强化学习实战 | 表格型Q-Learning玩井子棋(三)优化,优化
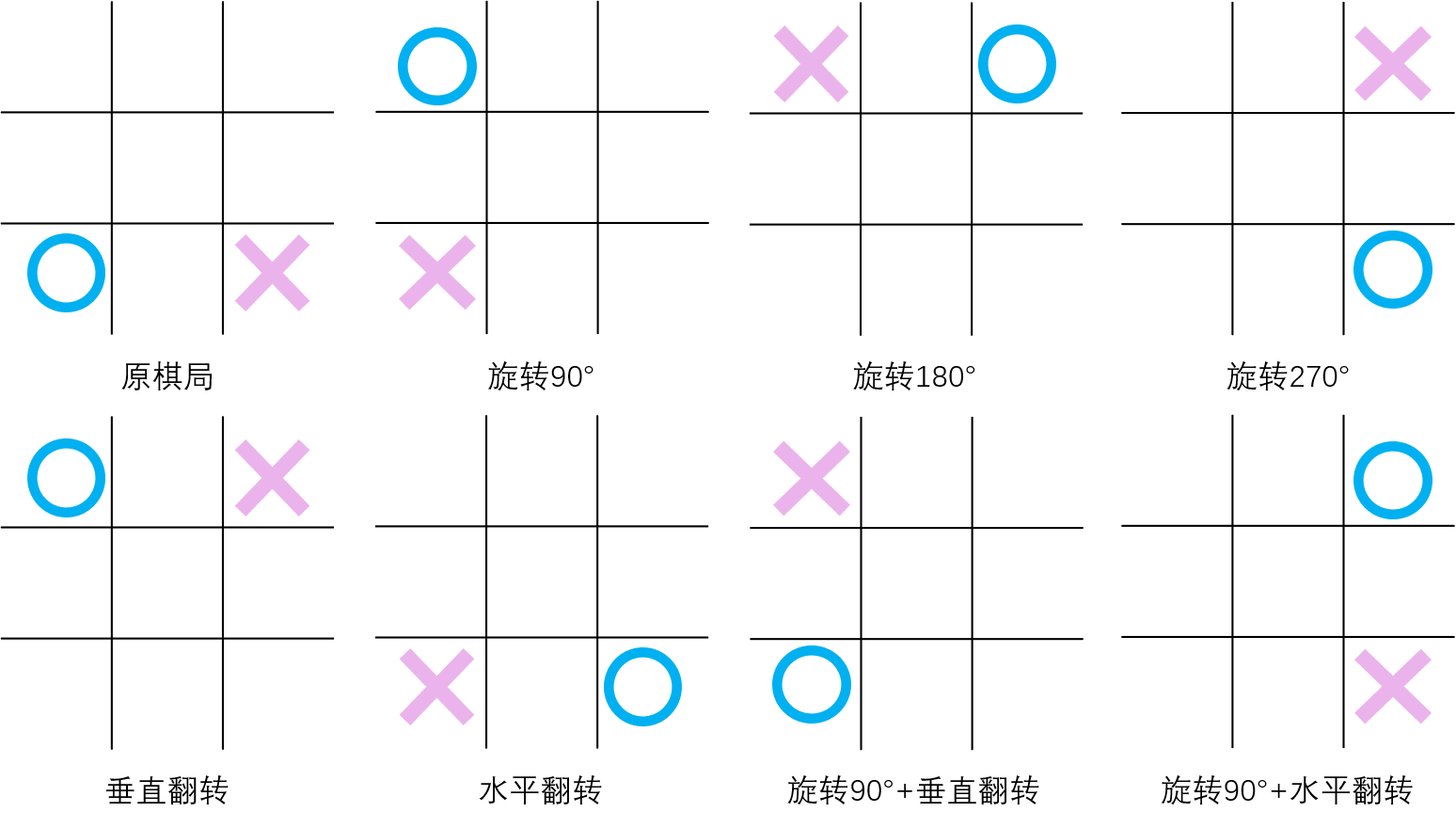
在 强化学习实战 | 表格型Q-Learning玩井字棋(二)开始训练!中,我们让agent“简陋地”训练了起来,经过了耗费时间的10万局游戏过后,却效果平平,尤其是初始状态的数值表现和预期相差不小。我想主要原因就是没有采用等价局面同步更新的方法,导致数据利用率较低。等价局面有7个,分别是:旋转90°,旋转180°,旋转270°,水平翻转,垂直翻转,旋转90°+水平翻转,旋转90°+垂直翻转,如下图所示。另外,在生成等价局面的同时,也要生成等价的动作,这样才能实现完整的Q值更新。
步骤1:写旋转和翻转函数
def rotate(array): # Input: np.array [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
list_ = list(array)
list_[:] = map(list,zip(*list_[::-1]))
return np.array(list_) # Output: np.array [[7,4,1],[8,5,2],[9,6,3]] def flip(array_, direction): # Input: np.array [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
array = array_.copy()
n = int(np.floor(len(array)/2))
if direction == 'vertical': # Output: np.array [[7,8,9],[4,5,6],[1,2,3]]
for i in range(n):
temp = array[i].copy()
array[i] = array[-i-1].copy()
array[-i-1] = temp
elif direction == 'horizon': # Output: np.array [[3,2,1],[6,5,4],[9,8,7]]
for i in range(n):
temp = array[:,i].copy()
array[:,i] = array[:,-i-1]
array[:,-i-1] = temp
return array
步骤2:写生成等价局面及等价动作的函数
函数名为 genEqualStateAndAction(state, action),定义在 Agent() 类中。
def genEqualStateAndAction(self, state_, action_): # Input: np.array, tuple(x,y)
state, action = state_.copy(), action_
equalStates, equalActions = [], [] # 原局面
equalStates.append(state)
equalActions.append(action) # 水平翻转
state_tf = state.copy()
action_state_tf = np.zeros(state.shape)
action_state_tf[action] = 1
state_tf = flip(state_tf, 'horizon')
action_state_tf = flip(action_state_tf, 'horizon')
index = np.where(action_state_tf == 1)
action_tf = (int(index[0]), int(index[1]))
equalStates.append(state_tf)
equalActions.append(action_tf) # 垂直翻转
state_tf = state.copy()
action_state_tf = np.zeros(state.shape)
action_state_tf[action] = 1
state_tf = flip(state_tf, 'vertical')
action_state_tf = flip(action_state_tf, 'vertical')
index = np.where(action_state_tf == 1)
action_tf = (int(index[0]), int(index[1]))
equalStates.append(state_tf)
equalActions.append(action_tf) # 旋转90°
state_tf = state.copy()
action_state_tf = np.zeros(state.shape)
action_state_tf[action] = 1
for i in range(1):
state_tf = rotate(state_tf)
action_state_tf = rotate(action_state_tf)
index = np.where(action_state_tf == 1)
action_tf = (int(index[0]), int(index[1]))
equalStates.append(state_tf)
equalActions.append(action_tf) # 旋转180°
state_tf = state.copy()
action_state_tf = np.zeros(state.shape)
action_state_tf[action] = 1
