input子系统事件处理层(evdev)的环形缓冲区【转】
在事件处理层(evdev.c)中结构体evdev_client定义了一个环形缓冲区(circular buffer),其原理是用数组的方式实现了一个先进先出的循环队列(circular queue),用以缓存内核驱动上报给用户层的input_event事件。
struct evdev_client {
unsigned int head; // 头指针
unsigned int tail; // 尾指针
unsigned int packet_head; // 包指针
spinlock_t buffer_lock;
struct fasync_struct *fasync;
struct evdev *evdev;
struct list_head node;
unsigned int clk_type;
bool revoked;
unsigned long *evmasks[EV_CNT];
unsigned int bufsize; // 循环队列大小
struct input_event buffer[]; // 循环队列数组
};
evdev_client对象维护了三个偏移量:head、tail以及packet_head。head、tail作为循环队列的头尾指针记录入口与出口偏移,那么包指针packet_head有什么作用呢?
packet_head
内核驱动处理一次输入,可能上报一到多个input_event事件,为表示处理完成,会在上报这些input_event事件后再上报一次同步事件。头指针head以input_event事件为单位,记录缓冲区的入口偏移量,而包指针packet_head则以“数据包”(一到多个input_event事件)为单位,记录缓冲区的入口偏移量。
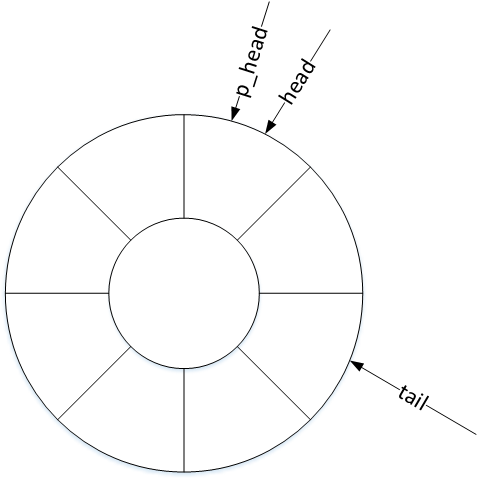
环形缓冲区的工作机制
- 循环队列入队算法:
head++;
head &= bufsize - 1;
- 循环队列出队算法:
tail++;
tail &= bufsize - 1;
- 循环队列已满条件:
head == tail
- 循环队列为空条件:
packet_head == tail
“求余”和“求与”
为解决头尾指针的上溢和下溢现象,使队列的元素空间可重复使用,一般循环队列的出入队算法都采用“求余”操作:
head = (head + 1) % bufsize; // 入队
tail = (tail + 1) % bufsize; // 出队
为避免计算代价高昂的“求余”操作,使内核运作更高效,input子系统的环形缓冲区采用了“求与”算法,这要求bufsize必须为2的幂,在后文中可以看到bufsize的值实际上是为64或者8的n倍,符合“求与”运算的要求。
环形缓冲区的构造以及初始化
用户层通过open()函数打开input设备节点时,调用过程如下:
open() -> sys_open() -> evdev_open()
在evdev_open()函数中完成了对evdev_client对象的构造以及初始化,每一个打开input设备节点的用户都在内核中维护了一个evdev_client对象,这些evdev_client对象通过evdev_attach_client()函数注册在evdev1对象的内核链表上。
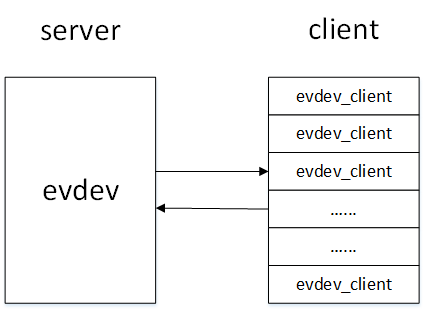
接下来我们具体分析evdev_open()函数:
static int evdev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
struct evdev *evdev = container_of(inode->i_cdev, struct evdev, cdev);
