【extjs6学习笔记】1.7 初始:加载第三方库
https://www.sencha.com/blog/integrating-ext-js-with-3rd-party-libraries-2/
Introduction
Ext JS provides a lot of built-in components right out of the box that are highly customizable. If it's not in the framework, you can easily extend the classes or even browse Sencha Market for anything you might need. That works great most of the time, but sometimes you might want to use a 3rd party library that is not built using the Ext JS component system. There are a number of ways you can address this situation, but the easiest one is to create a custom wrapper component to handle your library, which can be reused across any of your apps.
Implementation Overview
The goal of your wrapper component is to encapsulate the logic required by the 3rd party library to set itself up and interact with the Ext JS framework. You have the freedom over how much of that 3rd party API is available to use in your application. There are a few options for how you handle this. If the library is relatively simple and you want to control access to the API, you could wrap each of the API methods with a corresponding method in your wrapper. This allows you to hide methods you don't want exposed or intercept method calls where you want to introduce additional custom logic. Another option would be to expose some of the root objects in the API, so other controls are free to call any of the API methods directly on the object. In most cases, this would probably be the approach you'd end up with, but all projects are different.
To demonstrate this idea, we'll create a wrapper component around Leaflet, an open source mapping JavaScript library created by Vladimir Agafonkin. We'll use that wrapper component in an app that shows us a map and provides a button to move the map to a specified location.
Leaflet can integrate with mapping tiles from many different mapping services which gives you great flexibility in how your maps look. In this example, we'll use some map tiles provided by CloudMade. You can register for a free account there, where you'll get an API key to use in your requests (we'll use it later in this example). For more information about map tiles, visit the Leaflet site.
Add Library References
The first thing you'll need to do in your app is add the library references to your HTML file, so the library will be available for you to use. In our example, we'll add two lines to the head per the Leaflet docs. You can get more details on the Leaflet setup in the Leaflet Quick Start Guide.
<link rel="stylesheet" href="http://cdn.leafletjs.com/leaflet-0.5/leaflet.css" />
<script src="http://cdn.leafletjs.com/leaflet-0.5/leaflet.js"></script>
Build the Custom Component
The next thing we'll want to do is extend Ext.Component to create the wrapper component for Leaflet. Ext.Component will give us a bare bones control with an empty UI, but it has all the framework methods needed for it to play nice in any of the layouts.
When integrating with a third party library, we typically need to configure and initialize it to match our needs. For our example, we're going to handle our Leaflet initialization in an override of the 'afterRender' method. This method runs when our custom component has been rendered to the DOM and is ready for us to interact with. We'll also add a class alias and a config variable for our map reference.
Ext.define('Ext.ux.LeafletMapView', {
extend: 'Ext.Component',
alias: 'widget.leafletmapview',
config:{
map: null
},
afterRender: function(t, eOpts){
this.callParent(arguments);
var leafletRef = window.L;
if (leafletRef == null){
this.update('No leaflet library loaded');
} else {
var map = L.map(this.getId());
map.setView([42.3583, -71.0603], 13);
this.setMap(map);
L.tileLayer('http://{s}.tile.cloudmade.com/{key}/{styleId}/256/{z}/{x}/{y}.png', {
key: 'YOUR_API_KEY',
styleId: 997,
maxZoom: 18
}).addTo(map);
}
}
});
Stepping through the 'afterRender' code:
var leafletRef = window.L;
if (leafletRef == null){
this.update('No leaflet library loaded');
} else {
....
}
We try to get access to the Leaflet library which is loaded in the window.L namespace. If we can't get a reference to the library, we'll update the component html with a message stating there was an error loading the library.
var map = L.map(this.getId());
Here we create a Leaflet map object passing in the ID of the Ext JS component. By default, the HTML tag created by Ext.Component will be a div, which is what Leaflet requires to initialize the map control. Rather than hard code an ID to reference the div, we'll use the ID generated by the Ext framework when it renders the control. This will allow us to have multiple instances of the control in our application.
map.setView([42.3583, -71.0603], 13);
This will set the map to the latitude/longitude of the Boston, MA area using a zoom level of 13. There are many online tools for looking up lat/lon's for different locations.
this.setMap(map);
Sets the map reference to our map variable so we can access it later.
