python实战--数据结构二叉树
此文将讲述如何用python实战解决二叉树实验
前面已经讲述了python语言的基本用法,现在让我们实战一下具体明确python的用法
点击我进入python速成笔记
先看一下最终效果图:
首先我们要定义二叉树结点的一个类,在python中定义二叉树结点代码如下:
#二叉链表
class BiTree:
def __init__(self, elementType=None, lchild=None, rchild=None):
self.elementType = elementType
self.lchild = lchild
self.rchild = rchild
其次初始化二叉树头结点的代码如下:
#初始化二叉树新建头结点
def initTree(s):
temp=BiTree()
ptree=BiTree("A",temp,temp)
if s[2]==0:
ptree.lchild=None
if s[4]==0:
ptree.rchild=None
return ptree,temp
二叉树中经常需要访问子节点,那么子节点的代码:
#寻找下一个结点
def getNext(tree,temp):
if(tree.lchild ==temp ):
return tree
if (tree.lchild!=None):
if(getNext(tree.lchild,temp)!=None):
return getNext(tree.lchild,temp)
if (tree.rchild==temp):
return tree
if(tree.rchild !=None):
if (getNext(tree.rchild,temp) != None):
return getNext(tree.rchild,temp)
return None
有了头结点也能找到子节点,那么绘图二叉树的代码如下:
绘图需要传入图形窗口对象,根节点,初始根节点x,y坐标以及深度1
#画出二叉树图
def drawroot(graph,root,x,y,deep):
# 画椭圆
oval = Oval(Point(x-20, y-20), Point(x+20, y+20))
oval.setFill('blue') # 填充颜色
oval.draw(graph)
# 显示文字
message = Text(Point(x, y), root.elementType)
message.draw(graph)
if(root.lchild!=None):
# 画线
line = Line(Point(x - 10, y + 10), Point(x - 30*deep, y + 60))
line.draw(graph)
drawroot(graph,root.lchild,x-30*deep,y+60,deep-1)
if(root.rchild!=None):
# 画线
line = Line(Point(x+10, y + 10), Point(x + 30*deep, y + 60))
line.draw(graph)
drawroot(graph, root.rchild, x + 30*deep, y + 60,deep-1)
如何快速生成二叉树需要动用文件,根据文件链接子树代码:
读入根节点和一个临时结点,根节点名字和是否有左右子树开始链接
#根据文件建立二叉链表
def getTree(tree,temp,name,left,right):
child=BiTree(name,temp,temp)
if(not left):
child.lchild=None
if(not right):
child.rchild=None
if(tree.lchild==temp):
tree.lchild=child
elif(tree.rchild==temp):
tree.rchild=child
具体完整读取代码完全链接子树代码如下:
input = open('bt31.txt', 'r')
s = []
try:
for line in input:
s.append(line)
finally:
input.close()
ptree, temp = initTree(s[0])
for i in range(len(s)):
if i != 0:
getTree(getNext(ptree, temp), temp, s[i][0], eval(s[i][2]), eval(s[i][4]))
然后生成图形窗口绘制上面二叉树代码为:
gragh = GraphWin('CSSA', 1200, 700)
drawroot(gragh, ptree, 500, 20, 4)
效果如下:

以上便是二叉树生成的前提操作,后面代码即为数据结构实验五二叉树1-10题必做题源代码以及12,13,15选做题源码:
#三种二叉遍历
def DLR(tree):
order=[]
if(tree!=None):
order.append(tree.elementType)
if(tree.lchild!=None):
