Java-JUC(八):使用wait,notify|notifyAll完成生产者消费者通信,虚假唤醒(Spurious Wakeups)问题出现场景,及问题解决方案。
模拟通过线程实现消费者和订阅者模式:
首先,定义一个店员:店员包含进货、卖货方法;其次,定义一个生产者,生产者负责给店员生产产品;再者,定义一个消费者,消费者负责从店员那里消费产品。
店员:
/**
* 店员
*/
class Clerk {
private int product = 0; /**
* 进货
*/
public synchronized void purchase() {
if (product >= 10) {
System.out.println("产品已满。。。");
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + ++product);
}
} /**
* 卖货
*/
public synchronized void sell() {
if (product <= 0) {
System.out.println("产品缺貨。。。");
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + --product);
}
}
}
生产者
/**
* 生产者 不断的生产产品给店员
* */
class Productor implements Runnable{
private Clerk clerk;
public Productor(Clerk clerk){
this.clerk=clerk;
} public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<20;i++){
clerk.purchase();
}
}
}
消费者
/**
* 消费者 不断的从店员那里消费产品
* */
class Consumer implements Runnable{
private Clerk clerk;
public Consumer(Clerk clerk){
this.clerk=clerk;
} public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<20;i++){
clerk.sell();
}
}
}
此时,运行程序,运行结果如下:
Productor-A:1
Productor-A:2
Productor-A:3
Productor-A:4
Productor-A:5
Productor-A:6
Productor-A:7
Productor-A:8
Productor-A:9
Productor-A:10
产品已满。。。
产品已满。。。
产品已满。。。
产品已满。。。
产品已满。。。
产品已满。。。
产品已满。。。
产品已满。。。
产品已满。。。
产品已满。。。
Consumer-A:9
Consumer-A:8
Consumer-A:7
Consumer-A:6
Consumer-A:5
Consumer-A:4
Consumer-A:3
Consumer-A:2
Consumer-A:1
Consumer-A:0
产品缺貨。。。
产品缺貨。。。
产品缺貨。。。
产品缺貨。。。
产品缺貨。。。
产品缺貨。。。
产品缺貨。。。
产品缺貨。。。
产品缺貨。。。
产品缺貨。。。
从运行打印结果可以发现这里存在两个问题:
1)一旦生产者发现店员产品已满时,仍然没有停止生产产品,在不断地生产生产产品;
2)一旦消费者发现店员产品缺货时,依然时不断地消费消费。
这里明显是有缺陷的,现实中应该是:一旦发现货物满时,就不在进货,而是开启卖货行为;当卖货行为发现无货时,开始进货行为。
针对生产者消费者改进:
消费者、生产者、客户端调用代码不变,只修改店员类:
/**
* 店员
*/
class Clerk {
private int product = 0; /**
* 进货
*/
public synchronized void purchase() {
if (product >= 10) {
System.out.println("产品已满。。。");
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + ++product);
this.notifyAll();
}
} /**
* 卖货
*/
public synchronized void sell() {
if (product <= 0) {
System.out.println("产品缺貨。。。");
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + --product);
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}
此时运行结果:
Productor-A:1
Consumer-A:0
产品缺貨。。。
Productor-A:1
Productor-A:2
Productor-A:3
Productor-A:4
Productor-A:5
Productor-A:6
Productor-A:7
Productor-A:8
Productor-A:9
Productor-A:10
产品已满。。。
Consumer-A:9
Consumer-A:8
Consumer-A:7
Consumer-A:6
Consumer-A:5
Consumer-A:4
Consumer-A:3
Consumer-A:2
Consumer-A:1
Consumer-A:0
产品缺貨。。。
Productor-A:1
Productor-A:2
Productor-A:3
Productor-A:4
Productor-A:5
Productor-A:6
Productor-A:7
Productor-A:8
Consumer-A:7
Consumer-A:6
Consumer-A:5
Consumer-A:4
Consumer-A:3
Consumer-A:2
Consumer-A:1
此时,从结果运行来说是按照我们希望的结果出现了。
改进后带来问题一:
修改店员类的最大进货数为1,把生产者一次生产20修改为2,消费者一次消费20也修改为2。
/**
* 生产者 不断的生产产品给店员
*/
class Productor implements Runnable {
private Clerk clerk; public Productor(Clerk clerk) {
this.clerk = clerk;
} public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
clerk.purchase();
}
}
} /**
* 消费者 不断的从店员那里消费产品
*/
class Consumer implements Runnable {
private Clerk clerk; public Consumer(Clerk clerk) {
this.clerk = clerk;
} public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
clerk.sell();
}
}
}
店员类:
/**
* 店员
*/
class Clerk {
private int product = 0; /**
* 进货
*/
public synchronized void purchase() {
if (product >= 1) {
System.out.println("产品已满。。。");
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + ++product);
this.notifyAll();
}
} /**
* 卖货
*/
public synchronized void sell() {
if (product <= 0) {
System.out.println("产品缺貨。。。");
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + --product);
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}
此时运行结果:
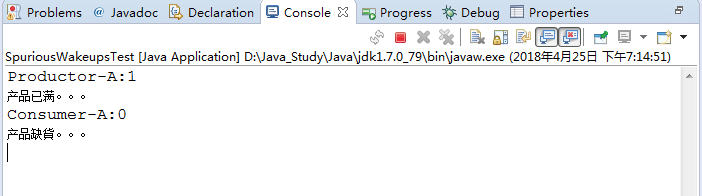
从运行结果上来看,程序是一个死锁现象。
为什么会发生死锁问题?
