python 音频可视化
代码整理好放在 github 上了: https://github.com/darkchii/visualize
bilibili 演示视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av77372866 2020-03-23 13:23:01 还是给一个 pydub(需要自己配置好ffmpeg)正确使用姿势,因为 mp3 格式太常见:
import numpy as np
import pyaudio
from pydub import AudioSegment, effects
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
sound = AudioSegment.from_file(file='../xxx.mp3')
left = sound.split_to_mono()[0]
fs = left.frame_rate
size = len(left.get_array_of_samples())
channels = left.channels
stream = p.open(
format=p.get_format_from_width(left.sample_width,),
channels=channels,
rate=fs,
# input=True,
output=True,
) stream.start_stream()
fig = plt.figure()
ax1, ax2 = fig.subplots(2, 1)
ax1.set_ylim(0, 0.5)
ax2.set_ylim(-1.5, 1.5)
ax1.set_axis_off()
ax2.set_axis_off()
window = int(0.02*fs) # 20ms
f = np.linspace(20, 20*1000, window // 2)
t = np.linspace(0, 20, window)
lf1, = ax1.plot(f, np.zeros(window // 2), lw=1)
lf2, = ax2.plot(t, np.zeros(window), lw=1) def update(frames):
if stream.is_active():
slice = left.get_sample_slice(frames, frames + window)
data = slice.raw_data
stream.write(data)
y = np.array(slice.get_array_of_samples()) / 30000 # 归一化
yft = np.abs(np.fft.fft(y)) / (window // 2) lf1.set_ydata(yft[:window // 2])
lf2.set_ydata(y) return lf1, lf2, ani = FuncAnimation(fig, update, frames=range(0, size, window), interval=0, blit=True)
plt.show()
截图:
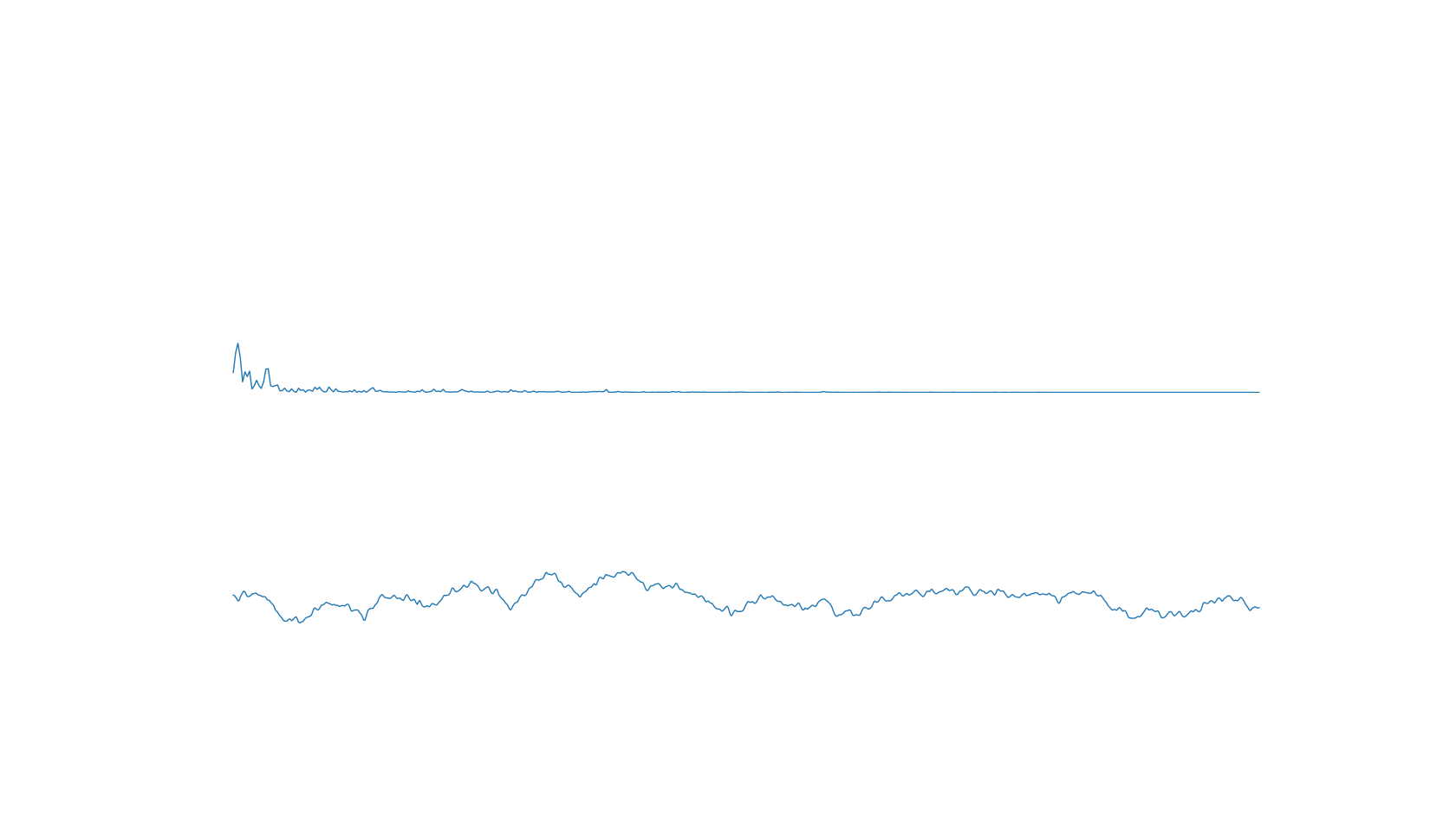
2020-02-25 14:50:27 Animation:
注:pyaudio open 调节参数 format 有惊喜(取值范围{1, 2, 4, 8, 16,...})
极坐标版:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.signal import detrend
# from scipy.fftpack import fft
import numpy as np
import pyaudio
from _tkinter import TclError
import struct
import wave
# import librosa
from pydub import AudioSegment
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation chunk = 1024
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
# sound = AudioSegment.from_file(file='../Music/xxx.mp3')
# rdata = sound.get_array_of_samples()
wf = wave.open('../Music/xxx.wav')
stream = p.open(
format=8,
channels=wf.getnchannels(),
rate=wf.getframerate(),
# input=True,
output=True,
# frames_per_buffer=chunk
) fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='polar')
# ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
ax.set_axis_off()
lf, = ax.plot(np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, chunk), np.zeros(chunk), lw=1) def init():
stream.start_stream()
