Spring Security 源码解析(一)
上篇 Spring Security基本配置已讲述了Spring Security最简单的配置,本篇将开始分析其基本原理
在上篇中可以看到,在访问 http://localhost:18081/user 时,直接跳转到登录页。那Security是怎么做的呢?本篇主要讲述跳转到登录页前的处理
首先来看一张时序图:
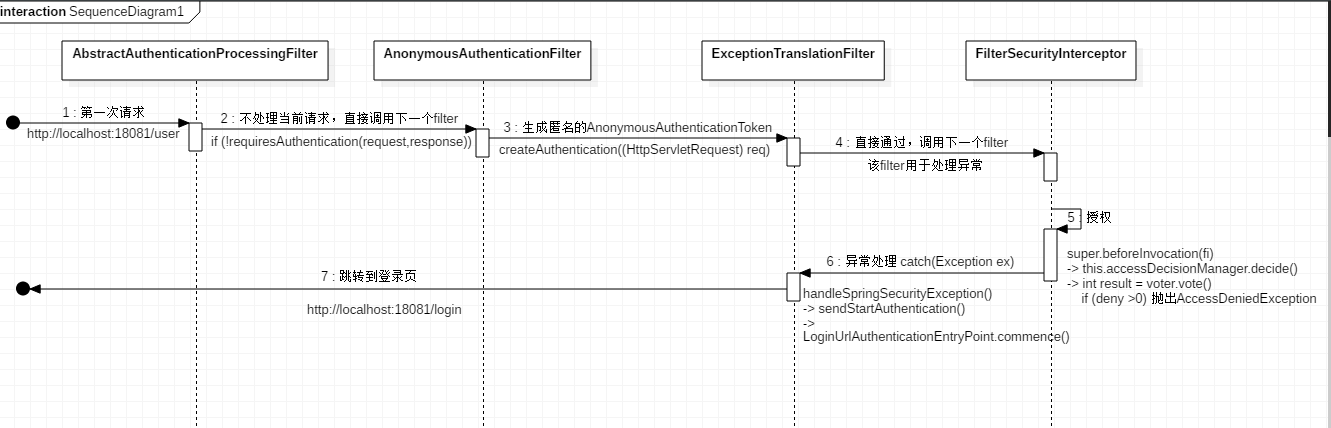
通过上图可以看到,请求顺序为AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter -> AnonymousAuthenticationFilter -> ExceptionTranslationFilter -> FilterSecurityInterceptor
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
请求先进入 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 的doFilter()方法。判断当前filter是否可以处理当前请求(也就是是否包含用户名密码信息),如果是,则调用其子类 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.attemptAuthentication() 方法进行验证(第一次请求时,没有用户名密码,是不会调用子类的)
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException { HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
//判断当前的filter是否可以处理当前请求,不可以的话则交给下一个filter处理
if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response); return;
} if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Request is to process authentication");
} Authentication authResult; try {
//抽象方法由子类UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter实现
authResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authResult == null) {
// return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn't completed
// authentication
return;
}
//认证成功后,处理一些与session相关的方法
sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response);
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) {
logger.error(
"An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.",
failed);
//认证失败后的的一些操作
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed); return;
}
catch (AuthenticationException failed) {
// Authentication failed
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed); return;
} // Authentication success
if (continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
//认证成功后的相关回调方法,主要将当前的认证放到SecurityContextHolder中
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
}
认证成功后的回调方法:
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult)
throws IOException, ServletException { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Authentication success. Updating SecurityContextHolder to contain: "
+ authResult);
} //将认证结果保存到SecurityContextHolder中
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult); rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult); // Fire event
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(
authResult, this.getClass()));
} //调用其它可扩展的 handlers 继续处理该认证成功以后的回调事件
//实现AuthenticationSuccessHandler接口即可
successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult);
}
认证失败后的回调方法:
protected void unsuccessfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException failed)
throws IOException, ServletException { //清除SecurityContextHolder的中数据
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Authentication request failed: " + failed.toString(), failed);
logger.debug("Updated SecurityContextHolder to contain null Authentication");
logger.debug("Delegating to authentication failure handler " + failureHandler);
} rememberMeServices.loginFail(request, response); //调用其它可扩展的 handlers 处理该认证失败以后的回调事件
//实现 AuthenticationFailureHandler 接口即可
failureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, failed);
关于自定义 handlers ,可参考 Spring Security认证配置(三)
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter本身不是过滤器,而是继承了AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter才拥有过滤器的性能,其主要是验证用户名密码。
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException { //认证请求的方法必须为POST
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
} //从request中获取 username 和 password
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request); if (username == null) {
username = "";
} if (password == null) {
password = "";
} username = username.trim(); //封装Authenticaiton的实现类UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
