Google单元测试框架gtest之官方sample笔记1--简单用例
1.0 通用部分
和常见的测试工具一样,gtest提供了单体测试常见的工具和组件。比如判断各种类型的值相等,大于,小于等,管理多个测试的测试组如testsuit下辖testcase,为了方便处理初始化数据减少重复代码,提供了setup和teardown函数。
官方文档称:TEST has two parameters: the test case name and the test name. 第一个是case名称,第二个是test名称,这是google的名次称呼方法,其实就是一般意义上的testsuit和testcase,前者是组,后者是测试用例,为了方便测试管理,把几个相关的测试放到一起统称为一个测试组。这是一个编程约定,但如果把不相干的测试放到一个test_case_name下,也不会报错,只是做测试总结和汇总的时候不方便而已。
# define TEST(test_case_name, test_name) GTEST_TEST(test_case_name, test_name)
关于TEST宏,这是一个一层包一层的宏定义,虽然google编程规范说不建议用宏,但是gtest却大量的使用宏来创建类和函数,使用宏可以给用户更加简洁的接口,在效率上也有优势,但是读起来很晦涩。一般的,在基础工具和底层API中,宏还是由广大的应用空间,因为这一部分基本上不怎么变化,那些写底层工具的大牛们有能力驾驭这种反常规的写法。
使用宏来实现底层的重复性工作或者封装复杂的接口,在开源项目中是很常见的方式。
Sample #1 shows the basic steps of using googletest to test C++ functions.
Sample #2 shows a more complex unit test for a class with multiple member functions.
Sample #3 uses a test fixture.
Sample #4 teaches you how to use googletest and
googletest.htogether to get the best of both libraries.Sample #5 puts shared testing logic in a base test fixture, and reuses it in derived fixtures.
Sample #6 demonstrates type-parameterized tests.
Sample #7 teaches the basics of value-parameterized tests.
Sample #8 shows using
Combine()in value-parameterized tests.Sample #9 shows use of the listener API to modify Google Test's console output and the use of its reflection API to inspect test results.
Sample #10 shows use of the listener API to implement a primitive memory leak checker.
1.1 sample1
官方sample1有2个函数,阶乘函数int Factorial()和判断素数函数bool IsPrime(int n)。
测试用例分为2个testsuit。
FactorialTest包含3个阶乘函数的测试用例:
Negative: 输入负数测试阶乘
Zero:输入为0测试阶乘
Positive:输入为正数测试阶乘
TEST(FactorialTest, Negative) {
// This test is named "Negative", and belongs to the "FactorialTest"
// test case.
EXPECT_EQ(1, Factorial(-5));
EXPECT_EQ(1, Factorial(-10));
EXPECT_GT(Factorial(-10), 0);
}
// Tests factorial of 0.
TEST(FactorialTest, Zero) { EXPECT_EQ(1, Factorial(0)); }
// Tests factorial of positive numbers.
TEST(FactorialTest, Positive) {
EXPECT_EQ(1, Factorial(1));
EXPECT_EQ(2, Factorial(2));
EXPECT_EQ(6, Factorial(3));
EXPECT_EQ(40320, Factorial(8));
}
IsPrimeTest包含3个素数检测函数的测试用例:
Negative:输入为负数和极限值INT_MIN
Trivial:输入为几个特殊的值如临界点的数
Positive:输入为正数
// Tests negative input.
TEST(IsPrimeTest, Negative) {
// This test belongs to the IsPrimeTest test case.
EXPECT_FALSE(IsPrime(-1));
EXPECT_FALSE(IsPrime(-2));
EXPECT_FALSE(IsPrime(INT_MIN));
}
// Tests some trivial cases.
TEST(IsPrimeTest, Trivial) {
EXPECT_FALSE(IsPrime(0));
EXPECT_FALSE(IsPrime(1));
EXPECT_TRUE(IsPrime(2));
EXPECT_TRUE(IsPrime(3));
}
// Tests positive input.