// 1.计算环形缓冲区大小bufsize以及evdev_client对象大小size
unsigned int bufsize = evdev_compute_buffer_size(evdev->handle.dev);
unsigned int size = sizeof(struct evdev_client) +
bufsize * sizeof(struct input_event);
struct evdev_client *client;
int error;
// 2. 分配内核空间
client = kzalloc(size, GFP_KERNEL | __GFP_NOWARN);
if (!client)
client = vzalloc(size);
if (!client)
return -ENOMEM;
client->bufsize = bufsize;
spin_lock_init(&client->buffer_lock);
client->evdev = evdev;
// 3. 注册到内核链表
evdev_attach_client(evdev, client);
error = evdev_open_device(evdev);
if (error)
goto err_free_client;
file->private_data = client;
nonseekable_open(inode, file);
return 0;
err_free_client:
evdev_detach_client(evdev, client);
kvfree(client);
return error;
}
在evdev_open()函数中,我们看到了evdev_client对象从构造到注册到内核链表的过程,然而它是在哪里初始化的呢?其实kzalloc()函数在分配空间的同时就通过__GFP_ZERO标志做了初始化:
static inline void *kzalloc(size_t size, gfp_t flags)
{
return kmalloc(size, flags | __GFP_ZERO);
}
生产者/消费者模型
内核驱动与用户程序就是典型的生产者/消费者模型,内核驱动产生input_event事件,然后通过input_event()函数写入环形缓冲区,用户程序通过read()函数从环形缓冲区中获取input_event事件。
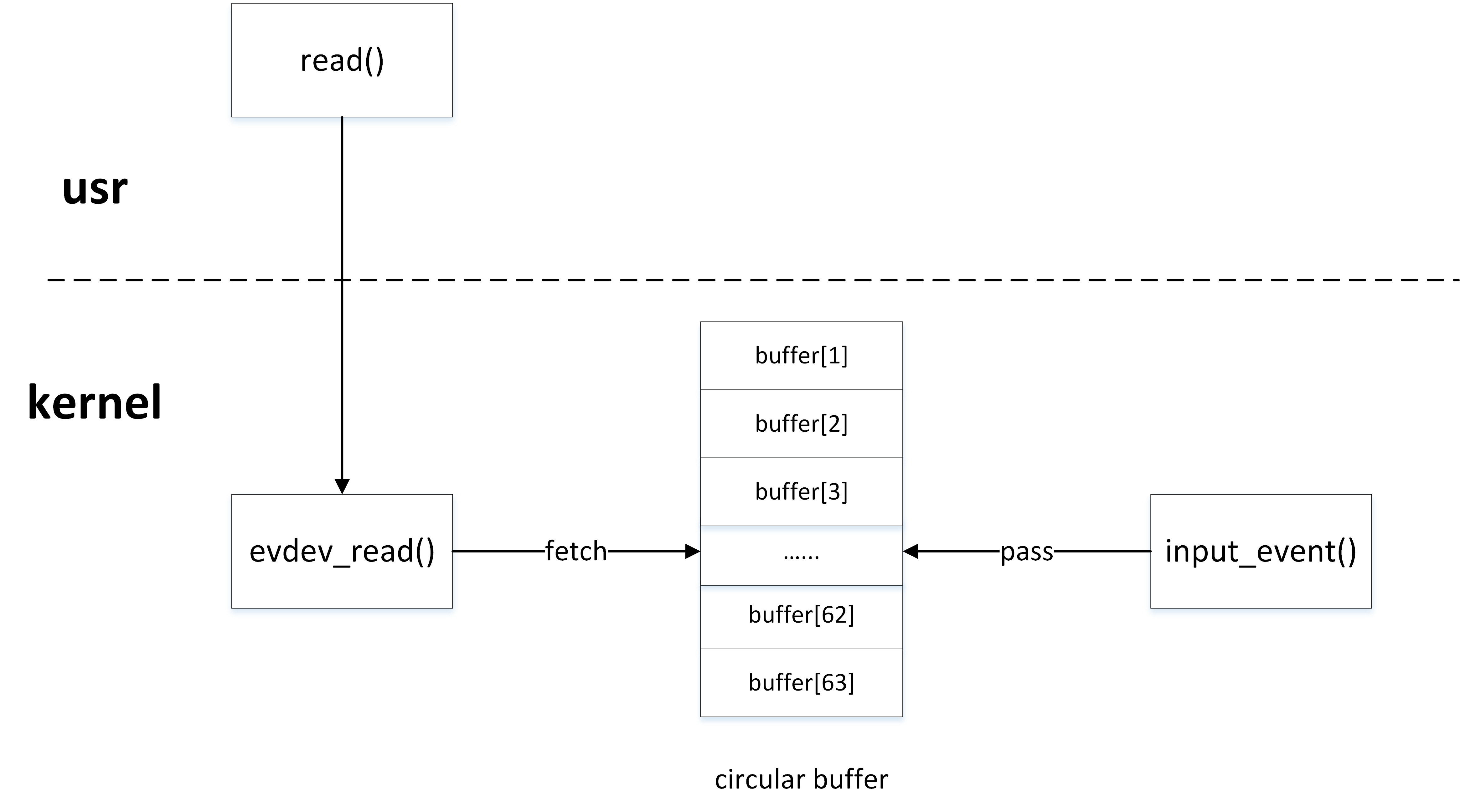
环形缓冲区的生产者
内核驱动作为生产者,通过input_event()上报input_event事件时,最终调用___pass_event()函数将事件写入环形缓冲区:
static void __pass_event(struct evdev_client *client,
const struct input_event *event)
{
// 将input_event事件存入缓冲区,队头head自增指向下一个元素空间
client->buffer[client->head++] = *event;
client->head &= client->bufsize - 1;
// 当队头head与队尾tail相等时,说明缓冲区空间已满
if (unlikely(client->head == client->tail)) {
/*
* This effectively "drops" all unconsumed events, leaving
* EV_SYN/SYN_DROPPED plus the newest event in the queue.
*/
client->tail = (client->head - 2) & (client->bufsize - 1);