return lf, def update(frame):
if stream.is_active():
data = wf.readframes(chunk)
stream.write(data)
data_int = struct.unpack(str(chunk * 4) + 'B', data)
y_detrend = detrend(data_int)
yft = np.abs(np.fft.fft(y_detrend))
y_vals = yft[:chunk] / (chunk * chunk * 4)
ind = np.where(y_vals > (np.max(y_vals) + np.min(y_vals)) / 2)
y_vals[ind[0]] *= 2
lf.set_ydata(y_vals)
return lf, ani = FuncAnimation(fig, update, frames=None,
init_func=init, interval=0, blit=True)
plt.show()
截图:
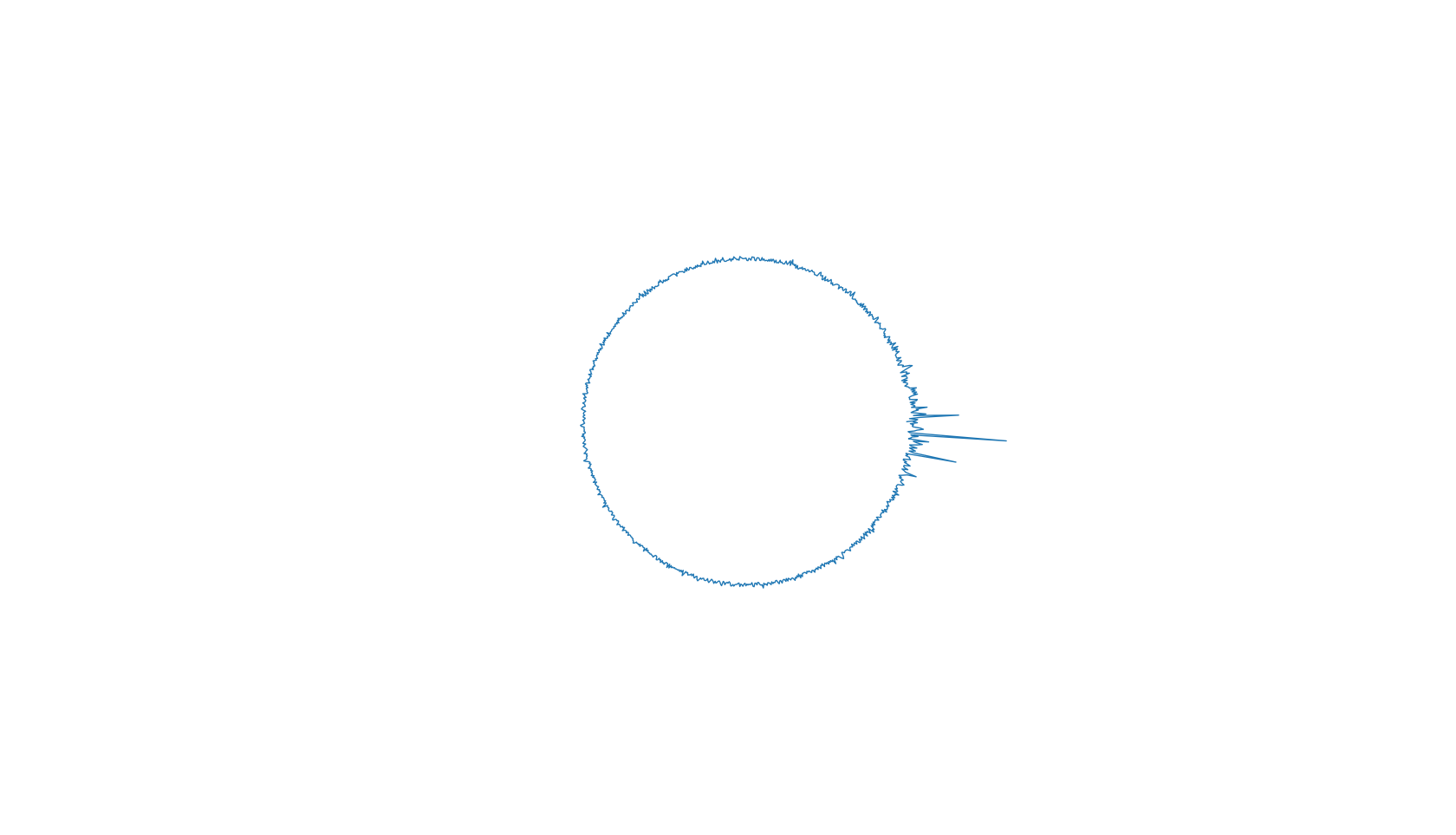
stem 版:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.signal import detrend
# from scipy.fftpack import fft
import numpy as np
import pyaudio
from _tkinter import TclError
import struct
import wave
# import librosa
from pydub import AudioSegment
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation chunk = 1024
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
# sound = AudioSegment.from_file(file='../Music/xxx.mp3')
# rdata = sound.get_array_of_samples()
wf = wave.open('../Music/xxx.wav')
stream = p.open(
format=8,
channels=wf.getnchannels(),
rate=wf.getframerate(),
# input=True,
output=True,
# frames_per_buffer=chunk
) fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca()
ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
ax.set_axis_off()
lf = ax.stem(np.linspace(20, 20000, chunk), np.zeros(chunk), basefmt=':', use_line_collection=True)
lf.markerline.set_color([0.8, 0.2, 0, 0.5]) def init():
stream.start_stream()
return lf def update(frame):
if stream.is_active():
data = wf.readframes(chunk)
stream.write(data)
data_int = struct.unpack(str(chunk * 4) + 'B', data)
y_detrend = detrend(data_int)
yft = np.abs(np.fft.fft(y_detrend))
y_vals = yft[:chunk] / (chunk * chunk)
ind = np.where(y_vals > (np.max(y_vals) + np.min(y_vals)) / 2)
y_vals[ind[0]] *= 4
lf.markerline.set_ydata(y_vals)
return lf ani = FuncAnimation(fig, update, frames=None,
init_func=init, interval=0, blit=True)
plt.show()
semilogx 版:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.signal import detrend
# from scipy.fftpack import fft
import numpy as np
import pyaudio
from _tkinter import TclError
import struct
import wave
# import librosa
from pydub import AudioSegment
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation chunk = 1024
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
# sound = AudioSegment.from_file(file='../Music/xxx.mp3')
# rdata = sound.get_array_of_samples()
wf = wave.open('../Music/xxx.wav')
