 0;
}
THE END
Thanks for reading!
「SOL」NOI2016 Day1 解题报告的更多相关文章
- 「FJOI2016」神秘数 解题报告
「FJOI2016」神秘数 这题不sb,我挺sb的... 我连不带区间的都不会哇 考虑给你一个整数集,如何求这个神秘数 这有点像一个01背包,复杂度和值域有关.但是你发现01背包可以求出更多的东西,就 ...
- 「ZJOI2016」大森林 解题报告
「ZJOI2016」大森林 神仙题... 很显然线段树搞不了 考虑离线操作 我们只搞一颗树,从位置1一直往后移动,然后维护它的形态试试 显然操作0,1都可以拆成差分的形式,就是加入和删除 因为保证了操 ...
- 「SCOI2016」背单词 解题报告
「SCOI2016」背单词 出题人sb 题意有毒 大概是告诉你,你给一堆n个单词安排顺序 如果当前位置为x 当前单词的后缀没在这堆单词出现过,代价x 这里的后缀是原意,但不算自己,举个例子比如abc的 ...
- 「NOI2015」寿司晚宴 解题报告
「NOI2015」寿司晚宴 这个题思路其实挺自然的,但是我太傻了...最开始想着钦定一些,结果发现假了.. 首先一个比较套路的事情是状压前8个质数,后面的只会在一个数出现一次的再想办法就好. 然后发现 ...
- 「SCOI2015」国旗计划 解题报告
「SCOI2015」国旗计划 蛮有趣的一个题 注意到区间互不交错,那么如果我们已经钦定了一个区间,它选择的下一个区间是唯一的,就是和它有交且右端点在最右边的,这个可以单调队列预处理一下 然后往后面跳拿 ...
- 「JLOI2015」骗我呢 解题报告?
「JLOI2015」骗我呢 这什么神仙题 \[\color{purple}{Link}\] 可以学到的东西 对越过直线的东西翻折进行容斥 之类的..吧? Code: #include <cstd ...
- 「JLOI2015」城池攻占 解题报告
「JLOI2015」城池攻占 注意到任意两个人的战斗力相对大小的不变的 可以离线的把所有人赛到初始点的堆里 然后做启发式合并就可以了 Code: #include <cstdio> #in ...
- 「JLOI2015」管道连接 解题报告
「JLOI2015」管道连接 先按照斯坦纳树求一个 然后合并成斯坦纳森林 直接枚举树的集合再dp一下就好了 Code: #include <cstdio> #include <cct ...
- 「JLOI2015」战争调度 解题报告
「JLOI2015」战争调度 感觉一到晚上大脑就宕机了... 题目本身不难,就算没接触过想想也是可以想到的 这个满二叉树的深度很浅啊,每个点只会和它的\(n-1\)个祖先匹配啊 于是可以暴力枚举祖先链 ...
- 「SHOI2014」三叉神经树 解题报告
「SHOI2014」三叉神经树 膜拜神仙思路 我们想做一个类似于动态dp的东西,首先得确保我们的运算有一个交换律,这样我们可以把一长串的运算转换成一块一块的放到矩阵上之类的东西,然后拿数据结构维护. ...
随机推荐
- [Swift] SwiftUI布局的一些写法基础(用Swift构造UI布局)
这个文档是在你 完全熟悉 Objective-C 上用代码构造UI的前提下写的 官方教程:https://developer.apple.com/tutorials/swiftui/creating- ...
- [746] Interlude Update 3
[746] Interlude Update 3 Client 00 SendProtocolVersion 01 MoveBackwardToLocation 02 Say 03 RequestEn ...
- 「SOL」行列式 (模拟赛)
1. 题面 有一个大小为 \(n\) (\(n\le10^6\))的方阵 \(A\),给定 \(d_1,d_2,d_3,\dots,d_n\),\((p_2,b_2,c_2),(p_3,b_3,c_3 ...
- JWT 工具类的编写
导入JWT pom依赖 <!--JWT 依赖--><dependency> <groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId> < ...
- 用 go 实现多线程下载器
本篇文章我们用Go实现一个简单的多线程下载器. 1.多线程下载原理 通过判断下载文件链接返回头信息中的 Accept-Ranges 字段,如果为 bytes 则表示支持断点续传. 然后在请求头中设置 ...
- transform2d转换、transition过渡、animation动画效果、@keyframes定义动画关键帧
transform:translate( 0 , 0 ); -ms-transform:translate( 0 , 0 ); /* IE 9 */ -webkit-transform:transla ...
- QueryDet: Cascaded Sparse Query for Accelerating High-Resolution Small Object Detection(QueryDet:用于加速高分辨率小目标检测的级联稀疏查询)
QueryDet: Cascaded Sparse Query for Accelerating High-Resolution Small Object Detection(QueryDet:用于加 ...
- CToolsDetachBehaviors
CTools dispatches the event "CToolsDetachBehaviors" when the modal gets closed. Careful th ...
- BigDecimal精度等注意事项
1.BigDecimal运算时尽量传入字符串, 反例: BigDecimal num=new BigDecimal(75); num.multiply(new BigDecimal(0.5)).set ...
- 【OBS Studio】使用 VLC 视频源播放视频报错:Unhandled exception: c0000005
使用 OBS Studio 和 VLC media player 可以实现视频播放列表的推流,参考『OBS如何添加播放列表?』. 但是使用过程中发现使用 VLC 视频源播放视频时,一个视频播放完切换下 ...
