4. SQL Server数据库状态监控 - 作业状态
原文:4. SQL Server数据库状态监控 - 作业状态
有很多地方可以设置定时任务,比如:Windows的计划任务,Linux下的crontab,各种开发工具里的timer组件。SQL Server也有它的定时任务组件 SQL Server Agent,基于它可以方便的部署各种数据库相关的作业(job)。
一. 作业历史纪录
作业的历史纪录按时间采用FIFO原则,当累积的作业历史纪录达到上限时,就会删除最老的纪录。
1. 作业历史纪录数配置
所有作业总计纪录条数默认为1000,最多为999999条;单个作业总计记录条数默认为100,最多为999999条。有下面2种方式可以进行修改:
(1) SSMS/SQL Server Agent/属性/历史;
(2) 未记载的扩展存储过程,SQL Server 2005及以后版本适用,以下脚本将记录数设回默认值:
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_set_sqlagent_properties
@jobhistory_max_rows=-1,
@jobhistory_max_rows_per_job=-1
GO
2. 删除作业历史纪录
(1) SSMS/SQL Server Agent/右击作业文件夹或某个作业/查看历史纪录/清除
在SQL Server 2000中会一次清除所有作业历史记录,SQL Server 2005 及以后版本可以有选择的清除某个作业/某个时间之前的历史纪录;
(2) SQL Server 2005及以后版本,提供了系统存储过程如下:
--清除所有作业15天前的纪录
DECLARE @OldestDate datetime
SET @OldestDate = GETDATE()-15
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_purge_jobhistory
@oldest_date=@OldestDate --清除作业”Test”3天前的纪录
DECLARE @OldestDate datetime
DECLARE @JobName varchar(256)
SET @OldestDate = GETDATE()-3
SET @JobName = 'Test'
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_purge_jobhistory
@job_name=@JobName,
@oldest_date=@OldestDate
作业历史纪录数有上限,通常不需要手动去删除。
3. 保留作业历史纪录
即便设置了历史记录上限到999999,如果作业很多,加之作业运行很频繁,最终历史记录还是会被慢慢删除掉。
如果想要保留某些作业历史的记录,可以打开作业属性/步骤/编辑/高级,选择将这个步骤的历史记录输出到文件/自定义表中,如下图:
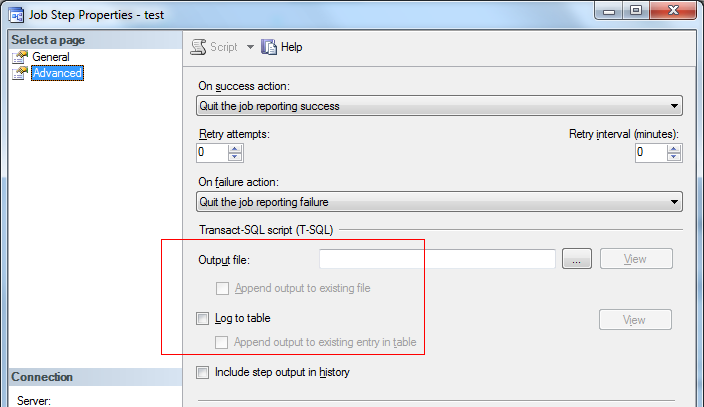
二. 作业运行状态
界面上可以通过: SSMS/SQL Server Agent/右击作业文件夹或某个作业/查看历史纪录,如下用SQL 语句检查作业状态。
1. 作业上次运行状态及时长
利用系统表msdb.dbo.sysjobhistory:
(1) 表中的run_status字段表示作业上次运行状态,有0~3共4种状态值,详见帮助文档,另外在2005的帮助文档中写到:sysjobhistory的run_status为4表示运行中,经测试是错误的,在2008的帮助中已没有4这个状态;
(2) 表中run_duration字段表示作业上次运行时长,格式为HHMMSS,比如20000则表示运行了2小时。
如下脚本查看所有作业最后一次运行状态及时长:
if OBJECT_ID('tempdb..#tmp_job') is not null
drop table #tmp_job
--只取最后一次结果
select job_id,
run_status,
CONVERT(varchar(20),run_date) run_date,
CONVERT(varchar(20),run_time) run_time,
CONVERT(varchar(20),run_duration) run_duration
into #tmp_job
from msdb.dbo.sysjobhistory jh1
where jh1.step_id = 0
and (select COUNT(1) from msdb.dbo.sysjobhistory jh2
where jh2.step_id = 0
and (jh1.job_id = jh2.job_id)
and (jh1.instance_id <= jh2.instance_id))=1
--排除syspolicy_purge_history这个系统作业