for i in range(2):
state_tf = rotate(state_tf)
action_state_tf = rotate(action_state_tf)
index = np.where(action_state_tf == 1)
action_tf = (int(index[0]), int(index[1]))
equalStates.append(state_tf)
equalActions.append(action_tf) # 旋转270°
state_tf = state.copy()
action_state_tf = np.zeros(state.shape)
action_state_tf[action] = 1
for i in range(3):
state_tf = rotate(state_tf)
action_state_tf = rotate(action_state_tf)
index = np.where(action_state_tf == 1)
action_tf = (int(index[0]), int(index[1]))
equalStates.append(state_tf)
equalActions.append(action_tf) # 旋转90° + 水平翻转
state_tf = state.copy()
action_state_tf = np.zeros(state.shape)
action_state_tf[action] = 1
for i in range(1):
state_tf = rotate(state_tf)
action_state_tf = rotate(action_state_tf)
state_tf = flip(state_tf, 'horizon')
action_state_tf = flip(action_state_tf, 'horizon')
index = np.where(action_state_tf == 1)
action_tf = (int(index[0]), int(index[1]))
equalStates.append(state_tf)
equalActions.append(action_tf) # 旋转90° + 垂直翻转
state_tf = state.copy()
action_state_tf = np.zeros(state.shape)
action_state_tf[action] = 1
for i in range(1):
state_tf = rotate(state_tf)
action_state_tf = rotate(action_state_tf)
state_tf = flip(state_tf, 'vertical')
action_state_tf = flip(action_state_tf, 'vertical')
index = np.where(action_state_tf == 1)
action_tf = (int(index[0]), int(index[1]))
equalStates.append(state_tf)
equalActions.append(action_tf) return equalStates, equalActions
细心的读者可能会发问了:你这生成等价局面不去重的么?是的,不去重了。原因之一是如果要去重,那么要比对大量的np.array,实现起来较麻烦,可能会增加很多代码时间;原因之二是对重复的局面多次更新,只是不符合逻辑,但应该没有副作用:毕竟只要数据够多,最后Q表中的值都会收敛到一个值,而重复出现次数多的局面只是收敛得更快罢了。
步骤3:修改Agent()中的相关代码
需要修改方法 addNewState(self, env_, currentMove) 和方法 updateQtable(self, env_, currentMove, done_),整体代码如下:


import gym
import random
import time
import numpy as np # 查看所有已注册的环境
# from gym import envs
# print(envs.registry.all()) def str2tuple(string): # Input: '(1,1)'
string2list = list(string)
return ( int(string2list[1]), int(string2list[4]) ) # Output: (1,1) def rotate(array): # Input: np.array [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
list_ = list(array)
list_[:] = map(list,zip(*list_[::-1]))
return np.array(list_) # Output: np.array [[7,4,1],[8,5,2],[9,6,3]] def flip(array_, direction): # Input: np.array [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
array = array_.copy()
n = int(np.floor(len(array)/2))
if direction == 'vertical': # Output: np.array [[7,8,9],[4,5,6],[1,2,3]]
