深入理解计算机系统_3e 第八章家庭作业 CS:APP3e chapter 8 homework
**8.9**
关于并行的定义我之前写过一篇文章,参考:
并发与并行的区别 The differences between Concurrency and Parallel
+----------------------------+
| Process pair Concurrent?|
+----------------------------+
| AB N |
| |
| AC Y |
| |
| AD Y |
| |
| BC Y |
| |
| BD Y |
| |
| CD Y |
+----------------------------+
8.10
A.
fork
B.
execve longjmp
C.
setjmp
8.11
4次
+--------------> printf("hello\n")
|
| Fork
| i = 1
+------------+--------------> printf("hello\n")
|
|
| +--------------> printf("hello\n")
| |
| |
| |
+--------+------------+--------------> printf("hello\n")
Fork Fork
i = 0 i = 1
8.12
8次
main
+-------> printf("hello\n")+--------> printf("hello\n")
| main
+-----+-------> printf("hello\n")+--------> printf("hello\n")
| Fork
Fork| Fork main
+-------------+-------> printf("hello\n")+--------> printf("hello\n")
| | main
+----+ +-------> printf("hello\n")+--------> printf("hello\n")
doit()
8.13
保证x=4在x=3之前即可(拓扑排序),有三种情况:
A.
x=2 x=4 x=3
B.
x=4 x=2 x=3
C.
x=4 x=3 x=2
"x=4" "x=3"
+-------> printf("%d\n", ++x) +---> printf("%d\n", --x) +-->
|
|
|
+---------+-------> printf("%d\n", --x) +---------------------------->
x = 3 Fork
"x=2"
8.14
3次
+-------> printf("hello\n") +--->
|
+-----+-------> printf("hello\n") +--->
| Fork
Fork| main
+-------------------------------------------------> printf("hello\n")
|
+----+
doit()
8.15
5次
main
+-------> printf("hello\n")+--------> printf("hello\n")
| main
+-----+-------> printf("hello\n")+--------> printf("hello\n")
| Fork
Fork| main
+-------------------------------------------------> printf("hello\n")
|
+----+
doit()
8.16
counter = 2
更新(李治霖指出错误):虽然子进程对counter进行了减一操作,但是子进程和父进程并没有共享内存,即不会影响父进程的变量
+--> counter-- +--+
| |
counter=1 | v
+--+-------------->Wait(NULL)+--> printf("counter = %d\n", ++counter);
Fork
8.17
假设子进程正常退出;构成拓扑排序即可,有三种情况:
A.
Hello 1 Bye 0 2 Bye
B.
Hello 1 0 Bye 2 Bye
C.
Hello 0 1 Bye 2 bye
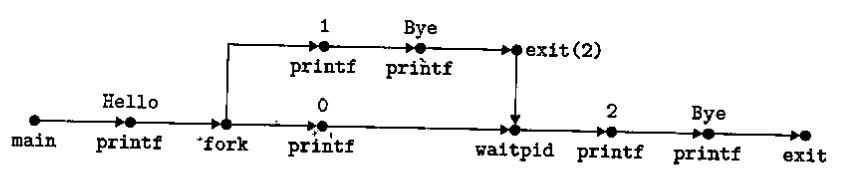
8.18
构成拓扑排序即可,ACE正确。
B中的第一个不可能是2。D中的第一个1后面不可能有两个2。
+-->printf("0")+--->printf("2")
|
+----->atexit+-+-->printf("1")+--->printf("2")
| Fork
| Fork
+---+--------------+-->printf("1")
Fork |
+-->printf("0")
8.19
2^n
每次Fork都会使原来的进程数翻倍,最后每一个进程都会输出一行,所以是2^n行。
8.20
书上说改变COLUMNS环境变量会使得ls改变输出的宽度,但是在我的机器上即使用export改变该环境变量后,如果我再调用ls ,其依然按照终端的宽度输出,而且COLUMNS被改变回原来的值,我怀疑是调用ls的时候系统重新探测终端宽度并设置了新的COLUMNS。
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[], const char *envp[])
{
if (execve("/bin/ls", argv, envp))
{
perror("Failed to execve /bin/ls:\n");
}
return 0;
}
类型不一致可能会报警,这里不会有问题。
8.21
满足拓扑排序即可,两种情况:
A.
abc
B.