select a.name job_name,
case b.run_status when 0 then 'Failed'
when 1 then 'Succeeded'
when 2 then 'Retry'
when 3 then 'Canceled'
else 'Unknown'
end as job_status,
LEFT(run_date,4)+'-'+SUBSTRING(run_date,5,2)+'-'+RIGHT(run_date,2)
+SPACE(1)
+LEFT(RIGHT(1000000+run_time,6),2)+':'
+SUBSTRING(RIGHT(1000000+run_time,6),3,2)+':'
+RIGHT(RIGHT(1000000+run_time,6),2) as job_started_time,
+LEFT(RIGHT(1000000+run_duration,6),2)+':'
+SUBSTRING(RIGHT(1000000+run_duration,6),3,2)+':'
+RIGHT(RIGHT(1000000+run_duration,6),2) as job_duration
from msdb.dbo.sysjobs a
left join #tmp_job b
on a.job_id=b.job_id
where a.name not in ('syspolicy_purge_history')
and a.enabled = 1
order by b.run_status asc,a.name,b.run_duration desc
2. 作业当前运行状态及时长
什么时候可能要检查作业的当前状态?
(1) 需要关闭SQL Server或SQL Server Agent服务时;
(2) 等到当前作业完成,有后续动作;
(3) 纯粹只是查看当前作业运行到哪个步骤等等。
通过SSMS/SQL Server Agent/右击作业文件夹或某个作业/查看历史纪录,看到的作业历史记录存放在:
select * from msdb.dbo.sysjobhistory
需要注意的是:至少作业已完成第一步运行,sysjobhistory表中才会有作业历史纪录,若当前作业没有完成任何一个步骤,那表里就不会有本次运行纪录。所以作业当前状态用有时无法通过sysjobhistory查看,尤其是作业只有1个步骤且运行时间很长时。
2.1. SQL Server 2005及以后版本
(1) 当前运行状态:系统存储过程msdb.dbo.sp_help_job,返回所有作业的运行状态(current_execution_status),共7种状态值,详见帮助文档。查看所有作业状态如下:
exec msdb..sp_help_job
(2) 当前运行时长:系统存储过程sp_help_job无法获得作业运行时长,可通过新增的系统表sysjobactivity来查看。查看正在运行的作业如下:
select a.name,
b.start_execution_date,
DATEDIFF(MI,b.start_execution_date,GETDATE()) as job_duration
from msdb..sysjobs a
inner join msdb..sysjobactivity b
on a.job_id = b.job_id
where b.start_execution_date is not null
and b.stop_execution_date is null
以下脚本结合sp_help_job和sysjobactivity,得到作业的当前状态及时长:
exec sp_configure 'show advanced options',1
RECONFIGURE
exec sp_configure 'Ad Hoc Distributed Queries',1
RECONFIGURE if OBJECT_ID('tempdb..#jobinfo') is not null
drop table #jobinfo select * into #jobinfo
from openrowset('sqloledb', 'server=(local);trusted_connection=yes','exec msdb.dbo.sp_help_job') select a.name,
j.current_execution_status,
b.start_execution_date,
DATEDIFF(MI,b.start_execution_date,GETDATE()) as job_duration_minute
from msdb..sysjobs a
inner join msdb..sysjobactivity b
on a.job_id = b.job_id
inner join #jobinfo j