stream = p.open(
format=8,
channels=wf.getnchannels(),
rate=wf.getframerate(),
# input=True,
output=True,
# frames_per_buffer=chunk
) fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca()
ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
ax.set_axis_off()
lf, = ax.semilogx(np.linspace(20, 20000, chunk), np.zeros(chunk), lw=1, color='lightblue') def init():
stream.start_stream()
return lf, def update(frame):
if stream.is_active():
data = wf.readframes(chunk)
stream.write(data)
data_int = struct.unpack(str(chunk * 4) + 'B', data)
y_detrend = detrend(data_int)
yft = np.abs(np.fft.fft(y_detrend))
y_vals = yft[:chunk] / (chunk * chunk)
ind = np.where(y_vals > (np.max(y_vals) + np.min(y_vals)) / 2)
y_vals[ind[0]] *= 4
lf.set_ydata(y_vals)
return lf, ani = FuncAnimation(fig, update, frames=None,
init_func=init, interval=0, blit=True)
plt.show()
2020-02-25 12:18:49 更新一下:
这次更新是给一个很勉强的通过音频数据来播放音乐并展示 fft 效果的代码,实际上仅仅只是播放音乐很简单,wav 波形文件只需要 wave 即可,想要 mp3 或者其他支持较广类型的音频文件格式,使用 pydub 包更好.。(更新:使用 pydub 不需要解包,只需要通过 get_array_of_samples() 就可以获取数据,raw_data 是字节数组,用于加载到输出流)
但还是给个代码:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from vispy.plot import Fig
from matplotlib.colors import LightSource
from matplotlib import cm
from scipy.signal import detrend
from scipy.fftpack import fftn
import numpy as np
import pyaudio
from _tkinter import TclError
import struct
import wave
# import librosa
import array
from pydub import AudioSegment
from pydub.utils import get_array_type chunk = 1024 p = pyaudio.PyAudio() # sound = AudioSegment.from_file(file='../Music/1563833285950.mp3')
# left = sound.split_to_mono()[1]
# bit_depth = left.sample_width * 8
# array_type = get_array_type(bit_depth)
# numeric_array = array.array(array_type, left.raw_data) wf = wave.open('../Music/1563833285950.wav')
stream = p.open(
format=p.get_format_from_width(wf.getsampwidth()),
channels=wf.getnchannels(),
rate=wf.getframerate(),
# input=True,
output=True,
# frames_per_buffer=chunk
)
stream.start_stream()
freq = np.linspace(20, 20000, chunk)
yf = np.zeros(chunk)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca()
lf, = ax.semilogx(freq, yf, lw=1, color='lightblue')
ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
ax.set_axis_off()
plt.show(block=False) start = 0
while stream.is_active():
data = wf.readframes(chunk)
if len(data) < chunk:
break
stream.write(data) data_int = struct.unpack(str(chunk * 4) + 'B', data) y_detrend = detrend(data_int)
