flume源码
IDEA查看源码
IDEA快捷键
1 查看接口的实现类:Ctrl+Alt+B
选中按快捷键,然后跳到实现类的地方去
2 切换页面:Alt+<- 和 Alt+->
Alt+->
3 查看Java方法调用树(被调/主调):Ctrl+Alt+H
分为调用当前方法的树、当前方法调用的下级方法
4 查看类继承关系图:Ctrl+Alt+U
5 查看当前类的继承树:Ctrl+H
6 查看定义的变量在哪里被调用:Ctrl+Alt+F7
7 查看一个类中有什么方法:Alt+7 或 点左侧边栏Structure
临时得到的不一定正确的结论,后续需要debug来跟踪研究
启动程序入口是org.apache.flume.node.Application#main
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
SSLUtil.initGlobalSSLParameters();
// 用了apache commons-cli的jar包实现的命令行提示
Options options = new Options();
Option option = new Option("n", "name", true, "the name of this agent");
option.setRequired(true);
options.addOption(option);
option = new Option("f", "conf-file", true,
"specify a config file (required if -z missing)");
option.setRequired(false);
options.addOption(option);
option = new Option(null, "no-reload-conf", false,
"do not reload config file if changed");
options.addOption(option);
// Options for Zookeeper
option = new Option("z", "zkConnString", true,
"specify the ZooKeeper connection to use (required if -f missing)");
option.setRequired(false);
options.addOption(option);
option = new Option("p", "zkBasePath", true,
"specify the base path in ZooKeeper for agent configs");
option.setRequired(false);
options.addOption(option);
option = new Option("h", "help", false, "display help text");
options.addOption(option);
CommandLineParser parser = new GnuParser();
CommandLine commandLine = parser.parse(options, args);
if (commandLine.hasOption('h')) {
new HelpFormatter().printHelp("flume-ng agent", options, true);
return;
}
String agentName = commandLine.getOptionValue('n');
boolean reload = !commandLine.hasOption("no-reload-conf");
// 代码待续
上面的代码是解析命令行参数
下面是使用zookeeper进行配置flume
// 代码接上面
boolean isZkConfigured = false;
if (commandLine.hasOption('z') || commandLine.hasOption("zkConnString")) {
isZkConfigured = true;
} Application application;
if (isZkConfigured) {
// get options
String zkConnectionStr = commandLine.getOptionValue('z');
String baseZkPath = commandLine.getOptionValue('p'); if (reload) {
EventBus eventBus = new EventBus(agentName + "-event-bus");
List<LifecycleAware> components = Lists.newArrayList();
PollingZooKeeperConfigurationProvider zookeeperConfigurationProvider =
new PollingZooKeeperConfigurationProvider(
agentName, zkConnectionStr, baseZkPath, eventBus);
components.add(zookeeperConfigurationProvider);
application = new Application(components);
eventBus.register(application);
} else {
StaticZooKeeperConfigurationProvider zookeeperConfigurationProvider =
new StaticZooKeeperConfigurationProvider(
agentName, zkConnectionStr, baseZkPath);
application = new Application();
application.handleConfigurationEvent(zookeeperConfigurationProvider.getConfiguration());
}
} else { // 代码待续
下面使用本地文件配置flume,判断配置文件是否存在
// 代码接上面 // 使用本地配置文件进行配置
File configurationFile = new File(commandLine.getOptionValue('f')); /*
* The following is to ensure that by default the agent will fail on
* startup if the file does not exist.
*/
if (!configurationFile.exists()) {
// If command line invocation, then need to fail fast
if (System.getProperty(Constants.SYSPROP_CALLED_FROM_SERVICE) ==
null) {
String path = configurationFile.getPath();
try {
path = configurationFile.getCanonicalPath();
} catch (IOException ex) {
logger.error("Failed to read canonical path for file: " + path,
ex);
}
throw new ParseException(
"The specified configuration file does not exist: " + path);
}
}
// 代码待续
下面代码,如果使用的shell命令中没有no-reload-conf,则每30秒钟会监控配置文件
// 代码接上方
List<LifecycleAware> components = Lists.newArrayList(); if (reload) {
EventBus eventBus = new EventBus(agentName + "-event-bus");
PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider configurationProvider =
new PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider(
agentName, configurationFile, eventBus, 30);
components.add(configurationProvider);
application = new Application(components);
eventBus.register(application);
} else {
......
// else块中代码在下方
}
}
application.start(); // 代码待续
eventbus
动态配置使用了PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider,其中中有FileWatcherRunnable来具体实现监控配置文件 变化,如果改动时间晚于文件最后修改时间,会eventBus.post(),该方法会激活带有@Subscribe的handleConfigurationEvent()方法
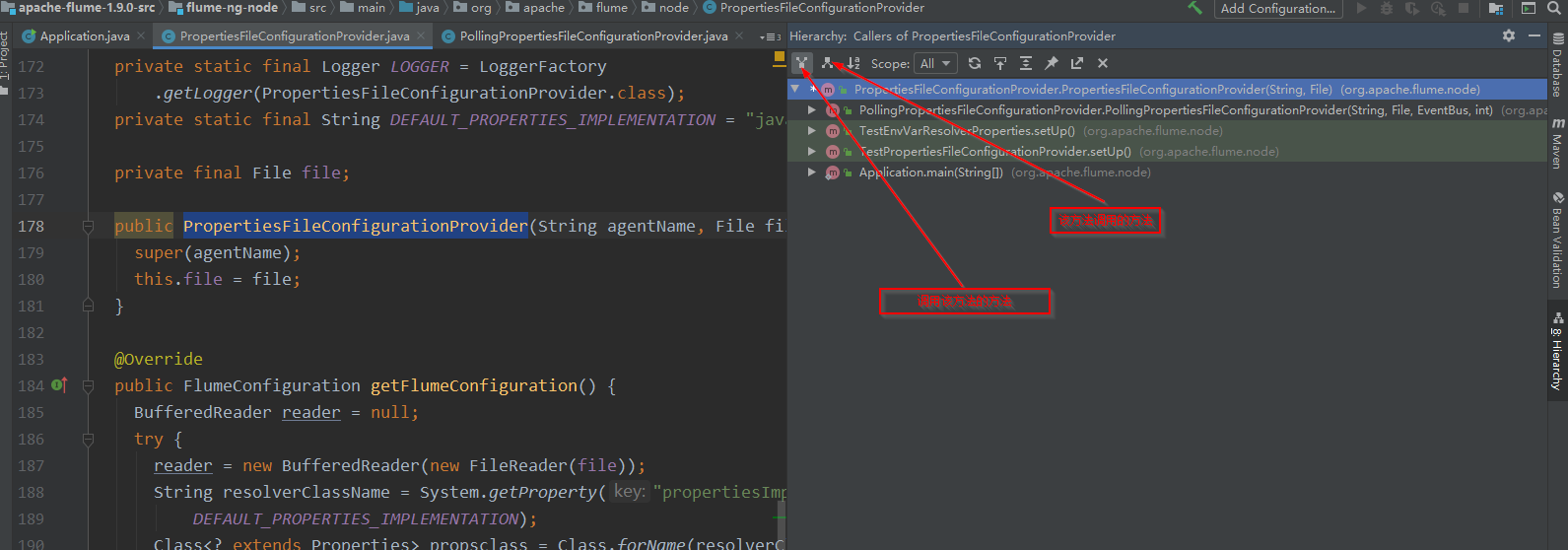
由components.add(configurationProvider),我们发现components是PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider
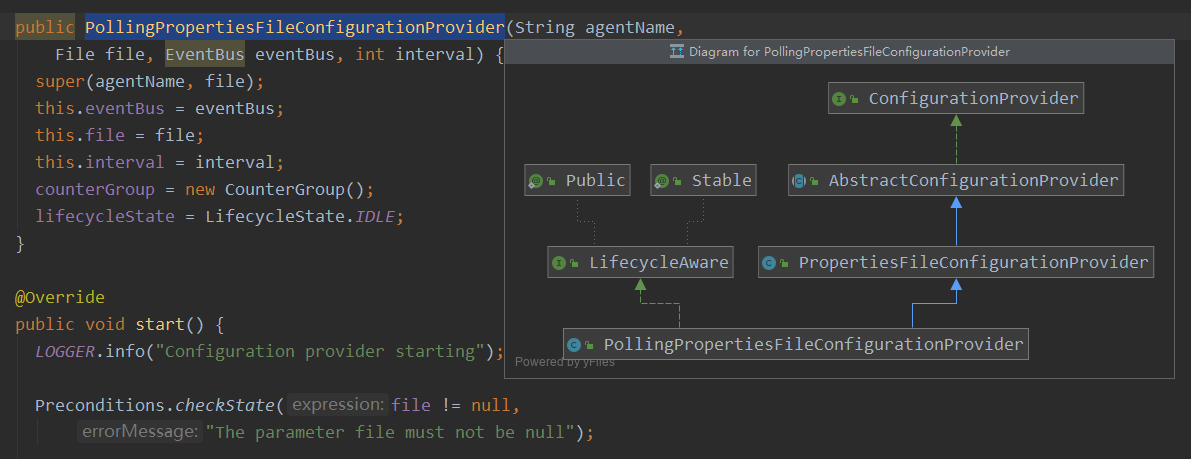
public PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider(String agentName,
File file, EventBus eventBus, int interval) {
super(agentName, file);
this.eventBus = eventBus;
this.file = file;
this.interval = interval;
counterGroup = new CounterGroup();
lifecycleState = LifecycleState.IDLE;
} @Override
public void start() {
LOGGER.info("Configuration provider starting"); Preconditions.checkState(file != null,
"The parameter file must not be null"); executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(
new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("conf-file-poller-%d")
.build()); FileWatcherRunnable fileWatcherRunnable =
new FileWatcherRunnable(file, counterGroup); executorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(fileWatcherRunnable, 0, interval,
TimeUnit.SECONDS); lifecycleState = LifecycleState.START; LOGGER.debug("Configuration provider started");
} @Override
public void stop() {
LOGGER.info("Configuration provider stopping"); executorService.shutdown();
try {
if (!executorService.awaitTermination(500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
LOGGER.debug("File watcher has not terminated. Forcing shutdown of executor.");