bac
+----->printf("a")+-------+
| |
| v
+---+----->printf("b")+--->waitpid+--->printf("c")+-->
fork
8.22
根据man 3 system 的部分描述:
The system() library function uses fork(2) to create a child process that executes the shell command specified in command using execl(3) as follows:
execl("/bin/sh", "sh", "-c", command, (char *) 0);
我们可以得到execl调用后的进程关系图:
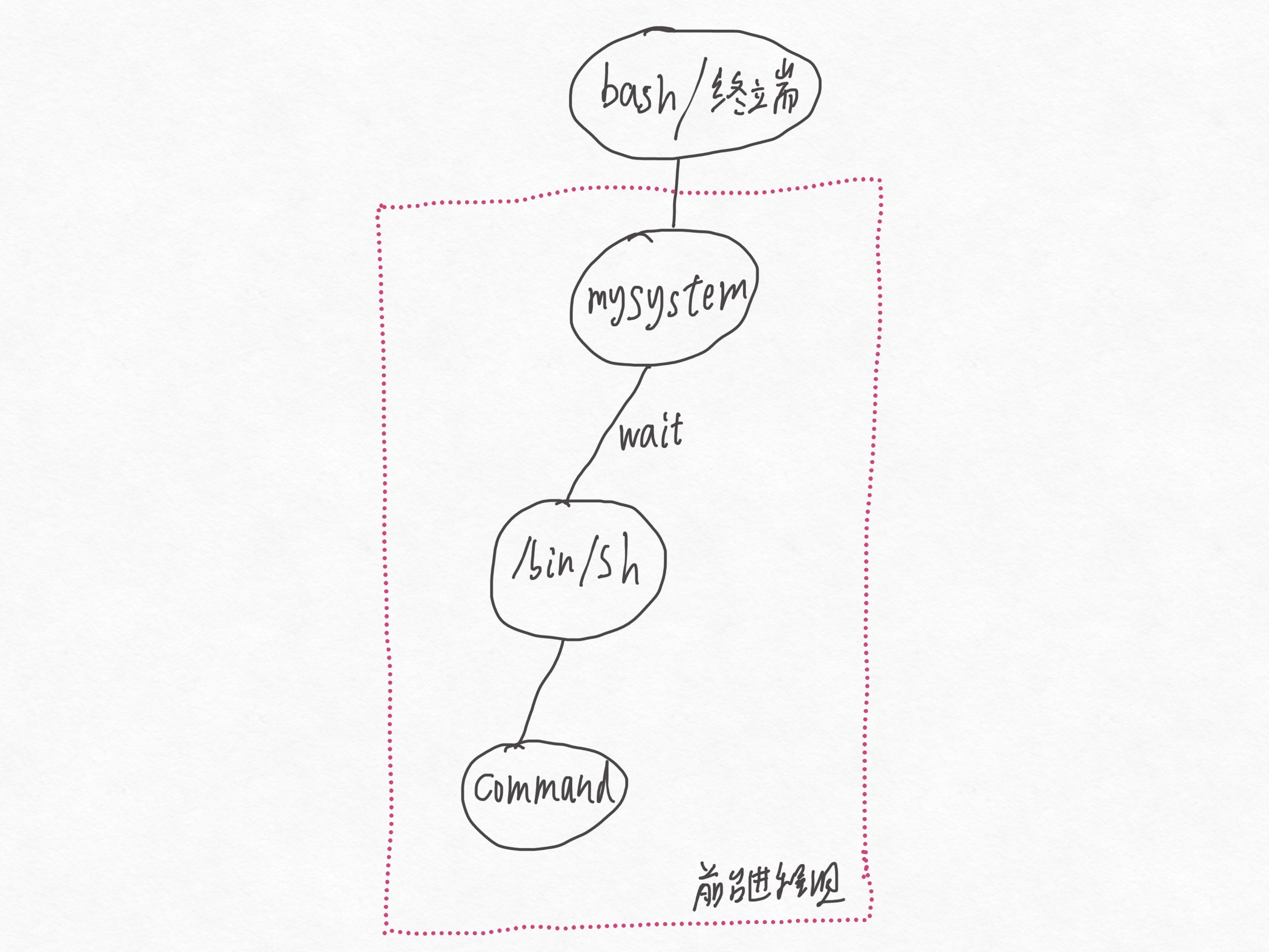
根据man sh的部分描述:
EXIT STATUS
Errors that are detected by the shell, such as a syntax error, will cause
the shell to exit with a non-zero exit status. If the shell is not an
interactive shell, the execution of the shell file will be aborted. Oth‐
erwise the shell will return the exit status of the last command exe‐
cuted, or if the exit builtin is used with a numeric argument, it will
return the argument.