L.tileLayer('http://{s}.tile.cloudmade.com/{key}/{styleId}/256/{z}/{x}/{y}.png', {
key: 'YOUR_API_KEY',
styleId: 997,
maxZoom: 18
}).addTo(map);
This will configure Leaflet to use CloudMade's map tiles. Assuming you created an account with them and registered your application, you'll get an API key that you will provide in place of 'YOUR_API_KEY'. Don't worry about the confusing URL, that is how Leaflet will dynamically load your tiles when you move around the map. For additional info, I'd recommend reviewing the Leaflet API docs.
At this point, you'll have a basic mapping control you can use in your applications. However, we're not quite done. If you use it as-is, you might not see what you expect. The sizing will not fit your layout. Leaflet requires us to call a method named 'invalidateSize()' any time the map size changes, and it then renders to that size. This is an easy problem to solve in our wrapper component. We can override the 'onResize' method, which gets called anytime the size is changed in the layout, and call the 'invalidateSize' method on the map.
We'll add this to our control:
onResize: function(w, h, oW, oH){
this.callParent(arguments);
var map = this.getMap();
if (map){
map.invalidateSize();
}
}
This will get called anytime the layout changes, and we'll see if we have a valid map reference. If we do, then we'll tell Leaflet to 'invalidateSize'.
Now we can use the component in our layout, and you can see that it'll respect the layout dimensions we're providing for it. If the layout changes due to a browser re-size or a slider, you'll see the new size get applied. With just a couple lines of code in our custom wrapper component, we've made the third party Leaflet control play nice with the Ext JS layout system.
Sample Usage
Let's build a simple Ext JS app that uses this new wrapper component.
Ext.Loader.setConfig({
enabled: true,
paths:{
'Ext.ux':'ux'
}
});
Ext.require(['Ext.ux.LeafletMapView']);
Ext.onReady(function() {
Ext.create('Ext.container.Viewport', {
layout: 'vbox',
items: [
{
xtype: 'leafletmapview',
flex: 1,
width: '100%'
}
]
})
});
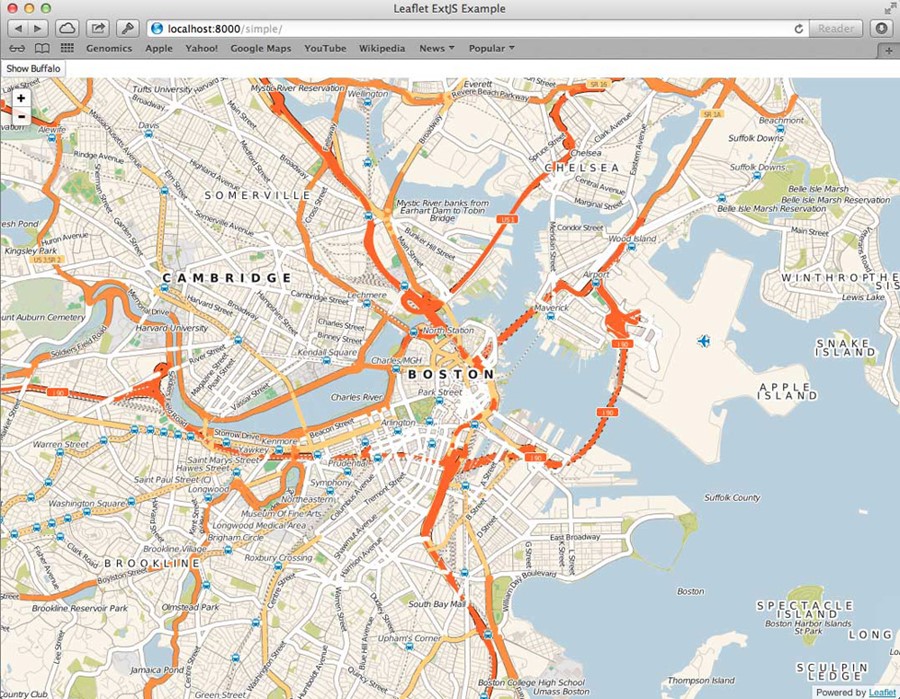
This will create a viewport to use the browser's full size and render out our map to use the whole view. You should see a large map of the Boston area with some simple zoom controls.