TEST(IsPrimeTest, Positive) {
EXPECT_FALSE(IsPrime(4));
EXPECT_TRUE(IsPrime(5));
EXPECT_FALSE(IsPrime(6));
EXPECT_TRUE(IsPrime(23));
}
gtest直接运行即可,代码中没有main函数也可以执行。输出结果提示使用了gtest_main.cc函数。
输出显示来自2个testcase的6个用例被执行。两个case就是测试组FactorialTest和IsPrimeTest。
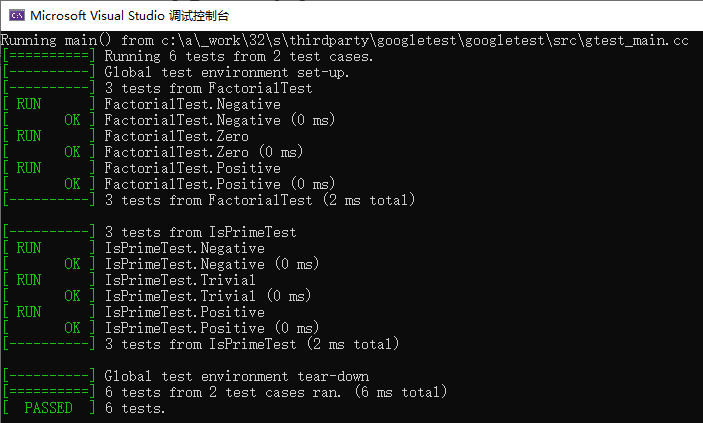
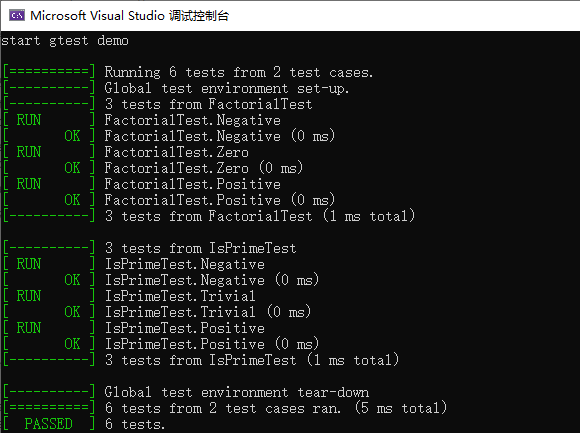
可以加上自己的main函数,调用RUN_ALL_TESTS()执行测试用例。
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
cout << "start gtest demo \r\n" << endl;
::testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv);
return RUN_ALL_TESTS();
}
1.2 sample2
官方sample 2,测试一个名为MyString的类,包括测试构造函数和成员函数。
该类有如下特征:默认构造函数把成员变量c_string指针初始化为nullptr,构造函数MyString接收一个char *字符串然后通过Set函数拷贝给c_string_。
class MyString {
private:
const char* c_string_;
const MyString& operator=(const MyString& rhs);
public:
// Clones a 0-terminated C string, allocating memory using new.
// 类方法
static const char* CloneCString(const char* a_c_string);
// The default c'tor constructs a NULL string.
// 默认构造函数
MyString() : c_string_(nullptr) {}
// Constructs a MyString by cloning a 0-terminated C string.
// 构造函数,禁止隐式转换
explicit MyString(const char* a_c_string) : c_string_(nullptr) {
Set(a_c_string);
}
// Copy c'tor
// 拷贝构造函数
MyString(const MyString& string) : c_string_(nullptr) {
Set(string.c_string_);
}
// D'tor. MyString is intended to be a final class, so the d'tor
// doesn't need to be virtual.
~MyString() { delete[] c_string_; }
// Gets the 0-terminated C string this MyString object represents.
const char* c_string() const { return c_string_; }
size_t Length() const { return c_string_ == nullptr ? 0 : strlen(c_string_); }
// Sets the 0-terminated C string this MyString object represents.
// 成员函数
void Set(const char* c_string);
};
类方法的实现和Set成员函数的实现。
// Clones a 0-terminated C string, allocating memory using new.
const char* MyString::CloneCString(const char* a_c_string) {
if (a_c_string == nullptr) return nullptr;
const size_t len = strlen(a_c_string);
char* const clone = new char[ len + 1 ];
memcpy(clone, a_c_string, len + 1);
return clone;
}
// Sets the 0-terminated C string this MyString object
// represents.