client->buffer[client->tail].time = event->time;
client->buffer[client->tail].type = EV_SYN;
client->buffer[client->tail].code = SYN_DROPPED;
client->buffer[client->tail].value = 0;
client->packet_head = client->tail;
}
// 当遇到EV_SYN/SYN_REPORT同步事件时,packet_head移动到队头head位置
if (event->type == EV_SYN && event->code == SYN_REPORT) {
client->packet_head = client->head;
kill_fasync(&client->fasync, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
}
}
环形缓冲区的消费者
用户程序作为消费者,通过read()函数读取input设备节点时,最终在内核调用evdev_fetch_next_event()函数从环形缓冲区中读取input_event事件:
static int evdev_fetch_next_event(struct evdev_client *client,
struct input_event *event)
{
int have_event;
spin_lock_irq(&client->buffer_lock);
// 判缓冲区中是否有input_event事件
have_event = client->packet_head != client->tail;
if (have_event) {
// 从缓冲区中读取一次input_event事件,队尾tail自增指向下一个元素空间
*event = client->buffer[client->tail++];
client->tail &= client->bufsize - 1;
if (client->use_wake_lock &&
client->packet_head == client->tail)
wake_unlock(&client->wake_lock);
}
spin_unlock_irq(&client->buffer_lock);
return have_event;
}
input子系统事件处理层(evdev)的环形缓冲区【转】的更多相关文章
- 【Linux高级驱动】input子系统框架
[1.input子系统框架(drivers\input)] 如何得出某个驱动所遵循的框架? 1) 通过网络搜索 2) 自己想办法跟内核代码! 2.1 定位此驱动是属于哪种类 ...
- 【Linux高级驱动】input子系统框架【转】
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/lcw/p/3802617.html [1.input子系统框架(drivers\input)] 如何得出某个驱动所遵循的框架? 1) 通过网 ...
- 【驱动】input子系统全面分析
初识linux输入子系统 linux输入子系统(linux input subsystem)从上到下由三层实现,分别为:输入子系统事件处理层(EventHandler).输入子系统核心层(InputC ...
- linux输入子系统(6)-input子系统介绍及结构图
注:本系列转自: http://www.ourunix.org/post/290.html input子系统介绍 输入设备(如按键,键盘,触摸屏,鼠标,蜂鸣器等)是典型的字符设备,其一 ...
