分类算法简介 基于R
最近的关键字:分类算法,outlier detection, machine learning
简介:
此文将 k-means,decision tree,random forest,SVM(support vector mechine),人工神经网络(Artificial Neural Network,简称ANN )这几种常见的算法 apply 在同一个数据集
spam,看各种方法预测错误率,或准确率,旨在追求预测准确性,辨识出这几种方法的实用性,对背后的理论依据,大量的数学公式,不作讨论(能力有限,看不懂数学公式,,,)
ps:这两天看代码。又发现不少好玩的方法和网站,哦哈哈
先分享几个tips、R blog:
a) 如何快速找到自己想要的R package。到 Available CRAN Packages By Date of Publication control+F 找,快得很。
b) 如何找到一个小领域 一些列相关的R包。以 randomForest 为例,到这个包的页面,你会看到一个 In views:Environmetrics, MachineLearning,接下来就可以把机器学习算法的R包一网打尽。帅呆了,好么,再也不用一个个查了。
c) 挺好的一个 R blog http://mkseo.pe.kr/stats/ 里面有韩文和英文写的文章,不知道博主是个是个韩国妹子呢,,,想多了,,,妹子怎么去coding,,,
d)再推荐一个blog  。拷过来,变成了这样,,戳吧,少年。
。拷过来,变成了这样,,戳吧,少年。
实际应用:
(1)k-means
#----------------------------
基于数据集 spam来看看k-means
library(kernlab)
library(magrittr)
data(spam)
set.seed(124)
res <- kmeans(spam[,-58]%>%sapply(scale),2)
table(spam$type,res$cluster)
1 2
nonspam 2754 34
spam 1813 0
# 错误率是 1-2754/nrow(spam) = 0.4014345
# 假设spam 和 nonspam 五五开,如果完全是蒙,出错率也就50%吧,,,
总结:
分类变量不能用于k-means,不能简单将分类变量编号为1,2,3。能给出每个类别之间的距离,是可以用kmeans的。
必须对每列预先scale。
#----------------------------
(2)decision tree
library(tree)
library(kernlab)
library(dplyr)
library(magrittr)
data(spam)
#create train and test dataset
set.seed(1859)
train <- sample(nrow(spam),nrow(spam)*0.7,replace = FALSE)
df.train <- spam[train,]
df.test <- spam[-train,]
#modeling
tree.fit <- tree(type~.,data=df.train)
summary(tree.fit)
# plot decision tree
plot(tree.fit, type ="uniform")
text(tree.fit, pretty =1, all=TRUE,cex=0.7)
# predication
pred <- predict(tree.fit,df.test,type = c("class"))
#查看预测结果
confusionMatrix(pred,df.test[,58])
Confusion Matrix and Statistics
Reference
Prediction nonspam spam
nonspam 819 84
spam 34 444
Accuracy : 0.9146
# decision tree 选择变量模型会自动帮你选择选择,预测错误率是 0.08
放个图
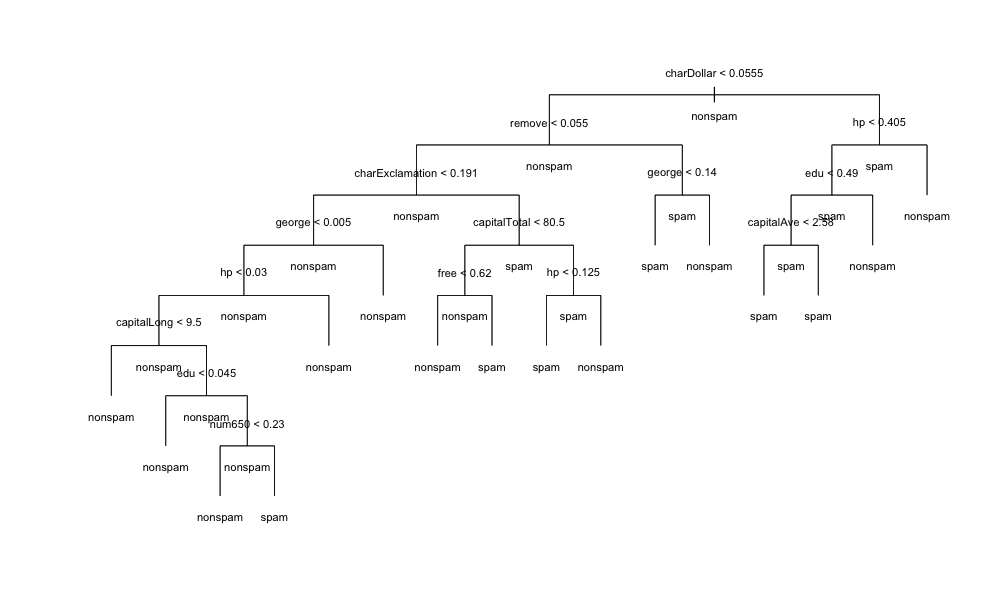
总结:
引用tree这个包帮助文档的一句话:The left-hand-side (response) should be either a numerical vector when a regression tree will be fitted or a factor,when a classification tree is produced. 既可以做classification 也可以 regression!
