Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) A B C D 水 二分 模拟
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Anton likes to play chess, and so does his friend Danik.
Once they have played n games in a row. For each game it's known who was the winner — Anton or Danik. None of the games ended with a tie.
Now Anton wonders, who won more games, he or Danik? Help him determine this.
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the number of games played.
The second line contains a string s, consisting of n uppercase English letters 'A' and 'D' — the outcome of each of the games. The i-th character of the string is equal to 'A' if the Anton won the i-th game and 'D' if Danik won the i-th game.
If Anton won more games than Danik, print "Anton" (without quotes) in the only line of the output.
If Danik won more games than Anton, print "Danik" (without quotes) in the only line of the output.
If Anton and Danik won the same number of games, print "Friendship" (without quotes).
6
ADAAAA
Anton
7
DDDAADA
Danik
6
DADADA
Friendship
In the first sample, Anton won 6 games, while Danik — only 1. Hence, the answer is "Anton".
In the second sample, Anton won 3 games and Danik won 4 games, so the answer is "Danik".
In the third sample, both Anton and Danik won 3 games and the answer is "Friendship".
题意:水
题解:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#define __int64 ll
using namespace std;
int n;
char a;
int s=,b=;
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
s=;
b=;
getchar();
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
{
scanf("%c",&a);
if(a=='A')
s++;
else
b++;
}
if(s>b)
cout<<"Anton"<<endl;
if(s<b)
cout<<"Danik"<<endl;
if(s==b)
cout<<"Friendship"<<endl;
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Recently Anton found a box with digits in his room. There are k2 digits 2, k3 digits 3, k5 digits 5 and k6 digits 6.
Anton's favorite integers are 32 and 256. He decided to compose this integers from digits he has. He wants to make the sum of these integers as large as possible. Help him solve this task!
Each digit can be used no more than once, i.e. the composed integers should contain no more than k2 digits 2, k3 digits 3 and so on. Of course, unused digits are not counted in the sum.
The only line of the input contains four integers k2, k3, k5 and k6 — the number of digits 2, 3, 5 and 6 respectively (0 ≤ k2, k3, k5, k6 ≤ 5·106).
Print one integer — maximum possible sum of Anton's favorite integers that can be composed using digits from the box.
5 1 3 4
800
1 1 1 1
256
In the first sample, there are five digits 2, one digit 3, three digits 5 and four digits 6. Anton can compose three integers 256 and one integer 32 to achieve the value 256 + 256 + 256 + 32 = 800. Note, that there is one unused integer 2 and one unused integer 6. They are not counted in the answer.
In the second sample, the optimal answer is to create on integer 256, thus the answer is 256.
题意:水
题解:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
ll a,b,c,d;
int main()
{
scanf("%I64d %I64d %I64d %I64d",&a,&b,&c,&d);
ll minx=;
minx=min(a,min(c,d));
ll ling=;
ll exm=max(ling,a-minx);
ll minx1=min(exm,b);
cout<<minx*+minx1*<<endl;
return ;
}
4 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Anton is playing a very interesting computer game, but now he is stuck at one of the levels. To pass to the next level he has to prepare n potions.
Anton has a special kettle, that can prepare one potions in x seconds. Also, he knows spells of two types that can faster the process of preparing potions.
- Spells of this type speed up the preparation time of one potion. There are m spells of this type, the i-th of them costs bi manapoints and changes the preparation time of each potion to ai instead of x.
- Spells of this type immediately prepare some number of potions. There are k such spells, the i-th of them costs di manapoints and instantly create ci potions.
Anton can use no more than one spell of the first type and no more than one spell of the second type, and the total number of manapoints spent should not exceed s. Consider that all spells are used instantly and right before Anton starts to prepare potions.
Anton wants to get to the next level as fast as possible, so he is interested in the minimum number of time he needs to spent in order to prepare at least n potions.
