Java数据结构与排序算法——堆和堆排序


//=================================================
// File Name : Heap_demo
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Author : Common //类名:Node_Heap
//属性:
//方法:
class Node_Heap{
public int iData; public Node_Heap(int iData) { //构造函数
super();
this.iData = iData;
} public int getiData() {
return iData;
} public void setiData(int iData) {
this.iData = iData;
}
} //类名:Heap
//属性:
//方法:
class Heap{
private Node_Heap[] heapArray;
public int maxSize;
private int currentSize; public Heap(int maxSize) { //构造函数
super();
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.currentSize = 0;
heapArray = new Node_Heap[maxSize];
} public boolean isEmpty(){
return currentSize ==0;
} public boolean insert(int key){
if(currentSize == maxSize){
return false;
}
Node_Heap newNode = new Node_Heap(key);
heapArray[currentSize] = newNode; //把插入的节点放在最后的位置
trickleUp(currentSize++); //插入节点并把currentSize加1
return true;
} //用于插入,把父类节点下移,然后把插入的节点放到合适的位置
public void trickleUp(int index){
int parent = (index-1)/2;
Node_Heap bottom = heapArray[index]; //暂存新插入的节点,因为需要把父节点下移
while(index>0 && heapArray[parent].getiData()<bottom.getiData()){ //如果小,就下移
heapArray[index] = heapArray[parent]; //把父类节点下移
index = parent; //用于递归
parent = (parent-1)/2;
}
heapArray[index] = bottom; //把插入的节点放到合适的位置
} public Node_Heap remove(){ //删除最大的节点
Node_Heap root = heapArray[0];
heapArray[0]=heapArray[--currentSize];
trickleDown(0);
return root;
} //用于删除,把子类节点上移
public void trickleDown(int index){
int largerChild;
Node_Heap top = heapArray[index]; //
while(index<currentSize/2){ //如果小,就下移
int leftChild = 2*index+1;
int rightChild = leftChild+1;
if(rightChild<currentSize && heapArray[leftChild].getiData() < heapArray[rightChild].getiData())
largerChild = rightChild;
else
largerChild = leftChild;
if(top.getiData()>=heapArray[largerChild].getiData())
break;
heapArray[index] = heapArray[largerChild];
index = largerChild;
}
heapArray[index] = top;
} public void displayHeap(){
System.out.print("heapArray:");
for(int i=0;i<heapArray.length;i++){
if(heapArray[i] != null)
System.out.print(heapArray[i].getiData()+" ");
else
System.out.print(" -- ");
}
System.out.println(); int nBlanks = 32; //定义空格
int itemsPerRow = 1;
int column = 0;
int j=0; //标记当前的数组下标,从0开始
System.out.println("......................................................");
while(currentSize > 0){
if(column == 0){
for(int i=0;i<nBlanks;i++){
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
System.out.print(heapArray[j].getiData());
if(++j == currentSize){
break;
}
if(++column==itemsPerRow){ //如果每一行计数等于这一行的上限,则换行
nBlanks /= 2; //空格数减半
itemsPerRow *= 2; //每一行的上限
column = 0;
System.out.println();
}else{
for(int i=0;i<nBlanks*2-2;i++){
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
}
System.out.println("\n"+"......................................................");
} } //主类
//Function : Heap_demo
public class Heap_demo { public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
int anArrays[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
Heap theHeap = new Heap(31);
// theHeap.insert(1);
// theHeap.insert(2);
// theHeap.insert(3);
// theHeap.insert(4);
// theHeap.insert(5);
// theHeap.insert(6);
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
theHeap.insert(anArrays[i]);
}
theHeap.displayHeap();
//theHeap.remove();
//theHeap.displayHeap();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
anArrays[i]=theHeap.remove().iData;
}
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
System.out.print(anArrays[i]+" ");
}
} }

Java数据结构与排序算法——堆和堆排序的更多相关文章
- JAVA数据结构(十一)—— 堆及堆排序
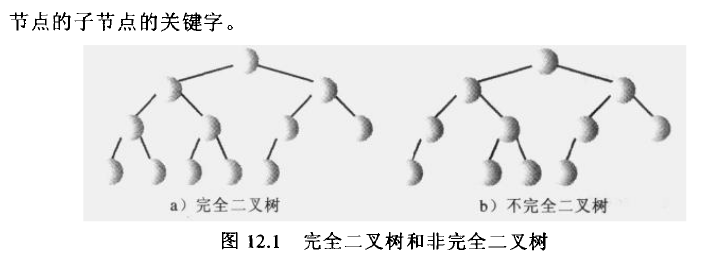
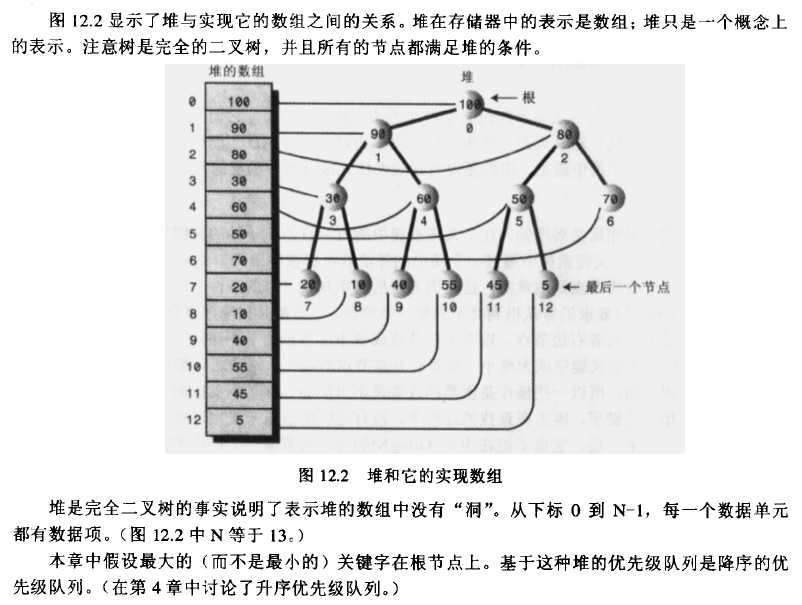
堆 堆基本介绍 堆排序是利用堆这种数据结构而设计的一种排序算法,堆排序是一种选择排序,最坏,最好,平均时间复杂度都是O(nlogn),不稳定的排序 堆是具有以下性质的完全二叉树:每个节点的值都大于或等 ...
