FCN笔记
FCN.py
- tensorflow命令行参数
FLAGS = tf.flags.FLAGS
tf.flags.DEFINE_integer("batch_size", "2", "batch size for training")
tf.flags.DEFINE_string("logs_dir", "logs/", "path to logs directory")
tf.flags.DEFINE_string("data_dir", "Data_zoo/MIT_SceneParsing/", "path to dataset")
tf.flags.DEFINE_float("learning_rate", "1e-5", "Learning rate for Adam Optimizer")
tf.flags.DEFINE_string("model_dir", "Model_zoo/", "Path to vgg model mat")
tf.flags.DEFINE_bool('debug', "False", "Debug mode: True/ False")
tf.flags.DEFINE_string('mode', "train", "Mode train/ test/ visualize")
深度学习神经网络往往有过多的Hyperparameter需要调优,优化算法、学习率、卷积核尺寸等很多参数都需要不断调整,使用命令行参数是非常方便的。有两种实现方式,一是调用tensorflow自带的app.flags(FCN用到的),一是利用python的argparse包实现。
1.利用tf.app.flags组件
TensorFlow项目例子中经常出现tf.app.flags,这个好像和tf.flags是一样,加不加中间的app没区别(要是不是这样还请大家指出错误之处),它支持应用从命令行接受参数,可以用来指定集群配置等。下面是个例子。
import tensorflow as tf
#调用flags内部的DEFINE_string函数来制定解析规则
tf.flags.DEFINE_string("para_name_1","default_val", "description")
tf.flags.DEFINE_integer("batch_size", 64, "Batch Size (default: 64)")
tf.flags.DEFINE_integer("num_epochs", 10, "Number of training epochs (default: 10)")
#FLAGS是一个对象,保存了解析后的命令行参数
FLAGS = tf.flags.FLAGS
FLAGS._parse_flags()#进行解析,加上这一句可以把FLAGS.__flags变成一个字典
print(FLAGS.batch_size)#运行结果输出64
print(FLAGS.__flags)#运行结果见下图
重点:它可以从命令行接受参数。
python FCN.py --mode=visualize
2.利用python的argparse包
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--echo", type=str,help="echo the string you use here")
parser.add_argument("--square", type=int, help="display a square of a given number")
args = parser.parse_args()
print(args.echo)
print(args.square**2)
这里第一个参数调用了系统的echo工具,将函数名称后的字符串打印在控制台显示。第二个参数做了平方运算。运行:
python argparse_example.py --echo ‘hello!’ --square 4

- 调用VGG
def vgg_net(weights, image):
## fcn的前五层网络就是vgg网络
layers = (
'conv1_1', 'relu1_1', 'conv1_2', 'relu1_2', 'pool1',
'conv2_1', 'relu2_1', 'conv2_2', 'relu2_2', 'pool2',
'conv3_1', 'relu3_1', 'conv3_2', 'relu3_2', 'conv3_3',
'relu3_3', 'conv3_4', 'relu3_4', 'pool3',
'conv4_1', 'relu4_1', 'conv4_2', 'relu4_2', 'conv4_3',
'relu4_3', 'conv4_4', 'relu4_4', 'pool4',
'conv5_1', 'relu5_1', 'conv5_2', 'relu5_2', 'conv5_3',
'relu5_3', 'conv5_4', 'relu5_4'
)
net = {}
current = image
for i, name in enumerate(layers):
kind = name[:4]
if kind == 'conv':
kernels, bias = weights[i][0][0][0][0]
# matconvnet: weights are [width, height, in_channels, out_channels]
# tensorflow: weights are [height, width, in_channels, out_channels]
kernels = utils.get_variable(np.transpose(kernels, (1, 0, 2, 3)), name=name + "_w")
bias = utils.get_variable(bias.reshape(-1), name=name + "_b")
current = utils.conv2d_basic(current, kernels, bias)
elif kind == 'relu':
current = tf.nn.relu(current, name=name)
if FLAGS.debug:
utils.add_activation_summary(current)
elif kind == 'pool':
current = utils.avg_pool_2x2(current)
net[name] = current
return net
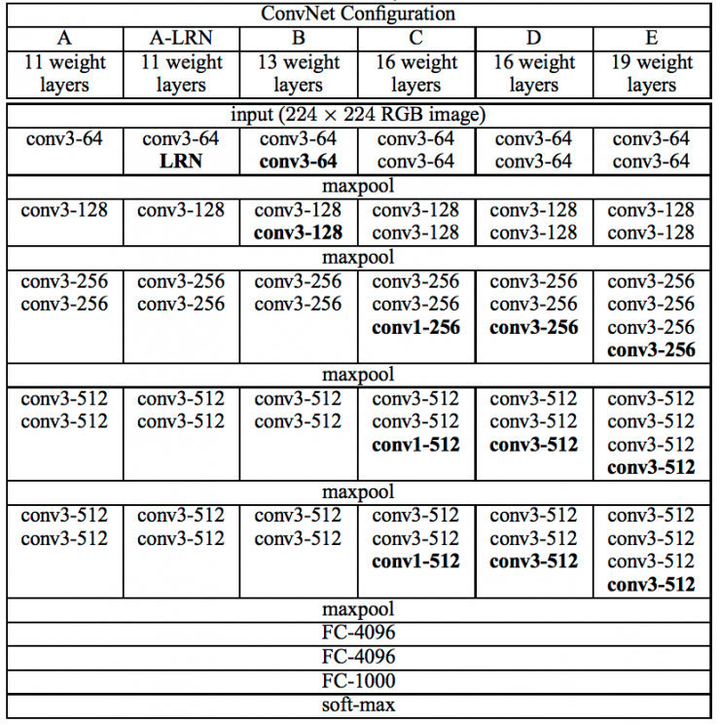 VGGNet各级别网络结构图,FCN用VGG-19
VGGNet各级别网络结构图,FCN用VGG-19
1.kernels, bias = weights[i][0][0][0][0]
weights 是vgg网络各层的权重集合,存储格式mat:MODEL_URL = 'http://www.vlfeat.org/matconvnet/models/beta16/imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat'