如果是做classification,Factor predictor variables can have up to 32 levels.
decision tree 会不会 overfitting?我看下来,是不会,用tree.fit对测试集预测时,准确率依然是很高。
帮助文档是这样说的:The split which maximizes the reduction in impurity is chosen, the data set split and the process repeated. Splitting continues until the terminal nodes are too small or too few to be split.
看下面的代码,也可以证明不存在overfitting吧
> summary(tree.fit)
Classification tree:
tree(formula = type ~ ., data = df.train)
Variables actually used in tree construction:
[1] "charDollar" "remove" "charExclamation"
[4] "george" "hp" "capitalLong"
[7] "edu" "num650" "capitalTotal"
[10] "free" "capitalAve"
Number of terminal nodes: 16
Residual mean deviance: 0.432 = 1384 / 3204
Misclassification error rate: 0.08416 = 271 / 3220
放一篇 文章 Decision Tree - Overfitting
#---------------------------
(3)random forest
library(randomForest)
library(magrittr)
library(dplyr)
data(spam)
train <- sample(nrow(spam),nrow(spam)*0.7,replace = FALSE)
df.train <- spam[train,]
df.test <- spam[-train,]
# random forest 要预先设定随机种子,结果才能一样。
set.seed(189)
spam.rf <- randomForest(type~.,data=df.train,mtry=3,do.trace=100,ntree=500,importance=TRUE,proximity=TRUE)
#下面是运行时,种到第几百棵树的时候,error rate是多少
ntree OOB 1 2
100: 5.56% 2.95% 9.49%
200: 5.59% 2.69% 9.96%
300: 5.53% 2.79% 9.65%
400: 5.40% 2.84% 9.26%
500: 5.28% 2.69% 9.18%
spam.rf
pred <- predict(spam.rf,df.test[,-58],type="class")
confusionMatrix(pred,df.test[,58])
Confusion Matrix and Statistics
Reference
Prediction nonspam spam
nonspam 833 41
spam 20 487
Accuracy : 0.9558
# 错误率很低
# random forest 已经自己选择了关键变量,不存在过度拟合的问题
# 下面的命令是看那些变量重要
varImpPlot(spam.rf)
varImpPlot(spam.rf)的运行结果是一张图,charExclamation 这个变量对于预测是不是垃圾邮件,至关重要。
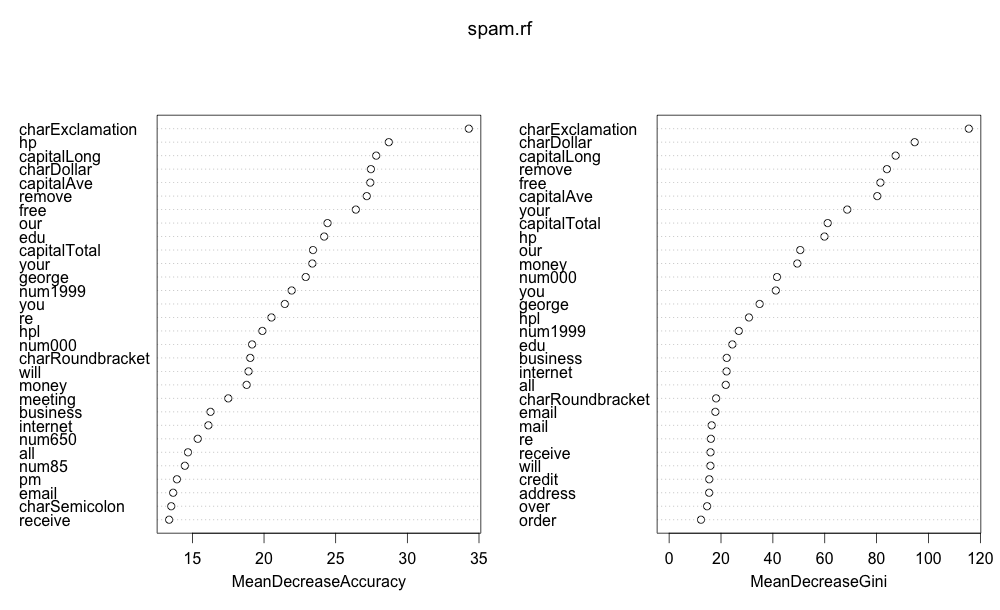
总结:
random forest会不会 overfitting?Random Forest - How to handle overfitting
Breiman claims that RF does not overfit. stat.berkeley.edu/~breiman/RandomForests/cc_home.htm
从预测结果看,是不会overfitting。另外这个包的开发者都声称不会overfitting了,,,
random forest 也是classification 和regression 都能做