可以看到Otherwise the shell will return the exitstatus of the last command executed这句话,也就是说,command执行的状态会称为sh的返回状态,所以我们回收sh并判断其返回状态即可。
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int mysystem(char *command)
{
pid_t sh_pid;
int sh_status;
if ((sh_pid = fork()) == 0)
{
execl("/bin/sh", "sh", "-c", command, (char *) 0);
}
else
{
if ((waitpid(sh_pid, &sh_status, 0)) == sh_pid)
{
if (WIFEXITED(sh_status))
{
return WEXITSTATUS(sh_status);
}
else if (WIFSIGNALED(sh_status))
{
fprintf(stderr, "command terminated by signal number %d.\n", WTERMSIG(sh_status));
if (WCOREDUMP(sh_status))
{
fprintf(stderr, "core dumped...\n", );
}
return WTERMSIG(sh_status);
}
else
{
fprintf(stderr, "command terminated abnormally.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "return status information...\n");
return sh_status;
}
}
else
{
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to reap /bin/sh.\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
}
}
8.23
一个典型的信号不能累加的问题。
当子进程连续向父进程发送5个SIGUSR2信号时,第一个信号传送过程如下,其中A代表子进程,C代表父进程:

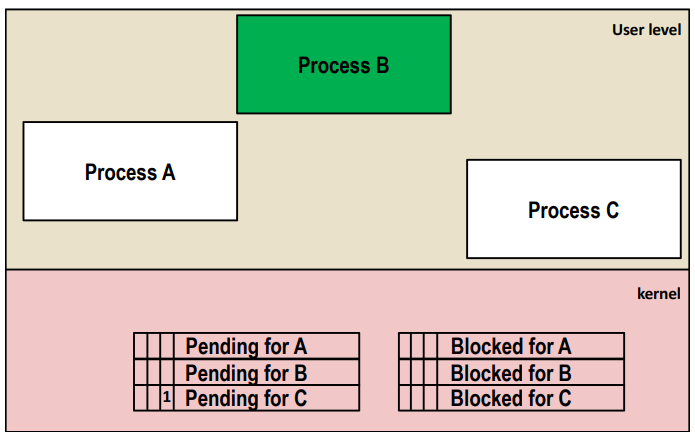

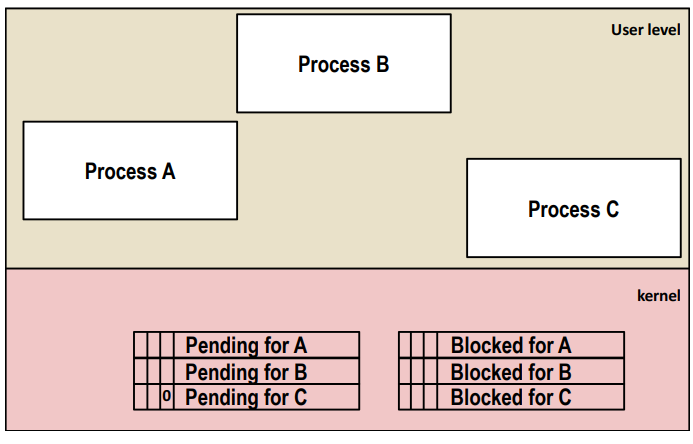
当父进程C接到信号后,它进入信号处理函数,并暂时将这个信号屏蔽(设置block位),这时子进程还在不断的向父进程发送所有剩下的同类信号,pending位被再次置1,而接下来的信号则会被遗弃(只有一个pending位,没办法计数),当父进程C的信号处理函数退出后,block位被置零,刚刚pending的信号再次被送入父进程C,父进程再次进入信号处理函数,这时子进程已经完成所有的信号发送,所以父进程不会再次进入信号处理函数了。综上,父进程C只会进入两次信号处理函数,即counter只会被加2而非5。
8.24
书上说要使用库函数psignal信号的描述,man 3 psignal描述如下:
#include <signal.h>
void psignal(int sig, const char *s);
The psignal() function displays a message on stderr consisting of the string s, a colon, a space, a string describing the signal number sig, and a trailing newline. If the string s is NULL or empty, the colon and space are omitted. If sig is invalid, the message displayed will indicate an unknown signal.