for i in range(n):
temp = array[i].copy()
array[i] = array[-i-1].copy()
array[-i-1] = temp
elif direction == 'horizon': # Output: np.array [[3,2,1],[6,5,4],[9,8,7]]
for i in range(n):
temp = array[:,i].copy()
array[:,i] = array[:,-i-1]
array[:,-i-1] = temp
return array class Game():
def __init__(self, env):
self.INTERVAL = 0 # 行动间隔
self.RENDER = False # 是否显示游戏过程
self.first = 'blue' if random.random() > 0.5 else 'red' # 随机先后手
self.currentMove = self.first
self.env = env
self.agent = Agent() def switchMove(self): # 切换行动玩家
move = self.currentMove
if move == 'blue': self.currentMove = 'red'
elif move == 'red': self.currentMove = 'blue' def newGame(self): # 新建游戏
self.first = 'blue' if random.random() > 0.5 else 'red'
self.currentMove = self.first
self.env.reset()
self.agent.reset() def run(self): # 玩一局游戏
self.env.reset() # 在第一次step前要先重置环境,不然会报错
while True:
print(f'--currentMove: {self.currentMove}--')
self.agent.updateQtable(self.env, self.currentMove, False) if self.currentMove == 'blue':
self.agent.lastState_blue = self.env.state.copy()
elif self.currentMove == 'red':
self.agent.lastState_red = self.agent.overTurn(self.env.state) # 红方视角需将状态翻转 action = self.agent.epsilon_greedy(self.env, self.currentMove)
if self.currentMove == 'blue':
self.agent.lastAction_blue = action['pos']
elif self.currentMove == 'red':
self.agent.lastAction_red = action['pos'] state, reward, done, info = self.env.step(action)
if done:
self.agent.lastReward_blue = reward
self.agent.lastReward_red = -1 * reward
self.agent.updateQtable(self.env, self.currentMove, True)
else:
if self.currentMove == 'blue':
self.agent.lastReward_blue = reward
elif self.currentMove == 'red':
self.agent.lastReward_red = -1 * reward if self.RENDER: self.env.render()
self.switchMove()
time.sleep(self.INTERVAL)
if done:
self.newGame()
if self.RENDER: self.env.render()
time.sleep(self.INTERVAL)
break class Agent():
def __init__(self):
self.Q_table = {}
self.EPSILON = 0.05
self.ALPHA = 0.5
self.GAMMA = 1 # 折扣因子
self.lastState_blue = None
self.lastAction_blue = None
self.lastReward_blue = None
self.lastState_red = None
self.lastAction_red = None
self.lastReward_red = None def reset(self):
self.lastState_blue = None
self.lastAction_blue = None
self.lastReward_blue = None
self.lastState_red = None
self.lastAction_red = None
self.lastReward_red = None def getEmptyPos(self, state): # 返回空位的坐标
action_space = []
