Convolutional Neural Network-week2编程题1(Keras tutorial - 笑脸识别)
本次我们将:
- 学习到一个高级的神经网络的框架,能够运行在包括TensorFlow和CNTK的几个较低级别的框架之上的框架。
看看如何在几个小时内建立一个深入的学习算法。 - 为什么我们要使用Keras框架呢?Keras是为了使深度学习工程师能够很快地建立和实验不同的模型的框架,正如TensorFlow是一个比Python更高级的框架,Keras是一个更高层次的框架,并提供了额外的抽象方法。最关键的是Keras能够以最短的时间让想法变为现实。
import numpy as np
from keras import layers
from keras.layers import Input, Dense, Activation, ZeroPadding2D, BatchNormalization, Flatten, Conv2D
from keras.layers import AveragePooling2D, MaxPooling2D, Dropout, GlobalMaxPooling2D, GlobalAveragePooling2D
from keras.models import Model
from keras.preprocessing import image
from keras.utils import layer_utils
from keras.utils.data_utils import get_file
from keras.applications.imagenet_utils import preprocess_input
import pydot
from IPython.display import SVG
from keras.utils.vis_utils import model_to_dot
from keras.utils import plot_model
from kt_utils import *
import keras.backend as K
K.set_image_data_format('channels_last')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow
%matplotlib inline
注意:正如你所看到的,我们已经从Keras中导入了很多功能, 只需直接调用它们即可轻松使用它们。 比如:X = Input(…) 或者X = ZeroPadding2D(…).
1. 任务描述
建立一个算法,它使用来自前门摄像头的图片来检查这个人是否快乐,只有在人高兴的时候,门才会打开。

你收集了你的朋友和你自己的照片,被前门的摄像头拍了下来。数据集已经标记好了

X_train_orig, Y_train_orig, X_test_orig, Y_test_orig, classes = load_dataset()
# Normalize image vectors
X_train = X_train_orig/255.
X_test = X_test_orig/255.
# Reshape
Y_train = Y_train_orig.T
Y_test = Y_test_orig.T
print ("number of training examples = " + str(X_train.shape[0]))
print ("number of test examples = " + str(X_test.shape[0]))
print ("X_train shape: " + str(X_train.shape))
print ("Y_train shape: " + str(Y_train.shape))
print ("X_test shape: " + str(X_test.shape))
print ("Y_test shape: " + str(Y_test.shape))
number of training examples = 600
number of test examples = 150
X_train shape: (600, 64, 64, 3)
Y_train shape: (600, 1)
X_test shape: (150, 64, 64, 3)
Y_test shape: (150, 1)
Details of the "Happy" dataset:
Images are of shape (64,64,3)
Training: 600 pictures
Test: 150 pictures
2. Building a model in Keras
Keras非常适合快速制作模型,它可以在很短的时间内建立一个很优秀的模型.
Here is an example of a model in Keras:
def model(input_shape):
# Define the input placeholder as a tensor with shape input_shape. Think of this as your input image!
X_input = Input(input_shape)
# Zero-Padding: pads the border of X_input with zeroes
X = ZeroPadding2D((3, 3))(X_input)
# CONV -> BN -> RELU Block applied to X
X = Conv2D(32, (7, 7), strides = (1, 1), name = 'conv0')(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = 'bn0')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X)
# MAXPOOL
X = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), name='max_pool')(X)
# FLATTEN X (means convert it to a vector) + FULLYCONNECTED
X = Flatten()(X)
X = Dense(1, activation='sigmoid', name='fc')(X)
# Create model. This creates your Keras model instance, you'll use this instance to train/test the model.
model = Model(inputs = X_input, outputs = X, name='HappyModel')
return model
注意:
Keras框架使用的变量名和我们以前使用的numpy和TensorFlow变量不一样。它不是在前向传播的每一步上创建新变量(比如X, Z1, A1, Z2, A2,…)以便于不同层之间的计算。
在Keras中,我们使用X覆盖了所有的值,没有保存每一层结果,我们只需要最新的值,唯一例外的就是
X_input,我们将它分离出来是因为它是输入的数据,我们要在最后的创建模型那一步中用到。
# GRADED FUNCTION: HappyModel
def HappyModel(input_shape):
"""
Implementation of the HappyModel.
