【SpringBoot】SpringBoot的基础,全面理解bean的生命周期
前言
前段时间直接上手使用springboot开发了一个数据平台的后台部分,但是自身对于springboot的原理和过程还不是很清晰,所以反过来学习下springboot的基础。
大家都知道springboot是基于注解的,IOC和AOP是它的两大重要特性,然后AOP又是基于IOC来实现的。那么弄懂IOC就很有必要了。
IOC:控制反转,一种设计思想,它是Spring的核心。简单点说就是spring管理bean的容器。IOC容器一般具备两个基本功能:
1、通过描述管理Bean,包括发布和获取。
2、描述Bean之间的依赖关系。这两个问题深究下去是没有边界的,尤其是Bean之间的依赖关系,这个就是spring的核心。
从IOC的概念和功能就引申出了一个重要概念: Bean
本文将全方位介绍Spring Bean的生命周期
Spring Bean的简要流程:

如上图所示,在XML或者其他文件定义bean之后,spring通过注解的方式将bean传递到IOC容器,IOC容器将bean注册后给类class调用并实例化-构建,之后将bean放入到容器的缓冲池供程序调用。
从图片可以看到Spring Bean 在整个SpringBoot 项目中至关重要,它经过的路径如下:
- 实例化 【IOC容器寻找Bean的定义信息并将其实例化】
- 设置bean的Aware 【Aware意指能提前感知的,是spring的一个重要接口,使用依赖注入,spring按照Bean定义信息配置Bean的所有属性】
- BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) 【如果BeanPostProcessor和Bean关联,那么其postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法将被调用,Spring 框架会遍历得到容器中所有的 BeanPostProcessor ,挨个执行】
- InitializingBean.afterPorpertiesSet 【初始化bean, springboot读取properties文件的过程,默认的application.properties 还有其他方式】
- BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) 【如果有BeanPostProcessor和Bean关联,那么其postProcessAfterInitialization()方法将被调用】
- SmartInitializingSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated
- SmartLifecycle.start
- 运行Bean
- SmartLifecycle.stop(Runnable callback)
- DisposableBean.destroy() 【销毁】
详细解释
1.实例化对应代码
【使用合适的初始化方案来创建一个新的bean实例,factory-method,构造器注入或者简单的直接实例化】
实例化策略类:
InstantiationStrategy
实例化具体方法:
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args)
构造器注入:
@CompnentScan 【启动类】查找beans,结合@Autowired构造注入【Service层】
Factory Mothod方式也分两种, 分别是静态工厂方法 和 实例工厂方法。
1. 先创建一个汽车car类
- public class Car {
- private int id;
- private String name;
- private int price;
- public int getId() {
- return id;
- }
- public void setId(int id) {
- this.id = id;
- }
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public int getPrice() {
- return price;
- }
- public void setPrice(int price) {
- this.price = price;
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return "Car [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", price=" + price + "]";
- }
- public Car(){
- }
- public Car(int id, String name, int price) {
- super();
- this.id = id;
- this.name = name;
- this.price = price;
- }
- }
2. 定义一个工厂类 (定义了1个静态的bean 容器map. 然后提供1个静态方法根据Car 的id 来获取容器里的car对象。)
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.Map;
- public class CarStaticFactory {
- private static Map<Integer, Car> map = new HashMap<Integer,Car>();
- static{
- map.put(1, new Car(1,"Honda",300000));
- map.put(2, new Car(2,"Audi",440000));
- map.put(3, new Car(3,"BMW",540000));
- }
- public static Car getCar(int id){
- return map.get(id);
- }
- }
3. 定义配置XML (利用静态工厂方法定义的bean item种, class属性不在是bean的全类名, 而是静态工厂的全类名, 而且还需要指定工厂里的getBean 静态方法名字和参数)
- <!--
- Static Factory method:
- class: the class of Factory
- factory-method: method of get Bean Object
- constructor-arg: parameters of factory-method
- -->
- <bean id="bmwCar" class="com.home.factoryMethod.CarStaticFactory" factory-method="getCar">
- <constructor-arg value="3"></constructor-arg>
- </bean>
- <bean id="audiCar" class="com.home.factoryMethod.CarStaticFactory" factory-method="getCar">