on a.job_id = j.job_id
where b.start_execution_date is not null
and b.stop_execution_date is null
2.2. SQL Server 2000沿用过来的方法
在SQL Server 2000时,没有sysjobactivity这个系统表,通常借助sysprocesses监视作业的当前运行状态及时长。
select j.name,
p.status as current_execution_status,
p.last_batch as start_execution_date,
ISNULL(DATEDIFF(MI, p.last_batch, GETDATE()), 0) as job_duration_minute
from msdb.dbo.sysjobs j, master..sysprocesses p
where p.program_name like 'SQLAgent - TSQL JobStep (Job%'
and substring((cast(j.job_id as varchar(36))),7,2) +
substring((cast(j.job_id as varchar(36))),5,2) +
substring((cast(j.job_id as varchar(36))),3,2) +
substring((cast(j.job_id as varchar(36))),1,2) +
substring((cast(j.job_id as varchar(36))),12,2) +
substring((cast(j.job_id as varchar(36))),10,2) +
substring((cast(j.job_id as varchar(36))),17,2) +
substring((cast(j.job_id as varchar(36))),15,2) +
substring((cast(j.job_id as varchar(36))),20,4) +
substring((cast(j.job_id as varchar(36))),25,12)
= substring((cast(p.program_name as varchar(75))),32,32)
sysprocesses里获得的作业编号跟sysjobs里是不一致的,所以上面进行了转换,通常只转换job_id的前8位字符也行,如下脚本做了job_id的简化转换,并检查作业已运行超过30分钟:
declare @MaxMinutes int
set @MaxMinutes = 30 select j.name,
p.status as current_execution_status,
p.last_batch as start_execution_date,
ISNULL(DATEDIFF(MI, p.last_batch, GETDATE()), 0) as job_duration_minute
from msdb..sysjobs j
inner join master..sysprocesses p
on substring(left(cast(j.job_id as varchar(36)),8),7,2) +
substring(left(cast(j.job_id as varchar(36)),8),5,2) +
substring(left(cast(j.job_id as varchar(36)),8),3,2) +
substring(left(cast(j.job_id as varchar(36)),8),1,2) = substring(p.program_name,32,8)
where p.program_name like 'SQLAgent - TSQL JobStep (Job%'
and ISNULL(DATEDIFF(MI, p.last_batch, GETDATE()), 0) > @MaxMinutes
还有种比较笨的方法,在要监视的所有作业中增加一个步骤,如 : select GETDATE() 放在第一步,这样在sysjobhistory中就会有步骤1的运行纪录了,以此为起点,可以计算已运行时长。如果有很多已经部署的job,这确实不是个好办法。
又或者,在每个作业最后一步,放一个检查的步骤,这样所有状态时长全都监视到了,问题是如果作业运行时间过长,最后的检查步骤根本无法被运行到。
三. 作业状态告警
作业在完成后,自己有状态检查和告警机制,通常选择邮件告警,如下图:
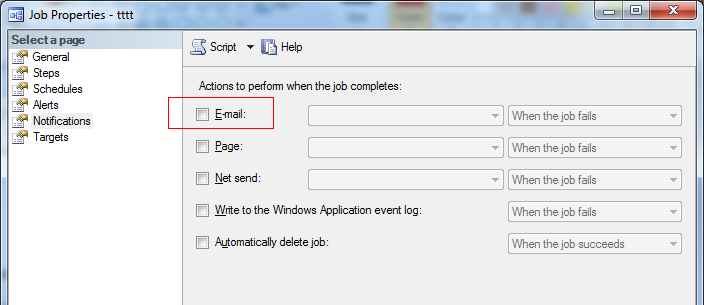
但这仅限对作业最终运行状态监视:
(1) 没有运行结束的作业无法告警,或者说对作业的运行时长没有监视;
(2) 如果作业在某个中间步骤设置了:失败后继续下一步,后续的作业步骤都成功,那么作业最终状态不会显示会失败,不会触发告警,如下脚本检查每个作业的所有步骤最后一次运行状态:
if OBJECT_ID('tempdb..#tmp_job_step') is not null
drop table #tmp_job_step
select jh1.job_id,
jh1.step_id,
jh1.run_status,
CONVERT(varchar(20),jh1.run_date) run_date,
CONVERT(varchar(20),jh1.run_time) run_time,
CONVERT(varchar(20),jh1.run_duration) run_duration
into #tmp_job_step
from msdb.dbo.sysjobhistory jh1
where (select COUNT(1) from msdb.dbo.sysjobhistory jh2
where (jh1.job_id = jh2.job_id and jh1.step_id = jh2.step_id)
and (jh1.instance_id <= jh2.instance_id))=1
select a.name job_name,
s.step_name,
case b.run_status when 0 then 'Failed'
when 1 then 'Succeeded'
when 2 then 'Retry'
when 3 then 'Canceled'
else 'Unknown'
end as job_status,
LEFT(run_date,4)+'-'+SUBSTRING(run_date,5,2)+'-'+RIGHT(run_date,2)
+SPACE(1)
+LEFT(RIGHT(1000000+run_time,6),2)+':'
+SUBSTRING(RIGHT(1000000+run_time,6),3,2)+':'
+RIGHT(RIGHT(1000000+run_time,6),2) as job_started_time,
+LEFT(RIGHT(1000000+run_duration,6),2)+':'
+SUBSTRING(RIGHT(1000000+run_duration,6),3,2)+':'
+RIGHT(RIGHT(1000000+run_duration,6),2) as job_duration
from msdb.dbo.sysjobs a
left join #tmp_job_step b
on a.job_id=b.job_id
inner join msdb.dbo.sysjobsteps s
on b.job_id = s.job_id and b.step_id = s.step_id
where a.name not in ('syspolicy_purge_history')
and a.enabled = 1
order by b.run_status asc,a.name,b.run_duration desc
小结
SQL Server Agent作业自身的告警机制,有时并不够用,所以还需要部署另外的作业,来检查其他所有作业的运行状况,大致步骤如下 :
(1) 部署数据库邮件;
(2) 部署作业:定时检查其他所有作业/步骤状态,发邮件告警;
作业运行时长可以在这一并检查,有时一些作业运行了很多天没结束还没人知道,也可以考虑放在性能监控里,和其他数据库请求一起监控。但是对于时长,通常需要有个性能基线,如果没有的话直接和历史最大值相比也是不错的选择。
4. SQL Server数据库状态监控 - 作业状态的更多相关文章
- sql server数据库状态监控
sql server数据库监控 转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/seusoftware/category/500793.html 6. SQL Server数据库监控 - 如 ...
- 2. SQL Server数据库状态监控 - 错误日志
原文:2. SQL Server数据库状态监控 - 错误日志 无论是操作系统 (Unix 或者Windows),还是应用程序 (Web 服务,数据库系统等等) ,通常都有自身的日志机制,以便故障时追溯 ...
- 3. SQL Server数据库状态监控 - 可用空间
原文:3. SQL Server数据库状态监控 - 可用空间 数据库用来存放数据,那么肯定需要存储空间,所以对磁盘空间的监视自然就很有必要了. 一. 磁盘可用空间 1. 操作系统命令或脚本.接口或工具 ...
- 5. SQL Server数据库性能监控 - 当前请求
原文:5. SQL Server数据库性能监控 - 当前请求 对于在线运行的系统,当前数据库性能监控,通常监视以下几点: (1) 是否有阻塞 (Blocking); (2) 是否有等待 (Waitin ...