Arguments:
input_shape -- shape of the images of the dataset
Returns:
model -- a Model() instance in Keras
"""
### START CODE HERE ###
# Feel free to use the suggested outline in the text above to get started, and run through the whole
# exercise (including the later portions of this notebook) once. The come back also try out other
# network architectures as well.
X_input = Input(input_shape)
# 使用0填充: X_input周围填充0, p=3
X = ZeroPadding2D((3, 3))(X_input)
# 使用CONV -> Batch归一化 -> Relu
X = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), strides = (1, 1), name = 'conv0')(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis=3, name='bn0')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X)
# MaxPool: 最大值池化层
X = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), name='max_pool')(X)
X = Conv2D(16, (3, 3), strides = (1, 1), name = 'conv1')(X) # 优化后
X = Activation('relu')(X)
X = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), name='max_pool1')(X)
# Flatten层, 矩阵-->向量
# 全连接层(full Connected)
X = Flatten()(X)
X = Dense(1, activation='sigmoid', name='fc')(X)
model = Model(inputs = X_input, outputs = X, name='HappyModel')
### END CODE HERE ###
return model
设计好模型,训练并测试模型需要:
创建一个模型实体。
编译模型,可以使用这个语句:
model.compile(optimizer = "...", loss = "...", metrics = ["accuracy"])。训练模型:
model.fit(x = ..., y = ..., epochs = ..., batch_size = ...)。评估模型:
model.evaluate(x = ..., y = ...)。
# step 1. create the model.
happyModel = HappyModel(X_train.shape[1:])
# step 2. compile the model to configure the learning process. accuracy是评价指标
happyModel.compile(optimizer = 'adam', loss = 'binary_crossentropy', metrics = ['accuracy'])
# step 3. 训练模型
happyModel.fit(x = X_train, y = Y_train, epochs = 40, batch_size = 50)
# step 4. 评价模型, 在测试集上评价
preds = happyModel.evaluate(x = X_test, y = Y_test)
print()
print ("Loss = " + str(preds[0]))
print ("Test Accuracy = " + str(preds[1]))
Epoch 1/40
600/600 [==============================] - 20s - loss: 0.7217 - acc: 0.6300
Epoch 2/40
600/600 [==============================] - 21s - loss: 0.4625 - acc: 0.8083
Epoch 3/40
600/600 [==============================] - 19s - loss: 0.3341 - acc: 0.8667
Epoch 4/40
600/600 [==============================] - 24s - loss: 0.2439 - acc: 0.9167
Epoch 5/40
600/600 [==============================] - 22s - loss: 0.1956 - acc: 0.9367
Epoch 6/40
600/600 [==============================] - 21s - loss: 0.1750 - acc: 0.9350
Epoch 7/40
600/600 [==============================] - 20s - loss: 0.1411 - acc: 0.9600
Epoch 8/40
600/600 [==============================] - 29s - loss: 0.1271 - acc: 0.9583
Epoch 9/40
600/600 [==============================] - 33s - loss: 0.1177 - acc: 0.9667
Epoch 10/40
600/600 [==============================] - 29s - loss: 0.0918 - acc: 0.9767
Epoch 11/40
600/600 [==============================] - 30s - loss: 0.0772 - acc: 0.9833
Epoch 12/40
600/600 [==============================] - 23s - loss: 0.0734 - acc: 0.9817
Epoch 13/40
600/600 [==============================] - 20s - loss: 0.0716 - acc: 0.9867
Epoch 14/40
600/600 [==============================] - 20s - loss: 0.0724 - acc: 0.9800
Epoch 15/40
600/600 [==============================] - 19s - loss: 0.0598 - acc: 0.9867
Epoch 16/40
600/600 [==============================] - 20s - loss: 0.0667 - acc: 0.9833
Epoch 17/40
600/600 [==============================] - 19s - loss: 0.0566 - acc: 0.9850
Epoch 18/40
600/600 [==============================] - 22s - loss: 0.0449 - acc: 0.9917
Epoch 19/40
600/600 [==============================] - 21s - loss: 0.0475 - acc: 0.9917
Epoch 20/40
600/600 [==============================] - 21s - loss: 0.0533 - acc: 0.9850
Epoch 21/40
600/600 [==============================] - 21s - loss: 0.0468 - acc: 0.9883
Epoch 22/40
600/600 [==============================] - 20s - loss: 0.0391 - acc: 0.9933
Epoch 23/40
600/600 [==============================] - 19s - loss: 0.0367 - acc: 0.9917
Epoch 24/40
600/600 [==============================] - 20s - loss: 0.0339 - acc: 0.9900
Epoch 25/40
600/600 [==============================] - 21s - loss: 0.0436 - acc: 0.9883
Epoch 26/40
600/600 [==============================] - 20s - loss: 0.0314 - acc: 0.9900
Epoch 27/40
600/600 [==============================] - 21s - loss: 0.0295 - acc: 0.9900
Epoch 28/40
600/600 [==============================] - 21s - loss: 0.0295 - acc: 0.9933