yft = np.abs(fftn(y_detrend))
y_vals = yft[:chunk] / (128 * chunk) lf.set_ydata(y_vals) try:
ax.figure.canvas.draw()
ax.figure.canvas.flush_events()
except TclError:
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
break
给个 pydub 将数据合成到包的源码截图:
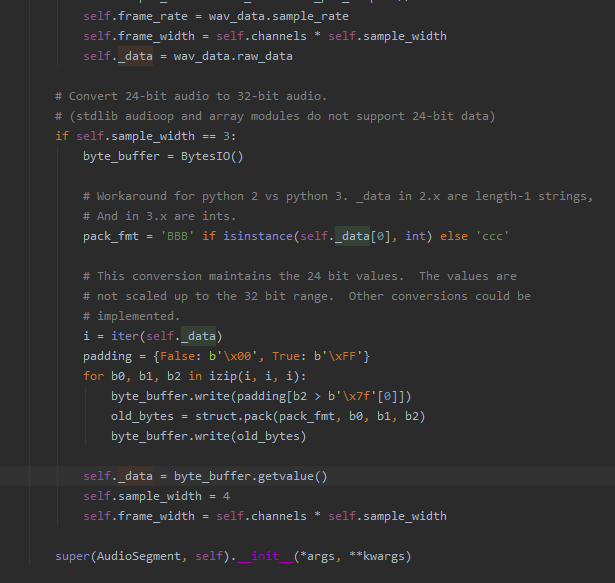
2019-12-31 15:45:34 再来一个:
极坐标版:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import LightSource
from matplotlib import cm
from scipy.signal import detrend
import numpy as np
import pyaudio
from _tkinter import TclError
import struct channels = 1
rate = 48000
chunk = 2048
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
stream = p.open(
format=pyaudio.paInt16,
channels=channels,
rate=rate,
input=True,
frames_per_buffer=chunk
)
stream.start_stream()
theta = np.linspace(0.0, rate, chunk)
radii = np.zeros(chunk)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='polar')
lf = ax.stem(theta, radii, basefmt=':', use_line_collection=True)
lf.markerline.set_color([0.8, 0.2, 0, 0.5])
ax.set_rorigin(0)
ax.set_axis_off()
plt.show(block=False)
while stream.is_active():
data = stream.read(chunk)
data_int = struct.unpack(str(chunk * 2) + 'B', data)
y_detrend = detrend(data_int)
yft = np.abs(np.fft.fft(y_detrend))
y_vals = yft[:chunk] / (128 * chunk)
lf.markerline.set_ydata(y_vals) try:
ax.figure.canvas.draw()
ax.figure.canvas.flush_events()
except TclError:
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
break
笛卡尔直角坐标版:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import LightSource
from matplotlib import cm
from scipy.signal import detrend
import numpy as np
import pyaudio
from _tkinter import TclError
import struct channels = 1
rate = 48000
chunk = 2048
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
stream = p.open(
format=pyaudio.paInt16,
channels=channels,
rate=rate,
input=True,
frames_per_buffer=chunk
)
stream.start_stream()
theta = np.linspace(0.0, rate, chunk)
radii = np.zeros(chunk)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca()
lf = ax.stem(theta, radii, basefmt=':', use_line_collection=True)
lf.markerline.set_color([0.8, 0.2, 0, 0.5])
ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
ax.set_axis_off()
plt.show(block=False)
while stream.is_active():
data = stream.read(chunk)
data_int = struct.unpack(str(chunk * 2) + 'B', data)
y_detrend = detrend(data_int)
yft = np.abs(np.fft.fft(y_detrend))
y_vals = yft[:chunk] / (128 * chunk)