kernels的获取方式是weights[第i层][0][0][0][0][0],形状为[width, height, in_channels, out_channels],bias的获取方式是weights[0][0][0][0][0],形状为[1,out_channels]。对于VGG-19的卷积,全部采用了3X3的filters,所以width为3,height为3。注意,这里面的层数i,指的是最细粒度的层数,包括conv、relu、pool、fc各种操作。因此,i=0为卷积核,i=1为relu,i=2为卷积核,i=3为relu,i=4为pool,i=5为卷积核……,i=37为全连接层,以此类推。VGG-19的pooling采用了长宽为2X2的max-pooling。
若是卷积层,如conv1_1:
print(weights[0][0][0][0][0])
得到的是参数矩阵和偏置:
[ array([[[[ 0.39416704, -0.08419707, -0.03631314, ..., -0.10720515,
-0.03804016, 0.04690642],
[ 0.46418372, 0.03355668, 0.10245045, ..., -0.06945956,
-0.04020201, 0.04048637],
[ 0.34119523, 0.09563112, 0.0177449 , ..., -0.11436455,
-0.05099866, -0.00299793]],
[[ 0.37740308, -0.07876257, -0.04775979, ..., -0.11827433,
-0.19008617, -0.01889699],
[ 0.41810837, 0.05260524, 0.09755926, ..., -0.09385028,
-0.20492788, -0.0573062 ],
[ 0.33999205, 0.13363543, 0.02129423, ..., -0.13025227,
-0.16508926, -0.06969624]],
[[-0.04594866, -0.11583115, -0.14462094, ..., -0.12290562,
-0.35782176, -0.27979308],
[-0.04806903, -0.00658076, -0.02234544, ..., -0.0878844 ,
-0.3915486 , -0.34632796],
[-0.04484424, 0.06471398, -0.07631404, ..., -0.12629718,
-0.29905206, -0.28253639]]],
[[[ 0.2671299 , -0.07969447, 0.05988706, ..., -0.09225675,
0.31764674, 0.42209673],
[ 0.30511212, 0.05677647, 0.21688674, ..., -0.06828708,
0.3440761 , 0.44033417],
[ 0.23215917, 0.13365699, 0.12134422, ..., -0.1063385 ,
0.28406844, 0.35949969]],
[[ 0.09986369, -0.06240906, 0.07442063, ..., -0.02214639,
0.25912452, 0.42349899],
[ 0.10385381, 0.08851637, 0.2392226 , ..., -0.01210995,
0.27064082, 0.40848857],
[ 0.08978214, 0.18505956, 0.15264879, ..., -0.04266965,
0.25779948, 0.35873157]],
[[-0.34100872, -0.13399366, -0.11510294, ..., -0.11911335,
-0.23109646, -0.19202407],
[-0.37314063, -0.00698938, 0.02153259, ..., -0.09827439,
-0.2535741 , -0.25541356],
[-0.30331427, 0.08002605, -0.03926321, ..., -0.12958746,
-0.19778992, -0.21510386]]],
[[[-0.07573577, -0.07806503, -0.03540679, ..., -0.1208065 ,
0.20088433, 0.09790061],
[-0.07646758, 0.03879711, 0.09974211, ..., -0.08732687,
0.2247974 , 0.10158388],
[-0.07260918, 0.10084777, 0.01313597, ..., -0.12594968,
0.14647409, 0.05009392]],
[[-0.28034249, -0.07094654, -0.0387974 , ..., -0.08843154,
0.18996507, 0.07766484],
[-0.31070709, 0.06031388, 0.10412455, ..., -0.06832542,
0.20279962, 0.05222717],
[-0.246675 , 0.1414054 , 0.02605635, ..., -0.10128672,
0.16340195, 0.02832468]],
[[-0.41602272, -0.11491341, -0.14672887, ..., -0.13079506,
-0.1379628 , -0.26588449],
[-0.46453714, -0.00576723, -0.02660675, ..., -0.10017379,
-0.15603794, -0.32566148],
[-0.33683276, 0.06601517, -0.08144748, ..., -0.13460518,
-0.1342358 , -0.27096185]]]], dtype=float32)
array([[ 0.73017758, 0.06493629, 0.03428847, 0.8260386 , 0.2578029 ,
0.54867655, -0.01243854, 0.34789944, 0.55108708, 0.06297145,
0.60699058, 0.26703122, 0.649414 , 0.17073655, 0.47723091,
0.38250586, 0.46373144, 0.21496128, 0.46911287, 0.23825859,
0.47519219, 0.70606434, 0.27007523, 0.68552732, 0.03216552,
0.60252881, 0.35034859, 0.446798 , 0.77326518, 0.58191687,
0.39083108, 1.75193536, 0.66117406, 0.30213955, 0.53059655,
0.67737472, 0.33273223, 0.49127793, 0.26548928, 0.18805602,
0.07412001, 1.10810876, 0.28224325, 0.86755145, 0.19422948,
0.810332 , 0.36062282, 0.50720042, 0.42472315, 0.49632648,