从运行结果上来看分析:
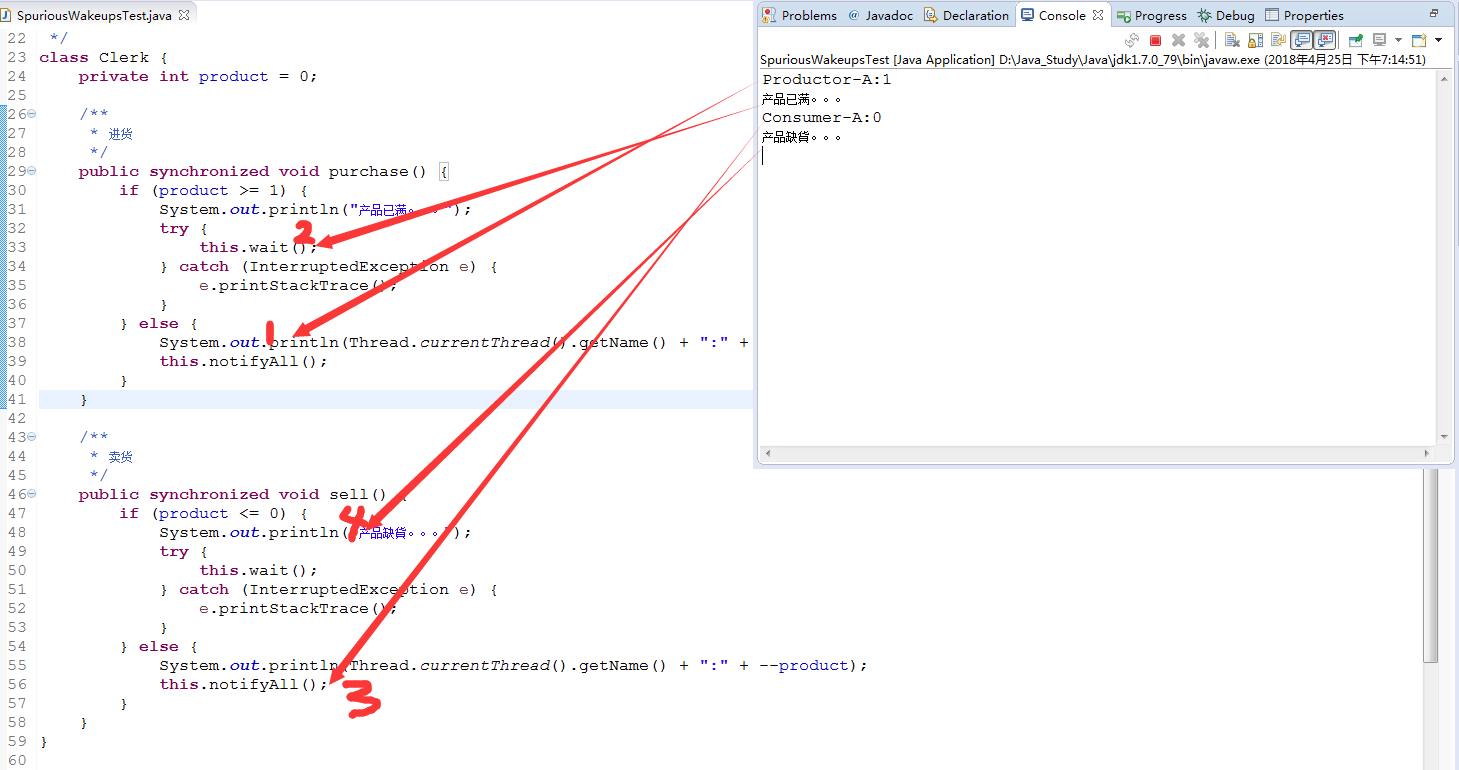
分析:
1)当purchase()运行“2”是处于this.wait()等待状态时,此时sell()开始运行;
2)sell()运行时,第一次走3当运行到this.notifyAll()时,开始运行4和purchase()等待向下执行(一旦向下执行purchase将不再被调用,原因生产者只有两次循环机会),而运行‘4’时打印‘产品缺货’,而且代码走入this.wait()处于一直等待状态。
因此会看到程序一直未结束状态,这个属于代码的一个BUG。
解决方法:
修改店员类:
/**
* 店员
*/
class Clerk {
private int product = 0; /**
* 进货
*/
public synchronized void purchase() {
if (product >= 1) {
System.out.println("产品已满。。。");
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + ++product);
this.notifyAll();
} /**
* 卖货
*/
public synchronized void sell() {
if (product <= 0) {
System.out.println("产品缺貨。。。");
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + --product);
this.notifyAll();
}
}
在运行发现程序正常结束,打印结果如下:
Productor-A:1
产品已满。。。
Consumer-A:0
产品缺貨。。。
Productor-A:1
Consumer-A:0
改进后带来问题二(虚假唤醒):
此时修改客户端调用代码:
public class SpuriousWakeupsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Clerk clerk = new Clerk();
Productor productor = new Productor(clerk);
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(clerk);
new Thread(productor, "Productor-A").start();
new Thread(consumer, "Consumer-A").start();
new Thread(productor, "Productor-B").start();
new Thread(consumer, "Consumer-B").start();
}
}
之前只有一个生产者和一个消费者,修改后让其拥有两个生产者和两个消费者,此时运行代码如下:
Consumer-A:-1
产品缺貨。。。
Productor-A:0
Productor-A:1
Consumer-A:0
Consumer-B:-1
产品缺貨。。。
Productor-B:0
Productor-B:1
