Android 自定义 View 详解
View 的绘制系列文章:
Android View 绘制流程之 DecorView 与 ViewRootImpl
Android View 的绘制流程之 Measure 过程详解 (一)
Android View 的绘制流程之 Layout 和 Draw 过程详解 (二)
Android View 的事件分发原理解析
对于 Android 开发者来说,原生控件往往无法满足要求,需要开发者自定义一些控件,因此,需要去了解自定义 view 的实现原理。这样即使碰到需要自定义控件的时候,也可以游刃有余。
基础知识
自定义 View 分类
自定义 View 的实现方式有以下几种:
| 类型 | 定义 |
| 自定义组合控件 | 多个控件组合成为一个新的控件,方便多处复用 |
| 继承系统 View 控件 | 继承自TextView等系统控件,在系统控件的基础功能上进行扩展 |
| 继承 View | 不复用系统控件逻辑,继承View进行功能定义 |
| 继承系统 ViewGroup | 继承自LinearLayout等系统控件,在系统控件的基础功能上进行扩展 |
| 继承 View ViewGroup | 不复用系统控件逻辑,继承ViewGroup进行功能定义 |
从上到下越来越难,需要的了解的知识也是越来越多的。
构造函数
当我们在自定义 View 的时候,构造函数都是不可缺少,需要对构造函数进行重写,构造函数有多个,至少要重写其中一个才行。例如我们新建 MyTextView:
public class MyTextView extends View {
/**
* 在java代码里new的时候会用到
* @param context
*/
public MyTextView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
/**
* 在xml布局文件中使用时自动调用
* @param context
*/
public MyTextView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
/**
* 不会自动调用,如果有默认style时,在第二个构造函数中调用
* @param context
* @param attrs
* @param defStyleAttr
*/
public MyTextView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
/**
* 只有在API版本>21时才会用到
* 不会自动调用,如果有默认style时,在第二个构造函数中调用
* @param context
* @param attrs
* @param defStyleAttr
* @param defStyleRes
*/
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP)
public MyTextView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
}
对于每一种构造函数的作用,都已经再代码里面写出来了。
自定义属性
写过布局的同学都知道,系统控件的属性在 xml 中都是以 android 开头的。对于自定义 View,也可以自定义属性,在 xml 中使用。
Android 自定义属性可分为以下几步:
自定义一个 View
编写 values/attrs.xml,在其中编写 styleable 和 item 等标签元素
在布局文件中 View 使用自定义的属性(注意 namespace)
在 View 的构造方法中通过 TypedArray 获取
e.g 还是以上面的 MyTextView 做演示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity"> <com.example.myapplication.MyTextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
app:testAttr="520"
app:text="helloWorld" /> </android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
然后我在 values/attrs.xml 中添加自定义属性:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="test">
<attr name="text" format="string" />
<attr name="testAttr" format="integer" />
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
记得在构造函数里面说过,xml 布局会调用第二个构造函数,因此在这个构造函数里面获取属性和解析:
/**
* 在xml布局文件中使用时自动调用
* @param context
*/
public MyTextView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
TypedArray ta = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.test);
int textAttr = ta.getInteger(R.styleable.test_testAttr, -1);
String text = ta.getString(R.styleable.test_text);
Log.d(TAG, " text = " + text + ", textAttr = " + textAttr);
// toast 显示获取的属性值
Toast.makeText(context, text + " " + textAttr, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
ta.recycle();
}
注意当你在引用自定义属性的时候,记得加上 name 前缀,否则会引用不到。
这里本想截图 log 的,奈何就是不显示,就搞成 toast 了。
当然,你还可以自定义很多其他属性,包括 color, string, integer, boolean, flag,甚至是混合等。
自定义组合控件
自定义组合控件就是将多个控件组合成为一个新的控件,主要解决多次重复使用同一类型的布局。如我们顶部的 HeaderView 以及 dailog 等,我们都可以把他们组合成一个新的控件。
我们通过一个自定义 MyView1 实例来了解自定义组合控件的用法。
xml 布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <TextView
android:id="@+id/feed_item_com_cont_title"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ellipsize="end"
android:includeFontPadding="false"
