梯度下降法VS随机梯度下降法 (Python的实现)

# -*- coding: cp936 -*-
import numpy as np
from scipy import stats
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 构造训练数据
x = np.arange(0., 10., 0.2)
m = len(x) # 训练数据点数目
x0 = np.full(m, 1.0)
input_data = np.vstack([x0, x]).T # 将偏置b作为权向量的第一个分量
target_data = 2 * x + 5 + np.random.randn(m) # 两种终止条件
loop_max = 10000 # 最大迭代次数(防止死循环)
epsilon = 1e-3 # 初始化权值
np.random.seed(0)
w = np.random.randn(2)
#w = np.zeros(2) alpha = 0.001 # 步长(注意取值过大会导致振荡,过小收敛速度变慢)
diff = 0.
error = np.zeros(2)
count = 0 # 循环次数
finish = 0 # 终止标志
# -------------------------------------------随机梯度下降算法----------------------------------------------------------
'''
while count < loop_max:
count += 1 # 遍历训练数据集,不断更新权值
for i in range(m):
diff = np.dot(w, input_data[i]) - target_data[i] # 训练集代入,计算误差值 # 采用随机梯度下降算法,更新一次权值只使用一组训练数据
w = w - alpha * diff * input_data[i] # ------------------------------终止条件判断-----------------------------------------
# 若没终止,则继续读取样本进行处理,如果所有样本都读取完毕了,则循环重新从头开始读取样本进行处理。 # ----------------------------------终止条件判断-----------------------------------------
# 注意:有多种迭代终止条件,和判断语句的位置。终止判断可以放在权值向量更新一次后,也可以放在更新m次后。
if np.linalg.norm(w - error) < epsilon: # 终止条件:前后两次计算出的权向量的绝对误差充分小
finish = 1
break
else:
error = w
print 'loop count = %d' % count, '\tw:[%f, %f]' % (w[0], w[1])
''' # -----------------------------------------------梯度下降法-----------------------------------------------------------
while count < loop_max:
count += 1 # 标准梯度下降是在权值更新前对所有样例汇总误差,而随机梯度下降的权值是通过考查某个训练样例来更新的
# 在标准梯度下降中,权值更新的每一步对多个样例求和,需要更多的计算
sum_m = np.zeros(2)
for i in range(m):
dif = (np.dot(w, input_data[i]) - target_data[i]) * input_data[i]
sum_m = sum_m + dif # 当alpha取值过大时,sum_m会在迭代过程中会溢出 w = w - alpha * sum_m # 注意步长alpha的取值,过大会导致振荡
#w = w - 0.005 * sum_m # alpha取0.005时产生振荡,需要将alpha调小 # 判断是否已收敛
if np.linalg.norm(w - error) < epsilon:
finish = 1
break
else:
error = w
print 'loop count = %d' % count, '\tw:[%f, %f]' % (w[0], w[1]) # check with scipy linear regression
slope, intercept, r_value, p_value, slope_std_error = stats.linregress(x, target_data)
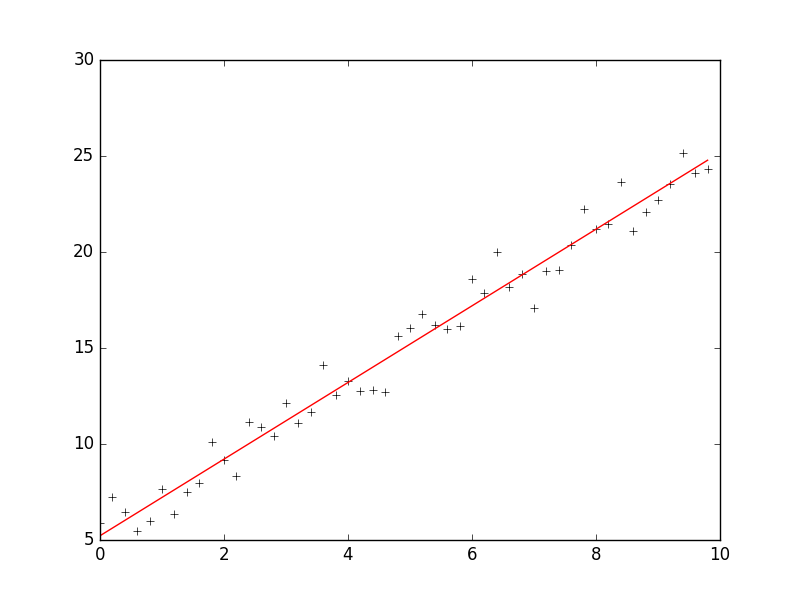
print 'intercept = %s slope = %s' %(intercept, slope) plt.plot(x, target_data, 'k+')
plt.plot(x, w[1] * x + w[0], 'r')
plt.show()
The Learning Rate
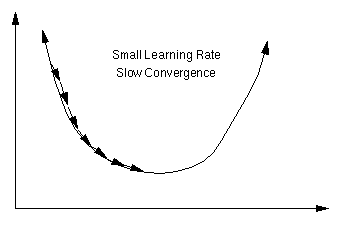
An important consideration is the learning rate µ, which determines by how much we change the weights w at each step. If µ is too small, the algorithm will take a long time to converge .