//传入用户名和密码,并将是否已经认证设为false
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password); //设置UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken中的详细信息。如remoteAddress、sessionId
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest); //调用 AuthenticationManager 的实现类 ProviderManager 进行验证
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
验证的过程,可以参考AuthenticationManager、ProviderManager
ExceptionTranslationFilter
ExceptionTranslationFilter是异常处理过滤器,该过滤器用来处理在系统认证授权过程中抛出的异常(也就是FilterSecurityInterceptor抛出来的),主要是处理
AccessDeniedException、AuthenticationException
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res; try {
chain.doFilter(request, response); logger.debug("Chain processed normally");
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
//判断是不是AuthenticationException
// Try to extract a SpringSecurityException from the stacktrace
Throwable[] causeChain = throwableAnalyzer.determineCauseChain(ex);
RuntimeException ase = (AuthenticationException) throwableAnalyzer
.getFirstThrowableOfType(AuthenticationException.class, causeChain); if (ase == null) {
//判断是不是AccessDeniedException
ase = (AccessDeniedException) throwableAnalyzer.getFirstThrowableOfType(
AccessDeniedException.class, causeChain);
} if (ase != null) {
//异常处理。包括缓存当前请求,跳转到登录页
handleSpringSecurityException(request, response, chain, ase);
}
else {
// Rethrow ServletExceptions and RuntimeExceptions as-is
if (ex instanceof ServletException) {
throw (ServletException) ex;
}
else if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
} // Wrap other Exceptions. This shouldn't actually happen
// as we've already covered all the possibilities for doFilter
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
在 handleSpringSecurityException 方法中,有一段:
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
//判断当前authentication是不是AnonymousAuthenticationToken(RememberMeAuthenticationToken)或者其子类
if (authenticationTrustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication) || authenticationTrustResolver.isRememberMe(authentication)) {
logger.debug(
"Access is denied (user is " + (authenticationTrustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication) ? "anonymous" : "not fully authenticated") + "); redirecting to authentication entry point",
exception); sendStartAuthentication(
request,
response,
chain,
new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
"Full authentication is required to access this resource"));
}
其中sendStartAuthentication方法:
protected void sendStartAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain,
AuthenticationException reason) throws ServletException, IOException {
//清空SecurityContext
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(null);
//缓存当前请求
requestCache.saveRequest(request, response);
logger.debug("Calling Authentication entry point.");
//调用AuthenticationEntryPoint的实现类LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint(可扩展,实现AuthenticationEntryPoint即可)
//跳转到可配置的登录页(如果不配置,则跳转到spring security默认的登录页)
authenticationEntryPoint.commence(request, response, reason);
}
FilterSecurityInterceptor
此过滤器为认证授权过滤器链中最后一个过滤器,该过滤器通过之后就是真正的 /user 服务
public void invoke(FilterInvocation fi) throws IOException, ServletException {
......
else {
// first time this request being called, so perform security checking
if (fi.getRequest() != null) {
fi.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
}
//调用父类AbstractSecurityInterceptor.beforeInvocation方法,进行最后一次过滤
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(fi);
try {
//请求真正的 /user 服务
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
}
finally {
super.finallyInvocation(token);
}
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
}
}
在beforeInvocation方法中,会调用AccessDecisionManager.decide方法来验证当前认证成功的用户是否有权限访问该资源
protected InterceptorStatusToken beforeInvocation(Object object) {
......