- input子系统详解
一.初识linux输入子系统 linux输入子系统(linux input subsystem)从上到下由三层实现,分别为:输入子系统事件处理层(EventHandler).输入子系统核心层(Inpu ...
- driver: Linux设备模型之input子系统详解
本节从整体上讲解了输入子系统的框架结构.有助于读者从整体上认识linux的输入子系统.在陷入代码分析的过程中,通过本节的知识能够找准方向,明白原理. 本节重点: 输入子系统的框架结构 各层对应内核中的 ...
- driver: Linux设备模型之input子系统具体解释
本节从总体上解说了输入子系统的框架结构.有助于读者从总体上认识linux的输入子系统.在陷入代码分析的过程中,通过本节的知识可以找准方向,明确原理. 本节重点: 输入子系统的框架结构 各层相应内核中的 ...
- linux kernel input 子系统分析
Linux 内核为了处理各种不同类型的的输入设备 , 比如说鼠标 , 键盘 , 操纵杆 , 触摸屏 , 设计并实现了一个对上层应用统一的试图的抽象层 , 即是Linux 输入子系统 . 输入子系统的层 ...
- Linux Input子系统
先贴代码: //input.c int input_register_handler(struct input_handler *handler) { //此处省略很多代码 list_for_each ...
随机推荐
- 用Eclipse导入Maven工程
步骤一 : 选择 “Import”操作 有两个途径可以选择 “Import”操作; 1>“File”--> "Import..." 2> 在 "Pro ...
- 2018.4.24-ml笔记(多元线性回归)
numpy.dot作用于两个向量则是它们内积,作用于矩阵则是矩阵积. RMSE解决量纲问题,即单位 RMSE会放大差值比较大的值,所以选用MSE更好.
- LeetCode刷题指南(字符串)
作者:CYC2018 文章链接:https://github.com/CyC2018/CS-Notes/blob/master/docs/notes/Leetcode+%E9%A2%98%E8%A7% ...
- 前端通信:ajax设计方案(十)--- 完善Promise A+规范,增加mock数据功能
半年不迭代,迭代搞半年,说的就是我,这里有点尴尬了,直接进入主题吧 我记得在这篇博客的时候集成了Promise的,不过那个时候就简简单单的写了一点最基础,在一些特殊的case上,还是有点问题的,所以才 ...
- Linux命令yum和rpm
yum命令使用 可以简化软件安装命令 yum可以做软件的 1自动安装,安装软件的时候会自动安装需要的依赖 yum install 软件名如安装epel源yum install epel-release ...
- RabbitMQ Exchange详解以及Spring中Topic实战
前言 AMQP,即Advanced Message Queuing Protocol,高级消息队列协议,是应用层协议的一个开放标准,为面向消息的中间件设计.消息中间件主要用于组件之间的解耦. 业务需求 ...
- Filebeat+Kafka+Logstash+ElasticSearch+Kibana 日志采集方案
前言 Elastic Stack 提供 Beats 和 Logstash 套件来采集任何来源.任何格式的数据.其实Beats 和 Logstash的功能差不多,都能够与 Elasticsearch 产 ...
- Java设计模式学习记录-桥接模式
前言 这次介绍结构型设计模式中的第二种模式,桥接模式. 使用桥接模式的目的就是为了解耦,松散的耦合更利于扩展,但是会增加相应的代码量和设计难度. 桥接模式 桥接模式是为了将抽象化与实现化解耦,让二者可 ...
- python装饰器带括号和不带括号的语法和用法
装饰器的写法补充: 通常装饰器的写法是@func(),而有的时候为了减少出错率,可能会写成@func,没有()括号,这时我们可以这样定义,来减少括号.下面通过两个例子还看. 一般装饰器的写法: def ...
- HAPRoxy(一):HAProxy基本配置、调度算法与tcp、http、heath模式配置示例
一.HAProxy安装 1.HAProxy简单介绍 HAProxy虽然名字前有HA,但它并不是一款高可用软件,而是一款用于实现负载均衡的软件,可实现四层与七层的负载均衡. 2.yum安装HAProxy ...