android:maxLines="2"
android:text="title" /> <TextView
android:id="@+id/feed_item_com_cont_desc"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/feed_item_com_cont_title"
android:ellipsize="end"
android:includeFontPadding="false"
android:maxLines="2"
android:text="desc" /> </merge>
自定义 View 代码 :
package com.example.myapplication; import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.RelativeLayout;
import android.widget.TextView; public class MyView1 extends RelativeLayout { /** 标题 */
private TextView mTitle;
/** 描述 */
private TextView mDesc; public MyView1(Context context) {
this(context, null);
} public MyView1(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
} public MyView1(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
initView(context);
} /**
* 初使化界面视图
*
* @param context 上下文环境
*/
protected void initView(Context context) {
View rootView = LayoutInflater.from(getContext()).inflate(R.layout.my_view1, this); mDesc = rootView.findViewById(R.id.feed_item_com_cont_desc);
mTitle = rootView.findViewById(R.id.feed_item_com_cont_title);
}
}
在布局当中引用该控件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity"> <TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:clickable="true"
android:enabled="false"
android:focusable="true"
android:text="trsfnjsfksjfnjsdfjksdhfjksdjkfhdsfsdddddddddddddddddddddddddd" /> <com.example.myapplication.MyTextView
android:id="@+id/myview"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:clickable="true"
android:enabled="false"
android:focusable="true"
app:testAttr="520"
app:text="helloWorld" /> <com.example.myapplication.MyView1
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </LinearLayout>
最终效果如下图所示 :

继承系统控件
继承系统的控件可以分为继承 View子类(如 TextView 等)和继承 ViewGroup 子类(如 LinearLayout 等),根据业务需求的不同,实现的方式也会有比较大的差异。这里介绍一个比较简单的,继承自View的实现方式。
业务需求:为文字设置背景,并在布局中间添加一条横线。
因为这种实现方式会复用系统的逻辑,大多数情况下我们希望复用系统的 onMeaseur 和 onLayout 流程,所以我们只需要重写 onDraw 方法 。实现非常简单,话不多说,直接上代码。
package com.example.myapplication; import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.LinearGradient;
import android.graphics.Shader;
import android.text.TextPaint;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.widget.TextView; import static android.support.v4.content.ContextCompat.getColor; /**
* 包含分割线的textView
* 文字左右两边有一条渐变的分割线
* 样式如下:
* ———————— 文字 ————————
*/
public class DividingLineTextView extends TextView {
/** 线性渐变 */
private LinearGradient mLinearGradient;
/** textPaint */
private TextPaint mPaint;
/** 文字 */
private String mText = "";
/** 屏幕宽度 */
private int mScreenWidth;
/** 开始颜色 */
private int mStartColor;
/** 结束颜色 */
private int mEndColor;
/** 字体大小 */
private int mTextSize; /**
* 构造函数
*/
public DividingLineTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
mTextSize = getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.text_size);
mScreenWidth = getCalculateWidth(getContext());
mStartColor = getColor(getContext(), R.color.colorAccent);
mEndColor = getColor(getContext(), R.color.colorPrimary);
mLinearGradient = new LinearGradient(0, 0, mScreenWidth, 0,
new int[]{mStartColor, mEndColor, mStartColor},
new float[]{0, 0.5f, 1f},
Shader.TileMode.CLAMP);
mPaint = new TextPaint();