将Figure 8.18的代码改为:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define N 2
int main()
{
int status;
pid_t pid;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if (((pid = fork()) == 0))
{
int *p = 0;
*p = 0; /* Segmentation fault (core dumped) */
return 0;
}
}
while ((pid = wait(&status)) > 0)
{
if (WIFEXITED(status))
{
printf("child %d terminated normally with exit status=%d\n"
, pid, WEXITSTATUS(status));
}
else if (WIFSIGNALED(status))
{
fprintf(stderr, "child %d terminated by signal %d"
, pid, WTERMSIG(status));
psignal(WTERMSIG(status), " ");
}
else
{
fprintf(stderr, "child %d terminated abnormally with status information=%d\n"
, pid, status);
}
}
if (errno != ECHILD)
{
fprintf(stderr, "waitpid error");
}
return 0;
}
运行输出:
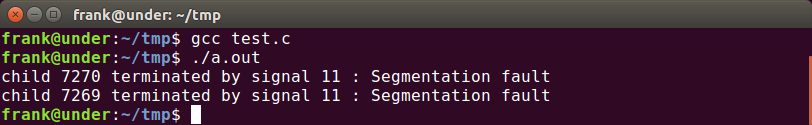
8.25
倒计时可以用alarm实现,其到指定时间后会raise一个SIGALRM信号, man 2 alarm部分描述:
#include <unistd.h>
unsigned int alarm(unsigned int seconds);
alarm() arranges for a SIGALRM signal to be delivered to the calling process in seconds seconds.
If seconds is zero, any pending alarm is canceled.
In any event any previously set alarm() is canceled.
我们收到这个信号后,就要想办法终止等待中的读入并返回NULL。其中一个办法是使用setjmp.h ,我们在第一次使用setjmp(buf)时进入正常的读入(此时setjmp返回值为0),但当信号出现(时间截止),信号处理函数就会longjmp(buf,1) (此时setjmp返回值为1),根据返回值的不同,这时我们便进入return NULL语句。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <setjmp.h>
#define TIMEOUT ((unsigned int)5)
#define SIZEOFBUF 1024
jmp_buf buf;
void SIGALRM_handler(int signum)
{
longjmp(buf, 1);
}
char *tfgets(char *s, int size, FILE *stream)
{
if (signal(SIGALRM, SIGALRM_handler) == SIG_ERR)
{
perror("Failed to install SIGALRM_handler");
return NULL;
}
else
{
alarm(TIMEOUT); /* raise SIGALRM after TIMEOUT seconds */
}
if (!setjmp(buf))
{
return fgets(s, size, stream);
}
else /* longjmp from SIGALRM_handler */
{
return NULL;
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
char temp_bufer[SIZEOFBUF];
char *result = tfgets(temp_bufer, SIZEOFBUF, stdin);
if (result)
{
printf("Input : %s\n", result);
}
else
{
fprintf(stderr, "Time out!\n");
}
return 0;
}
运行输出(第二次输入超时):

8.26
这个四星的题目实际上就是本章对应的ShellLab(tsh)实验,我做了以后会把该实验对应的writeup链接发上来。
**更新:CS:APP3e 深入理解计算机系统_3e ShellLab(tsh)实验 **
深入理解计算机系统_3e 第八章家庭作业 CS:APP3e chapter 8 homework的更多相关文章
- 深入理解计算机系统_3e 第九章家庭作业 CS:APP3e chapter 9 homework
9.11 A. 00001001 111100 B. +----------------------------+ | Parameter Value | +--------------------- ...
- 深入理解计算机系统_3e 第十章家庭作业 CS:APP3e chapter 10 homework
10.6 1.若成功打开"foo.txt": -->1.1若成功打开"baz.txt": 输出"4\n" -->1.2若未能成功 ...