放一篇这个包作者的文章:http://www.bios.unc.edu/~dzeng/BIOS740/randomforest.pdf
#---------------------------
(4)SVM (supprot vector mechine)
先看e1071这个包的SVM
library(e1071)
library(rpart)
set.seed(1871)
train <- sample(nrow(spam),nrow(spam)*0.7,replace = FALSE)
df.train <- spam[train,]
df.test <- spam[-train,]
model <- svm(df.train[,-58], df.train[,58])
print(model)
summary(model)
pred <- predict(model, df.test[,-58])
confusionMatrix(pred,df.test[,58])
Confusion Matrix and Statistics
Reference
Prediction nonspam spam
nonspam 789 59
spam 37 496
Accuracy : 0.9305
再看另一个,来自于caret包,参考 Computational Prediction这篇文章
library(caret)
library(doMC)
data(spam)
set.seed(89)
train <- sample(nrow(spam),nrow(spam)*0.7,replace = FALSE)
df.train <- spam[train,]
df.test <- spam[-train,]
# 多线程,是doMC包的函数,看了监视器,确实cpu使用率瞬间飙到90%+。
# 回头仔细研究下和parallel包有什么区别
registerDoMC(cores=4)
model <- train(df.train[, -58], df.train[, 58], method="svmRadial")
predict(model,df.test[,-58])%>%confusionMatrix(df.test[,58])
# 准确率也还可以
Confusion Matrix and Statistics
Reference
Prediction nonspam spam
nonspam 816 70
spam 42 453 Accuracy : 0.9189
Computational Prediction 这篇里面还发现一个好玩的地方,就是可以用一小函数人为的造出一些缺失值,然后用Bagged tree imputation 补缺失值,还没研究它补缺失值的逻辑是什么,先放一篇文章备查。
Bagged tree imputation for missing values using caret。
fillInNa <- function(d) {
naCount <- NROW(d) * 0.1
for (i in sample(NROW(d), naCount)) {
d[i, sample(4, 1)] <- NA
}
return(d)
}
#---------------------------
(5)人工神经网络(Artificial Neural Network)
参考 R语言中最强的神经网络包RSNNS 和RSNNS 帮助文档,帮助文档在 confusionMatrix(iris$targetsTrain,fitted.values(model)),这一句有错误,必须encodeClassLabels才可以,正确的写法是:confusionMatrix(encodeClassLabels(iris$targetsTrain),encodeClassLabels(fitted.values(model)))
library(RSNNS)
library(doMC)
data(spam)
set.seed(199)
spam <- spam[sample(1:nrow(spam) ,nrow(spam)), 1:ncol(spam)]
spamValues <- spam[,-58]
spamTargets <- spam[,58]
spamDecTargets <- decodeClassLabels(spamTargets)
spam <- splitForTrainingAndTest(spamValues, spamDecTargets, ratio = 0.3)
spam <- normTrainingAndTestSet(spam)
#The model is then built with:
# registerDoMC(cores=4) 看了下活动监视器,CPU使用率在30%左右,这东西在这里没卵用。
# 下面这个函数很耗时
model <- mlp(spam$inputsTrain, spam$targetsTrain, size = 5
,learnFuncParams = c(0.1), maxit = 60
,inputsTest = spam$inputsTest
,targetsTest = spam$targetsTest) predictions <- predict(model, spam$inputsTest)
confusionMatrix(encodeClassLabels(spam$targetsTest),encodeClassLabels(predictions))
Confusion Matrix and Statistics
Reference
Prediction 1 2
1 805 42
2 34 500 Accuracy : 0.945
95% CI : (0.9316, 0.9564)
No Information Rate : 0.6075
P-Value [Acc > NIR] : <2e-16 Kappa : 0.8843
Mcnemar's Test P-Value : 0.422 Sensitivity : 0.9595
Specificity : 0.9225
Pos Pred Value : 0.9504
Neg Pred Value : 0.9363
Prevalence : 0.6075
Detection Rate : 0.5829
Detection Prevalence : 0.6133
Balanced Accuracy : 0.9410 'Positive' Class : 1
预测准确率略低于randomForest,和之前老板提到几个算法中randomForest最牛逼是吻合的。不过人工神经网络计算很耗时间,又回去重新计算,看了下时间
用户 系统 流逝
248.671 26.796 283.194
#---------------------------
(6)贝叶斯网络
最后:
以上各种方法的理论部分,还需继续学习。
对于上面的几种方法介绍,我的代码肯定还有纰漏,或者错误,请允许我慢慢改进,轻拍。
2015-08-23更新:
决策树有很多包都可以实现,不局限于tree这个包,这篇文章A Brief Tour of the Trees and Forests,介绍的很详细。
C50包也可以做decision tree
library(C50)
library(kernlab)
data(spam)
train <- sample(1:nrow(spam),nrow(spam)*0.7,replace=F)
df.train <- spam[train,]
df.test <- spam[-train,]
model <- C50::C5.0(type~.,data=df.train)
summary(model)
pre <- C50::predict.C5.0(model,newdata=df.test[,-58],type='class')
confusionMatrix(pre,df.test[,58])
分类算法简介 基于R的更多相关文章
- 分类算法简介 分类: B10_计算机基础 2015-03-09 11:08 257人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
一.决策树 决策树是用于分类和预测的主要技术之一,决策树学习是以实例为基础的归纳学习算法,它着眼于从一组无次序.无规则的实例中 推理出以决策树表示的分类规则.构造决策树的目的是找出属性和类别间的关系, ...
- Newton-Raphson算法简介及其R实现
本文简要介绍了Newton-Raphson方法及其R语言实现并给出几道练习题供参考使用. 下载PDF格式文档(Academia.edu) Newton-Raphson Method Let $f(x) ...
- Mahout 分类算法
实验简介 本次课程学习了Mahout 的 Bayes 分类算法. 一.实验环境说明 1. 环境登录 无需密码自动登录,系统用户名 shiyanlou 2. 环境介绍 本实验环境采用带桌面的Ubuntu ...
- R语言与分类算法的绩效评估(转)
关于分类算法我们之前也讨论过了KNN.决策树.naivebayes.SVM.ANN.logistic回归.关于这么多的分类算法,我们自然需要考虑谁的表现更加的优秀. 既然要对分类算法进行评价,那么我们 ...