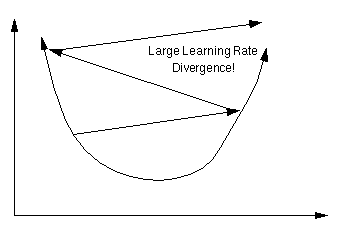
Conversely, if µ is too large, we may end up bouncing around the error surface out of control - the algorithm diverges. This usually ends with an overflow error in the computer's floating-point arithmetic.
Batch vs. Online Learning
Above we have accumulated the gradient contributions for all data points in the training set before updating the weights. This method is often referred to as batch learning. An alternative approach is online learning, where the weights are updated immediately after seeing each data point. Since the gradient for a single data point can be considered a noisy approximation to the overall gradient, this is also called stochastic gradient descent.
Online learning has a number of advantages:
- it is often much faster, especially when the training set is redundant (contains many similar data points),
- it can be used when there is no fixed training set (new data keeps coming in),
- it is better at tracking nonstationary environments (where the best model gradually changes over time),
- the noise in the gradient can help to escape from local minima (which are a problem for gradient descent in nonlinear models)
These advantages are, however, bought at a price: many powerful optimization techniques (such as: conjugate and second-order gradient methods, support vector machines, Bayesian methods, etc.) are batch methods that cannot be used online.A compromise between batch and online learning is the use of "mini-batches": the weights are updated after every n data points, where n is greater than 1 but smaller than the training set size.
参考:http://www.tuicool.com/articles/MRbee2i
https://www.willamette.edu/~gorr/classes/cs449/linear2.html
http://www.bogotobogo.com/python/python_numpy_batch_gradient_descent_algorithm.php
梯度下降法VS随机梯度下降法 (Python的实现)的更多相关文章
- 对数几率回归法(梯度下降法,随机梯度下降与牛顿法)与线性判别法(LDA)
本文主要使用了对数几率回归法与线性判别法(LDA)对数据集(西瓜3.0)进行分类.其中在对数几率回归法中,求解最优权重W时,分别使用梯度下降法,随机梯度下降与牛顿法. 代码如下: #!/usr/bin ...
- 机器学习算法(优化)之一:梯度下降算法、随机梯度下降(应用于线性回归、Logistic回归等等)
本文介绍了机器学习中基本的优化算法—梯度下降算法和随机梯度下降算法,以及实际应用到线性回归.Logistic回归.矩阵分解推荐算法等ML中. 梯度下降算法基本公式 常见的符号说明和损失函数 X :所有 ...
- NN优化方法对照:梯度下降、随机梯度下降和批量梯度下降
1.前言 这几种方法呢都是在求最优解中常常出现的方法,主要是应用迭代的思想来逼近.在梯度下降算法中.都是环绕下面这个式子展开: 当中在上面的式子中hθ(x)代表.输入为x的时候的其当时θ參数下的输出值 ...