The next thing we'll want to do is handle interacting with the map from some outside controls. Let's add a button and have it zoom to a location on the map when clicked. According to the Leaflet docs, all you need to do is call 'setView' on the map object, passing in a coordinate array of the latitude/longitude and a zoom level. So all we have to do is have our wrapper component expose the map object we created in 'afterRender', and then we can have the button access that object and call that method on it.
Place this control above our map control in the viewport items array:
{
xtype: 'button',
text: 'Show Buffalo',
listeners:{
click: function(){
var map = Ext.ComponentQuery.query("viewport leafletmapview")[0];
map.getMap().setView([42.8864, -78.8786], 13);
}
}
}
The above code will display a button where when it's clicked will try to get a reference to the map object and update it's view to a new location. There are many ways to reference a component in an Ext JS application, including Controller refs, Ext.ComponentQuery(), etc. For convenience in this example, we'll use a component query to find our map component in this viewport. Once we have the reference, we can call 'getMap' to get the Leaflet map instance and call any Leaflet API methods directly on it.
From here, you can be as fancy as you'd like your component to get. You can add config properties for all the required setup parameters so you could customize each instance of the component using Ext JS configuration parameters instead of the third party library's conventions. You could also add new properties to toggle library features. For example, you could add a property to enable Leaflet's 'locate' ability, which will attempt to use your browser's Geolocation API to find your location. You can see a more complete example in my GitHub repository.
Conclusion
All libraries are different, and may present additional challenges, but this concept will help you get your Ext JS or Sencha Touch apps integrated with them. There are a number of wrapper components available in the Sencha Market and GitHub already, so you may not need to create your own. But if one doesn't exist for a library you need, now you know how to create your own and share it with the rest of the Sencha developer community.
Written by Kevin Kazmierczak
来自 <https://www.sencha.com/blog/integrating-ext-js-with-3rd-party-libraries-2/>
翻译:
http://blog.csdn.net/tianxiaode/article/details/9178861
说明:
官网论坛上描述如下
That's a really old blog post you are referring to. Nowadays, preferred way is to reference third party library in app.json. Simply add your 3rd party javascript to JS array and css to CSS array:
Code:
"js": [
{
"path": "app.js",
"bundle": true,
"update": "full"
},
{
"path": "resources/introjs/intro.min.js"
}
],
"css": [
{
"path": "${build.out.css.path}",
"bundle": true,
"exclude": ["fashion"],
"update": "full"
},
{
"path": "resources/introjs/introjs.min.css"
}]
The files will be copied to build folder and loaded automatically when application starts.
来自 <https://www.sencha.com/forum/showthread.php?330047>
【extjs6学习笔记】1.7 初始:加载第三方库的更多相关文章
- [置顶] iOS学习笔记47——图片异步加载之EGOImageLoading
上次在<iOS学习笔记46——图片异步加载之SDWebImage>中介绍过一个开源的图片异步加载库,今天来介绍另外一个功能类似的EGOImageLoading,看名字知道,之前的一篇学习笔 ...
- Flutter学习笔记(19)--加载本地图片
如需转载,请注明出处:Flutter学习笔记(19)--加载本地图片 上一篇博客正好用到了本地的图片,记录一下用法: 首先新建一个文件夹,这个文件夹要跟目录下 然后在pubspec.yaml里面声明出 ...
- XV6学习笔记(1) : 启动与加载
XV6学习笔记(1) 1. 启动与加载 首先我们先来分析pc的启动.其实这个都是老生常谈了,但是还是很重要的(也不知道面试官考不考这玩意), 1. 启动的第一件事-bios 首先启动的第一件事就是运行 ...
- [OpenCV学习笔记3][图像的加载+修改+显示+保存]
正式进入OpenCV学习了,前面开始的都是一些环境搭建和准备工作,对一些数据结构的认识主要是Mat类的认识: [1.学习目标] 图像的加载:imread() 图像的修改:cvtColor() 图像的显 ...