- <constructor-arg value="2"></constructor-arg>
- </bean>
4. 客户端调用factory-method的bean
- public static void h(){
- ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean-factoryMethod.xml");
- Car car1 = (Car) ctx.getBean("bmwCar");
- System.out.println(car1);
- car1 = (Car) ctx.getBean("audiCar");
- System.out.println(car1);
- }
2.设置bean的Aware
【InitializingBean.afterPorpertiesSet,BeanPostProcessor对bean的加工处理基本上在一块出现。】
设置Aware方法顺序:
- BeanNameAware
- BeanClassLoaderAware
- BeanFactoryAware
BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization
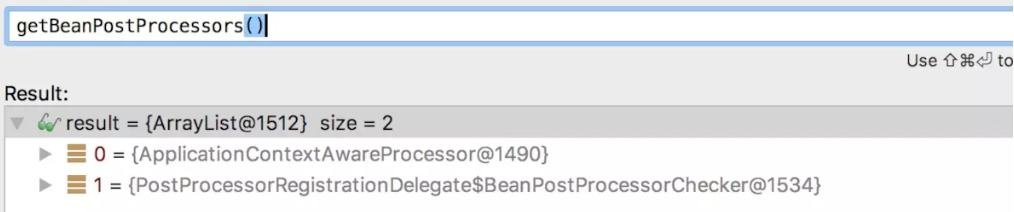
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor也会设置Aware:
- EnvironmentAware
- EmbeddedValueResolverAware
- ResourceLoaderAware
- ApplicationEventPublisherAware
- MessageSourceAware
- ApplicationContextAware
调用afterpropertiesSet方法:位于AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd)方法中
源码:
- protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
- // 设置Aware
- if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
- AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
- @Override
- public Object run() {
- invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
- return null;
- }
- }, getAccessControlContext());
- }
- else {
- invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
- }
- //BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization
- Object wrappedBean = bean;
- if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
- wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
- }
- try {
- //调用init方法,其判断是否是InitializingBean的实例,然后调用afterPropertiesSet
- invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
- }
- catch (Throwable ex) {
- throw new BeanCreationException(
- (mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
- beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
- }
- //BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization
- if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
- wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
- }
- return wrappedBean;
- }
3. SmartInitializingSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated的调用位置
- @Override
- public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
- if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
- this.logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
- }
- // Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
- // While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
- List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
- // Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
- // 触发实例化所有的非懒加载的单例
- for (String beanName : beanNames) {
- ...
- }
- // Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
- // 触发应用bean的post-initialization回调,也就是afterSingletonsInstantiated方法
- for (String beanName : beanNames) {
- Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
- if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
- final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
- if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
- AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
- @Override
- public Object run() {
- smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
- return null;
- }
- }, getAccessControlContext());
- }
- else {
- smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
- }
- }
- }
- }
4. SmartLifecycle.start
在ApplicationContext结束刷新finishRefresh时,getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
判断bean是否为SmartLifecycle并且autoStartup。
位于:
DefaultLifecycleProcessor.onRefresh
5. stop方法
在Application.close的时候,调用getLifecycleProcessor().stop()方法仍然在DefaultLifecycleProcessor内部
6. DisposableBean.destroy方法
doCreateBean方法中会判断bean是否有销毁相关操作,实现了DisposableBean方法或定义了销毁方法。
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args)
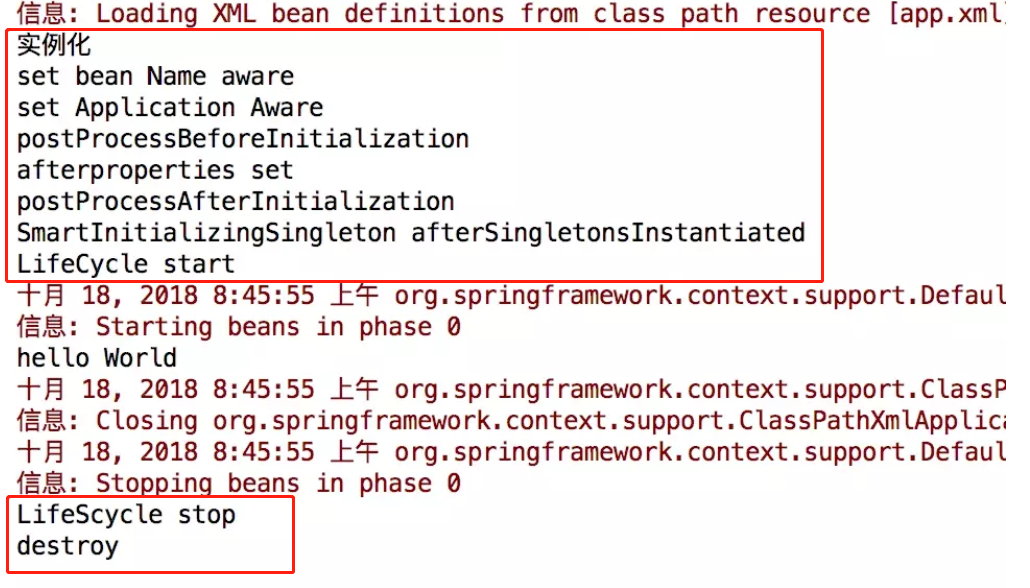
7. Bean 生命周期演示代码以及运行结果
- public class HelloWorld implements SmartInitializingSingleton,SmartLifecycle,InitializingBean,
- DisposableBean,MyInterface,BeanNameAware,ApplicationContextAware
- {
- private final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
- private boolean isRunning;
- public HelloWorld() {
- System.out.println("实例化");
- }
- public void sayHello(){
- System.out.println("hello World");
- }
- public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
- System.out.println("SmartInitializingSingleton afterSingletonsInstantiated");
- }
- public void start() {
- isRunning = true;
- System.out.println("LifeCycle start");
- }
- public void stop() {
- System.out.println("LifeCycle stop");
- }
- public boolean isRunning() {
- return isRunning;
- }
- public boolean isAutoStartup() {
- return true;
- }
- public void stop(Runnable callback) {
- System.out.println("LifeScycle stop");
- callback.run();
- }
- public int getPhase() {
- return 0;
- }
- public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
- System.out.println("afterproperties set");
- }
- public void destroy() throws Exception {
- System.out.println("destroy");
- }
- public void my(String str) {
- System.out.println(str);
- }
- public void setBeanName(String name) {
- System.out.println("set bean Name aware");
- }
- public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
- System.out.println("set Application Aware");
- }
- }
- //MyInterface接口
- public interface MyInterface {
- void my(String str);
- }
- //app.xml
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
- <bean id="porcessor" class="me.aihe.MyBeanPostProcessor" />
- <bean id="hello" class="me.aihe.HelloWorld">
- </bean>
- </beans>
- //SpringApp
- public class SpringApp {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("app.xml");
- HelloWorld hello = (HelloWorld) applicationContext.getBean("hello");
- hello.sayHello();
- applicationContext.close();
- }
- }
总结:
Spring Bean 是整个Spring的基石,意义不言而喻,通过bean可以获取对象,实现容器,反射,简化配置,中间件,线程池等等。所以学习它非常有必要。
【SpringBoot】SpringBoot的基础,全面理解bean的生命周期的更多相关文章
- Spring 框架基础(02):Bean的生命周期,作用域,装配总结
本文源码:GitHub·点这里 || GitEE·点这里 一.装配方式 Bean的概念:Spring框架管理的应用程序中,由Spring容器负责创建,装配,设置属性,进而管理整个生命周期的对象,称为B ...
- Spring原理系列一:Spring Bean的生命周期
一.前言 在日常开发中,spring极大地简化了我们日常的开发工作.spring为我们管理好bean, 我们拿来就用.但是我们不应该只停留在使用层面,深究spring内部的原理,才能在使用时融汇贯通. ...
- Spring重点—— IOC 容器中 Bean 的生命周期
一.理解 Bean 的生命周期,对学习 Spring 的整个运行流程有极大的帮助. 二.在 IOC 容器中,Bean 的生命周期由 Spring IOC 容器进行管理. 三.在没有添加后置处理器的情况 ...