executorService.shutdownNow();
while (!executorService.awaitTermination(500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
LOGGER.debug("Waiting for file watcher to terminate");
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
LOGGER.debug("Interrupted while waiting for file watcher to terminate");
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
lifecycleState = LifecycleState.STOP;
LOGGER.debug("Configuration provider stopped");
} @Override
public synchronized LifecycleState getLifecycleState() {
return lifecycleState;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "{ file:" + file + " counterGroup:" + counterGroup + " provider:"
+ getClass().getCanonicalName() + " agentName:" + getAgentName() + " }";
} public class FileWatcherRunnable implements Runnable { private final File file;
private final CounterGroup counterGroup; private long lastChange; public FileWatcherRunnable(File file, CounterGroup counterGroup) {
super();
this.file = file;
this.counterGroup = counterGroup;
this.lastChange = 0L;
} @Override
public void run() {
LOGGER.debug("Checking file:{} for changes", file); counterGroup.incrementAndGet("file.checks"); long lastModified = file.lastModified(); if (lastModified > lastChange) {
LOGGER.info("Reloading configuration file:{}", file); counterGroup.incrementAndGet("file.loads"); lastChange = lastModified; try {
eventBus.post(getConfiguration());
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("Failed to load configuration data. Exception follows.",
e);
} catch (NoClassDefFoundError e) {
LOGGER.error("Failed to start agent because dependencies were not " +
"found in classpath. Error follows.", e);
} catch (Throwable t) {
// caught because the caller does not handle or log Throwables
LOGGER.error("Unhandled error", t);
}
}
}
} }
org.apache.flume.node.Application#handleConfigurationEvent方法,会调用先终止所有components,再启动components
@Subscribe
public void handleConfigurationEvent(MaterializedConfiguration conf) {
try {
lifecycleLock.lockInterruptibly();
stopAllComponents();
startAllComponents(conf);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
logger.info("Interrupted while trying to handle configuration event");
return;
} finally {
// If interrupted while trying to lock, we don't own the lock, so must not attempt to unlock
if (lifecycleLock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) {
lifecycleLock.unlock();
}
}
}
application.start();会将component传入supervise方法
public void start() {
lifecycleLock.lock();
try {
for (LifecycleAware component : components) {
supervisor.supervise(component,
new SupervisorPolicy.AlwaysRestartPolicy(), LifecycleState.START);
}
} finally {
lifecycleLock.unlock();
}
}
supervise方法对组件进行监督
该方法中对每一个component会通过线程池ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor monitorService起一个MonitorRunnable线程执行,在monitorRunnable中的run()方法中,是每一个component的执行逻辑,根据desiredState的不同,选择不同的状态执行方法去执行
public synchronized void supervise(LifecycleAware lifecycleAware,
SupervisorPolicy policy, LifecycleState desiredState) {
if (this.monitorService.isShutdown()
|| this.monitorService.isTerminated()
|| this.monitorService.isTerminating()) {
throw new FlumeException("Supervise called on " + lifecycleAware + " " +
"after shutdown has been initiated. " + lifecycleAware + " will not" +
" be started");
} Preconditions.checkState(!supervisedProcesses.containsKey(lifecycleAware),
"Refusing to supervise " + lifecycleAware + " more than once"); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Supervising service:{} policy:{} desiredState:{}",
new Object[] { lifecycleAware, policy, desiredState });
} Supervisoree process = new Supervisoree();
process.status = new Status(); process.policy = policy;
process.status.desiredState = desiredState;
process.status.error = false; MonitorRunnable monitorRunnable = new MonitorRunnable();
monitorRunnable.lifecycleAware = lifecycleAware;
monitorRunnable.supervisoree = process;
monitorRunnable.monitorService = monitorService; supervisedProcesses.put(lifecycleAware, process); ScheduledFuture<?> future = monitorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(
monitorRunnable, 0, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
monitorFutures.put(lifecycleAware, future);
}
monitorService 是一个线程池,在对象创建的时候初始化用,该线程池,来启动 Channels Sources , Sinks 的Runner 实例
monitorRunnable中的run()方法
PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider是实现了LifecycleAware接口的,component是PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider,因此run()方法会调用PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider的start()方法,
也就是application.start()最终调用了PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider.start(),组件启动了
同时,启动了后,我们设置了要持续监控配置文件,因此要保证周期性监控配置文件。恰好,PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider.start()会新建FileWatcherRunnable,该runnable会监控文件的变化,如果配置文件发生变化,会调用里面的eventBus.post(),从而激活了handleConfigurationEvent(),进而会stopAllComponents然后startAllComponents
PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider.start()中使用了executorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(fileWatcherRunnable, 0, interval, TimeUnit.SECONDS)来使用上面提到的runnable,每隔30秒监控变化
@Override
public void run() {
logger.debug("checking process:{} supervisoree:{}", lifecycleAware,
supervisoree); long now = System.currentTimeMillis(); try {
if (supervisoree.status.firstSeen == null) {
logger.debug("first time seeing {}", lifecycleAware); supervisoree.status.firstSeen = now;
} supervisoree.status.lastSeen = now;
synchronized (lifecycleAware) {
if (supervisoree.status.discard) {
// Unsupervise has already been called on this.