Epoch 29/40
600/600 [==============================] - 20s - loss: 0.0261 - acc: 0.9917
Epoch 30/40
600/600 [==============================] - 21s - loss: 0.0286 - acc: 0.9933
Epoch 31/40
600/600 [==============================] - 22s - loss: 0.0237 - acc: 0.9933
Epoch 32/40
600/600 [==============================] - 23s - loss: 0.0192 - acc: 0.9983
Epoch 33/40
600/600 [==============================] - 22s - loss: 0.0218 - acc: 0.9967
Epoch 34/40
600/600 [==============================] - 21s - loss: 0.0272 - acc: 0.9950
Epoch 35/40
600/600 [==============================] - 19s - loss: 0.0188 - acc: 0.9983
Epoch 36/40
600/600 [==============================] - 19s - loss: 0.0166 - acc: 0.9933
Epoch 37/40
600/600 [==============================] - 19s - loss: 0.0193 - acc: 0.9983
Epoch 38/40
600/600 [==============================] - 19s - loss: 0.0134 - acc: 0.9967
Epoch 39/40
600/600 [==============================] - 20s - loss: 0.0147 - acc: 0.9983
Epoch 40/40
600/600 [==============================] - 19s - loss: 0.0174 - acc: 0.9983
<keras.callbacks.History at 0x1cc49470>
150/150 [==============================] - 1s
Loss = 0.10337299724419911
Test Accuracy = 0.9733333309491475
准确度大于80%就算正常,如果你的准确度没有大于80%,你可以尝试改变模型:
X = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), strides = (1, 1), name = 'conv0')(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = 'bn0')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X)
直到 height and width dimensions 十分小, channels数 十分大(≈32 for example)
- 你可以在每个块后面使用最大值池化层,它将会减少宽、高的维度。
- Change your optimizer. 这里使用的是Adam
- 如果模型难以运行,并且遇到了内存不够的问题,那么就降低batch_size (12通常是一个很好的折中方案)
- Run on more epochs, until you see the train accuracy plateauing.
Note: If you perform hyperparameter tuning on your model, the test set actually becomes a dev set, and your model might end up overfitting to the test (dev) set. But just for the purpose of this assignment, we won't worry about that here.
3. 总结
模型构建过程,Create -> Compile -> Fit/Train -> Evaluate/Test.
4. 测试你的图片
### START CODE HERE ###
img_path = 'images/smail01.png'
### END CODE HERE ###
img = image.load_img(img_path, target_size=(64, 64))
imshow(img)
x = image.img_to_array(img)
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=0)
x = preprocess_input(x)
print(happyModel.predict(x))
[[1.]]

### START CODE HERE ###
img_path = 'images/smail08.png'
### END CODE HERE ###
img = image.load_img(img_path, target_size=(64, 64))
imshow(img)
x = image.img_to_array(img)
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=0)
x = preprocess_input(x)
print(happyModel.predict(x))
[[0.]]

5. 其他一些有用的功能
model.summary():打印出你的每一层的大小细节plot_model(): 绘制出布局图
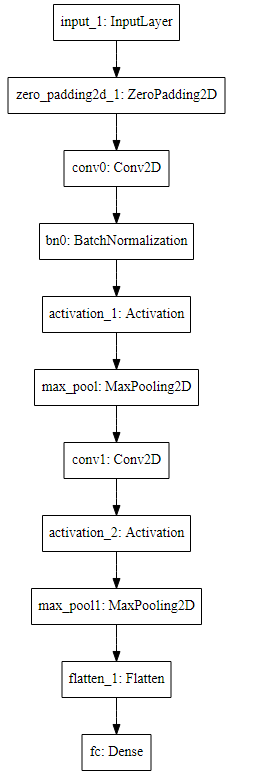
happyModel.summary()
______________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_3 (InputLayer) (None, 64, 64, 3) 0
_________________________________________________________________
zero_padding2d_3 (ZeroPaddin (None, 70, 70, 3) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv0 (Conv2D) (None, 68, 68, 32) 896
_________________________________________________________________
bn0 (BatchNormalization) (None, 68, 68, 32) 128
_________________________________________________________________
activation_3 (Activation) (None, 68, 68, 32) 0
_________________________________________________________________
max_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 34, 34, 32) 0
_________________________________________________________________
flatten_3 (Flatten) (None, 36992) 0
_________________________________________________________________
fc (Dense) (None, 1) 36993
=================================================================
Total params: 38,017
Trainable params: 37,953
Non-trainable params: 64
_________________________________________________________________
执行下面:
需要安装:Graphviz, 参考这个https://www.cnblogs.com/shuodehaoa/p/8667045.html
执行:pip install pydot-ng & pip install graphviz
plot_model(happyModel, to_file='HappyModel.png')
SVG(model_to_dot(happyModel).create(prog='dot', format='svg'))
Convolutional Neural Network-week2编程题1(Keras tutorial - 笑脸识别)的更多相关文章
- 《ABCNN: Attention-Based Convolutional Neural Network for Modeling Sentence Pairs》
代码: keras:https://github.com/phdowling/abcnn-keras tf:https://github.com/galsang/ABCNN 本文是Wenpeng Yi ...