void MyString::Set(const char* a_c_string) {
// Makes sure this works when c_string == c_string_
const char* const temp = MyString::CloneCString(a_c_string);
delete[] c_string_;
c_string_ = temp;
}
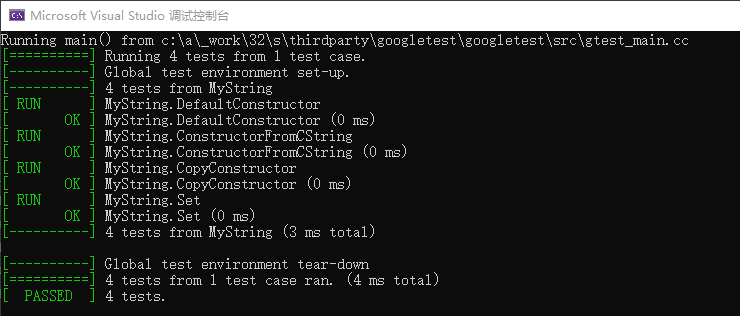
测试用例,构建了一个测试testcase叫做MyString,包含了4个test用例。
第一个用例:TEST(MyString, DefaultConstructor),测试默认构造函数, MyString() : c_string_(nullptr) {}。
const MyString s;
EXPECT_STREQ(nullptr, s.c_string());
EXPECT_EQ(0u, s.Length());
第二个用例:TEST(MyString, ConstructorFromCString),测试 MyString(const char* a_c_string) 构造函数,sizeof(kHelloString)-1和 s.Length()相等,是因为这是c类型的字符串,最后结尾是\0,sizeof计算的是分配给这个字符串的空间。
const char kHelloString[] = "Hello, world!";
// Tests the c'tor that accepts a C string.
TEST(MyString, ConstructorFromCString) {
const MyString s(kHelloString);
EXPECT_EQ(0, strcmp(s.c_string(), kHelloString));
EXPECT_EQ(sizeof(kHelloString)/sizeof(kHelloString[0]) - 1,
s.Length());
}
第三个用例:TEST(MyString, CopyConstructor),测试拷贝构造函数。
// Tests the copy c'tor.
TEST(MyString, CopyConstructor) {
const MyString s1(kHelloString);
const MyString s2 = s1;
EXPECT_EQ(0, strcmp(s2.c_string(), kHelloString));
}
第四个用例:TEST(MyString, Set) ,测试Set成员函数。
// Tests the Set method.
TEST(MyString, Set) {
MyString s;
s.Set(kHelloString);
EXPECT_EQ(0, strcmp(s.c_string(), kHelloString));
// Set should work when the input pointer is the same as the one
// already in the MyString object.
s.Set(s.c_string());
EXPECT_EQ(0, strcmp(s.c_string(), kHelloString));
// Can we set the MyString to NULL?
s.Set(nullptr);
EXPECT_STREQ(nullptr, s.c_string());
}
最终运行结果如下图,1个test case,4个tests,全部成功。
1.3 sample3
官方sample 3,展示了测试夹具的概念,为测试准备环境,每个test case都使用相同的环境初始化数据等。sample 3测试了一个自己编写的Queue模板类,这个Q实现了一个单向的链表。元素项使用template <typename E> class QueueNode 实现,内部有友元类Queue<E>。队列Queue类具有默认构造函数和以下成员:
SIze() --大小
Head() --队列头
Last() --队列尾
void Enqueue(const E& element) --入队
E* Dequeue() --出队,返回出队的元素
Queue* Map(F function) const -- 实现队列拷贝,并且对元素执行function操作,比如测试中就对元素乘以2倍入队,返回新的队列的每个元素都是旧队列元素的二倍大小。
sample3 例子展示了“test fixture”(测试夹具)的概念,“test fixture”就是实现测试前准备,比如创造一系列共用的函数和数据,每个测试case运行前都可以引用这些共有的条件。最常见的就是初始化Setup或善后处理TearDown函数,所以使用“test fixture”可以避免重复的代码。
test fixture 怎么写公共部分
test fixture的类名没有限制,可以按照测试需求起名字,这个类需要继承testing::Test类,class QueueTestSmpl3 : public testing::Test ,在测试夹具类中重写SetUp和TearDown方法。
如果使用了测试夹具,那么测试用例名就不能使用TEST来创建,而是使用TEST_F来创建,在TEST_F宏的第一个参数里,写测试夹具类名。
测试启动后,每个测试case执行前都会运行测试夹具类。达到一个准备测试环境的目的。
例如在测试夹具中加入一句打印:
void SetUp() override {
std::cout << "this test fixture" << std::endl;
q1_.Enqueue(1);
q2_.Enqueue(2);
q2_.Enqueue(3);
}
三个测试用例,会调用setup3次。
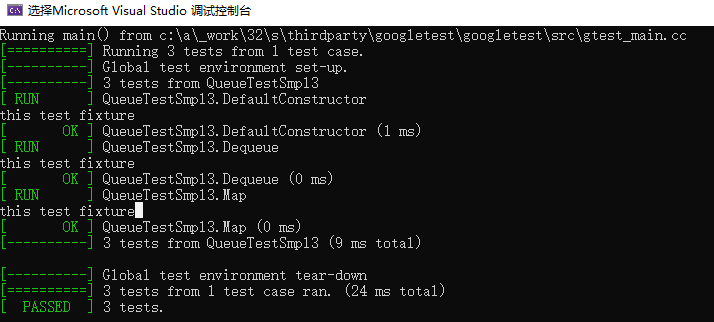
每个TEST_F都会创建一个类,并且继承test fixture类。例如TEST_F(QueueTestSmpl3, DefaultConstructor) 会被扩展为:
class QueueTestSampl3_DefaultConstructor_Test:public QueueTestSmpl3 {}所以每个TEST_F运行时,都会调用一次QueueTestSmpl3类。
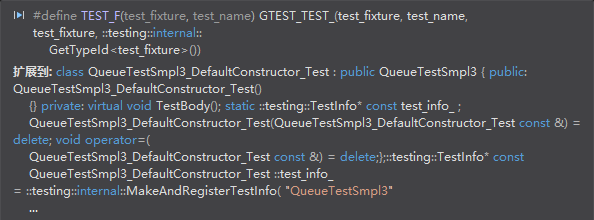
下面分析下第二个用例:
// Tests Dequeue().