Consumer-B:0
从代码分析逻辑来看,输出解雇貌似毫无逻辑,此现象就是一个虚假唤醒现象。
问题分析:
1)缺货时,两个consumer线程都进入wait状态;
2)当另外一个生产者生产了产品并调用了notifyall,此时两个consumer线程都被唤醒并跳过wait,进入消费代码
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + --product);
,因此导致一个输出产品数为0,另外一个产品数为-1。
解决办法:
基于while来反复判断进入正常操作的临界条件是否满足:
synchronized (obj) {
while (<condition does not hold>)
obj.wait();
... // Perform action appropriate to condition
}
此处理方案来此ava.lang.Object API的wati方法说明信息中。
店员修改:
/**
* 店员
*/
class Clerk {
private int product = 0; /**
* 进货
*/
public synchronized void purchase() {
while (product >= 1) {
System.out.println("产品已满。。。");
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + ++product);
this.notifyAll();
} /**
* 卖货
*/
public synchronized void sell() {
while (product <= 0) {
System.out.println("产品缺貨。。。");
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + --product);
this.notifyAll();
}
}
运行结果:
Productor-A:1
产品已满。。。
Consumer-B:0
产品缺貨。。。
Productor-B:1
产品已满。。。
Consumer-A:0
产品缺貨。。。
Productor-B:1
Consumer-B:0
Productor-A:1
Consumer-A:0
Java-JUC(八):使用wait,notify|notifyAll完成生产者消费者通信,虚假唤醒(Spurious Wakeups)问题出现场景,及问题解决方案。的更多相关文章
- java多线程 生产者消费者案例-虚假唤醒
package com.java.juc; public class TestProductAndConsumer { public static void main(String[] args) { ...
- java 多线程之wait(),notify,notifyAll(),yield()
wait(),notify(),notifyAll()不属于Thread类,而是属于Object基础类,也就是说每个对像都有wait(),notify(),notifyAll()的功能.因为都个对像都 ...