- ISSCC 2017论文导读 Session 14 Deep Learning Processors,A 2.9TOPS/W Deep Convolutional Neural Network
最近ISSCC2017大会刚刚举行,看了关于Deep Learning处理器的Session 14,有一些不错的东西,在这里记录一下. A 2.9TOPS/W Deep Convolutional N ...
- ISSCC 2017论文导读 Session 14 Deep Learning Processors,A 2.9TOPS/W Deep Convolutional Neural Network SOC
最近ISSCC2017大会刚刚举行,看了关于Deep Learning处理器的Session 14,有一些不错的东西,在这里记录一下. A 2.9TOPS/W Deep Convolutional N ...
- 论文阅读(Weilin Huang——【TIP2016】Text-Attentional Convolutional Neural Network for Scene Text Detection)
Weilin Huang--[TIP2015]Text-Attentional Convolutional Neural Network for Scene Text Detection) 目录 作者 ...
- 卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network,CNN)
全连接神经网络(Fully connected neural network)处理图像最大的问题在于全连接层的参数太多.参数增多除了导致计算速度减慢,还很容易导致过拟合问题.所以需要一个更合理的神经网 ...
- Convolutional Neural Network in TensorFlow
翻译自Build a Convolutional Neural Network using Estimators TensorFlow的layer模块提供了一个轻松构建神经网络的高端API,它提供了创 ...
- 卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network, CNN)简析
目录 1 神经网络 2 卷积神经网络 2.1 局部感知 2.2 参数共享 2.3 多卷积核 2.4 Down-pooling 2.5 多层卷积 3 ImageNet-2010网络结构 4 DeepID ...
- HYPERSPECTRAL IMAGE CLASSIFICATION USING TWOCHANNEL DEEP CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORK阅读笔记
HYPERSPECTRAL IMAGE CLASSIFICATION USING TWOCHANNEL DEEP CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORK 论文地址:https:/ ...
- A NEW HYPERSPECTRAL BAND SELECTION APPROACH BASED ON CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORK文章笔记
A NEW HYPERSPECTRAL BAND SELECTION APPROACH BASED ON CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORK 文章地址:https://ieeex ...
随机推荐
- 详细解读go语言中的chnanel
Channel 底层数据结构 type hchan struct { qcount uint // 当前队列中剩余元素个数 dataqsiz uint // 环形队列长度,即可以存放的元素个数 buf ...
- Appium自动化(8) - 可定位的控件属性
如果你还想从头学起Appium,可以看看这个系列的文章哦! https://www.cnblogs.com/poloyy/category/1693896.html 前言 在前面几篇文章可以看到,一个 ...
- 初学AOP小结
Spring AOP理解 参考链接 AOP简介 AOP(面向切面编程),可以说时OOP的补充,使用OOP时,我们在日常编写代码的时候,一旦牵涉到大型一点的项目,项目不可或缺的事务处理,安全处理,验证处 ...
- JS010. 三元运算符扩展运用(多层判断语句 / 多条表达式)
MDN - 三元运算符 语法 Condition ? exprIfTrue : exprIfFalse 用例: function getFee(isMember) { return(isMember ...
- freeswitch编译安装依赖
ncurses:提供字符界面 zlib:数据压缩 libjpeg:JPEG图片格式数据的解码/编码/其他. lua:lua解释器 libedit:一种编辑操作的库,对一些可以交互操作的场景,或转为了自 ...
- 查看elasticsearch版本的方法
查看elasticsearch版本的方法: 1.elasticsearch已经启动的情况下 使用curl -XGET localhost:9200命令查看: "version" : ...
- 跨 Docker 宿主机网络 overlay 类型
跨 Docker 宿主机网络 overlay 类型 前言 a. 本文主要为 Docker的视频教程 笔记. b. 环境为 三台 CentOS 7.0 虚拟机 (Vmware Workstation 1 ...
- PHP的Mcrypt加密扩展知识了解
今天我们来学习的是 PHP 中的一个过时的扩展 Mcrypt .在 PHP7 之前,这个扩展是随 PHP 安装包一起内置发布的,但是现在新版本的 PHP 中已经没有了,需要使用这个扩展的话我们需要单独 ...
- Java基础系列(41)- 冒泡排序
冒泡排序 冒泡排序无疑是最为出名的排序算法之一,总共有八大排序 冒泡的代码还是相当简单的,两层循环,外层冒泡轮数,里层依次比较,江湖中人人尽皆知 我们看到的嵌套循环,应该立马就可以得出这个算法的时间复 ...
- sonar扫描java项目报错
安装maven 配置path 验证maven,看到以下信息证明已经成功 扫描项目 扫描以下项目: kf-buss-nhgip-smartoffice-business-thirdparty 项目的配置 ...