} public DividingLineTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
} public DividingLineTextView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
} @Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint.setTextSize(mTextSize);
int len = getTextLength(mText, mPaint);
// 文字绘制起始坐标
int sx = mScreenWidth / 2 - len / 2;
// 文字绘制结束坐标
int ex = mScreenWidth / 2 + len / 2;
int height = getMeasuredHeight();
mPaint.setShader(mLinearGradient);
// 绘制左边分界线,从左边开始:左边距15dp, 右边距距离文字15dp
canvas.drawLine(mTextSize, height / 2, sx - mTextSize, height / 2, mPaint);
mPaint.setShader(mLinearGradient);
// 绘制右边分界线,从文字右边开始:左边距距离文字15dp,右边距15dp
canvas.drawLine(ex + mTextSize, height / 2,
mScreenWidth - mTextSize, height / 2, mPaint);
} /**
* 返回指定文字的宽度,单位px
*
* @param str 要测量的文字
* @param paint 绘制此文字的画笔
* @return 返回文字的宽度,单位px
*/
private int getTextLength(String str, TextPaint paint) {
return (int) paint.measureText(str);
} /**
* 更新文字
*
* @param text 文字
*/
public void update(String text) {
mText = text;
setText(mText);
// 刷新重绘
requestLayout();
} /**
* 获取需要计算的宽度,取屏幕高宽较小值,
*
* @param context context
* @return 屏幕宽度值
*/
public static int getCalculateWidth(Context context) {
int height = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().heightPixels;
// 动态屏幕宽度,在折叠屏手机上宽度在分屏时会发生变化
int Width = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().widthPixels; return Math.min(Width, height);
}
}
对于 View 的绘制还需要对 Paint()、canvas 以及 Path 的使用有所了解,不清楚的可以稍微了解一下。
看下布局里面的引用:
xml 布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity"> // ...... 跟前面一样忽视
<com.example.myapplication.DividingLineTextView
android:id="@+id/divide"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center" /> </LinearLayout>
activty 里面代码如下 :
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
DividingLineTextView te = findViewById(R.id.divide);
te.update("DividingLineTextView");
}
这里通过 update() 对来重新绘制,确保边线在文字的两边。视觉效果如下:
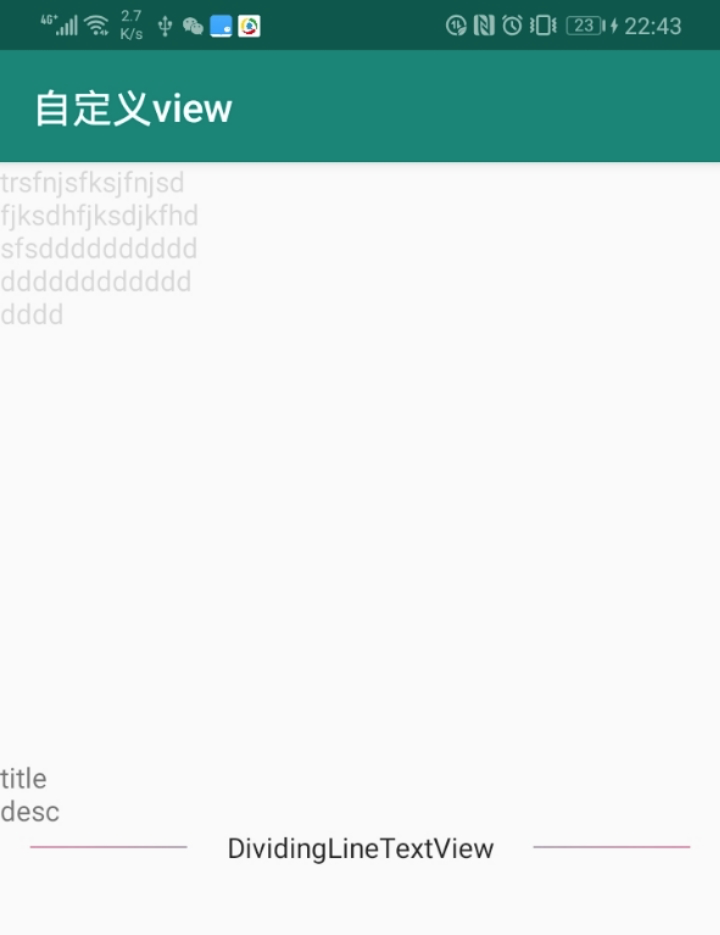
直接继承View
直接继承 View 会比上一种实现方复杂一些,这种方法的使用情景下,完全不需要复用系统控件的逻辑,除了要重写 onDraw 外还需要对 onMeasure 方法进行重写。
我们用自定义 View 来绘制一个正方形。
首先定义构造方法,以及做一些初始化操作
ublic class RectView extends View{
//定义画笔
private Paint mPaint = new Paint();
/**
* 实现构造方法
* @param context
*/
public RectView(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public RectView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public RectView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
private void init() {
mPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
}
}
重写 draw 方法,绘制正方形,注意对 padding 属性进行设置:
/**
* 重写draw方法
* @param canvas
*/
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
//获取各个编剧的padding值
int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft();
int paddingRight = getPaddingRight();
int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();
int paddingBottom = getPaddingBottom();
//获取绘制的View的宽度
int width = getWidth()-paddingLeft-paddingRight;
//获取绘制的View的高度
int height = getHeight()-paddingTop-paddingBottom;
//绘制View,左上角坐标(0+paddingLeft,0+paddingTop),右下角坐标(width+paddingLeft,height+paddingTop)
canvas.drawRect(0+paddingLeft,0+paddingTop,width+paddingLeft,height+paddingTop,mPaint);
}