logger.info("Component has already been stopped {}", lifecycleAware);
return;
} else if (supervisoree.status.error) {
logger.info("Component {} is in error state, and Flume will not"
+ "attempt to change its state", lifecycleAware);
return;
} supervisoree.status.lastSeenState = lifecycleAware.getLifecycleState(); if (!lifecycleAware.getLifecycleState().equals(
supervisoree.status.desiredState)) { logger.debug("Want to transition {} from {} to {} (failures:{})",
new Object[] { lifecycleAware, supervisoree.status.lastSeenState,
supervisoree.status.desiredState,
supervisoree.status.failures }); switch (supervisoree.status.desiredState) {
case START:
try {
lifecycleAware.start();
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("Unable to start " + lifecycleAware
+ " - Exception follows.", e);
if (e instanceof Error) {
// This component can never recover, shut it down.
supervisoree.status.desiredState = LifecycleState.STOP;
try {
lifecycleAware.stop();
logger.warn("Component {} stopped, since it could not be"
+ "successfully started due to missing dependencies",
lifecycleAware);
} catch (Throwable e1) {
logger.error("Unsuccessful attempt to "
+ "shutdown component: {} due to missing dependencies."
+ " Please shutdown the agent"
+ "or disable this component, or the agent will be"
+ "in an undefined state.", e1);
supervisoree.status.error = true;
if (e1 instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) e1;
}
// Set the state to stop, so that the conf poller can
// proceed.
}
}
supervisoree.status.failures++;
}
break;
case STOP:
try {
lifecycleAware.stop();
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("Unable to stop " + lifecycleAware
+ " - Exception follows.", e);
if (e instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) e;
}
supervisoree.status.failures++;
}
break;
default:
logger.warn("I refuse to acknowledge {} as a desired state",
supervisoree.status.desiredState);
} if (!supervisoree.policy.isValid(lifecycleAware, supervisoree.status)) {
logger.error(
"Policy {} of {} has been violated - supervisor should exit!",
supervisoree.policy, lifecycleAware);
}
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Unexpected error", t);
}
logger.debug("Status check complete");
}
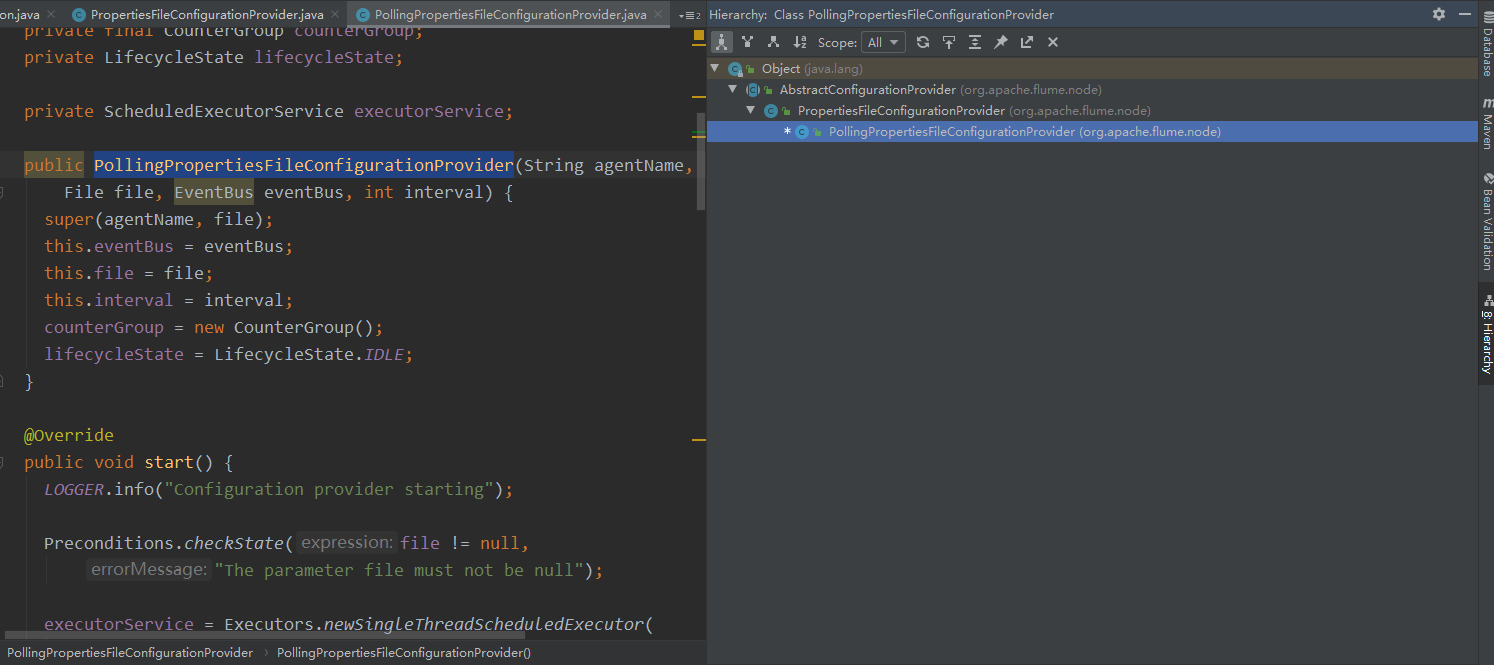
PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider 继承了 PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider 继承了 :AbstractConfigurationProvider,在抽象类:AbstractConfigurationProvider
启动不是瞎启动,而是根据配置文件
eventBus.post(getConfiguration());
激活
handleConfigurationEvent(MaterializedConfiguration conf)
里面
startAllComponents(conf);
org.apache.flume.node.AbstractConfigurationProvider#getConfiguration 方法.