- 基于机器学习和TFIDF的情感分类算法,详解自然语言处理
摘要:这篇文章将详细讲解自然语言处理过程,基于机器学习和TFIDF的情感分类算法,并进行了各种分类算法(SVM.RF.LR.Boosting)对比 本文分享自华为云社区<[Python人工智能] ...
- 分类算法的R语言实现案例
最近在读<R语言与网站分析>,书中对分类.聚类算法的讲解通俗易懂,和数据挖掘理论一起看的话,有很好的参照效果. 然而,这么好的讲解,作者居然没提供对应的数据集.手痒之余,我自己动手整理了一 ...
- R语言分类算法之随机森林
R语言分类算法之随机森林 1.原理分析: 随机森林是通过自助法(boot-strap)重采样技术,从原始训练样本集N中有放回地重复随机抽取k个样本生成新的训练集样本集合,然后根据自助样本集生成k个决策 ...
- LM-MLC 一种基于完型填空的多标签分类算法
LM-MLC 一种基于完型填空的多标签分类算法 1 前言 本文主要介绍本人在全球人工智能技术创新大赛[赛道一]设计的一种基于完型填空(模板)的多标签分类算法:LM-MLC,该算法拟合能力很强能感知标签 ...
- 第二篇:基于K-近邻分类算法的约会对象智能匹配系统
前言 假如你想到某个在线约会网站寻找约会对象,那么你很可能将该约会网站的所有用户归为三类: 1. 不喜欢的 2. 有点魅力的 3. 很有魅力的 你如何决定某个用户属于上述的哪一类呢?想必你会分析用户的 ...
随机推荐
- Django视图系统
Django的view(视图) 一个视图函数(类),简称视图,是一个简单的Python 函数(类),它接受Web请求并且返回Web响应. ...
- mapreduce去重
现有一个某电商网站的数据文件,名为buyer_favorite1,记录了用户收藏的商品以及收藏的日期,文件buyer_favorite1中包含(用户id,商品id,收藏日期)三个字段,数据内容以“\t ...
- spring中注解注入 context:component-scan 的使用说明
通常情况下我们在创建spring项目的时候在xml配置文件中都会配置这个标签,配置完这个标签后,spring就会去自动扫描base-package对应的路径或者该路径的子包下面的java文件,如果扫描 ...
- ECharts基本设置
theme = { // 全图默认背景 // backgroundColor: ‘rgba(0,0,0,0)’, // 默认色板 color: ['#ff7f50','#87cefa','#da70d ...
- 关系型数据库---MySQL---对中文字段排序
1.对中文进行排序时会发生错误,原因是使用的字符集不是中文的字符集: 解决:CONVERT函数 SELECT a.id,a.`name`,a.ch_name FROM `user` a ORDER B ...
- 3d Max 2015安装失败怎样卸载3dsmax?错误提示某些产品无法安装
AUTODESK系列软件着实令人头疼,安装失败之后不能完全卸载!!!(比如maya,cad,3dsmax等).有时手动删除注册表重装之后还是会出现各种问题,每个版本的C++Runtime和.NET f ...
- stm32中断优先级快速入门
1.基本概念 STM32(Cortex-M3架构)中有两个优先级的概念--抢占式优先级和响应优先级.有人把响应优先级称作'亚优先级'或'副优先级',每个中断源都需要被指定这两种优先级. 具有高抢占式优 ...
- 百度BAE数据库连接问题
今天第一次使用百度的开发平台BAE,按照入门文档上的操作一步步来,进行的很顺利,可是我在上传了一个cms系统后,进行安装时,卡在了数据库连接这个地方,弄了一下午,终于有了结果,在这里记录起来,希望能帮 ...
- DEDE模板中如何运行php脚本和php变量的使用
在使用dede模板的时候,经常会需要直接对dede数据库的底层字段进行处理,如果dede中没有相应的函数的时候,往往就需要我们想办法来处理了. 举例:我想取出数据表addonimages中的某一条记录 ...
- Windows Server 2012 R2
Windows Server 2012 R2 历史上的Server有2003 server, 2008 server, 2012 server windows server 2012 r2对计算机的消 ...