在 View 的源码当中并没有对 AT_MOST 和 EXACTLY 两个模式做出区分,也就是说 View 在 wrap_content 和 match_parent 两个模式下是完全相同的,都会是 match_parent,显然这与我们平时用的 View 不同,所以我们要重写 onMeasure 方法。
/**
* 重写onMeasure方法
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec
* @param heightMeasureSpec
*/
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); //处理wrap_contentde情况
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(300, 300);
} else if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(300, heightSize);
} else if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, 300);
}
}
最终效果如图所示:
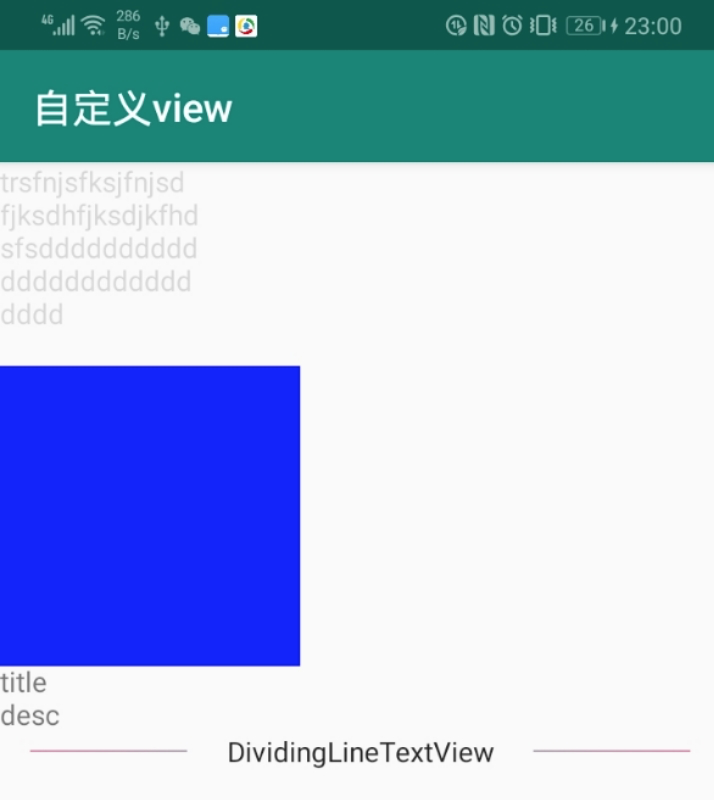
可以发现,我们设置的是 wrap_content,但是最后还是有尺寸的。
整个过程大致如下,直接继承 View 时需要有几点注意:
在 onDraw 当中对 padding 属性进行处理。
在 onMeasure 过程中对 wrap_content 属性进行处理。
至少要有一个构造方法。
继承ViewGroup
自定义 ViewGroup 的过程相对复杂一些,因为除了要对自身的大小和位置进行测量之外,还需要对子 View 的测量参数负责。
需求实例
实现一个类似于 Viewpager 的可左右滑动的布局。
布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<com.example.myapplication.MyHorizonView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/colorAccent"
android:layout_height="400dp"> <ListView
android:id="@+id/list1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/colorAccent" /> <ListView
android:id="@+id/list2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary" /> <ListView
android:id="@+id/list3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/colorPrimaryDark" /> </com.example.myapplication.MyHorizonView> <TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:clickable="true"
android:focusable="true"
android:text="trsfnjsfksjfnjsdfjksdhfjksdjkfhdsfsdddddddddddddddddddddddddd" /> <com.example.myapplication.MyTextView
android:id="@+id/myview"
android:layout_width="1dp"
android:layout_height="2dp"
android:clickable="true"
android:enabled="false"
android:focusable="true"
app:testAttr="520"
app:text="helloWorld" /> <com.example.myapplication.RectView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <com.example.myapplication.MyView1
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <com.example.myapplication.DividingLineTextView
android:id="@+id/divide"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center" /> </LinearLayout>
一个 ViewGroup 里面放入 3 个 ListView,注意 ViewGroup 设置的宽是 wrap_conten,在测量的时候,会对 wrap_content 设置成与父 View 的大小一致,具体实现逻辑可看后面的代码。
代码比较多,我们结合注释分析。
public class MyHorizonView extends ViewGroup {
private static final String TAG = "HorizontaiView";
private List<View> mMatchedChildrenList = new ArrayList<>();
public MyHorizonView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyHorizonView(Context context, AttributeSet attributes) {
super(context, attributes);
}
public MyHorizonView(Context context, AttributeSet attributes, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attributes, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childCount = getChildCount();
int left = 0;
View child;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() != View.GONE) {
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
// 因为是水平滑动的,所以以宽度来适配
child.layout(left, 0, left + childWidth, child.getMeasuredHeight());
left += childWidth;
}
}
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
mMatchedChildrenList.clear();
int widthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
// 如果不是确定的的值,说明是 AT_MOST,与父 View 同宽高
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren = heightSpecMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ||
widthSpecMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
int childCount = getChildCount();
View child;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() != View.GONE) {
final LayoutParams layoutParams = child.getLayoutParams();
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
if (measureMatchParentChildren) {
// 需要先计算出父 View 的高度来再来测量子 view
if (layoutParams.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT
|| layoutParams.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
mMatchedChildrenList.add(child);
}
}
}
}
if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
// 如果宽高都是AT_MOST的话,即都是wrap_content布局模式,就用View自己想要的宽高值
setMeasuredDimension(getMeasuredWidth(), getMeasuredHeight());
} else if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
// 如果只有宽度都是AT_MOST的话,即只有宽度是wrap_content布局模式,宽度就用View自己想要的宽度值,高度就用父ViewGroup指定的高度值
setMeasuredDimension(getMeasuredWidth(), heightSpecSize);
} else if (heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
// 如果只有高度都是AT_MOST的话,即只有高度是wrap_content布局模式,高度就用View自己想要的宽度值,宽度就用父ViewGroup指定的高度值
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize, getMeasuredHeight());
}
for (int i = 0; i < mMatchedChildrenList.size(); i++) {
View matchChild = getChildAt(i);
if (matchChild.getVisibility() != View.GONE) {
final LayoutParams layoutParams = matchChild.getLayoutParams();
// 计算子 View 宽的 MeasureSpec
final int childWidthMeasureSpec;
if (layoutParams.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(getMeasuredWidth(), MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec, 0, layoutParams.width);
}
// 计算子 View 高的 MeasureSpec
final int childHeightMeasureSpec;
if (layoutParams.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(getMeasuredHeight(), MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec, 0, layoutParams.height);
}
// 根据 MeasureSpec 计算自己的宽高
matchChild.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
}
这里我们只是重写了两个绘制过程中的重要的方法:onMeasure 和 onLayout 方法。
对于 onMeasure 方法具体逻辑如下:
super.onMeasure 会先计算自定义 view 的大小;
- 调用 measureChild 对 子 View 进行测量;
自定义 view 设置的宽高参数不是 MeasureSpec.EXACTLY 的话,对于子 View 是 match_parent 需要额外处理,同时也需要对 MeasureSpec.AT_MOST 情况进行额外处理。
当自定义View 的大小确定后,在对子 View 是 match_parent 重新测量;
上述的测量过程的代码也是参考 FrameLayout 源码的,具体可以参看文章:
对于 onLayout 方法,因为是水平滑动的,所以要根据宽度来进行layout。
到这里我们的 View 布局就已经基本结束了。但是要实现 Viewpager 的效果,还需要添加对事件的处理。事件的处理流程之前我们有分析过,在制作自定义 View 的时候也是会经常用到的,不了解的可以参考文章 Android Touch事件分发超详细解析。
private void init(Context context) {
mScroller = new Scroller(context);
mTracker = VelocityTracker.obtain();
}
/**
* 因为我们定义的是ViewGroup,从onInterceptTouchEvent开始。
* 重写onInterceptTouchEvent,对横向滑动事件进行拦截
*
* @param event
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
boolean intercepted = false;
int x = (int) event.getX();
int y = (int) event.getY();
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
intercepted = false;//必须不能拦截,否则后续的ACTION_MOME和ACTION_UP事件都会拦截。
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