- SQL SERVER数据库状态(脱机,联机,可疑)及SQL设置语句详解
首先我们应该知道数据库总是处于一个特定的状态中,下面先来了解一下数据库的常见的三种状态:1,脱机:我们可以在Microsoft SQL Server Management中看到该数据库,但该数据库 ...
- SQL SERVER数据库状态
一个SQL SERVER数据库会处于很多种状态,例如 ONLINE .RESTORING .RECOVERING .RECOVERY_PENDING .SUSPECT.EMERGENCY .OFFL ...
- SQL Server 数据库状态选项
选项 1. single_user(单用户),multi_user(多用户),restricted_user(受限用户); 描述数据库的用户访问属性,它们互斥,设置其中任何一个选项就会取消对其它选项的 ...
- SQL Server 数据库状态选项-用户使用
选项 1. single_user(单用户),multi_user(多用户),restricted_user(受限用户); 描述数据库的用户访问属性,它们互斥,设置其中任何一个选项就会取消对其它选项的 ...
- SQL Server数据库状态和文件状态
数据库状态 (database states) 查询数据库的当前状态 : 1.查询所有数据库的状态 ,通过sys.databases目录视图的state_desc列 user master go se ...
随机推荐
- 移动端 new CustomEvent('input') 兼容问题
最近在 安卓自带浏览器 上发现 new CustomEvent('input') 不兼容 解决办法 (function () { if(!!window.CustomEvent) return; f ...
- Codeforces 338D GCD Table 中国剩余定理
主题链接:点击打开链接 特定n*m矩阵,[i,j]分值为gcd(i,j) 给定一个k长的序列,问能否匹配上 矩阵的某一行的连续k个元素 思路: 我们要求出一个解(i,j) 使得 i<=n &am ...
- Groovy与Java集成常见的坑(转)
groovy特性 Groovy是一门基于JVM的动态语言,同时也是一门面向对象的语言,语法上和Java非常相似.它结合了Python.Ruby和Smalltalk的许多强大的特性,Groovy 代码能 ...
- window.open的小技巧分享(转)
今天再次谈起window.open是因为发现了一个比较好玩的小技巧,详细内容我们稍后详细说明. 聊到window.open,不得不说明一下他的使用方法,主要有两种形式: window. ...
- [置顶] think in java interview-高级开发人员面试宝典(二)
从现在开始,以样题的方式一一列出各种面试题以及点评,考虑到我在前文中说的,对于一些大型的外资型公司,你将会面临全程英语面试,因此我在文章中也会出现许多全英语样题. 这些题目来自于各个真实的公司,公司名 ...
- Android深入研究Adapter重绘
一直以来Adapter的使用都仅仅是流于表面,仅仅知道要实现几个抽象的方法,把Adapter设置给某种listView,就能够非常好的工作起来.所谓理解仅仅是建立在主观的猜想上面,认为应该是这样,对, ...
- 【MongoDB】在windows平台mongodb切片集群(三)
在过去的两年我们博客详细阐述了零碎工作集群和打造过程.在这篇博客中,我们主要分析测试结果一起支离破碎集群. 首先来看看碎片集群的每个状态.你可以看出来复制集A和B都是正常的: 一.开启分片集合 开启一 ...
- 体验安装金蝶K/3 Wise 13.0(图像)
金蝶13.0它提供windows7支持,而数据库也升级到SQL server 2008,有许多功能上的改善和增强.原本在位置低版本号需要时间来管理此功能,因为有这个模块没有原因一直没能起来,现在,新版 ...
- ScrollView 在嵌套 ViewPager 时出现的问题
1.在ViewPager 外面嵌套ScrollView 时导致ViewPager 中内容不显示,解决的办法是在ScrollView 标签下增加 android:fillViewport="t ...
- Unity3D移动端内存优化(NGUI方面)
Unity3D引擎技术交流QQ群:[21568554] 做3d移动端内存一直是人们头疼的问题,载入的资源释放了,还有其它的须要释放.比方ngui释放,事实上主要是NGUI的Texture和Spr ...