order=order+DLR(tree.lchild)
if(tree.rchild!=None):
order=order+DLR(tree.rchild)
return order
def LDR(tree):
order=[]
if (tree != None):
if (tree.lchild != None):
order = order + LDR(tree.lchild)
order.append(tree.elementType)
if (tree.rchild != None):
order = order + LDR(tree.rchild)
return order
def LRD(tree):
order=[]
if (tree != None):
if (tree.lchild != None):
order = order + LRD(tree.lchild)
if (tree.rchild != None):
order = order + LRD(tree.rchild)
order.append(tree.elementType)
return order
#打印题目一信息
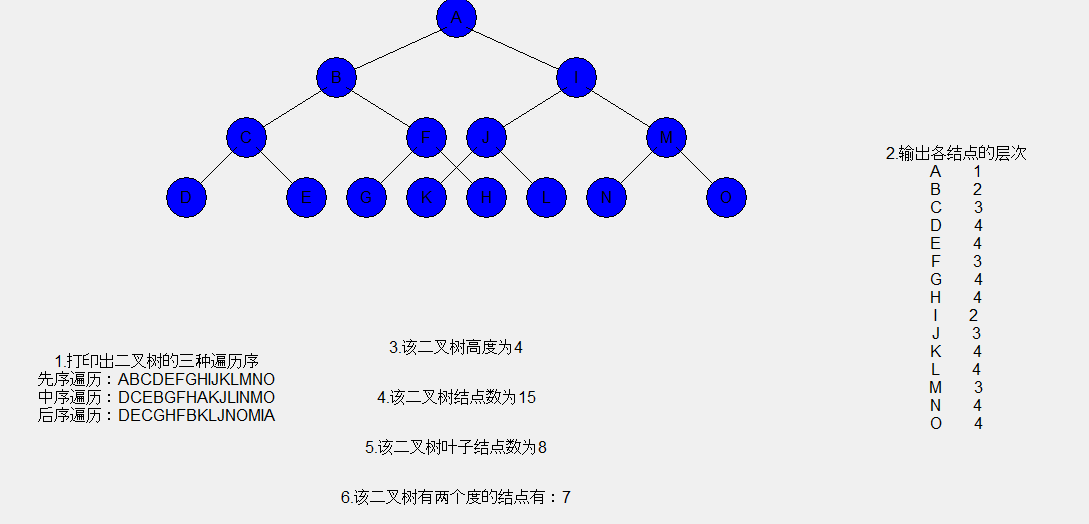
def exp1(gragh,ptree):
str=""
str += "先序遍历:"
for i in range(len(DLR(ptree))):
str+=DLR(ptree)[i]
str +="\n"
str += "中序遍历:"
for i in range(len(LDR(ptree))):
str +=LDR(ptree)[i]
str +="\n"
str += "后序遍历:"
for i in range(len(LRD(ptree))):
str +=LRD(ptree)[i]
str +="\n"
message = Text(Point(200, 400), "1.打印出二叉树的三种遍历序\n"+str)
message.draw(gragh)
#遍历结点层次
def DLRDeep(tree,deep):
order=""
if(tree!=None):
order=order+tree.elementType+" "+repr(deep)+"\n"
if(tree.lchild!=None):
order=order+DLRDeep(tree.lchild,deep+1)
if(tree.rchild!=None):
order=order+DLRDeep(tree.rchild,deep+1)
return order
def exp2(gragh,ptree):
str=DLRDeep(ptree,1)
message = Text(Point(1000, 300), "2.输出各结点的层次\n"+str)
message.draw(gragh)
#查找树的高度
def height(tree):
h=0
if(tree!=None):
left=height(tree.lchild)
right=height(tree.rchild)
if(left>right):
h=left+1
else :
h=right+1
return h
def exp3(gragh,ptree):
str="3.该二叉树高度为"+repr(height(ptree))
message = Text(Point(500, 350), str)
message.draw(gragh)
#查询结点数量
def getnum(tree):
num=0
if(tree!=None):
num=num+1
num+=getnum(tree.lchild)
num+=getnum(tree.rchild)
return num
def exp4(gragh,ptree):
str="4.该二叉树结点数为"+repr(getnum(ptree))
message = Text(Point(500, 400), str)
message.draw(gragh)
#查询叶子结点数量
def getleaf(tree):
num=0
if(tree!=None):
num+=getleaf(tree.lchild)
num+=getleaf(tree.rchild)
if(tree.lchild==None and tree.rchild==None):
return 1
return num
def exp5(gragh,ptree):
str="5.该二叉树叶子结点数为"+repr(getleaf(ptree))
message = Text(Point(500, 450), str)
message.draw(gragh)
#查询两个度的结点数量
def getTwo(tree):
num=0
if(tree!=None):
num+=getTwo(tree.lchild)
num+=getTwo(tree.rchild)
if(tree.lchild!=None and tree.rchild!=None):