TEST_F(QueueTestSmpl3, Dequeue) {
int * n = q0_.Dequeue(); // q0 队列没有任何元素,setup没有设置q0,出队只会是nullptr
EXPECT_TRUE(n == nullptr);
n = q1_.Dequeue(); // q1 对列有一个元素:1
ASSERT_TRUE(n != nullptr);
EXPECT_EQ(1, *n);
EXPECT_EQ(0u, q1_.Size()); // 出队后,q1队列没有元素了
delete n;
n = q2_.Dequeue(); // q2在setup时候输入了2,3两个元素
ASSERT_TRUE(n != nullptr);
EXPECT_EQ(2, *n);
EXPECT_EQ(1u, q2_.Size());
delete n;
}
1.4 sample4
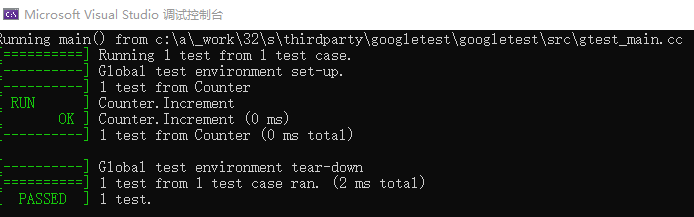
官方sample 4测试了一个Counter类,该类实现了Increment和Decrement两个函数,一个int类型数值自增,一个自减,值为0时不再减直接返回0。
TEST(Counter, Increment) {
Counter c;
// Test that counter 0 returns 0
EXPECT_EQ(0, c.Decrement());
// EXPECT_EQ() evaluates its arguments exactly once, so they
// can have side effects.
EXPECT_EQ(0, c.Increment());
EXPECT_EQ(1, c.Increment());
EXPECT_EQ(2, c.Increment());
EXPECT_EQ(3, c.Decrement());
}
测试很简单,注意的是第一次c.Increment()调用后,依然为0,是由于Incremen函数先返回值写入临时变量,然后再执行++操作。3个加执行完,c.counter_ = 3,减方法返回3,然后c.counter_=2.