The first line of the input contains three integers n, m, k (1 ≤ n ≤ 2·109, 1 ≤ m, k ≤ 2·105) — the number of potions, Anton has to make, the number of spells of the first type and the number of spells of the second type.
The second line of the input contains two integers x and s (2 ≤ x ≤ 2·109, 1 ≤ s ≤ 2·109) — the initial number of seconds required to prepare one potion and the number of manapoints Anton can use.
The third line contains m integers ai (1 ≤ ai < x) — the number of seconds it will take to prepare one potion if the i-th spell of the first type is used.
The fourth line contains m integers bi (1 ≤ bi ≤ 2·109) — the number of manapoints to use the i-th spell of the first type.
There are k integers ci (1 ≤ ci ≤ n) in the fifth line — the number of potions that will be immediately created if the i-th spell of the second type is used. It's guaranteed that ci are not decreasing, i.e. ci ≤ cj if i < j.
The sixth line contains k integers di (1 ≤ di ≤ 2·109) — the number of manapoints required to use the i-th spell of the second type. It's guaranteed that di are not decreasing, i.e. di ≤ dj if i < j.
Print one integer — the minimum time one has to spent in order to prepare n potions.
20 3 2
10 99
2 4 3
20 10 40
4 15
10 80
20
20 3 2
10 99
2 4 3
200 100 400
4 15
100 800
200
In the first sample, the optimum answer is to use the second spell of the first type that costs 10 manapoints. Thus, the preparation time of each potion changes to 4 seconds. Also, Anton should use the second spell of the second type to instantly prepare 15 potions spending 80 manapoints. The total number of manapoints used is 10 + 80 = 90, and the preparation time is 4·5 = 20 seconds (15 potions were prepared instantly, and the remaining 5 will take 4 seconds each).
In the second sample, Anton can't use any of the spells, so he just prepares 20 potions, spending 10 seconds on each of them and the answer is 20·10 = 200.
题意:
题解:枚举第一种魔法 二分第二种魔法 取最优解
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
ll n,m,k;
ll x,s;
struct node
{
ll w;
ll cost;
} N[],M[],zha[];
bool check(int xx,ll cc)
{
if(M[xx].cost<=cc)
return true;
else
return false;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%I64d %I64d %I64d",&n,&m,&k);
scanf("%I64d %I64d",&x,&s);
N[].w=x;
N[].cost=;
M[].w=;
M[].cost=;
for(int i=; i<=m; i++)
scanf("%I64d",&N[i].w);
for(int i=; i<=m; i++)
scanf("%I64d",&N[i].cost);
for(int i=; i<=k; i++)
scanf("%I64d",&M[i].w);
for(int i=; i<=k; i++)
scanf("%I64d",&M[i].cost);
ll ans=n*x;
for(int i=; i<=m; i++)
{
if((s-N[i].cost)>=){
int l=,r=k,mid;
int aaa=;
while(l<=r)
{
mid=(l+r)/;
if(check(mid,s-N[i].cost))
{
aaa=mid;
l=mid+;
}
else
{
r=mid-;
}
}
if(M[aaa].w>=n)
ans=;
else
ans=min(ans,N[i].w*(n-M[aaa].w));
}
}
printf("%I64d\n",ans);
return ;
}
4 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Anton likes to play chess. Also, he likes to do programming. That is why he decided to write the program that plays chess. However, he finds the game on 8 to 8 board to too simple, he uses an infinite one instead.
The first task he faced is to check whether the king is in check. Anton doesn't know how to implement this so he asks you to help.
Consider that an infinite chess board contains one white king and the number of black pieces. There are only rooks, bishops and queens, as the other pieces are not supported yet. The white king is said to be in check if at least one black piece can reach the cell with the king in one move.
Help Anton and write the program that for the given position determines whether the white king is in check.
Remainder, on how do chess pieces move:
- Bishop moves any number of cells diagonally, but it can't "leap" over the occupied cells.
- Rook moves any number of cells horizontally or vertically, but it also can't "leap" over the occupied cells.