这个方法分两步.
1.读取配置文件. 使用的是 FlumeConfiguration fconfig = getFlumeConfiguration();
2.生成 source、channel、sink 对应的 runner . 加入到 MaterializedConfiguration 中
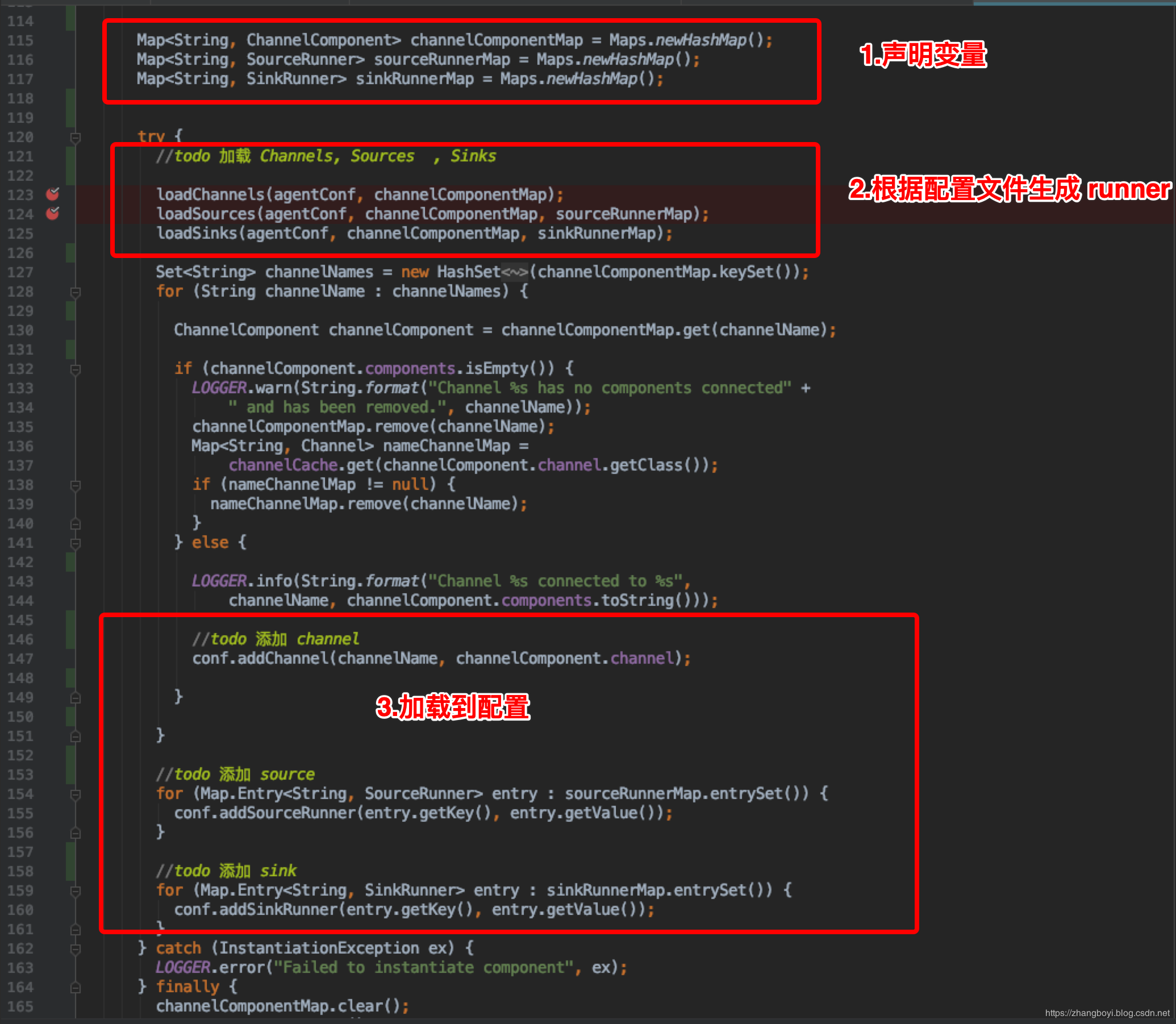
public MaterializedConfiguration getConfiguration() {
MaterializedConfiguration conf = new SimpleMaterializedConfiguration();
FlumeConfiguration fconfig = getFlumeConfiguration();
AgentConfiguration agentConf = fconfig.getConfigurationFor(getAgentName());
if (agentConf != null) {
Map<String, ChannelComponent> channelComponentMap = Maps.newHashMap();
Map<String, SourceRunner> sourceRunnerMap = Maps.newHashMap();
Map<String, SinkRunner> sinkRunnerMap = Maps.newHashMap();
try {
loadChannels(agentConf, channelComponentMap);
loadSources(agentConf, channelComponentMap, sourceRunnerMap);
loadSinks(agentConf, channelComponentMap, sinkRunnerMap);
Set<String> channelNames = new HashSet<String>(channelComponentMap.keySet());
for (String channelName : channelNames) {
ChannelComponent channelComponent = channelComponentMap.get(channelName);
if (channelComponent.components.isEmpty()) {
LOGGER.warn(String.format("Channel %s has no components connected" +
" and has been removed.", channelName));
channelComponentMap.remove(channelName);
Map<String, Channel> nameChannelMap =
channelCache.get(channelComponent.channel.getClass());
if (nameChannelMap != null) {
nameChannelMap.remove(channelName);
}
} else {
LOGGER.info(String.format("Channel %s connected to %s",
channelName, channelComponent.components.toString()));
conf.addChannel(channelName, channelComponent.channel);
}
}
for (Map.Entry<String, SourceRunner> entry : sourceRunnerMap.entrySet()) {
conf.addSourceRunner(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
for (Map.Entry<String, SinkRunner> entry : sinkRunnerMap.entrySet()) {
conf.addSinkRunner(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
LOGGER.error("Failed to instantiate component", ex);
} finally {
channelComponentMap.clear();
sourceRunnerMap.clear();
sinkRunnerMap.clear();
}
} else {
LOGGER.warn("No configuration found for this host:{}", getAgentName());
}
return conf;
}
loadChannels( agentConf , channelComponentMap );//创建channel,并存入channelComponentMap中
loadSources( agentConf , channelComponentMap , sourceRunnerMap );//创建source,并存入sourceRunnerMap中。在source中,读取创建的多个channel,并根据多个channel创建ChannelSelector,根据selector,创建ChannelProcessor。选择器和拦截器会传入ChannelProcessor。
loadSinks( agentConf , channelComponentMap , sinkRunnerMap );//创建sink,并存入sinkRunnerMap中
loadChannels(agentConf, channelComponentMap);
这个方法主要干了四件事件事.