0.15117475, 0.79454446, 0.33494323, 0.47283995, 0.41552398,
0.08496041, 0.37947032, 0.60067391, 0.47174454, 0.81309211,
0.45521152, 1.08920074, 0.47757268, 0.4072122 ]], dtype=float32)]
若是激活函数,如relu1_1:
print(weights[1][0][0][0][0])
输出:
relu
若是池化层,如pool1:
print(weights[4][0][0][0][0])
输出:
pool1
2.由于 imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat 中的参数矩阵和我们定义的长宽位置颠倒了,所以需要交换↓
matconvnet: weights are [width, height, in_channels, out_channels]
tensorflow: weights are [height, width, in_channels, out_channels]
np.transpose(kernels, (1, 0, 2, 3))
2.bias.reshape(-1)
numpy.reshape(a, newshape, order='C')[source],参数`newshape`是啥意思?
根据Numpy文档(https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.reshape.html#numpy-reshape)的解释:
newshape : int or tuple of ints
The
new shape should be compatible with the original shape. If an integer,
then the result will be a 1-D array of that length. One shape dimension
can be -1. In this case, **the value is inferred from the length of the array and remaining dimensions**.
大意是说,数组新的shape属性应该要与原来的配套,如果等于-1的话,那么Numpy会根据剩下的维度计算出数组的另外一个shape属性值。
所以reshape(-1)=不分行列,改成1串;reshape(-1, 1)=我也不知道几行,反正是1列。
- tensorflow可视化
keep_probability = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name="keep_probabilty")
image = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3], name="input_image")
annotation = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 1], name="annotation") pred_annotation, logits = inference(image, keep_probability)
tf.summary.image("input_image", image, max_outputs=2)
tf.summary.image("ground_truth", tf.cast(annotation, tf.uint8), max_outputs=2)
tf.summary.image("pred_annotation", tf.cast(pred_annotation, tf.uint8), max_outputs=2)
loss = tf.reduce_mean((tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,
labels=tf.squeeze(annotation, squeeze_dims=[3]),
name="entropy")))
loss_summary = tf.summary.scalar("entropy", loss) trainable_var = tf.trainable_variables()
if FLAGS.debug:
for var in trainable_var:
utils.add_to_regularization_and_summary(var)
train_op = train(loss, trainable_var) print("Setting up summary op...")
summary_op = tf.summary.merge_all() print("Setting up image reader...")
train_records, valid_records = scene_parsing.read_dataset(FLAGS.data_dir)
print(len(train_records))
print(len(valid_records)) print("Setting up dataset reader")
image_options = {'resize': True, 'resize_size': IMAGE_SIZE}
if FLAGS.mode == 'train':
train_dataset_reader = dataset.BatchDatset(train_records, image_options)
validation_dataset_reader = dataset.BatchDatset(valid_records, image_options) sess = tf.Session() print("Setting up Saver...")
saver = tf.train.Saver() # create two summary writers to show training loss and validation loss in the same graph
# need to create two folders 'train' and 'validation' inside FLAGS.logs_dir
train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(FLAGS.logs_dir + '/train', sess.graph)
validation_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(FLAGS.logs_dir + '/validation') sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(FLAGS.logs_dir)
if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:
saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
print("Model restored...")