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource()
.getAttributes(object);
......
Authentication authenticated = authenticateIfRequired();
// Attempt authorization
try {
//授权认证
this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);
}
catch (AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) {
publishEvent(new AuthorizationFailureEvent(object, attributes, authenticated,
accessDeniedException));
throw accessDeniedException;
}
}
上面的object和attributes是什么?调试一下:
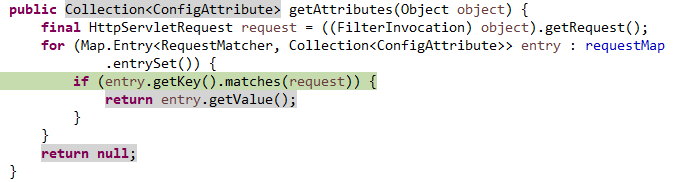
object为当前请求 URL:/user
requestMap的值有两个,如下图:

可以看到,这两个值对应SecurityConfig中的配置。第一个为antMatchs返回permitAll即不需要认证,第二个为anyRequest返回authenticated即其它请求需要认证
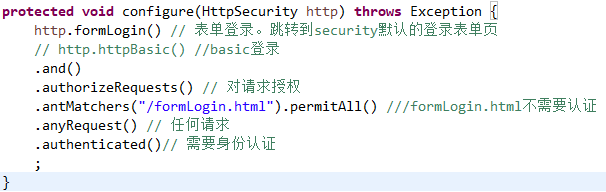
所以 getAttributes 就是使用当前请求路径去匹配我们自定义的规则,attributes为匹配后的结果
我们继续来看最核心的授权认证:
this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes)
此时,authenticated为匿名AnonymousAuthenticationToken,attributes为authenticated
AccessDecisionManager是如何授权的呢?
Spring Security默认使用AccessDecisionManager的子类 AffirmativeBased,通过实现decide方法来鉴定用户是否有访问对应资源(方法或URL)的权限
public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes) throws AccessDeniedException {
int deny = ; //调用AccessDecisionVoter进行vote(投票)
for (AccessDecisionVoter voter : getDecisionVoters()) {
int result = voter.vote(authentication, object, configAttributes); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Voter: " + voter + ", returned: " + result);
} switch (result) {
//voter投票为ACCESS_GRANTED,表示同意,直接返回
case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_GRANTED:
return;
//voter投票为ACCESS_DENIED,表示反对,则记录一下
case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_DENIED:
deny++; break;
//voter投票为其它值,则表示弃权。都弃权也会通过
default:
break;
}
} //只要有一个voter投票为ACCESS_DENIED,则直接就不通过了
if (deny > ) {
throw new AccessDeniedException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractAccessDecisionManager.accessDenied", "Access is denied"));
} // To get this far, every AccessDecisionVoter abstained
checkAllowIfAllAbstainDecisions();
}
第一次请求,这里将抛出AccessDeniedException。然后被ExceptionTranslationFilter捕获,跳转到授权登录认证页面
Spring Security 源码解析(一)的更多相关文章
- Spring Security源码解析一:UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter之登录流程
一.前言 spring security安全框架作为spring系列组件中的一个,被广泛的运用在各项目中,那么spring security在程序中的工作流程是个什么样的呢,它是如何进行一系列的鉴权和 ...
- Spring Security 源码解析(一)AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
# 前言 最近在做 Spring OAuth2 登录,并在登录之后保存 Cookies.具体而言就是 Spring OAuth2 和 Spring Security 集成.Google一下竟然没有发现 ...
- spring事务源码解析
前言 在spring jdbcTemplate 事务,各种诡异,包你醍醐灌顶!最后遗留了一个问题:spring是怎么样保证事务一致性的? 当然,spring事务内容挺多的,如果都要讲的话要花很长时间, ...