- IoC容器装配Bean(xml配置方式)(Bean的生命周期)
1.Spring管理Bean,实例化Bean对象 三种方式 第一种:使用类构造器实例化(默认无参数) package cn.itcast.spring.initbean; /** * 使用构造方法 实 ...
- 深究Spring中Bean的生命周期
前言 这其实是一道面试题,是我在面试百度的时候被问到的,当时没有答出来(因为自己真的很菜),后来在网上寻找答案,看到也是一头雾水,直到看到了<Spring in action>这本书,书上 ...
- spring框架中Bean的生命周期
一.Bean 的完整生命周期 在传统的Java应用中,bean的生命周期很简单,使用Java关键字 new 进行Bean 的实例化,然后该Bean 就能够使用了.一旦bean不再被使用,则由Java自 ...
- 通过BeanPostProcessor理解Spring中Bean的生命周期
通过BeanPostProcessor理解Spring中Bean的生命周期及AOP原理 Spring源码解析(十一)Spring扩展接口InstantiationAwareBeanPostProces ...
- (spring-第1回【IoC基础篇】)Spring容器中Bean的生命周期
日出日落,春去秋来,花随流水,北雁南飞,世间万物皆有生死轮回.从调用XML中的Bean配置信息,到应用到具体实例中,再到销毁,Bean也有属于它的生命周期. 人类大脑对图像的认知能力永远高于文字,因此 ...
- 深入理解Spring中bean的生命周期
[Spring中bean的生命周期] bean的生命周期 1.以ApplocationContext上下文单例模式装配bean为例,深入探讨bean的生命周期: (1).生命周期图: (2).具体事例 ...
随机推荐
- JavaScript高级程序设计(第3版) 第四章(变量、作用域和内存问题)
4.1 基本类型和引用类型的值 1.基本类型的值是(简单的数据段),引用类型的值是(保存在内存中的对象). 基本类型的值在内存中占据固定大小的空间,因此被保存在栈中.(lifo ...
- IOS-swift5.1快速入门之旅
快速之旅 传统表明,新语言中的第一个程序应在屏幕上打印“Hello,world!”字样.在Swift中,这可以在一行中完成: print("Hello, world!") // P ...
- [Codeforces 316E3]Summer Homework(线段树+斐波那契数列)
[Codeforces 316E3]Summer Homework(线段树+斐波那契数列) 顺便安利一下这个博客,给了我很大启发(https://gaisaiyuno.github.io/) 题面 有 ...
- [Codeforces 555E]Case of Computer Network(Tarjan求边-双连通分量+树上差分)
[Codeforces 555E]Case of Computer Network(Tarjan求边-双连通分量+树上差分) 题面 给出一个无向图,以及q条有向路径.问是否存在一种给边定向的方案,使得 ...
- highcharts.js两种数据绑定方式和异步加载数据的使用
一,我们先来看看异步加载数据的写法(这是使用MVC的例子) 1>js写法 <script src="~/Scripts/jquery-2.1.4.min.js"> ...
- 快速部署业务类为webapi服务
接着前一篇博文,将接口快速打包固定请求格式,不需要修改代码,可以自动完成接口调用,实际上就是生成了一个接口的代理类. 那么仅仅是接口请求代理,没有服务端怎么行?所以需要将实现接口的类部署为webapi ...
- 数组Array的方法调用
<script language="JavaScript" type="text/javascript"> var arr = ["11& ...
- js 程序执行与顺序实现详解
JavaScript是一种描述型脚本语言,由浏览器进行动态的解析与执行,浏览器对于不同的方式有不同的解析顺序,详细介绍如下,感兴趣的朋友可以参考下哈 函数的声明和调用 JavaScript是一种描述型 ...
- 270-VC709E 增强版 基于FMC接口的Xilinx Vertex-7 FPGA V7 XC7VX690T PCIeX8 接口卡
VC709E 增强版 基于FMC接口的Xilinx Vertex-7 FPGA V7 XC7VX690T PCIeX8 接口卡 一.板卡概述 本板卡基于Xilinx公司的FPGA XC7V ...
- Error- Overloaded method value createDirectStream in error Spark Streaming打包报错
直接上代码 StreamingExamples.setStreamingLogLevels() val Array(brokers, topics) = args // Create context ...