1.summary
tensorflow的可视化是使用summary和tensorboard合作完成的。
基本用法
首先明确一点,summary也是op.
输出网络结构
with tf.Session() as sess:
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(your_dir, sess.graph)
命令行运行tensorboard --logdir your_dir,然后浏览器输入127.0.1.1:6006注:tf1.1.0 版本的tensorboard端口换了(0.0.0.0:6006)
这样你就可以在tensorboard中看到你的网络结构图了
可视化参数
#ops
loss = ...
tf.summary.scalar("loss", loss)
merged_summary = tf.summary.merge_all()
init = tf.global_variable_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(your_dir, sess.graph)
sess.run(init)
for i in xrange(100):
_,summary = sess.run([train_op,merged_summary], feed_dict)
writer.add_summary(summary, i)
这时,打开tensorboard,在EVENTS可以看到loss随着i的变化了,如果看不到的话,可以在代码最后加上writer.flush()试一下,原因后面说明。
函数介绍
tf.summary.merge_all: 将之前定义的所有summary op整合到一起FileWriter: 创建一个file writer用来向硬盘写summary数据,tf.summary.scalar(summary_tags, Tensor/variable, collections=None): 用于标量的summarytf.summary.image(tag, tensor, max_images=3, collections=None, name=None):tensor,必须4维,形状[batch_size, height, width, channels],max_images(最多只能生成3张图片的summary),觉着这个用在卷积中的kernel可视化很好用.max_images确定了生成的图片是[-max_images: ,height, width, channels],还有一点就是,TensorBord中看到的image summary永远是最后一个global step的tf.summary.histogram(tag, values, collections=None, name=None):values,任意形状的tensor,生成直方图summarytf.summary.audio(tag, tensor, sample_rate, max_outputs=3, collections=None, name=None)
- 训练、可视化、测试(测试自己加的)
if FLAGS.mode == "train":
for itr in xrange(MAX_ITERATION):
train_images, train_annotations = train_dataset_reader.next_batch(FLAGS.batch_size)
feed_dict = {image: train_images, annotation: train_annotations, keep_probability: 0.85} sess.run(train_op, feed_dict=feed_dict) if itr % 10 == 0:
train_loss, summary_str = sess.run([loss, loss_summary], feed_dict=feed_dict)
print("Step: %d, Train_loss:%g" % (itr, train_loss))
train_writer.add_summary(summary_str, itr) if itr % 500 == 0:
valid_images, valid_annotations = validation_dataset_reader.next_batch(FLAGS.batch_size)
valid_loss, summary_sva = sess.run([loss, loss_summary], feed_dict={image: valid_images, annotation: valid_annotations,
keep_probability: 1.0})
print("%s ---> Validation_loss: %g" % (datetime.datetime.now(), valid_loss)) # add validation loss to TensorBoard
validation_writer.add_summary(summary_sva, itr)
saver.save(sess, FLAGS.logs_dir + "model.ckpt", itr) elif FLAGS.mode == "visualize":
valid_images, valid_annotations = validation_dataset_reader.get_random_batch(FLAGS.batch_size)
pred = sess.run(pred_annotation, feed_dict={image: valid_images, annotation: valid_annotations,
keep_probability: 1.0})
valid_annotations = np.squeeze(valid_annotations, axis=3)
pred = np.squeeze(pred, axis=3) for itr in range(FLAGS.batch_size):
utils.save_image(valid_images[itr].astype(np.uint8), FLAGS.logs_dir, name="inp_" + str(5+itr))
utils.save_image(valid_annotations[itr].astype(np.uint8), FLAGS.logs_dir, name="gt_" + str(5+itr))
utils.save_image(pred[itr].astype(np.uint8), FLAGS.logs_dir, name="pred_" + str(5+itr))
print("Saved image: %d" % itr)
这个部分是容易理解的。
FCN笔记的更多相关文章
- 笔记︱图像语义分割(FCN、CRF、MRF)、论文延伸(Pixel Objectness、)
图像语义分割的意思就是机器自动分割并识别出图像中的内容,我的理解是抠图- 之前在Faster R-CNN中借用了RPN(region proposal network)选择候选框,但是仅仅是候选框,那 ...