lf.markerline.set_ydata(y_vals) try:
ax.figure.canvas.draw()
ax.figure.canvas.flush_events()
except TclError:
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
break
运行截图:
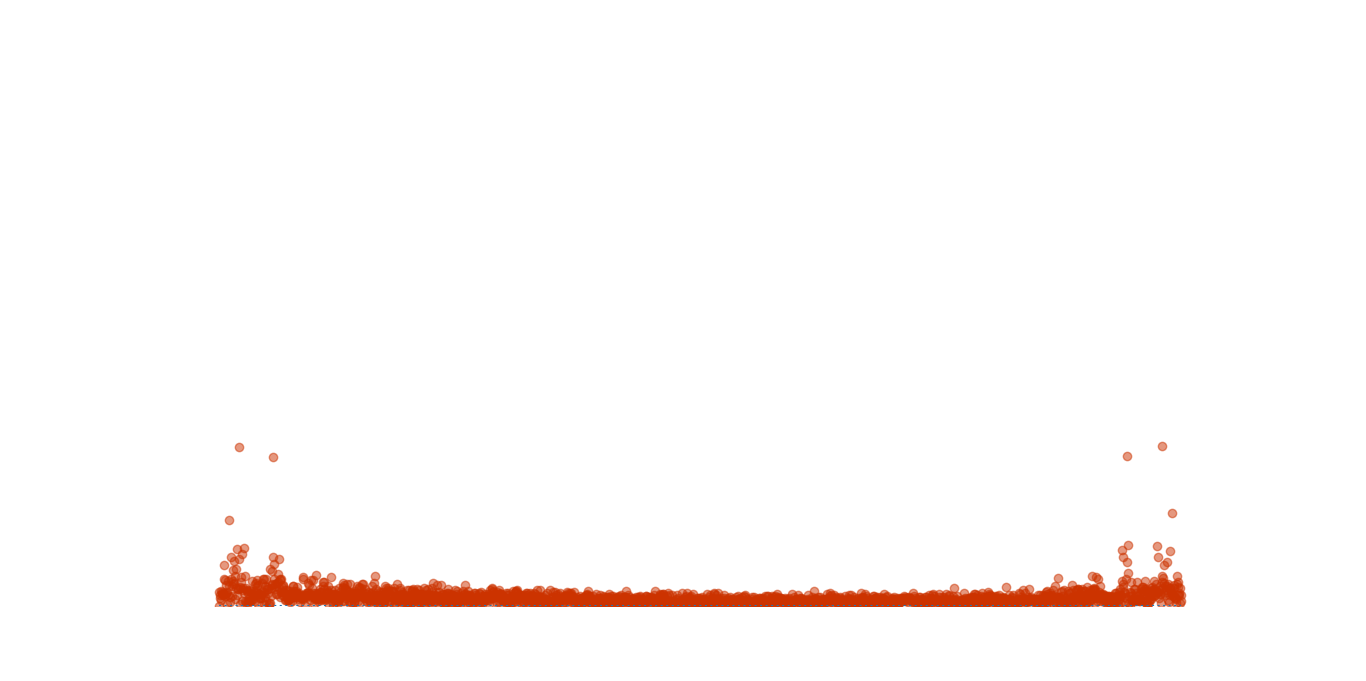
2019-12-30 14:05:57 再来更新一个版本(可惜我的电脑跑起来非常卡):
from scipy.signal import detrend
import numpy as np
import pyaudio
from _tkinter import TclError
import struct channels = 1
rate = 48000
chunk = 2048 p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
stream = p.open(
format=pyaudio.paInt16,
channels=channels,
rate=rate,
input=True,
frames_per_buffer=chunk
) stream.start_stream()
theta = np.linspace(0.0, 2. * np.pi, chunk, endpoint=False)
radii = np.zeros(chunk)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='polar')
lf = ax.bar(x=theta, height=radii, width=0.02, bottom=-2.0, alpha=0.5)
ax.set_axis_off()
plt.show(block=False) while stream.is_active():
data = stream.read(chunk)
data_int = struct.unpack(str(chunk * 2) + 'B', data)
y_detrend = detrend(data_int)
yft = np.abs(np.fft.fft(y_detrend))
y_vals = yft[:chunk] / (128 * chunk) for rect, y_val, color in zip(lf.patches, y_vals, plt.cm.Spectral(y_vals * 8)):
rect.set_height(y_val)
rect.set_facecolor(color) try:
ax.figure.canvas.draw()
ax.figure.canvas.flush_events()
except TclError:
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
break
2019-11-28 20:58:07 更新,围绕在圆环上的2d 版(一开始sb了,直接加在 y 轴上 = =,幸好马上意识到需要做向量旋转):
from _tkinter import TclError
import pyaudio
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import struct
from scipy.signal import savgol_filter, detrend, lfilter channels = 1
rate = 48000
chunk = 1024 * 2 p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
stream = p.open(
format=pyaudio.paInt16,
channels=channels,
rate=rate,
input=True,
# output=True,
frames_per_buffer=chunk
) stream.start_stream() R = 2
t = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, chunk * 2)
xf = R*np.cos(t)
yf = R*np.sin(t)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 7))
lf, = ax.plot(xf, yf, lw=1)
ax.set_xlim(-3, 3)
ax.set_ylim(-3, 3)
ax.set_axis_off()
plt.show(block=False) fwhm = 20 while stream.is_active():
data = stream.read(chunk)
data_int = struct.unpack(str(chunk * 2) + 'B', data)
y_detrend = detrend(data_int)
# z_smooth = savgol_filter(data_int, window_length=len(data_int) - 1, mode='valid')
# box = np.ones(fwhm) / fwhm
# z_smooth = np.convolve(y_detrend, box, mode='valid')
yft = np.abs(np.fft.fft(y_detrend))