for i, row in enumerate(state):
for j, one in enumerate(row):
if one == 0: action_space.append((i,j))
return action_space def randomAction(self, env_, mark): # 随机选择空格动作
actions = self.getEmptyPos(env_)
action_pos = random.choice(actions)
action = {'mark':mark, 'pos':action_pos}
return action def overTurn(self, state): # 翻转状态
state_ = state.copy()
for i, row in enumerate(state_):
for j, one in enumerate(row):
if one != 0: state_[i][j] *= -1
return state_ def genEqualStateAndAction(self, state_, action_): # Input: np.array, tuple(x,y)
state, action = state_.copy(), action_
equalStates, equalActions = [], [] # 原局面
equalStates.append(state)
equalActions.append(action) # 水平翻转
state_tf = state.copy()
action_state_tf = np.zeros(state.shape)
action_state_tf[action] = 1
state_tf = flip(state_tf, 'horizon')
action_state_tf = flip(action_state_tf, 'horizon')
index = np.where(action_state_tf == 1)
action_tf = (int(index[0]), int(index[1]))
equalStates.append(state_tf)
equalActions.append(action_tf) # 垂直翻转
state_tf = state.copy()
action_state_tf = np.zeros(state.shape)
action_state_tf[action] = 1
state_tf = flip(state_tf, 'vertical')
action_state_tf = flip(action_state_tf, 'vertical')
index = np.where(action_state_tf == 1)
action_tf = (int(index[0]), int(index[1]))
equalStates.append(state_tf)
equalActions.append(action_tf) # 旋转90°
state_tf = state.copy()
action_state_tf = np.zeros(state.shape)
action_state_tf[action] = 1
for i in range(1):
state_tf = rotate(state_tf)
action_state_tf = rotate(action_state_tf)
index = np.where(action_state_tf == 1)
action_tf = (int(index[0]), int(index[1]))
equalStates.append(state_tf)
equalActions.append(action_tf) # 旋转180°
state_tf = state.copy()
action_state_tf = np.zeros(state.shape)
action_state_tf[action] = 1
for i in range(2):
state_tf = rotate(state_tf)
action_state_tf = rotate(action_state_tf)
index = np.where(action_state_tf == 1)
action_tf = (int(index[0]), int(index[1]))
equalStates.append(state_tf)
equalActions.append(action_tf) # 旋转270°
state_tf = state.copy()
action_state_tf = np.zeros(state.shape)
action_state_tf[action] = 1
for i in range(3):
state_tf = rotate(state_tf)
action_state_tf = rotate(action_state_tf)
index = np.where(action_state_tf == 1)
action_tf = (int(index[0]), int(index[1]))
equalStates.append(state_tf)
equalActions.append(action_tf) # 旋转90° + 水平翻转
state_tf = state.copy()
action_state_tf = np.zeros(state.shape)
action_state_tf[action] = 1