- Quartz.net 2.x 学习笔记03-使用反射加载定时任务
将定时任务信息存储在XML文件中,使用反射加载定时任务 首先新建一个MVC的空站点,使用NuGet添加对Quartz.net和Common.Logging.Log4Net1213的引用,同时使用NuG ...
- 【OpenCV学习笔记之一】图像加载,修改及保存
加载图像(用cv::imread)imread功能是加载图像文件成为一个Mat对象 其中第一个参数表示图像文件名称第二个参数 表示加载的图像是什么类型 支持常见的三个参数值IMREAD_UNCHANG ...
- WMS学习笔记:1.尝试加载WMS
1.首先找一个可用的WMS栅格地图服务:http://demo.cubewerx.com/demo/cubeserv/cubeserv.cgi 获取GetCapabilities: http://de ...
- Android学习笔记_51_转android 加载大图片防止内存溢出
首先来还原一下堆内存溢出的错误.首先在SD卡上放一张照片,分辨率为(3776 X 2520),大小为3.88MB,是我自己用相机拍的一张照片.应用的布局很简单,一个Button一个ImageView, ...
- Android学习笔记_36_ListView数据异步加载与AsyncTask
一.界面布局文件: 1.加入sdcard写入和网络权限: <!-- 访问internet权限 --> <uses-permission android:name="andr ...
- Laravel 学习笔记之 Composer 自动加载
说明:本文主要以Laravel的容器类Container为例做简单说明Composer的自动加载机制. Composer的自动加载机制 1.初始化一个composer项目 在一个空目录下compose ...
随机推荐
- 最短路径 一 Dijkstra 模板(O(n^2))
题目传送:http://hihocoder.com/problemset/problem/1081 #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #i ...
- va_list函数学习
当你的函数的参数个数不确定时,就可以使用上述宏进行动态处理,这无疑为你的程序增加了灵活性. va_list的使用方法: a) 首先在函数中定义一个具有va_list型的变量,这个变量是指向参数的指针 ...
- JavaScript高级程序设计学习笔记第一章
作为学习javascript的小白,为了督促自己读书,写下自己在读书时的提炼的关键点. 第一章: 1.JavaScript简史:Netscape Navigator中的JavaScript与Inter ...
- WPF ChangePropertyAction中TargetName和TargetObject的区别
在wpf页面布局中经常用到ChangePropertyAction来更改属性,在这个里面有TargetName和TargetObject两个属性,都表示需要修改的控件名称,那么这两个有什么区别呢,通过 ...
- java 获取路径与各文件目录的…
java 获取路径 博客分类: MyJava JavaJSPWebTomcat编程 转至:http://geeksun.iteye.com/blog/356339 (1).request.getRe ...
- phpcms后台栏目权限修改无效的原因和解决方法
现象:在phpcms后台中,新建角色,然后修改角色对应栏目权限,结果一直只能选择一半数量的栏目.剩下的栏目怎么修改都不生效. 对比: step1:再另一个phpcms后台做同样操作,依旧是这个结果.跟 ...
- c/c++语言实现tesseract ocr引擎编程实例
编译下面的程序操作系统必须在安装了tesseract库和leptonica库才可以 Basic example c++ code: #include <tesseract/baseapi.h&g ...
- 1.4 DVWA亲测文件上传漏洞
Low 先看看源代码: <?php if(isset( $_POST[ 'Upload' ] ) ) { // Where are we going to be writing to? $tar ...
- POJ 3281 Dining (网络流之最大流)
题意:农夫为他的 N (1 ≤ N ≤ 100) 牛准备了 F (1 ≤ F ≤ 100)种食物和 D (1 ≤ D ≤ 100) 种饮料.每头牛都有各自喜欢的食物和饮料, 而每种食物或饮料只能分配给 ...
- Docker环境下的前后端分离项目部署与运维(七)Redis高速缓存
Redis高速缓存 利用内存保存数据,读写速度远超硬盘:可以减少I/O操作,降低I/O压力. 发红包.抢红包的数据可以存在高速缓存中,加快处理速度,不需要经过数据库 淘宝首页一些优惠活动商品等热数据可 ...