- 深入理解计算机系统_3e 第二章家庭作业 CS:APP3e chapter 2 homework
初始完成日期:2017.9.26 许可:除2.55对应代码外(如需使用请联系 randy.bryant@cs.cmu.edu),任何人可以自由的使用,修改,分发本文档的代码. 本机环境: (有一些需要 ...
- 深入理解计算机系统_3e 第七章家庭作业 CS:APP3e chapter 7 homework
7.6 +-----------------------------------------------------------------------+ |Symbol entry? Symbol ...
- 深入理解计算机系统_3e 第六章家庭作业 CS:APP3e chapter 6 homework
6.22 假设磁道沿半径均匀分布,即总磁道数和(1-x)r成正比,设磁道数为(1-x)rk: 由题单个磁道的位数和周长成正比,即和半径xr成正比,设单个磁道的位数为xrz: 其中r.k.z均为常数. ...
- 深入理解计算机系统_3e 第五章家庭作业 CS:APP3e chapter 5 homework
5.13 A. B. 由浮点数加法的延迟,CPE的下界应该是3. C. 由整数加法的延迟,CPE的下界应该是1. D. 由A中的数据流图,虽然浮点数乘法需要5个周期,但是它没有"数据依赖&q ...
- 深入理解计算机系统_3e 第三章家庭作业 CS:APP3e chapter 3 homework
3.58 long decode2(long x, long y, long z) { int result = x * (y - z); if((y - z) & 1) result = ~ ...
- 深入理解计算机系统_3e 第十一章家庭作业 CS:APP3e chapter 11 homework
注:tiny.c csapp.c csapp.h等示例代码均可在Code Examples获取 11.6 A. 书上写的示例代码已经完成了大部分工作:doit函数中的printf("%s&q ...
- 深入理解计算机系统_3e 第二章家庭作业答案
初始完成者:哈尔滨工业大学 李秋豪 许可:除2.55对应代码外(如需使用请联系randy.bryant@cs.cmu.edu),任何人可以自由的使用,修改,分发本文档的代码. 本机环境: (有一些需要 ...
随机推荐
- 无状态的web应用(单个py文件的Django占位图片服务器)
本文为作者原创,转载请注明出处(http://www.cnblogs.com/mar-q/)by 负赑屃 阅读本文建议了解Django框架的基本工作流程,了解WSGI应用,如果对以上不是很清楚,建议结 ...
- 将Excel文件数据导入到SqlServer数据库的三种方案
方案一: 通过OleDB方式获取Excel文件的数据,然后通过DataSet中转到SQL Server,这种方法的优点是非常的灵活,可以对Excel表中的各个单元格进行用户所需的操作. openFil ...
- linux系统下手动安装Angular-cli
安装Angular-cli 背景 由于公司linux服务器没有外网,无法通过npm包管理器直接安装,只能手动安装一个Angular-cli平台环境! 安装步骤 1. 先再linux系统下安装好node ...
- MS10_087漏洞学习研究
类别:栈溢出,fileformat类别漏洞 描述: This module exploits a stack-based buffer overflow in the handling of the ...
- mysql数据库相关知识
什么是数据库? 数据库(Database)是按照数据结构来组织.存储和管理数据的建立在计算机存储设备上的仓库.(来自:百度) 什么是sql? 结构化查询语言(Struct ...
- android shape 大全 (转)
1. 各属性的配置语法 在项目 res/drawable 文件夹中创建一个以 shape 为根节点的 XML 文件,基本语法如下: <?xml version="1.0" e ...
- 3721:和数-poj
总时间限制: 1000ms 内存限制: 65536kB 描述 给定一个正整数序列,判断其中有多少个数,等于数列中其他两个数的和. 比如,对于数列1 2 3 4, 这个问题的答案就是2, 因为3 = ...
- 用JS实现Ajax请求
AJAX核心(XMLHttpRequest) 其实AJAX就是在Javascript中多添加了一个对象:XMLHttpRequest对象.所有的异步交互都是使用XMLHttpServlet对象完成的. ...
- 【原创】2、小程序域名配置之申请支持SSL(https)
要把一个网站对接进小程序,一.网站的域名必须通过备案(ICP备案).在买域名的时候,各个域名服务商都有提供相应的备案平台,可以方便的提交备案.工信部官网:http://www.miitbeian.go ...
- php中session 入库的实现
ini_set("session.save_handler","user");//session.gc_probability = 1 分子ini_set(&q ...