1.将缓存的 channel 加入到一个 ListMultimap<Class<? extends Channel>, String>集合中
2. 创建具有ComponentConfiguration 对象的Channel 实例
3. 创建没有ComponentConfiguration 对象, 但是配置 context 的Channel 实例
4.将缓存中的 channel 与新生成的 channel 做匹配, 去掉配置项中没有的 channel
private void loadChannels(AgentConfiguration agentConf,
Map<String, ChannelComponent> channelComponentMap)
throws InstantiationException {
LOGGER.info("Creating channels"); //todo 缓存中的 channel
ListMultimap<Class<? extends Channel>, String> channelsNotReused =
ArrayListMultimap.create();
// assume all channels will not be re-used
for (Map.Entry<Class<? extends Channel>, Map<String, Channel>> entry :
channelCache.entrySet()) {
Class<? extends Channel> channelKlass = entry.getKey();
Set<String> channelNames = entry.getValue().keySet();
channelsNotReused.get(channelKlass).addAll(channelNames);
} Set<String> channelNames = agentConf.getChannelSet();
Map<String, ComponentConfiguration> compMap = agentConf.getChannelConfigMap(); for (String chName : channelNames) {
ComponentConfiguration comp = compMap.get(chName);
if (comp != null) { // todo 使用工厂类创建Channel
Channel channel = getOrCreateChannel(channelsNotReused,
comp.getComponentName(), comp.getType()); try { //todo 更新配置 , 因为 channelComponentMap 刚开始传进来的时候是空值
Configurables.configure(channel, comp);
channelComponentMap.put(comp.getComponentName(),
new ChannelComponent(channel));
LOGGER.info("Created channel " + chName); } catch (Exception e) {
String msg = String.format("Channel %s has been removed due to an " +
"error during configuration", chName);
LOGGER.error(msg, e);
}
}
} //todo 组合没有 ComponentConfiguration配置, 仅仅使用Context的对象.
for (String chName : channelNames) {
Context context = agentConf.getChannelContext().get(chName);
if (context != null) {
// todo 使用工厂类创建Channel
Channel channel = getOrCreateChannel(channelsNotReused, chName,
context.getString(BasicConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_TYPE)); try { // todo 更新配置 , 因为 channelComponentMap 刚开始传进来的时候是空值
Configurables.configure(channel, context);
channelComponentMap.put(chName, new ChannelComponent(channel)); LOGGER.info("Created channel " + chName);
} catch (Exception e) {
String msg = String.format("Channel %s has been removed due to an " +
"error during configuration", chName);
LOGGER.error(msg, e);
}
}
} for (Class<? extends Channel> channelKlass : channelsNotReused.keySet()) {
Map<String, Channel> channelMap = channelCache.get(channelKlass);
if (channelMap != null) {
for (String channelName : channelsNotReused.get(channelKlass)) {
if (channelMap.remove(channelName) != null) {
LOGGER.info("Removed {} of type {}", channelName, channelKlass);
}
}
if (channelMap.isEmpty()) {
//todo 有一些 channel 在配置中没有重新使用, 将会将其从缓存中移除.
channelCache.remove(channelKlass); }
}
}
}
private Channel getOrCreateChannel(
ListMultimap<Class<? extends Channel>, String> channelsNotReused,
String name, String type)
throws FlumeException { // todo 根据传入的类型, 获取对应的类
Class<? extends Channel> channelClass = channelFactory.getClass(type); /*
* Channel has requested a new instance on each re-configuration
* todo 根据新的配置, 实例化对象.
*/
//todo 如何类的注解 Disposable 存在, 则直接进行实例化,并返回 只有 jdbc 和 file 模式用到了
if (channelClass.isAnnotationPresent(Disposable.class)) {
Channel channel = channelFactory.create(name, type);
channel.setName(name);
return channel;
} Map<String, Channel> channelMap = channelCache.get(channelClass); //todo 如果缓存中不存在 channel 的话, 那么直接加入缓存.
if (channelMap == null) {
channelMap = new HashMap<String, Channel>();
channelCache.put(channelClass, channelMap);
}
//todo 如果channelMap 中的 channel 为 null ,使用工厂类创建.
Channel channel = channelMap.get(name);
if (channel == null) {
channel = channelFactory.create(name, type);
channel.setName(name);
channelMap.put(name, channel);
}
//todo 如果缓存中已经存在对应的 channel 的话,那么移除它, 后续的方法会更新它 .