int Counter::Increment() {
return counter_++;
}
1.5 sample5
sample 3展示了测试夹具的概念,可以方便的为每个测试用例创建共用的部分,比如准备测试环境和数据。但是如果多个测试需要的环境类似,只有细小的差别,那么就可以把共用的部分抽出来放到基类--创建一个超级的test fixture,而各自的不同的测试夹具用继承来实现个性化--派生出各自的test fixture。
sample 5先创建了一个超级测试夹具,类名叫QuickTest,继承testing::Test类,QuickTest计算每个测试case的执行时间,方式很简单,SetUp里记录start_time,TearDown里记录end_time,相减就是执行时间。如果故意在test中Sleep(6),则会超时报错显示如下:
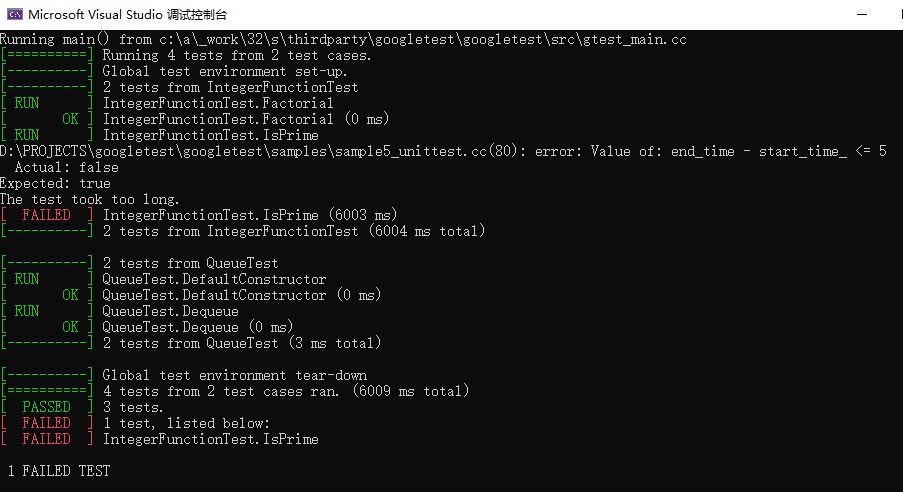
测试用例如下,TEST_F使用IntegerFunctionTest类作为test_fixture名字,而IntegerFunctionTest类继承于QuickTest,所以也可以计算时间。
class IntegerFunctionTest : public QuickTest {
// We don't need any more logic than already in the QuickTest fixture.
// Therefore the body is empty.
};
TEST_F(IntegerFunctionTest, Factorial) {
// **** 阶乘函数的tests
}
TEST_F(IntegerFunctionTest, IsPrime) {
// **** 判断素数函数的tests
}
第二个测试case展示了共用测试夹具的方法,如sample 3中,测试Queue时候,需要初始化队列,那么可以在这个test fixture类中初始化对列,并且继承于QuickTest类,那么测试case运行时候就可以执行统计执行时间的功能。
class QueueTest : public QuickTest {
protected:
void SetUp() override {
// First, we need to set up the super fixture (QuickTest).
QuickTest::SetUp();
// Second, some additional setup for this fixture.
q1_.Enqueue(1);
q2_.Enqueue(2);
q2_.Enqueue(3);
}
// By default, TearDown() inherits the behavior of
// QuickTest::TearDown(). As we have no additional cleaning work
// for QueueTest, we omit it here.
//
// virtual void TearDown() {
// QuickTest::TearDown();
// }
Queue<int> q0_;
Queue<int> q1_;
Queue<int> q2_;
};
测试case部分和sample 3一样,但是由于test fixture类继承了QuickTest,这个测试用例可以统计执行时间,并且执行TearDown函数里面的超时报错。
最终的执行结果如下图。共两个test case:IntegerFunctionTest和QueueTest,每个case有2个tests。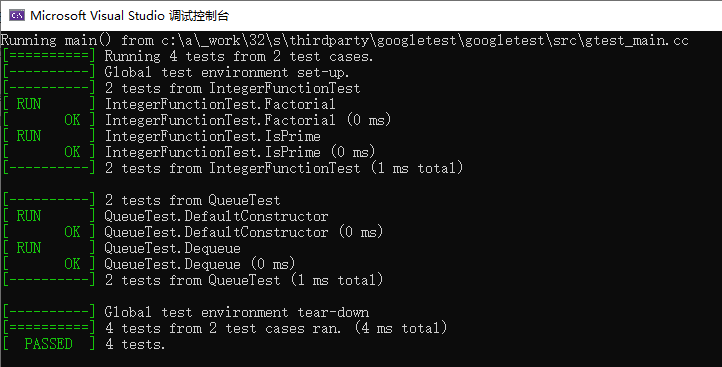
Google单元测试框架gtest之官方sample笔记1--简单用例的更多相关文章
- Google单元测试框架gtest之官方sample笔记3--值参数化测试
1.7 sample7--接口测试 值参数不限定类型,也可以是类的引用,这就可以实现对类接口的测试,一个基类可以有多个继承类,那么可以测试不同的子类功能,但是只需要写一个测试用例,然后使用参数列表实现 ...
- Google单元测试框架gtest之官方sample笔记2--类型参数测试
gtest 提供了类型参数化测试方案,可以测试不同类型的数据接口,比如模板测试.可以定义参数类型列表,按照列表定义的类型,每个测试case都执行一遍. 本例中,定义了2种计算素数的类,一个是实时计算, ...