y_vals = yft / (256 * chunk)
ind = np.where(y_vals > np.mean(y_vals))
y_vals[ind[0]] *= 4
lf.set_xdata(xf + y_vals * np.cos(t))
lf.set_ydata(yf + y_vals * np.sin(t)) try:
ax.figure.canvas.draw()
ax.figure.canvas.flush_events()
except TclError:
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
break
运行截图:

2019-11-28 16:47:13 更新,3D 版:
from _tkinter import TclError
import pyaudio
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import struct
from scipy.signal import savgol_filter, detrend, lfilter channels = 1
rate = 48000
chunk = 1024 * 2 p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
stream = p.open(
format=pyaudio.paInt16,
channels=channels,
rate=rate,
input=True,
# output=True,
frames_per_buffer=chunk
) stream.start_stream()
R = 20
t = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, chunk * 2)
xf = R*np.cos(t)
yf = R*np.sin(t)
# fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(14, 5))
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
lf, = ax.plot(xf, yf, np.zeros(chunk * 2), lw=2)
# ax.set_xlim(20, rate / 2)
# ax.set_ylim(20, rate / 2)
ax.set_zlim(-0.2, 1.2)
ax.set_axis_off()
plt.show(block=False) fwhm = 20 while stream.is_active():
data = stream.read(chunk)
data_int = struct.unpack(str(chunk * 2) + 'B', data)
z_detrend = detrend(data_int)
# z_smooth = savgol_filter(data_int, window_length=len(data_int) - 1, mode='valid')
# box = np.ones(fwhm) / fwhm
# z_smooth = np.convolve(z_detrend, box, mode='valid')
zf = np.abs(np.fft.fft(z_detrend))
z_vals = zf / (256 * chunk)
ind = np.where(z_vals > np.mean(z_vals))
z_vals[ind[0]] *= 4
lf.set_xdata(xf)
lf.set_ydata(yf)
lf.set_3d_properties(z_vals) try:
ax.figure.canvas.draw()
ax.figure.canvas.flush_events()
except TclError:
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
break
运行截图:
23:27:12 更新,为了更加突出重要的频率,我又加了一些代码,就是把振幅大于平均值的那些振幅加倍,主要代码如下:
y_vals = yf[:chunk] / (256 * chunk)
ind = np.where(y_vals > np.mean(y_vals))
y_vals[ind[0]] *= 4
lf.set_ydata(y_vals)
22:17:15 更新,因为 python 3.8 和 scipy 暂时不兼容,所以用不了scipy 对信号做平滑处理,不过网上找了一段代码,效率不错,这是链接,或者直接把下面代码加到合适的地方。
width = 20
box = np.ones(width) / width
y_smooth = np.convolve(data_int, box, mode='same')
yf = np.fft.fft(y_smooth)
...
21:58:43 更新,测试了一下对原始信号做平滑处理,发现效率十分低,完全没法看效果,不过目前用的是自己实现的高斯滤波算法。。。
以下为原文
这里的简单原理就是获取输入输出设备中的数据(注意驱动什么的没有问题,能用麦克风),然后 matplotlib 绘制出来,想要看到音乐的节奏振动就再 fft 一下。至于如何不断更新波形,matplotlib 有一个 animation 方法可以用(见下面第二种方法),但实际上我用了之后发现显示效果不如第一种(可能是姿势不对)。之前用 matlab 做的,也很不错。