intercepted = Math.abs(x - mLastX) > Math.abs(y - mLastY);
break;
}
Log.d(TAG, "onInterceptTouchEvent: intercepted " + intercepted);
mLastX = x;
mLastY = y;
return intercepted ? intercepted : super.onInterceptHoverEvent(event);
}
/**
* 当ViewGroup拦截下用户的横向滑动事件以后,后续的Touch事件将交付给`onTouchEvent`进行处理。
* 重写onTouchEvent方法
*/
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
mTracker.addMovement(event);
int x = (int) event.getX();
int y = (int) event.getY();
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
int deltaX = x - mLastX;
Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent: deltaX " + deltaX);
// scrollBy 方法将对我们当前 View 的位置进行偏移
scrollBy(-deltaX, 0);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent: " + getScrollX());
// getScrollX()为在X轴方向发生的便宜,mChildWidth * currentIndex表示当前View在滑动开始之前的X坐标
// distance存储的就是此次滑动的距离
int distance = getScrollX() - mChildWidth * mCurrentIndex;
//当本次滑动距离>View宽度的1/2时,切换View
if (Math.abs(distance) > mChildWidth / 2) {
if (distance > 0) {
mCurrentIndex++;
} else {
mCurrentIndex--;
}
} else {
//获取X轴加速度,units为单位,默认为像素,这里为每秒1000个像素点
mTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000);
float xV = mTracker.getXVelocity();
//当X轴加速度>50时,也就是产生了快速滑动,也会切换View
if (Math.abs(xV) > 50) {
if (xV < 0) {
mCurrentIndex++;
} else {
mCurrentIndex--;
}
}
}
//对currentIndex做出限制其范围为【0,getChildCount() - 1】
mCurrentIndex = mCurrentIndex < 0 ? 0 : mCurrentIndex > getChildCount() - 1 ? getChildCount() - 1 : mCurrentIndex;
//滑动到下一个View
smoothScrollTo(mCurrentIndex * mChildWidth, 0);
mTracker.clear();
break;
}
Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent: ");
mLastX = x;
mLastY = y;
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}
private void smoothScrollTo(int destX, int destY) {
// startScroll方法将产生一系列偏移量,从(getScrollX(), getScrollY()),destX - getScrollX()和destY - getScrollY()为移动的距离
mScroller.startScroll(getScrollX(), getScrollY(), destX - getScrollX(), destY - getScrollY(), 1000);
// invalidate方法会重绘View,也就是调用View的onDraw方法,而onDraw又会调用computeScroll()方法
invalidate();
}
// 重写computeScroll方法
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
super.computeScroll();
// 当scroller.computeScrollOffset()=true时表示滑动没有结束
if (mScroller.computeScrollOffset()) {
// 调用scrollTo方法进行滑动,滑动到scroller当中计算到的滑动位置
scrollTo(mScroller.getCurrX(), mScroller.getCurrY());
// 没有滑动结束,继续刷新View
postInvalidate();
}
}
具体效果如下图所示:

对于 Scroller 的用法总结如下:
调用 Scroller 的 startScroll() 方法来进行一些滚动的初始化设置,然后迫使 View 进行绘制 (调用 View 的 invalidate() 或 postInvalidate() 就可以重新绘制 View);
绘制 View 的时候 drawchild 方法会调用 computeScroll() 方法,重写 computeScroll(),通过 Scroller 的 computeScrollOffset() 方法来判断滚动有没有结束;
scrollTo() 方法虽然会重新绘制 View,但还是要调用下 invalidate() 或者 postInvalidate() 来触发界面重绘,重新绘制 View 又触发 computeScroll();
如此往复进入一个循环阶段,即可达到平滑滚动的效果;
也许有人会问,干嘛还要调用来调用去最后在调用 scrollTo() 方法,还不如直接调用 scrollTo() 方法来实现滚动,其实直接调用是可以,只不过 scrollTo() 是瞬间滚动的,给人的用户体验不太好,所以 Android 提供了 Scroller 类实现平滑滚动的效果。
为了方面大家理解,我画了一个简单的调用示意图:
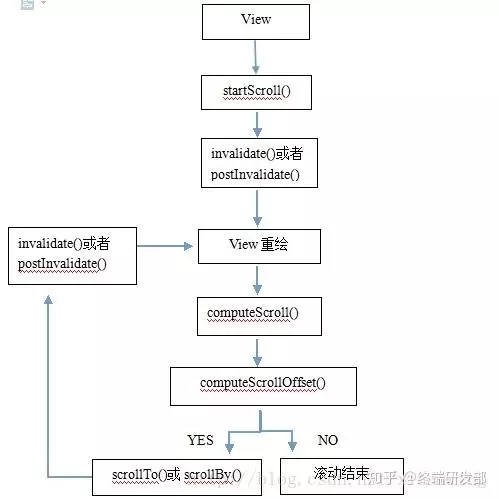
到此,自定义 view 的方法就讲完了。希望对大家有用。
参考文献:
Android 自定义 View 详解的更多相关文章
- android 自定义view详解
1.自定义View前首先要了解一下View的方法,虽然有些不一定要实现. 分类 方法 描述 创建 Constructors View中有两种类型的构造方法,一种是在代码中构建View,另一种是填充布局 ...