channelsNotReused.get(channelClass).remove(name);
return channel;
}
loadSources(agentConf, channelComponentMap, sourceRunnerMap);
读取配置文件生成 source , 然后创建 sourceRunner, 并注册到 channel
private void loadSources(AgentConfiguration agentConf,
Map<String, ChannelComponent> channelComponentMap,
Map<String, SourceRunner> sourceRunnerMap)
throws InstantiationException { Set<String> sourceNames = agentConf.getSourceSet();
Map<String, ComponentConfiguration> compMap =
agentConf.getSourceConfigMap();
/*
* Components which have a ComponentConfiguration object
*/
for (String sourceName : sourceNames) {
ComponentConfiguration comp = compMap.get(sourceName);
if (comp != null) {
SourceConfiguration config = (SourceConfiguration) comp; Source source = sourceFactory.create(comp.getComponentName(),
comp.getType());
try {
Configurables.configure(source, config); //配置source
Set<String> channelNames = config.getChannels();
List<Channel> sourceChannels =
getSourceChannels(channelComponentMap, source, channelNames);
if (sourceChannels.isEmpty()) {
String msg = String.format("Source %s is not connected to a " +
"channel", sourceName);
throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
}
ChannelSelectorConfiguration selectorConfig =
config.getSelectorConfiguration(); ChannelSelector selector = ChannelSelectorFactory.create(
sourceChannels, selectorConfig); //创建channel 选择器 ChannelProcessor channelProcessor = new ChannelProcessor(selector);
Configurables.configure(channelProcessor, config); // 这里实际是调用ChannelProcessor的configure()方法,设置拦截器链 source.setChannelProcessor(channelProcessor);
sourceRunnerMap.put(comp.getComponentName(),
SourceRunner.forSource(source));
for (Channel channel : sourceChannels) {
ChannelComponent channelComponent =
Preconditions.checkNotNull(channelComponentMap.get(channel.getName()),
String.format("Channel %s", channel.getName()));
channelComponent.components.add(sourceName);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
String msg = String.format("Source %s has been removed due to an " +
"error during configuration", sourceName);
LOGGER.error(msg, e);
}
}
}
/*
* Components which DO NOT have a ComponentConfiguration object
* and use only Context
*/
Map<String, Context> sourceContexts = agentConf.getSourceContext();
for (String sourceName : sourceNames) {
Context context = sourceContexts.get(sourceName);
if (context != null) {
Source source =
sourceFactory.create(sourceName,
context.getString(BasicConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_TYPE));
try {
Configurables.configure(source, context);
String[] channelNames = context.getString(
BasicConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_CHANNELS).split("\\s+");
List<Channel> sourceChannels =
getSourceChannels(channelComponentMap, source, Arrays.asList(channelNames));
if (sourceChannels.isEmpty()) {
String msg = String.format("Source %s is not connected to a " +
"channel", sourceName);
throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
}
Map<String, String> selectorConfig = context.getSubProperties(
BasicConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_SOURCE_CHANNELSELECTOR_PREFIX); ChannelSelector selector = ChannelSelectorFactory.create(
sourceChannels, selectorConfig); ChannelProcessor channelProcessor = new ChannelProcessor(selector);
Configurables.configure(channelProcessor, context);
source.setChannelProcessor(channelProcessor);
sourceRunnerMap.put(sourceName,
SourceRunner.forSource(source));
for (Channel channel : sourceChannels) {
ChannelComponent channelComponent =
Preconditions.checkNotNull(channelComponentMap.get(channel.getName()),
String.format("Channel %s", channel.getName()));
channelComponent.components.add(sourceName);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
String msg = String.format("Source %s has been removed due to an " +
"error during configuration", sourceName);
LOGGER.error(msg, e);
}
}
}
}
在loadSources()方法中,把source封装进SourceRunner类中,再把sourceRunner存入sourceRunnerMap中。
SourceRunner是一个抽象类,有两个类继承它。
从名字可以看出,一个是事件驱动,一个是主动拉取。
通过抽象类中的forSource()方法执行是哪个类。forSource()方法在loadSources()方法中被调用
public static SourceRunner forSource(Source source) {
SourceRunner runner = null;
if (source instanceof PollableSource) {
runner = new PollableSourceRunner();
((PollableSourceRunner) runner).setSource((PollableSource) source);
} else if (source instanceof EventDrivenSource) {
runner = new EventDrivenSourceRunner();
((EventDrivenSourceRunner) runner).setSource((EventDrivenSource) source);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No known runner type for source "
+ source);
}
return runner;
}
loadSinks(agentConf, channelComponentMap, sinkRunnerMap);
读取配置文件生成 sink , 并注册到 channel , 然后根据分组情况 sinkRunner, 未设置分组的,单独创建sinkRunner
private void loadSinks(AgentConfiguration agentConf,
Map<String, ChannelComponent> channelComponentMap, Map<String, SinkRunner> sinkRunnerMap)
throws InstantiationException { Set<String> sinkNames = agentConf.getSinkSet();
Map<String, ComponentConfiguration> compMap =
agentConf.getSinkConfigMap();
Map<String, Sink> sinks = new HashMap<String, Sink>();
/*
* Components which have a ComponentConfiguration object
* todo 组合配置ComponentConfiguration 的对象
*/
for (String sinkName : sinkNames) {
ComponentConfiguration comp = compMap.get(sinkName);
if (comp != null) { //todo 使用SinkFactory 直接采用根据类型,采用反射方式 实例化 Sink
SinkConfiguration config = (SinkConfiguration) comp;
Sink sink = sinkFactory.create(comp.getComponentName(), comp.getType()); try { //todo 为 Sink 匹配对应的 channel
Configurables.configure(sink, config);
ChannelComponent channelComponent = channelComponentMap.get(config.getChannel());
if (channelComponent == null) {
String msg = String.format("Sink %s is not connected to a " +
"channel", sinkName);
throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
} //todo 检查 channel 是否可用 : sink 的 batch size 要小于 channel 的 transaction capacity
checkSinkChannelCompatibility(sink, channelComponent.channel); sink.setChannel(channelComponent.channel); sinks.put(comp.getComponentName(), sink); //todo Sink 向 channel 反向注册 SinkName
channelComponent.components.add(sinkName);
} catch (Exception e) {
String msg = String.format("Sink %s has been removed due to an " +
"error during configuration", sinkName);
LOGGER.error(msg, e);
}
}
}
/*
* Components which DO NOT have a ComponentConfiguration object
* and use only Context
* todo 组合没有配置 ComponentConfiguration 但是使用 context 的对象
*/
Map<String, Context> sinkContexts = agentConf.getSinkContext();
for (String sinkName : sinkNames) {
Context context = sinkContexts.get(sinkName);
if (context != null) { //todo 直接采用根据类型,采用反射方式 实例化 Sink
Sink sink = sinkFactory.create(sinkName, context.getString(
BasicConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_TYPE)); try { //todo 为 Sink 匹配对应的 channel
Configurables.configure(sink, context);
ChannelComponent channelComponent =
channelComponentMap.get(
context.getString(BasicConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_CHANNEL));
if (channelComponent == null) {