for i in range(1):
state_tf = rotate(state_tf)
action_state_tf = rotate(action_state_tf)
state_tf = flip(state_tf, 'horizon')
action_state_tf = flip(action_state_tf, 'horizon')
index = np.where(action_state_tf == 1)
action_tf = (int(index[0]), int(index[1]))
equalStates.append(state_tf)
equalActions.append(action_tf) # 旋转90° + 垂直翻转
state_tf = state.copy()
action_state_tf = np.zeros(state.shape)
action_state_tf[action] = 1
for i in range(1):
state_tf = rotate(state_tf)
action_state_tf = rotate(action_state_tf)
state_tf = flip(state_tf, 'vertical')
action_state_tf = flip(action_state_tf, 'vertical')
index = np.where(action_state_tf == 1)
action_tf = (int(index[0]), int(index[1]))
equalStates.append(state_tf)
equalActions.append(action_tf) return equalStates, equalActions def addNewState(self, env_, currentMove): # 若当前状态不在Q表中,则新增状态
state = env_.state if currentMove == 'blue' else self.overTurn(env_.state) # 如果是红方行动则翻转状态
eqStates, eqActions = self.genEqualStateAndAction(state, (0,0)) for one in eqStates:
if str(one) not in self.Q_table:
self.Q_table[str(one)] = {}
actions = self.getEmptyPos(one)
for action in actions:
self.Q_table[str(one)][str(action)] = 0 def epsilon_greedy(self, env_, currentMove): # ε-贪心策略
state = env_.state if currentMove == 'blue' else self.overTurn(env_.state) # 如果是红方行动则翻转状态
Q_Sa = self.Q_table[str(state)]
maxAction, maxValue, otherAction = [], -100, []
for one in Q_Sa:
if Q_Sa[one] > maxValue:
maxValue = Q_Sa[one]
for one in Q_Sa:
if Q_Sa[one] == maxValue:
maxAction.append(str2tuple(one))
else:
otherAction.append(str2tuple(one)) try:
action_pos = random.choice(maxAction) if random.random() > self.EPSILON else random.choice(otherAction)
except: # 处理从空的otherAction中取值的情况
action_pos = random.choice(maxAction)
action = {'mark':currentMove, 'pos':action_pos}
return action def updateQtable(self, env_, currentMove, done_): judge = (currentMove == 'blue' and self.lastState_blue is None) or \
(currentMove == 'red' and self.lastState_red is None)
if judge: # 边界情况1:若agent无上一状态,说明是游戏中首次动作,那么只需要新增状态就好,无需更新Q值
self.addNewState(env_, currentMove)
return if done_: # 边界情况2:若当前状态S_是终止状态,则无需把S_添加至Q表格中,直接令maxQ_S_a = 0,并同时更新双方Q值
for one in ['blue', 'red']:
S = self.lastState_blue if one == 'blue' else self.lastState_red
a = self.lastAction_blue if one == 'blue' else self.lastAction_red
eqStates, eqActions = self.genEqualStateAndAction(S, a)
R = self.lastReward_blue if one == 'blue' else self.lastReward_red