- 论文阅读笔记(一)FCN
本文先对FCN的会议论文进行了粗略的翻译,使读者能够对论文的结构有个大概的了解(包括解决的问题是什么,提出了哪些方案,得到了什么结果).然后,给出了几篇博文的连接,对文中未铺开解释的或不易理解的内容作 ...
- 论文阅读笔记六:FCN:Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation(CVPR2015)
今天来看一看一个比较经典的语义分割网络,那就是FCN,全称如题,原英文论文网址:https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~jonlong/long_shelhamer_fcn ...
- 深度学习tensorflow实战笔记(1)全连接神经网络(FCN)训练自己的数据(从txt文件中读取)
1.准备数据 把数据放进txt文件中(数据量大的话,就写一段程序自己把数据自动的写入txt文件中,任何语言都能实现),数据之间用逗号隔开,最后一列标注数据的标签(用于分类),比如0,1.每一行表示一个 ...
- 论文笔记之:Visual Tracking with Fully Convolutional Networks
论文笔记之:Visual Tracking with Fully Convolutional Networks ICCV 2015 CUHK 本文利用 FCN 来做跟踪问题,但开篇就提到并非将其看做 ...
- extjs笔记
1. ExtJs 结构树.. 2 2. 对ExtJs的态度.. 3 3. Ext.form概述.. 4 4. Ext.TabPanel篇.. 5 5. Functio ...
- faster-rcnn系列笔记(一)
目录: 1. 序言 2.正文 2.1 关于ROI 2.2 关于RPN 2.3 关于anchor 3. 关于数据集合制作 4. 关于参数设置 5. 参考 1.序言 叽歪一下目标检测这个模型吧,这篇笔 ...
- [学习一个] Matlab GUI 学习笔记 Ⅰ
Matlab GUI 学习笔记 Ⅰ 1. Foreword Matlab 是严格意义上的编程语言吗?曾经有人告诉我他是通过 Matlab 学会了面对对象编程,我是不信的,但这依然不妨碍它在特殊领域的强 ...
- 论文笔记:语音情感识别(三)手工特征+CRNN
一:Emotion Recognition from Human Speech Using Temporal Information and Deep Learning(2018 InterSpeec ...
随机推荐
- 用JS实现输出两个数范围内的随机数
const rs = require("readline-sync"); function roundNum(min = 0, max = 0) { if (!isNaN(min) ...
- webpack--splitChunksPlugin配置学习随笔
该配置用于代码抽离.官方文档 官方默认配置: module.exports = { //... optimization: { splitChunks: { chunks: 'async', // 异 ...
- UCOSIII钩子函数
OSIdleTaskHook 空闲任务调用这个函数,可以用来让CPU进入低功耗模式 void OSIdleTaskHook (void) { #if OS_CFG_APP_HOOKS_EN > ...
- Docker安装与部署
安装Docker: 查看你当前的内核版本: uname -r 更新yum包: sudo yum update 卸载旧版本(如果安装过旧版本的话): sudo yum remove docker doc ...
- IDEA远程连接和上传文件到服务器
公司电脑是win,所以远程控制服务器就不能用之前自己笔记本ubuntu自带的终端了. 后来在万能的群友的提醒下,IDEA本身就自带了远程功能,摸索了一下,使用IDEA连接服务器并且可以上传文件了. 这 ...
- QEMU简介
参考:What Is the Difference between QEMU and KVM? 注意:上面参考文章有个错误,他把KVM算成类型一虚拟化,应该是类型2虚拟化. 关于类型一虚拟化和类型二虚 ...
- WIN8输入法的问题
在win8下输入法的添加和删除,使用第三方的软件很难处理好,而且容易造成系统的不稳定.比如搜狗输入法有个输入法管理器. 正确的做法: 1.Win+C打开侧边栏,点击 设置,选择“更改电脑设置” 这个选 ...
- Java 使用Builder解决构造函数参数过多的问题
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/michael_f2008/article/details/77715075 //Builder Pattern public class Nutri ...
- 使用BERT模型生成句子序列向量
之前我写过一篇文章,利用bert来生成token级向量(对于中文语料来说就是字级别向量),参考我的文章:<使用BERT模型生成token级向量>.但是这样做有一个致命的缺点就是字符序列长度 ...
- Webpack快速入门
什么是Webpack 顾名思义它是一个前端打包工具,通过给定的入口文件自动梳理所有依赖资源(包括css.图片.js等),并按照配置的规则进行一系列处理(转es5.压缩等),打包生成适合现代生产环境要求 ...