- Java多线程之wait(),notify(),notifyAll()
在多线程的情况下,因为同一进程的多个线程共享同一片存储空间,在带来方便的同一时候,也带来了訪问冲突这个严重的问题.Java语言提供了专门机制以解决这样的冲突,有效避免了同一个数据对象被多个线程同一时候 ...
- 如何在 Java 中正确使用 wait, notify 和 notifyAll – 以生产者消费者模型为例
wait, notify 和 notifyAll,这些在多线程中被经常用到的保留关键字,在实际开发的时候很多时候却并没有被大家重视.本文对这些关键字的使用进行了描述. 在 Java 中可以用 wait ...
- 转:【Java并发编程】之十:使用wait/notify/notifyAll实现线程间通信的几点重要说明
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/ns_code/article/details/17225469 在Java中,可以通过配合调用Object对象的wait()方法和no ...
- 【java线程系列】java线程系列之线程间的交互wait()/notify()/notifyAll()及生产者与消费者模型
关于线程,博主写过java线程详解基本上把java线程的基础知识都讲解到位了,但是那还远远不够,多线程的存在就是为了让多个线程去协作来完成某一具体任务,比如生产者与消费者模型,因此了解线程间的协作是非 ...
- 【Java并发编程】:使用wait/notify/notifyAll实现线程间通信
在java中,可以通过配合调用Object对象的wait()方法和notify()方法或notifyAll()方法来实现线程间的通信.在线程中调用wait()方法,将阻塞等待其他线程的通知(其他线程调 ...
- 【Java并发编程】之十:使用wait/notify/notifyAll实现线程间通信的几点重要说明
在Java中,可以通过配合调用Object对象的wait()方法和notify()方法或notifyAll()方法来实现线程间的通信.在线程中调用wait()方法,将阻塞等待其他线程的通知(其他线程调 ...
- java并发编程(十)使用wait/notify/notifyAll实现线程间通信
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/ns_code/article/details/17225469 wait()方法:public final void wait() thr ...
随机推荐
- SIMATIC PID温度控制
SIMATIC PID温度控制 // VAR_INPUT ------------------------------------------------------------------- #if ...
- MySQL是如何利用索引的
http://fordba.com/spend-10-min-to-understand-how-mysql-use-index.html
- Modbus读写模拟量寄存器具体解释
读可读写模拟量寄存器: 发送命令(主机向从机)格式: [设备地址] [命令号03] [起始寄存器地址高8位] [低8位] [读取的寄存器数高8位] [低8位] [CRC校验的低8位] [CRC校验的高 ...
- 在Brackets中使用Emmet
当在Brackets中安装上Emmet插件后,就可以使用Emmet的语法来加速前端编写. 有关html ● 子关系> div>ul>li ● 相邻+ div+p+bq ● 上一级^ ...
- shapefile与字符集编码设置
在 ArcGIS Desktop (ArcMap, ArcCatalog, and ArcToolbox) 中,有编码页转换功能(CODE PAGE CONVERSION),可以读写多种字符编码的 s ...
- JMeter学习(二十三)关联
话说LoadRunner有的一些功能,比如:参数化.检查点.集合点.关联,Jmeter也都有这些功能,只是功能可能稍弱一些,今天就关联来讲解一下. JMeter的关联方法有两种:后置处理器-正则表达式 ...
- WordPress主题开发:WP_Query常用参数
常用参数 用途 调用文章或页面 s 查询和某个关键词相关的所有的文章/页面信息 p 文章或页面id post__in 多篇id post__not_in 多篇id以外 post_type 查询的信息类 ...
- iOS 去掉UITableView风格为group时候的最顶部的空白距离
CGRect frame=CGRectMake(0, 0, 0, CGFLOAT_MIN); self.tableView.tableHeaderView=[[UIView alloc]initW ...
- Linux学习16-CentOS安装gitlab环境
前言 在学习Gitlab的环境搭建之前,首先需要了解Git,Gitlab,GitHub他们三者之间的关系 Git 它是一个源代码版本控制系统,可让您在本地跟踪更改并从远程资源推送或提取更改. GitH ...
- Unity3D——SendMessage方法的使用
SendMessage效率不高,因为每次调用的时候都会去遍历检测自身或者子节点上要调用的方法. 一.方法 GameObject自身的Script SendMessage("函数名" ...