- 深入了解View实现原理以及自定义View详解
下面几篇文章对View的原理讲的非常详细. Android LayoutInflater原理分析,带你一步步深入了解View(一) Android视图绘制流程完全解析,带你一步步深入了解View(二) ...
- android开发之自定义View 详解 资料整理 小冰原创整理,原创作品。
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> /** * 作者:David Zheng on 2015/11/7 15:38 * * 网站:http://www.93sec ...
- 【朝花夕拾】Android自定义View篇之(四)自定义View的三种实现方式及自定义属性使用介绍
前言 转载请声明,转自[https://www.cnblogs.com/andy-songwei/p/10979161.html],谢谢! 尽管Android系统提供了不少控件,但是有很多酷炫效果仍然 ...
- Android 自定义View合集
自定义控件学习 https://github.com/GcsSloop/AndroidNote/tree/master/CustomView 小良自定义控件合集 https://github.com/ ...
- Android之canvas详解
首先说一下canvas类: Class Overview The Canvas class holds the "draw" calls. To draw something, y ...
- 【转】Android Canvas绘图详解(图文)
转自:http://www.jcodecraeer.com/a/anzhuokaifa/androidkaifa/2012/1212/703.html Android Canvas绘图详解(图文) 泡 ...
- android自定义View之NotePad出鞘记
现在我们的手机上基本都会有一个记事本,用起来倒也还算方便,记事本这种东东,如果我想要自己实现,该怎么做呢?今天我们就通过自定义View的方式来自定义一个记事本.OK,废话不多说,先来看看效果图. 整个 ...
- Android自定义View(RollWeekView-炫酷的星期日期选择控件)
转载请标明出处: http://blog.csdn.net/xmxkf/article/details/53420889 本文出自:[openXu的博客] 目录: 1分析 2定义控件布局 3定义Cus ...
随机推荐
- VM虚拟机安装Windows Server 2008操作系统
镜像链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1_Hv6U3xulqkkKzCYXmNvNQ 提取码:uwph Windows 2008 版本 有标准版.有企业版 群集 双击热备 clus ...
- [转载]2.2 UiPath条件判断活动Flow Decision的介绍和使用
一.Flow Decision介绍 FlowDecision节点是一个条件节点,它根据指定条件是否成立来控制流程的两个分支. 当条件为True时,流程执行一个分支 当条件为False时,流程执行另外一 ...
- linux 自启动 | 三种方式自启动
linux 实现自启动有多种方式,通过Linux 底层启动原理介绍,便可以理解以下几种方式 这里简单介绍一下这几种方式 一.自定义开机程序 /etc/rc.d/rc.local 1.vim / ...
- kubespray2.11安装kubernetes1.15
关于kubespray Kubespray是开源的kubernetes部署工具,整合了ansible,可以方便的部署高可用集群环境,官网地址:https://github.com/kubernetes ...
- 监听器以及在监听类里面获得bean的方法
1实现HttpSessionListener和ServletContextListener,2个接口 2然后在contextInitialized初始化方法里面: ServletContext app ...
- 关于GDAL读写Shp乱码的问题总结
目录 1. 正文 1.1. shp文件本身的编码的问题 1.2. 设置读取的编码方式 1.2.1. GDAL设置 1.2.2. 解码方式 1.2.3. 其他 2. 参考 1. 正文 最近在使用GDAL ...
- Hadoop2.8.2 运行wordcount
1 例子jar位置 [hadoop@hadoop02 mapreduce]$ pwd /hadoop/hadoop-2.8.2/share/hadoop/mapreduce [hadoop@hadoo ...
- HTML学习 day02
1.HTML的相关概念 网站建设流程 网页组成 网页主要由三部分组成:结构(Structure).表现(Presentation)和行为(Behavior). html(Hypertext Mark ...
- Python 编程语言要掌握的技能之一:善用变量来改善代码质量
如何为变量起名 在计算机科学领域,有一句著名的格言(俏皮话): There are only two hard things in Computer Science: cache invalidati ...
- python爬虫项目-一见倾心壁纸
方法1 import re import urllib import urllib.request def getHtml(url): page = urllib.request.urlopen(ur ...