- Queen is able to move any number of cells horizontally, vertically or diagonally, but it also can't "leap".
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 500 000) — the number of black pieces.
The second line contains two integers x0 and y0 ( - 109 ≤ x0, y0 ≤ 109) — coordinates of the white king.
Then follow n lines, each of them contains a character and two integers xi and yi ( - 109 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 109) — type of the i-th piece and its position. Character 'B' stands for the bishop, 'R' for the rook and 'Q' for the queen. It's guaranteed that no two pieces occupy the same position.
The only line of the output should contains "YES" (without quotes) if the white king is in check and "NO" (without quotes) otherwise.
2
4 2
R 1 1
B 1 5
YES
2
4 2
R 3 3
B 1 5
NO
Picture for the first sample:
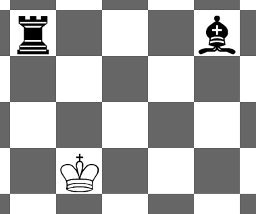 White king is in check, because the black bishop can reach the cell with the white king in one move. The answer is "YES".
White king is in check, because the black bishop can reach the cell with the white king in one move. The answer is "YES".
Picture for the second sample:
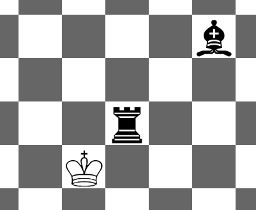 Here bishop can't reach the cell with the white king, because his path is blocked by the rook, and the bishop cant "leap" over it. Rook can't reach the white king, because it can't move diagonally. Hence, the king is not in check and the answer is "NO".
Here bishop can't reach the cell with the white king, because his path is blocked by the rook, and the bishop cant "leap" over it. Rook can't reach the white king, because it can't move diagonally. Hence, the king is not in check and the answer is "NO".
题意:国际象棋中 判断king是否被check
题解:模拟 找的8个方向最近的棋子
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
int n;
ll x,y;
ll xx[],yy[];
char a[];
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
scanf("%I64d %I64d",&x,&y);
a[]='#';
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
getchar();
scanf("%c %I64d %I64d",&a[i],&xx[i],&yy[i]);}
int s1=,s2=,s3=,s4=,s5=,s6=,s7=,s8=;
ll minx=1e10;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(xx[i]==x&&yy[i]>y){
if(minx>yy[i]){
s1=i;
minx=yy[i];
}
}
}
minx=-1e10;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(xx[i]==x&&yy[i]<y){
if(minx<yy[i]){
s2=i;
minx=yy[i];
}
}
}
minx=1e10;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(xx[i]>x&&yy[i]==y){
if(minx>xx[i]){
s3=i;
minx=xx[i];
}
}
}
minx=-1e10;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(xx[i]<x&&yy[i]==y){
if(minx<xx[i]){
s4=i;
minx=xx[i];
}
}
}
minx=1e10;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(xx[i]>x&&yy[i]>y&&(xx[i]-yy[i])==(x-y)){
if(minx>yy[i]){
s5=i;
minx=yy[i];
}
}
}
minx=-1e10;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(xx[i]<x&&yy[i]<y&&(xx[i]-yy[i])==(x-y)){
if(minx<yy[i]){
s6=i;
minx=yy[i];
}
}
}
minx=-1e10;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(xx[i]>x&&yy[i]<y&&(xx[i]+yy[i])==(x+y)){
if(minx<yy[i]){
s7=i;
minx=yy[i];
}
}
}
minx=1e10;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(xx[i]<x&&yy[i]>y&&(xx[i]+yy[i])==(x+y)){
if(minx>yy[i]){
s8=i;
minx=yy[i];
}
}
}
if((s1!=&&a[s1]!='B')||(s2!=&&a[s2]!='B')||(s3!=&&a[s3]!='B')
||(s4!=&&a[s4]!='B')||(s5!=&&a[s5]!='R')
||(s6!=&&a[s6]!='R')||(s7!=&&a[s7]!='R')||(s8!=&&a[s8]!='R'))
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
else
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) A B C D 水 二分 模拟的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) D. Anton and Chess 水题
D. Anton and Chess 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/734/problem/D Description Anton likes to play ...
- Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) B. Anton and Digits 水题
B. Anton and Digits 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/734/problem/B Description Recently Anton fou ...
- Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) A. Anton and Danik 水题
A. Anton and Danik 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/734/problem/A Description Anton likes to play ...
- Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) C. Anton and Making Potions —— 二分
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/734/problem/C C. Anton and Making Potions time limit per test 4 s ...
- Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) C. Anton and Making Potions 二分
C. Anton and Making Potions time limit per test 4 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input ...
- Codeforces Round #297 (Div. 2)A. Vitaliy and Pie 水题
Codeforces Round #297 (Div. 2)A. Vitaliy and Pie Time Limit: 2 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MBSubmit: xxx ...
- Codeforces Round #396 (Div. 2) A B C D 水 trick dp 并查集
A. Mahmoud and Longest Uncommon Subsequence time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 ...
- Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) Analyses By Team:Red & Black
A.Anton and Danik Problems: 给你长度为N的,只含'A','D'的序列,统计并输出何者出现的较多,相同为"Friendship" Analysis: lu ...
- Codeforces Round #379 (Div. 2) E. Anton and Tree 缩点 直径
E. Anton and Tree 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/734/problem/E Description Anton is growing a t ...
随机推荐
- iOS开发者证书申请过程
真机测试前准备工作:1.苹果的MAC一台.如果你用的是***不知道可不可以,反正我没用过...一般公司都会给你配开发工具的.2.iphone手机一部.(本人纯屌丝,用的iphone4)3.开发者账号. ...
- 高性能javascript(记录一)
脚本位置:将js脚本放置在body底部,由于脚本会阻塞页面渲染,导致明显延迟,通常表现为空白页面,用户无法游览页面的内容,也无法与页面进行交互.故因此推荐js脚本放在body底部,尽可能减少对整个页面 ...
- jdbc链接mysql插入数据后显示问号
1.在cmd中进入mysql查看默认的编码格式:mysql> show variables like "%char%"; 若不是utf8(因为我用的是utf8),关掉mysq ...
- textbox只能输入数字或中文的常用正则表达式和验证方法
验证数字的正则表达式集 验证数字:^[0-9]*$ 验证n位的数字:^\d{n}$ 验证至少n位数字:^\d{n,}$ 验证m-n位的数字:^\d{m,n}$ 验证零和非零开头的数字:^(0|[1-9 ...
- 入门struts2.0
框架是什么? 1.应用程序的半成品. 2.可重用行公共的结构. 3.按一定规则组织的一组组件. model2 其实并不是一种全新的概念,很对人指出model2其实正好是经典的"模型(mode ...
- LINUX centos 忘记密码
entos7采用的是grub2,和centos6.x进入单用户的方法不同.但是因为用的是真机环境无法截图,所以只是大概描述以下思路. init方法 1.centos7的grub2界面会有两个入口,正常 ...
- 黑马程序员——C语言基础 变量类型 结构体
Java培训.Android培训.iOS培训..Net培训.期待与您交流! (以下内容是对黑马苹果入学视频的个人知识点总结) (一)变量类型 1)局部变量 1> 定义:在函数内部定义的变量,称为 ...
- c语言-四阶龙格-库塔法
#include<stdio.h> #include<math.h> #define n 14 //double func1(double x, double y); doub ...
- centos上libreoffice+unoconv安装步骤,实现word转pdf
一.libreoffice安装 1.yum search libreoffice查询一下系统自带的安装包 安装libreoffice.x86_64这个就可以了 2.yum install lib ...
- matlab初学之textread
文章出处:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_9e67285801010bju.html 基本语法是: [A,B,C,-] = textread(filename,forma ...