# print('lastState S:\n', S)
# print('lastAction a: ', a)
# print('lastReward R: ', R)
# print('\n')
maxQ_S_a = 0
for S, a in zip(eqStates, eqActions):
self.Q_table[str(S)][str(a)] = (1 - self.ALPHA) * self.Q_table[str(S)][str(a)] \
+ self.ALPHA * (R + self.GAMMA * maxQ_S_a)
return # 其他情况下:Q表无当前状态则新增状态,否则直接更新Q值
self.addNewState(env_, currentMove)
S_ = env_.state if currentMove == 'blue' else self.overTurn(env_.state)
S = self.lastState_blue if currentMove == 'blue' else self.lastState_red
a = self.lastAction_blue if currentMove == 'blue' else self.lastAction_red
eqStates, eqActions = self.genEqualStateAndAction(S, a)
R = self.lastReward_blue if currentMove == 'blue' else self.lastReward_red
# print('lastState S:\n', S)
# print('State S_:\n', S_)
# print('lastAction a: ', a)
# print('lastReward R: ', R)
# print('\n')
Q_S_a = self.Q_table[str(S_)]
maxQ_S_a = -100
for one in Q_S_a:
if Q_S_a[one] > maxQ_S_a:
maxQ_S_a = Q_S_a[one]
for S, a in zip(eqStates, eqActions):
self.Q_table[str(S)][str(a)] = (1 - self.ALPHA) * self.Q_table[str(S)][str(a)] \
+ self.ALPHA * (R + self.GAMMA * maxQ_S_a) env = gym.make('TicTacToeEnv-v0')
game = Game(env)
for i in range(10000):
print('episode', i)
game.run()
Q_table = game.agent.Q_table
测试
经过了上述优化,agent能够在一轮对局中更新16个Q值,比起上一节 强化学习实战 | 表格型Q-Learning玩井字棋(二)开始训练! 中的更新2个Q值要多8倍,不妨就玩1万局游戏,看看是否能玩出之前玩8万局游戏的效果。
项目1:查看Q表格的状态数

一般般,仍然有状态没有覆盖到。
项目2:查看初始状态
先手开局:
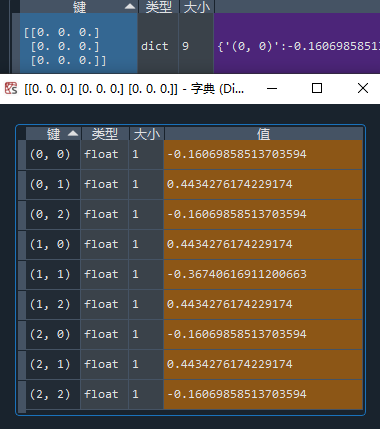
这效果也太好了吧!不但有完美的对称,还有泾渭分明的胜负判断: 第一步走四边就稳了,走四角和走中间都是输面大。看来优化之后,Q值的整体方差这一块表现得非常好了。
再贴一个后手开局的情况:
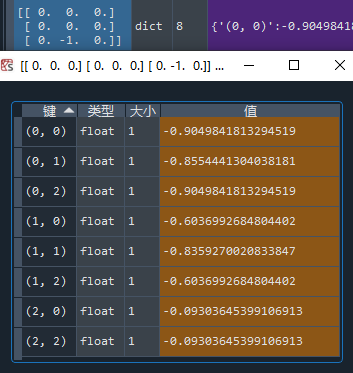
项目3:测试代码时间
引入了更复杂的trick,确实是完美地争取到了一些收益,但玩一局游戏的时间一定是增加了,增加了多少呢?我们用上一节的老算法和本节的算法分别跑2000局游戏,记录一下时间(本人使用的CPU是:Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-9750H)。
双向更新+等价局面同步更新:

双向更新:

增加了不到两倍的时间,换来了大约8倍的更新量提高,还降低了方差,看来这优化是赚的。
小结
拿着优化好的算法,心里也有了些底气,可以放心大胆地增加训练时间了。下一节,我们将用训练完全Q表,用pygame做一个拥有人机对阵,机机对战,作弊功能的井字棋游戏。还可以做一些对战的数据分析,比如AI内战的胜率多高?AI对阵随机策略的胜率多高?下节见!
强化学习实战 | 表格型Q-Learning玩井子棋(三)优化,优化的更多相关文章
- 强化学习实战 | 表格型Q-Learning玩井字棋(二)
在 强化学习实战 | 表格型Q-Learning玩井字棋(一)中,我们构建了以Game() 和 Agent() 类为基础的框架,本篇我们要让agent不断对弈,维护Q表格,提升棋力.那么我们先来盘算一 ...
- 强化学习实战 | 表格型Q-Learning玩井字棋(四)游戏时间
在 强化学习实战 | 表格型Q-Learning玩井字棋(三)优化,优化 中,我们经过优化和训练,得到了一个还不错的Q表格,这一节我们将用pygame实现一个有人机对战,机机对战和作弊功能的井字棋游戏 ...
- 强化学习实战 | 表格型Q-Learning玩井字棋(一)
在 强化学习实战 | 自定义Gym环境之井子棋 中,我们构建了一个井字棋环境,并进行了测试.接下来我们可以使用各种强化学习方法训练agent出棋,其中比较简单的是Q学习,Q即Q(S, a),是状态动作 ...