String msg = String.format("Sink %s is not connected to a " +
"channel", sinkName);
throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
}
//todo 检查 channel 是否可用 : sink 的 batch size 要大于 channel 的 transaction capacity
checkSinkChannelCompatibility(sink, channelComponent.channel); sink.setChannel(channelComponent.channel);
sinks.put(sinkName, sink);
channelComponent.components.add(sinkName); } catch (Exception e) {
String msg = String.format("Sink %s has been removed due to an " +
"error during configuration", sinkName);
LOGGER.error(msg, e);
}
}
} //todo 对 sink 进行分组
loadSinkGroups(agentConf, sinks, sinkRunnerMap);
}
private void loadSinkGroups(AgentConfiguration agentConf,
Map<String, Sink> sinks, Map<String, SinkRunner> sinkRunnerMap)
throws InstantiationException { // todo 获取配置中的 group 分组
Set<String> sinkGroupNames = agentConf.getSinkgroupSet(); Map<String, ComponentConfiguration> compMap =
agentConf.getSinkGroupConfigMap(); Map<String, String> usedSinks = new HashMap<String, String>(); for (String groupName: sinkGroupNames) { ComponentConfiguration comp = compMap.get(groupName); if (comp != null) {
SinkGroupConfiguration groupConf = (SinkGroupConfiguration) comp;
List<Sink> groupSinks = new ArrayList<Sink>();
for (String sink : groupConf.getSinks()) {
Sink s = sinks.remove(sink);
if (s == null) {
String sinkUser = usedSinks.get(sink);
if (sinkUser != null) {
throw new InstantiationException(String.format(
"Sink %s of group %s already " +
"in use by group %s", sink, groupName, sinkUser));
} else {
throw new InstantiationException(String.format(
"Sink %s of group %s does "
+ "not exist or is not properly configured", sink,
groupName));
}
}
groupSinks.add(s);
usedSinks.put(sink, groupName);
}
try { SinkGroup group = new SinkGroup(groupSinks);
Configurables.configure(group, groupConf); //todo 创建 sinkRunner
sinkRunnerMap.put(comp.getComponentName(),
new SinkRunner(group.getProcessor())); } catch (Exception e) {
String msg = String.format("SinkGroup %s has been removed due to " +
"an error during configuration", groupName);
LOGGER.error(msg, e);
}
}
} // add any unassigned sinks to solo collectors
// todo 对未分组的 sink 进行处理
for (Entry<String, Sink> entry : sinks.entrySet()) {
if (!usedSinks.containsValue(entry.getKey())) {
try { SinkProcessor pr = new DefaultSinkProcessor();
List<Sink> sinkMap = new ArrayList<Sink>();
sinkMap.add(entry.getValue());
pr.setSinks(sinkMap);
Configurables.configure(pr, new Context()); //todo 创建 SinkRunner
sinkRunnerMap.put(entry.getKey(), new SinkRunner(pr)); } catch (Exception e) {
String msg = String.format("SinkGroup %s has been removed due to " +
"an error during configuration", entry.getKey());
LOGGER.error(msg, e);
}
}
} }
else块中的内容
PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider configurationProvider = new PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider(agentName, configurationFile);
application = new Application();
application.handleConfigurationEvent(configurationProvider.getConfiguration());
静态获取配置文件,由于静态所以不需要eventBus和PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider,只要PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider
也是用handleConfigurationEvent(),根据配置文件重启components
钩子函数Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook,主要是用来进行内存清理、对象销毁等操作
// 代码接上方
final Application appReference = application;
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread("agent-shutdown-hook") {
@Override
public void run() {
appReference.stop();
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("A fatal error occurred while running. Exception follows.", e);
}
}
}
Flume 1.9.0 源码解析 : 一篇文章弄清Flume 程序启动流程
channel的主要功能就是put和take
@InterfaceAudience.Public
@InterfaceStability.Stable
public interface Channel extends LifecycleAware, NamedComponent { public void put(Event event) throws ChannelException;
public Event take() throws ChannelException;
public Transaction getTransaction();
}
Channel中还有两个重要的类ChannelProcessor和ChannelSelector
ChannelProcessor 的作用就是执行put操作,将数据放到channel里面。每个ChannelProcessor实例都会配备一个ChannelSelector来决定event要put到那个channl当中,这个selector是作为参数传入的,从中获取对应的channel来执行event的put操作
public class ChannelProcessor implements Configurable {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ChannelProcessor.class);
private final ChannelSelector selector;
private final InterceptorChain interceptorChain;
public ChannelProcessor(ChannelSelector selector) {
this.selector = selector;
this.interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain();
}
......
public ChannelSelector getSelector() {
return this.selector;
}
public void processEventBatch(List<Event> events) {
...
while(i$.hasNext()) {
Event optChannel = (Event)i$.next();
List tx = this.selector.getRequiredChannels(optChannel);
...//将event放到Required队列
t1 = this.selector.getOptionalChannels(optChannel);
Object eventQueue;
...//将event放到Optional队列
}
...//event的分配操作
}
public void processEvent(Event event) {
event = this.interceptorChain.intercept(event);
if(event != null) {
List requiredChannels = this.selector.getRequiredChannels(event);
Iterator optionalChannels = requiredChannels.iterator();
...//event的分配操作
List optionalChannels1 = this.selector.getOptionalChannels(event);
Iterator i$1 = optionalChannels1.iterator();
...//event的分配操作
}
}
}
ChannelSelector是一个接口,我们可以通过ChannelSelectorFactory来创建它的子类,Flume提供了两个实现类MultiplexingChannelSelector和ReplicatingChannelSelector。
public interface ChannelSelector extends NamedComponent, Configurable {
void setChannels(List<Channel> var1);
List<Channel> getRequiredChannels(Event var1);
List<Channel> getOptionalChannels(Event var1);
List<Channel> getAllChannels();
}
通过ChannelSelectorFactory 的create来创建,create中调用getSelectorForType来获得一个selector,通过配置文件中的type来创建相应的子类
public static ChannelSelector create(List<Channel> channels,
ChannelSelectorConfiguration conf) {
String type = ChannelSelectorType.REPLICATING.toString();
if (conf != null) {
type = conf.getType();
}
ChannelSelector selector = getSelectorForType(type);
selector.setChannels(channels);
Configurables.configure(selector, conf);
return selector;
}
Sink是一个接口,里面最主要的方法是process(),用来处理从Channel中获取的数据。Sink的实例是由SinkFactory.create()生成的。
@InterfaceAudience.Public
@InterfaceStability.Stable
public interface Sink extends LifecycleAware, NamedComponent {
public void setChannel(Channel channel);
public Channel getChannel();
/* 用来处理channel中取来的event*/
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException;
public static enum Status {
READY, BACKOFF
}
}
sink由一个sink运行器管理,sink运行器只是一个负责运行该sink的线程
public class SinkRunner implements LifecycleAware {
...
@Override
public void start() {
SinkProcessor policy = getPolicy();
policy.start();
runner = new PollingRunner();
runner.policy = policy;
runner.counterGroup = counterGroup;
runner.shouldStop = new AtomicBoolean();
runnerThread = new Thread(runner);
runnerThread.setName("SinkRunner-PollingRunner-" +
policy.getClass().getSimpleName());
runnerThread.start();
lifecycleState = LifecycleState.START;
}
...