- Spring Security 源码分析(四):Spring Social实现微信社交登录
社交登录又称作社会化登录(Social Login),是指网站的用户可以使用腾讯QQ.人人网.开心网.新浪微博.搜狐微博.腾讯微博.淘宝.豆瓣.MSN.Google等社会化媒体账号登录该网站. 前言 ...
- Spring IoC源码解析之invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
一.Bean工厂的后置处理器 Bean工厂的后置处理器:BeanFactoryPostProcessor(触发时机:bean定义注册之后bean实例化之前)和BeanDefinitionRegistr ...
- Spring IoC源码解析之getBean
一.实例化所有的非懒加载的单实例Bean 从org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh方法开发,进入到 ...
- Spring系列(五):Spring AOP源码解析
一.@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解 在主配置类中添加@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解,开启aop支持,那么@EnableAspectJAutoProxy到底做了什 ...
- Spring系列(六):Spring事务源码解析
一.事务概述 1.1 什么是事务 事务是一组原子性的SQL查询,或者说是一个独立的工作单元.要么全部执行,要么全部不执行. 1.2 事务的特性(ACID) ①原子性(atomicity) 一个事务必须 ...
- Spring系列(三):Spring IoC源码解析
一.Spring容器类继承图 二.容器前期准备 IoC源码解析入口: /** * @desc: ioc原理解析 启动 * @author: toby * @date: 2019/7/22 22:20 ...
随机推荐
- asp.net excel导出功能
以下是我在项目开发中所做的关于Excel导出功能,不足之处还望大家指正,相互学习 protected void btn_Export_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) ...
- c#实现AOP
AOP:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式或运行期动态代理实现程序功能的中统一处理业务逻辑的一种技术,比较常见的场景是:日志记录,错误捕获.性能监控等 AOP详解:https://www.cnblogs.c ...
- 国际化SEO优化的最佳实践
作者:Kristopher Jones 翻译 :吴祺深 欢迎访问网易云社区,了解更多网易技术产品运营经验. 让我们来说一下hreflang属性.如果你还没有关掉这个页面,那么你已经完成了这个教程最重要 ...
- git生成Key操作保存到GITHUB中
https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_23880167/article/details/78502528 1. 在git中通过命令: $ ssh-keygen Generating ...
- jQuery基础笔记(1)
day54 参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/liwenzhou/p/8178806.html 1. 为什么要学jQuery? MySQL Python ...
- 三,mysql优化--sql语句优化之索引一
1,需求:如何在一个项目中,找到慢查询的select,mysql数据库支持把慢查询语句,记录到日志中.供程序员分析.(默认不启用此功能,需要手动启用) 修改my.cnf文件(有些地方是my.ini) ...
- NLP1 —— Python自然语言处理环境搭建
最近开始研究自然语言处理了,所以准备好好学习一下,就跟着<Python自然语言处理>这本书,边学边整理吧 安装 Mac里面自带了python2.7,所以直接安装nltk就可以了. 默认执行 ...
- linux下mysql主从复制搭建
目标:搭建两台MySQL服务器,一台作为主服务器,一台作为从服务器,实现主从复制 环境: 主数据库: 192.168.1.1 从数据库: 192.168.1.2 mysql安装可参考:https:// ...
- IIS 8 配置错误
1) ProtocolException: The remote server returned an unexpected response: (405) Method Not Allowed Th ...
- 腾讯云域名申请+ssl证书申请+springboot配置https
阿里云域名申请 域名申请比较简单,使用微信注册阿里云账号并登陆,点击产品,选择域名注册 输入你想注册的域名 进入域名购买页面,搜索可用的后缀及价格,越热门的后缀(.com,.cn)越贵一般,并且很可能 ...