- Google单元测试框架gtest之官方sample笔记4--事件监控之内存泄漏测试
sample 10 使用event listener监控Water类的创建和销毁.在Water类中,有一个静态变量allocated,创建一次值加一,销毁一次值减一.为了实现这个功能,重载了new和d ...
- Google单元测试框架gtest--值参数测试
测试一个方法,需要较多个参数进行测试,比如最大值.最小值.异常值和正常值.这中间会有较多重复代码工作,而值参数测试就是避免这种重复性工作,并且不会损失测试的便利性和准确性. 如果测试一个函数,需要些各 ...
- C++单元测试框架gtest使用
作用 作为代码编码人员,写完代码,不仅要保证编译通过和运行,还要保证逻辑尽量正确.单元测试是对软件可测试最小单元的检查和校验.单元测试与其他测试不同,单元测试可看作是编码工作的一部分,应该由程序员完成 ...
- 简单易懂的单元测试框架-gtest(一)
简介 gtest是google开源的一个单元测试框架,以其简单易学的特点被广泛使用.该框架以第三方库的方式插入被测代码中.同其他单元测试框架相似,gtest也通过制作测试样例来进行代码测试.同 ...
- Google C++单元测试框架---Gtest框架简介(译文)
一.设置一个新的测试项目 在用google test写测试项目之前,需要先编译gtest到library库并将测试与其链接.我们为一些流行的构建系统提供了构建文件: msvc/ for Visual ...
- 简单易懂的单元测试框架-gtest(二)
简介 事件机制用于在案例运行前后添加一些操作(相当于挂钩函数).目前,gtest提供了三种等级的事件,分别: 全局级,所有案例执行的前后 TestSuite级,某一个案例集的前后 TestCa ...
- 玩转Google开源C++单元测试框架Google Test系列(gtest)之八 - 打造自己的单元测试框架
转载来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/coderzh/archive/2009/04/12/1434155.html 一.前言 上一篇我们分析了gtest的一些内部实现,总的来说整 ...
随机推荐
- dedecms织梦的安全问题解决办法
很多新手用户在使用织梦CMS程序过程中,难免会碰到挂马中毒现象,所以事先我们要对网站及服务器安全做好预防备份处理. 织梦作为国内第一大开源免费CMS程序,无疑是很多HACK研究的对象,在本身不安全的互 ...
- for循环语句学习
for循环又称为遍历循环,从名字就可以知道,它用于对象的遍历 语法格式: 会从可迭代对象对象中依次拿出值来赋值给变量,变量的值每次都会被修改 for 变量1[变量2...] in 可迭代对象: 代码块 ...
- hdu5489 Removed Interval
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others) Total Submission ...
- WSL2 新建dotnet core mvc项目
我们知道dotnet sdk会有很多命令,但在我们完全不知道如何去使用哪个命令. 我们使用dotnet -h进行查看: 我们看到SDK的new命令,但是new命令又如何使用呢? 我们再次使用帮助: 可 ...
- JVM你了解?
1.谈谈你对JAVA的理解 平台无关性(一次编译,到处运行) GC(不必手动释放堆内存) 语言特性(泛型.lambda) 面向对象(继承,封装,多态) 类库 异常处理 2.平台无关性怎么实现
- C++构造函数、复制函数易错点
C++中复制函数在三种情况下自动调用: 用一个对象初始化另一个对象 函数的参数为对象 函数的返回值为对象 下面用几个代码片段解释复制函数的调用中的一些常见"坑": 一:默认复制函数 ...
- SpringBoot整合Swagger初探
当下的Web项目大都采用前后端分离+分布式微服务的架构.前后端分离式的开发中,前端开发人员要与后端开发人员协商通信接口,约定接口规范.因此对于开发人员来说能够维持一份及时更新且完整全面的API文档会大 ...
- Nginx基础 - 配置代理web服务
1.反向代理及负载均衡Nginx实现负载均衡用到了proxy_pass代理模块核心配置,将客户端请求代理转发至一组upstream虚拟服务池. 1)upstream配置语法 Syntax: upstr ...
- MySQL 多实例及其主从复制
目录 Mysql 实例 Mysql 多实例 创建多实例目录 编辑配置文件 初始化多实例数据目录 授权目录 启动多实例 连接多实例并验证 Mysql 多实例设置密码 设置密码后连接 Mysql 多实例主 ...
- 使用SignTool对软件安装包进行数字签名(二)--进行数字签名
四.使用signcode.exe为安装程序.库或cab包签名 1.运行signcode.exe. 2.点击"下一步",选择需要签名的文件(安装程序.库或cab包). 3.点击&qu ...