num+=1
return num
def exp6(gragh,ptree):
str="6.该二叉树有两个度的结点有:"+repr(getTwo(ptree))
message = Text(Point(500, 500), str)
message.draw(gragh)
#查询父亲结点,兄弟结点,子节点
def findFather(tree,name):
if(tree!=None):
if(tree.lchild!=None and tree.lchild.elementType==name):
return tree
if(tree.rchild!=None and tree.rchild.elementType==name):
return tree
if findFather(tree.rchild,name)!=None:
return findFather(tree.rchild,name)
if findFather(tree.lchild,name)!=None:
return findFather(tree.lchild,name)
return None
def info(tree,name):
father=findFather(tree,name)
if(father.lchild!=None and father.lchild.elementType==name):
brother=father.rchild
son1=father.lchild.lchild
son2=father.lchild.rchild
else :
brother=father.lchild
son1=father.rchild.lchild
son2=father.rchild.rchild
return father,brother,son1,son2
def exp7(gragh ,tree,name):
str=""
father,brother,son1,son2=info(tree,name)
if(father==None):
str+="8.父节点不存在"+"\n"
else:
str+="8.父节点为:"+repr(father.elementType)+"\n"
if(brother==None):
str+="兄弟结点不存在"+"\n"
else:
str+="兄弟结点为:"+repr(brother.elementType)+"\n"
if(son1==None):
str+="左子结点不存在"+"\n"
else:
str+="左子结点为:"+repr(son1.elementType)+"\n"
if (son1 == None):
str += "右子结点不存在"+"\n"
else:
str+="右子结点为:"+repr(son2.elementType)+"\n"
message = Text(Point(400, 550), str)
message.draw(gragh)
#查询指定结点深度
def getdeep(tree,name,deep): #EXP8
if (tree != None):
if (tree.elementType==name):
return deep
deepleft=getdeep(tree.lchild,name,deep+1)
deepright=getdeep(tree.rchild,name,deep+1)
if(deepleft!=0):
return deepleft
if(deepright!=0):
return deepright
return 0
def exp8(gragh,tree,name):
deep=getdeep(tree,name,1)
if(deep==0):
message = Text(Point(400, 500), "7.本结点不存在")
message.draw(gragh)
return 0
else:
message = Text(Point(400, 500), "7.本结点:"+repr(name)+"深度为"+repr(deep))
message.draw(gragh)
return 1
#顺序存储变为二叉链表存储
def seqToNode(s,tree,i):
if(tree!=None):
if(i*2>len(s)):
tree.lchild=None
elif (s[i*2]==None) :
tree.lchild=None
else:
temp = BiTree(s[i*2])
tree.lchild=temp
if(i*2+1>len(s)):
tree.rchild=None
elif (s[i*2+1]==None):
tree.rchild=None
else:
temp = BiTree(s[i*2 + 1])
tree.rchild=temp
seqToNode(s,tree.lchild,i*2)
seqToNode(s,tree.rchild,i*2+1)
#交换左右二叉树
def change(tree):# EXP10
if(tree!=None):