- 机器学习(ML)十五之梯度下降和随机梯度下降
梯度下降和随机梯度下降 梯度下降在深度学习中很少被直接使用,但理解梯度的意义以及沿着梯度反方向更新自变量可能降低目标函数值的原因是学习后续优化算法的基础.随后,将引出随机梯度下降(stochastic ...
- 线性回归(最小二乘法、批量梯度下降法、随机梯度下降法、局部加权线性回归) C++
We turn next to the task of finding a weight vector w which minimizes the chosen function E(w). Beca ...
- online learning,batch learning&批量梯度下降,随机梯度下降
以上几个概念之前没有完全弄清其含义及区别,容易混淆概念,在本文浅析一下: 一.online learning vs batch learning online learning强调的是学习是实时的,流 ...
- 梯度下降之随机梯度下降 -minibatch 与并行化方法
问题的引入: 考虑一个典型的有监督机器学习问题,给定m个训练样本S={x(i),y(i)},通过经验风险最小化来得到一组权值w,则现在对于整个训练集待优化目标函数为: 其中为单个训练样本(x(i),y ...
- 梯度下降VS随机梯度下降
样本个数m,x为n维向量.h_theta(x) = theta^t * x梯度下降需要把m个样本全部带入计算,迭代一次计算量为m*n^2 随机梯度下降每次只使用一个样本,迭代一次计算量为n^2,当m很 ...
- 梯度下降、随机梯度下降、方差减小的梯度下降(matlab实现)
梯度下降代码: function [ theta, J_history ] = GradinentDecent( X, y, theta, alpha, num_iter ) m = length(y ...
随机推荐
- Android的适配器
//====================ArrayAdapter=================================== public class List1 extends Ac ...
- ILOG的一个基本应用——解决运输问题、转运问题
一.Ilog软件 该软件用来解决优化问题,大部分是线性问题,深一点的其他内容还不清楚.只知道一些基础的应用,网上相关内容很少.接下来就解决一个简单的运输问题 二.运输问题 数学模型 ILOG OPL程 ...
- eclipse字体颜色设置
修改编码:window-->perference--->General--> Configure.--> Configure.-->workspace修改编辑背景色:wi ...
- filesort是什么意思?
我们碰到有order by 或者group by,或者distinct语句的时候,如果查看执行计划,通常会看到using filesort的字眼,那么这个filesort是不是真是文件排序呢?其实不然 ...
- Delphi内嵌汇编语言BASM精要(转帖)
1 BASM概念简要 汇编语句由指令和零至三个表达式构成.表达式由常数(立即数).寄存器和标识符构成.例如: movsb // 单指令语句 jmp @Here // 一个表达式: ...
- linux,Mac下lu 一把
习惯Terminal没有不知道ls命令的(等同于DOS的dir),经常只是需要查看目录的内容大小,但ls -h显示的只是目录的本身大小,而且很多项内容 ls 在这方面的两个诟病出现了: 小诟1. 显示 ...
- 2.1:你的第一个AngularJS App
本章,带你体验一个简单的开发流程,将一个静态的使用模拟数据的应用,变成具有AngularJS特性的动态web应用.在6-8章,作者将展示如何创建一个更复杂,更真实的AngularJS应用. 1.准备项 ...
- vmdk虚拟机转换为OVF模板,导入esxi
VMware WorkStation安装目录下,有一个OVFTool文件夹,例如我电脑上的路径为:D:\VMware\VMware\OVFTool.通过CMD进入到命令行模式,更改到该目录下,运行如下 ...
- Android网络传输中必用的两个加密算法:MD5 和 RSA (附java完成测试代码)
MD5和RSA是网络传输中最常用的两个算法,了解这两个算法原理后就能大致知道加密是怎么一回事了.但这两种算法使用环境有差异,刚好互补. 一.MD5算法 首先MD5是不可逆的,只能加密而不能解密.比如明 ...
- MongoDB Shell
MongoDB Shell 1.连接指定主机及数据库 mongo 127.0.0.1:30000/myDB 链接到127.0.0.1的30000端口的myDB 2.启动后连接指定数据库 *.&qu ...