- 【Java】 大话数据结构(16) 排序算法(3) (堆排序)
本文根据<大话数据结构>一书,实现了Java版的堆排序. 更多:数据结构与算法合集 基本概念 堆排序种的堆指的是数据结构中的堆,而不是内存模型中的堆. 堆:可以看成一棵完全二叉树,每个结点 ...
- Java中的数据结构及排序算法
(明天补充) 主要是3种接口:List Set Map List:ArrayList,LinkedList:顺序表ArrayList,链表LinkedList,堆栈和队列可以使用LinkedList模 ...
- 数据结构和算法(Golang实现)(24)排序算法-优先队列及堆排序
优先队列及堆排序 堆排序(Heap Sort)由威尔士-加拿大计算机科学家J. W. J. Williams在1964年发明,它利用了二叉堆(A binary heap)的性质实现了排序,并证明了二叉 ...
- Java中的排序算法(2)
Java中的排序算法(2) * 快速排序 * 快速排序使用分治法(Divide and conquer)策略来把一个序列(list)分为两个子序列(sub-lists). * 步骤为: * 1. 从数 ...
- java实现各种排序算法
java实现各种排序算法 import java.util.Arrays; public class SomeSort { public static void main(String[] args) ...
- Java学习笔记——排序算法之进阶排序(堆排序与分治并归排序)
春蚕到死丝方尽,蜡炬成灰泪始干 --无题 这里介绍两个比较难的算法: 1.堆排序 2.分治并归排序 先说堆. 这里请大家先自行了解完全二叉树的数据结构. 堆是完全二叉树.大顶堆是在堆中,任意双亲值都大 ...
- 数据结构Java版之排序算法(二)
排序按时间复杂度和空间复杂度可分为 低级排序 和 高级排序 算法两种.下面将对排序算法进行讲解,以及样例的展示. 低级排序:冒泡排序.选择排序.插入排序. 冒泡排序: 核心思想,小的数往前移.假设最小 ...
- Java实现常见排序算法
常见的排序算法有冒泡排序.选择排序.插入排序.堆排序.归并排序.快速排序.希尔排序.基数排序.计数排序,下面通过Java实现这些排序 1.冒泡排序 package com.buaa; import j ...
随机推荐
- 1025基础REDIS
-- 登录AUTHPING -- 通用命令EXISTS KEY EXPIRE KEY seconds 为给定 KEY 设置过期时间 -- 字符SET runoobkey redisDEL runoob ...
- php csv导出
/** * 下载csv * @param unknown $orders_id * @param unknown $orders_date_start * @param unknown $orders ...
- linux core dump 文件 gdb分析
core dump又叫核心转储, 当程序运行过程中发生异常, 程序异常退出时, 由操作系统把程序当前的内存状况存储在一个core文件中, 叫core dump. (linux中如果内存越界会收到SIG ...
- 利用反射,泛型,静态方法快速获取表单值到Model
在项目中经常需要处理表单,给model赋值,很烦人的一些重复代码.如下边的代码: News news = new News(); news.Id = int.Parse(Request.Form[&q ...
- [转]javascript Date format(js日期格式化)
方法一:这个很不错,好像是 csdn 的 Meizz 写的: // 对Date的扩展,将 Date 转化为指定格式的String // 月(M).日(d).小时(h).分(m).秒(s).季度(q) ...
- ES6 变量的解构赋值
数组的解构赋值 var [a,b,c] = [1,2,3]; 左边是变量,右边是值,根据数据结构一一对应 只要等号两边的模式相同,左边的变量就会被赋予右边对应的值,必须模式相同 如果等号 ...
- angular指令大全
这篇文章的案例都是来自官方,引用的cdn来自bootcss, 因为angular的官方网站被屏了, 所以要翻, 不过我把整个文档下回来了,方便大家下载可以点击: 打开下载英文版 angular的指令 ...
- eclipse-搭建maven的war项目集合spring注解方式
工具:eclipse 4.4.2 版本号:20150219-0600 jdk:1.7 1.下图创建maven工程,然后next 下图选择工程保存位置(这里选择默认),next 下图选择webapp项目 ...
- HTTP之referer(网上搜集)
1.打开httpfox抓包插件,在百度中搜索126.com,搜索项中点击网站入口,通过抓包工具,查看http请求 在http请求的Headers部分可见Referer. Referer http:// ...
- Python列表、元组、字典和字符串的常用函数
Python列表.元组.字典和字符串的常用函数 一.列表方法 1.ls.extend(object) 向列表ls中插入object中的每个元素,object可以是字符串,元组和列表(字符串“abc”中 ...