第一种方法(波形显示更流畅,代码参考这个视频):
from _tkinter import TclError
import pyaudio
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import struct channels = 1
rate = 44100
chunk = 1024 * 2 p = pyaudio.PyAudio() stream = p.open(
format=pyaudio.paInt16,
channels=channels,
rate=rate,
input=True,
output=True,
frames_per_buffer=chunk
) stream.start_stream() xf = np.linspace(0, rate, chunk)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
lf, = ax.semilogx(xf, np.zeros(chunk), '-', lw=1)
ax.set_xlim(20, rate / 2)
ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
plt.show(block=False) while stream.is_active():
data = stream.read(chunk)
data_int = struct.unpack(str(chunk * 2) + 'B', data)
yf = np.fft.fft(data_int)
lf.set_ydata(np.abs(yf[:chunk]) / (128 * chunk)) try:
ax.figure.canvas.draw()
ax.figure.canvas.flush_events()
except TclError:
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
break
第二种方法:
import pyaudio
import numpy as np
# from scipy.fftpack import fft
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import struct
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation channels = 1
rate = 44100
chunk = 1024 * 2
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
stream = p.open(
format=pyaudio.paInt16,
channels=channels,
rate=rate,
input=True,
output=True,
) stream.start_stream()
x = np.arange(0, 2*chunk, 2)
xf = np.linspace(0, rate, chunk)
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2)
l, = ax1.plot(x, np.zeros(chunk), '-', lw=1)
lf, = ax2.semilogx(xf, np.zeros(chunk), '-', lw=1)
ax1.set_xlim(0, 2*chunk)
ax1.set_ylim(0, 255)
ax2.set_xlim(20, rate / 2)
ax2.set_ylim(0, 1)
plt.setp(ax1, xticks=[0, chunk, 2 * chunk], yticks=[0, 128, 255]) def gen():
while stream.is_active():
data = stream.read(chunk)
data_int = struct.unpack(str(chunk*2) + 'B', data)
data_np = np.array(data_int, dtype='b')[::2] + 128
yf = np.fft.fft(data_int)
yield data_np, yf def init():
lf.set_ydata(np.random.rand(chunk))
return lf, def update(data):
ax1.figure.canvas.draw()
ax2.figure.canvas.draw()
l.set_ydata(data[0])
lf.set_ydata(np.abs(data[1][:chunk]) / (128 * chunk))
return lf, animate = FuncAnimation(fig, update, gen, blit=True, interval=0, repeat=False, init_func=init)
plt.show()
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
python 音频可视化的更多相关文章
- Python数据可视化编程实战——导入数据
1.从csv文件导入数据 原理:with语句打开文件并绑定到对象f.不必担心在操作完资源后去关闭数据文件,with的上下文管理器会帮助处理.然后,csv.reader()方法返回reader对象,通过 ...