temp=tree.lchild
tree.lchild=tree.rchild
tree.rchild=temp
if(tree.lchild!=None):
change(tree.lchild)
if(tree.rchild!=None):
change(tree.rchild)
#找所有结点的路径
def road(s,tree,all):
if(tree.rchild==None and tree.lchild==None):
all.append(repr(tree.elementType))
all.append("到根节点的路径为"+reverse1(s)+"A"+"\n")
if(tree.lchild!=None):
road(s+tree.lchild.elementType,tree.lchild,all)
if(tree.rchild!=None):
road(s+(tree.rchild.elementType),tree.rchild,all)
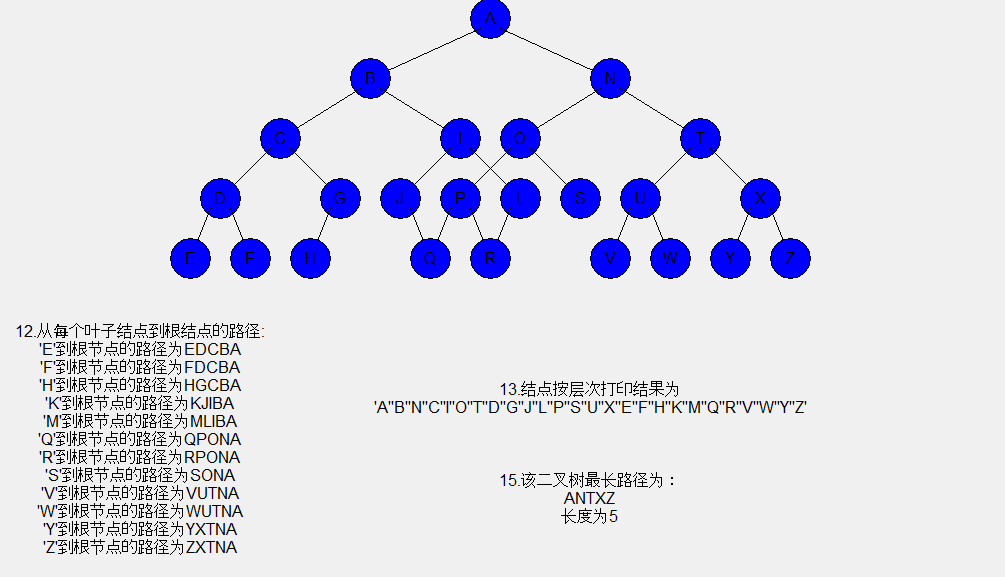
def exp12(all,gragh,ptree):
str=""
road(str, ptree, all)
for i in range (len(all)):
str+=all[i]
message = Text(Point(150, 450), "12.从每个叶子结点到根结点的路径:\n"+str)
message.draw(gragh)
#按层次打印结点
def exp13(gragh,tree):
que=Queue()
que.enqueue(tree)
str="13.结点按层次打印结果为\n"
while(not que.isEmpty()):
if(que.getTop().lchild!=None):
que.enqueue(que.getTop().lchild)
if(que.getTop().rchild!=None):
que.enqueue(que.getTop().rchild)
str+=repr(que.getTop().elementType)
que.outqueue()
message = Text(Point(600, 400), str)
message.draw(gragh)
#查找最长路径
def maxpath(temp,tree,path,deep):
if (tree.rchild == None and tree.lchild == None):
return temp,deep
deep1,deep2=0,0
if (tree.lchild != None):
path1,deep1=maxpath(temp + tree.lchild.elementType, tree.lchild, path,deep+1)
if (tree.rchild != None):
path2,deep2=maxpath(temp + (tree.rchild.elementType), tree.rchild, path,deep+1)
if(deep1>deep2):
return path1,deep1
else :
return path2,deep2
def exp15(gragh,tree):
temp=""
path=""
path,deep=maxpath(temp,tree,path,1)
message = Text(Point(600, 500), "15.该二叉树最长路径为:\nA"+path+"\n长度为"+repr(deep))
message.draw(gragh)
值得注意的是13题需要用到队列,需要提前写好队列的代码如下:
class Queue:
"""模拟队列"""
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
def isEmpty(self):
return self.items == []
def enqueue(self, item):
self.items.insert(0, item)
def outqueue(self):
return self.items.pop()
def size(self):
return len(self.items)
def getTop(self):
return self.items[self.size()-1]
上述便是代码的全部代码,效果如下
python实战--数据结构二叉树的更多相关文章
- python 与数据结构
在上面的文章中,我写了python中的一些特性,主要是简单为主,主要是因为一些其他复杂的东西可以通过简单的知识演变而来,比如装饰器还可以带参数,可以使用装饰类,在类中不同的方法中调用,不想写的太复杂, ...
- [0x00 用Python讲解数据结构与算法] 概览
自从工作后就没什么时间更新博客了,最近抽空学了点Python,觉得Python真的是很强大呀.想来在大学中没有学好数据结构和算法,自己的意志力一直不够坚定,这次想好好看一本书,认真把基本的数据结构和算 ...