- 强化学习系列之:Deep Q Network (DQN)
文章目录 [隐藏] 1. 强化学习和深度学习结合 2. Deep Q Network (DQN) 算法 3. 后续发展 3.1 Double DQN 3.2 Prioritized Replay 3. ...
- 强化学习实战 | 自定义Gym环境之井字棋
在文章 强化学习实战 | 自定义Gym环境 中 ,我们了解了一个简单的环境应该如何定义,并使用 print 简单地呈现了环境.在本文中,我们将学习自定义一个稍微复杂一点的环境--井字棋.回想一下井字棋 ...
- 强化学习实战 | 自定义Gym环境之扫雷
开始之前 先考虑几个问题: Q1:如何展开无雷区? Q2:如何计算格子的提示数? Q3:如何表示扫雷游戏的状态? A1:可以使用递归函数,或是堆栈. A2:一般的做法是,需要打开某格子时,再去统计周围 ...
- 强化学习实战 | 自定义Gym环境
新手的第一个强化学习示例一般都从Open Gym开始.在这些示例中,我们不断地向环境施加动作,并得到观测和奖励,这也是Gym Env的基本用法: state, reward, done, info = ...
- 强化学习实战 | 自定义gym环境之显示字符串
如果想用强化学习去实现扫雷.2048这种带有数字提示信息的游戏,自然是希望自定义 gym 环境时能把字符显示出来.上网查了很久,没有找到gym自带的图形工具Viewer可以显示字符串的信息,反而是通过 ...
- 深度强化学习:入门(Deep Reinforcement Learning: Scratching the surface)
RL的方案 两个主要对象:Agent和Environment Agent观察Environment,做出Action,这个Action会对Environment造成一定影响和改变,继而Agent会从新 ...
随机推荐
- 2017final英文语句格式简单检查
英文书写中,句首字母通常为大写,其余为小写,单词"I"除外,单词与单词之间用一个空格隔开,句中用","断句,句末用"."结束,", ...
- Effective C++ 总结笔记(三)
三.资源管理 13.以对象管理资源 1.为了防止资源泄漏,请使用RAII对象,在构造函数里面获得资源,并在析构函数里面释放资源. 2. 引用计数型智慧指针(RCSP):持续追踪多少个指针指向该资源,无 ...
- 性能优化 | Go Ballast 让内存控制更加丝滑
关于 Go GC 优化的手段你知道的有哪些?比较常见的是通过调整 GC 的步调,以调整 GC 的触发频率. 设置 GOGC 设置 debug.SetGCPercent() 这两种方式的原理和效果都是一 ...
- python爬取豆瓣电影第一页数据and使用with open() as读写文件
# _*_ coding : utf-8 _*_ # @Time : 2021/11/2 9:58 # @Author : 秋泊酱 # @File : 获取豆瓣电影第一页 # @Project : 爬 ...
- Java String 转成 二位数组
... package str; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.HashMap; impo ...
- Python 全局变量和局部变量,global 和 nonlocal关键字
全局变量和局部变量 全局变量:定义在函数外的变量 局部变量:定义在函数内部变量 获取变量值时候先获取当前作用域变量名称和变量值,如果没找到到上一层作用域招变量的值,在没有就报错,先获 ...
- [hdu6989]Didn't I Say to Make My Abilities Average in the Next Life?!
显然问题即求$\frac{\sum_{x\le l\le r\le y}(\max_{l\le i\le r}a_{i}+\min_{l\le i\le r}a_{i})}{(y-x+2)(y-x+1 ...
- [luogu2303]Longge的问题
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define ll long long 4 ll n,ans; 5 ll phi(l ...
- [noi109]排队
题目要求其实相当于要让大于和小于m的数的个数都不超过n/2,因此当要对一个数处理时,要么把它改成m,要么不作修改,根据这个贪心就可以完成了. 1 #include<bits/stdc++.h&g ...
- [bzoj1077]天平
先考虑如何求出任意两数的最大差值和最小差值,直接差分约束建图跑floyd求最短路和最长路即可然后枚举i和j,考虑dA+dB和di+dj的关系,分两种情况移项,转化成dA-di和dj-dB的关系或dA- ...