- Python数据可视化——使用Matplotlib创建散点图
Python数据可视化——使用Matplotlib创建散点图 2017-12-27 作者:淡水化合物 Matplotlib简述: Matplotlib是一个用于创建出高质量图表的桌面绘图包(主要是2D ...
- 【转】Python——plot可视化数据,作业8
Python——plot可视化数据,作业8(python programming) subject1k和subject1v的形状相同 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import sc ...
- Python数据可视化-seaborn库之countplot
在Python数据可视化中,seaborn较好的提供了图形的一些可视化功效. seaborn官方文档见链接:http://seaborn.pydata.org/api.html countplot是s ...
- Python数据可视化编程实战pdf
Python数据可视化编程实战(高清版)PDF 百度网盘 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1vAvKwCry4P4QeofW-RqZ_A 提取码:9pcd 复制这段内容后打开百度 ...
- [Python] Python 学习 - 可视化数据操作(一)
Python 学习 - 可视化数据操作(一) GitHub:https://github.com/liqingwen2015/my_data_view 目录 折线图 散点图 随机漫步 骰子点数概率 文 ...
- 【数据科学】Python数据可视化概述
注:很早之前就打算专门写一篇与Python数据可视化相关的博客,对一些基本概念和常用技巧做一个小结.今天终于有时间来完成这个计划了! 0. Python中常用的可视化工具 Python在数据科学中的地 ...
- Python数据可视化的四种简易方法
摘要: 本文讲述了热图.二维密度图.蜘蛛图.树形图这四种Python数据可视化方法. 数据可视化是任何数据科学或机器学习项目的一个重要组成部分.人们常常会从探索数据分析(EDA)开始,来深入了解数据, ...
- python --数据可视化(一)
python --数据可视化 一.python -- pyecharts库的使用 pyecharts--> 生成Echarts图标的类库 1.安装: pip install pyecharts ...
随机推荐
- Linux运维----03.制作trove-mysql5.7镜像
安装mysql yum install http://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql57-community-release-el7-9.noarch.rpm yum remove m ...
- Ajax0002: 省市县三级联动案例
- 探究Redis两种持久化方式下的数据恢复
对长期奋战在一线的后端开发人员来说,都知道redis有两种持久化方式RDB和AOF,虽说大家都知道这两种方式大概运作方式,但想必有实操的人不会太多. 这里是自己实操两种持久化方式的一点点记录. 先看以 ...
- fatal error LNK1169: one or more multiply defined symbols found
在 Project/Setting/Link/General中的 Project Options: 加入 /FORCE:MULTIPLE即可")可以解决报错问题,但是这些问题全部变成了war ...
- Spring boot mvn
https://www.cnblogs.com/xiebq/p/9181517.html https://www.cnblogs.com/sun-yang-/p/7700415.html https: ...
- 【14】Softmax回归
在下面的内容中,我们用C来表示需要分的类数. 最后一层的隐藏单元个数为4,为所分的类的数目,输出的值表示属于每个类的概率. Softmax函数的具体步骤如下图: 简单来说有三步: 计算z值(4×1矩阵 ...
- jquery赋值
$("#test1").text("Hello world!"); $("#test2").html("<b>Hell ...
- Hadoop学习之路(5)Mapreduce程序完成wordcount
程序使用的测试文本数据: Dear River Dear River Bear Spark Car Dear Car Bear Car Dear Car River Car Spark Spark D ...
- Qt Installer Framework翻译(8)
好了,到这里翻译就结束了.各位可以下载源码,结合examples示例,使用repogen和binarycreator好好实操一下,就能掌握基础用法了.祝各位使用顺利. 官方文档网址:https://d ...
- CSS:display:flex详解
水平居中很容易实现,但是一般垂直居中好像不是很好实现,一般我们都会用position.left等等进行定位:但是flex很好的解决了这个问题 Flex就是"弹性布局",现在应用很多 ...