}
启动SinkRunner实际上就是调用它的start(),而在start()中可以看到主要是启动了一个SinkProcessor
public interface SinkProcessor extends LifecycleAware, Configurable {
Status process() throws EventDeliveryException;
void setSinks(List<Sink> sinks);
}
SinkProcesor是一个接口,他的实现类由SinkProcessorFactory的getProcessor()生成,在AbstractConfigurationProvider中的loadSinkGroup()调用SinkGroup中的configure()生成。
public class SinkGroup implements Configurable, ConfigurableComponent {
List<Sink> sinks;
SinkProcessor processor;
SinkGroupConfiguration conf;
public SinkGroup(List<Sink> groupSinks) {
sinks = groupSinks;
}
public SinkProcessor getProcessor() {
return processor;
}
@Override
public void configure(ComponentConfiguration conf) {
this.conf = (SinkGroupConfiguration) conf;
processor =
SinkProcessorFactory.getProcessor(this.conf.getProcessorContext(),
sinks);
}
}
sink groups使多个不同的sink组成一个整体,而sink processor提供了组内负载均衡和故障转移的功能。
有三种sink processor :default sink processor,failover sink processor,Load balancing Sink Processor。
default sink processor
一般的单独的sink
public class DefaultSinkProcessor implements SinkProcessor, ConfigurableComponent {
private Sink sink;
private LifecycleState lifecycleState;
@Override
public void start() {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(sink, "DefaultSinkProcessor sink not set");
sink.start();
lifecycleState = LifecycleState.START;
}
@Override
public void stop() {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(sink, "DefaultSinkProcessor sink not set");
sink.stop();
lifecycleState = LifecycleState.STOP;
}
@Override
public LifecycleState getLifecycleState() {
return lifecycleState;
}
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
}
@Override
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
return sink.process();
}
@Override
public void setSinks(List<Sink> sinks) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(sinks);
Preconditions.checkArgument(sinks.size() == 1, "DefaultSinkPolicy can "
+ "only handle one sink, "
+ "try using a policy that supports multiple sinks");
sink = sinks.get(0);
}
@Override
public void configure(ComponentConfiguration conf) {
}
}
default sink processor执行的就是sink的start、stop和process方法
failover sink processor
维护了一个sinks的优先级列表,保证只要有一个sink事件就可以被处理(即故障转移)。
sink优先级高的会被优先激活,若没有设置优先级则按照snk被声明的顺序来决定优先级。
Load balancing Sink Processor
提供了多个sinks负载均衡的能力。它维护了一个active sinks的索引列表,列表中fenb的sinks的负载必须是分布式的。
通过round_robin (轮询)或 random(随机)选择机制实现了分布式负载。选择机制默认为round_robin ,也可通过设置重载。自定义选举类须继承AbstractSinkSelector。
当被调用时,选择器根据配置文件的选择机制挑选下一个sink,并且调用该sink。如果所选的Sink传递Event失败,则通过选择机制挑选下一个可用的Sink,以此类推。失效的sink不会被加入到黑名单里,选择器会继续尝试所有可用的sink。所有的被调用的sink都失败后,选择器才会把失败发送给sink runner。
flume源码的更多相关文章
- 修改flume源码,使其HTTPSource具备访问路径功能
目前有一个需求,就是Flume可以作为一个类似于tomcat的服务器,可以通过post请求进行访问,并且路径需要:ip:port/contextPath格式. 经过一些资料获悉,httpSource只 ...
- <Flume><Source Code><Flume源码阅读笔记>
Overview source采集的日志首先会传入ChannelProcessor, 在其内首先会通过Interceptors进行过滤加工,然后通过ChannelSelector选择channel. ...
- Flume源码更改
1.源码更改场景:如果使用 0.8 版本 Kafka 并配套 1.6 版本 Flume,由于 Flume 1.6 版本没有Taildir Source 组件,因此,需要将 Flume 1.7 中的 T ...
- Flume源码-LoggerSink
package org.apache.flume.sink; import com.google.common.base.Strings; import org.apache.flume.Channe ...
- Apache Flume 1.7.0 源码编译 导入Eclipse
前言 最近看了看Apache Flume,在虚拟机里跑了一下flume + kafka + storm + mysql架构的demo,功能很简单,主要是用flume收集数据源(http上报信息),放入 ...
- Spark Streaming从Flume Poll数据案例实战和内幕源码解密
本节课分成二部分讲解: 一.Spark Streaming on Polling from Flume实战 二.Spark Streaming on Polling from Flume源码 第一部分 ...
- flume1.4.0源码结构剖析
flume基本思想: source负责收集数据,channel负责缓存数据,sink负责消费channel中的数据,具体使用方式这里不赘述 生命周期管理: 生命周期相关代码在flume-ng-core ...
- 如何在IDEA里给大数据项目导入该项目的相关源码(博主推荐)(类似eclipse里同一个workspace下单个子项目存在)(图文详解)
不多说,直接上干货! 如果在一个界面里,可以是单个项目 注意:本文是以gradle项目的方式来做的! 如何在IDEA里正确导入从Github上下载的Gradle项目(含相关源码)(博主推荐)(图文详解 ...
- Flume 实战(2)--Flume-ng-sdk源码分析
具体参考: 官方用户手册和开发指南 http://flume.apache.org/FlumeDeveloperGuide.html *) 定位和简单例子 1). Flume-ng-sdk是用于编写往 ...
随机推荐
- 人生苦短_我用Python_pymysql库对Mysql数据库操作_009
# coding=utf-8 import pymysql ''' 数据库的登录信息: config={ 'host':'118.126.108.xxx', # :主机 'user':'python' ...
- Ubuntu新建用户组
新建用户组 sudo addgroup groupname 把现有用户加入新建的用户组 sudo adduser username groupname
- 4412 RS485
一.485硬件原理 差分对传输数据的原理 IO数据的传输→差分对 rs232传输的距离在15米以下,RS485传输距离是几十米到1000米以上 为什么485可以传输这么远 差分对的机制可以降低电磁场的 ...
- BZOJ 5137: [Usaco2017 Dec]Standing Out from the Herd(后缀自动机)
传送门 解题思路 这个似乎和以前做过的一道题很像,只不过这个是求本质不同子串个数.肯定是先把广义\(SAM\)造出来,然后\(dfs\)时把子节点的信息合并到父节点上,看哪个只被一个串覆盖,\(ans ...
- 禁止多用户进入win7系统的方法(图文)
windows7系统可以支持多用户登陆,虽然它能为使用者提供方便,但是为安全起见,一些用户想要禁止多用户进入win7系统,因为我们并不能保证其他账户用户在使用过程中是否会安装病毒程序.那么如何禁止多用 ...
- 如果遇到找不到元素如何处理? Exception in thread "main" org.openqa.selenium.NoSuchElementException: no such element: Unable to locate element: {"method":"id","selector":"investmentframe"}
常见几种原因与应对,详细参见http://www.blogjava.net/qileilove/archive/2014/12/11/421309.html 1,动态ID无法找到,用xpath路径解决 ...
- 通过TCP/IP连接Mysql数据库
问题:mysql只能用localhost或127.0.0.1连接 解决:mysql安装完后,默认是root用户,root用户只能在服务器登录,需要分配新用户. 1.以root用户登陆mysql数据库. ...
- 记录Liunx 命令常用的
df -h 查询硬盘容量(GB方式)
- gitlab fatal: Authentication failed for 'http://10.2.80.17:8090/yeyichao/201904041026PROj.git/'
fatal: Authentication failed for 'http://10.2.80.17:8090/yeyichao/201904041026PROj.git/' git config ...
- Spring clound 微服务--理解篇
定义:微服务就是一些协调工作的小而自治的服务 优点: 异构性:不同微服务可以使用不同的语言实现, 后端数据库也可以根据自身业务定义服务. 弹性: 一个组件不可用,不会导致级联故障.一个系统出了问题,不 ...