- 用Python实现数据结构之二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树 二叉搜索树是一种特殊的二叉树,它的特点是: 对于任意一个节点p,存储在p的左子树的中的所有节点中的值都小于p中的值 对于任意一个节点p,存储在p的右子树的中的所有节点中的值都大于p中的值 ...
- 用Python实现数据结构之优先级队列
优先级队列 如果我们给每个元素都分配一个数字来标记其优先级,不妨设较小的数字具有较高的优先级,这样我们就可以在一个集合中访问优先级最高的元素并对其进行查找和删除操作了.这样,我们就引入了优先级队列 这 ...
- zeromq 学习和python实战
参考文档: 官网 http://zeromq.org/ http://www.cnblogs.com/rainbowzc/p/3357594.html 原理解读 zeromq只是一层针对socke ...
- Python实战:美女图片下载器,海量图片任你下载
Python应用现在如火如荼,应用范围很广.因其效率高开发迅速的优势,快速进入编程语言排行榜前几名.本系列文章致力于可以全面系统的介绍Python语言开发知识和相关知识总结.希望大家能够快速入门并学习 ...
- Python实战:Python爬虫学习教程,获取电影排行榜
Python应用现在如火如荼,应用范围很广.因其效率高开发迅速的优势,快速进入编程语言排行榜前几名.本系列文章致力于可以全面系统的介绍Python语言开发知识和相关知识总结.希望大家能够快速入门并学习 ...
- Python -- 堆数据结构 heapq - I love this game! - 博客频道 - CSDN.NET
Python -- 堆数据结构 heapq - I love this game! - 博客频道 - CSDN.NET Python -- 堆数据结构 heapq 分类: Python 2012-09 ...
- python实现数据结构单链表
#python实现数据结构单链表 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- class Node(object): """节点""" ...
随机推荐
- LINUX 笔记-ln 命令
给文件创建软链接 命令:ln -s log2013.log link2013 给文件创建硬链接 命令:ln log2013.log ln2013
- 【ASP.NET MVC 学习笔记】- 19 REST和RESTful Web API
本文参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/willick/p/3441432.html 1.目前使用Web服务的三种主流的方式是:远程过程调用(RPC),面向服务架构(SOA)以及表征性 ...
- Java Swing学习
在Java学习的过程中,我们时常会因为控制台程序的枯燥而失去了学习Java的乐趣,那么今天我们就开始学习Java的Swing.也就是GUI(Graphical user interface),在应用到 ...
- python常用模块上篇
python常见模块 分两篇分别介绍下述模块 time模块 random模块 hashlib模块 os模块 sys模块 logging模块 序列号模块 configparser模块 re模块 time ...
- .1-Vue源码起步
搞事!搞事! 截止2017.5.16,终于把vue的源码全部抄完,总共有9624行,花时大概一个月时间,中间迭代了一个版本(2.2-2.3),部分代码可能不一致,不过没关系! 上一个链接https:/ ...
- 事件轮询中的task与microtask
event loop 网上看到的一篇文章,关于介绍task和Tasks, microtasks, queues and schedules,尝试简单翻译一下写进来吧! 原文地址:https://jak ...
- python基础6 迭代器 生成器
可迭代的:内部含有__iter__方法的数据类型叫可迭代的,也叫迭代对象实现了迭代协议的对象 运用dir()方法来测试一个数据类型是不是可迭代的的. 迭代器协议是指:对象需要提供next方法,它要么返 ...
- Hdu 1698(线段树 区间修改 区间查询)
In the game of DotA, Pudge's meat hook is actually the most horrible thing for most of the heroes. T ...
- ajax跨域请求解决方案
大家好,今天我们学习了js的跨域请求的解决方案,由于JS中存在同源策略,当请求不同协议名,不同端口号.不同主机名下面的文件时,将会违背同源策略,无法请求成功!需要进行跨域处理! 方案一.后台PHP进行 ...
- IdentityServer4 登录成功后,跳转到原来页面
IdentityServer4 登录成功后,默认会跳转到Config.Client配置的RedirectUris地址http://localhost:5003/callback.html,用于获取 T ...
