Summary: Lowest Common Ancestor in a Binary Tree & Shortest Path In a Binary Tree
转自:Pavel's Blog
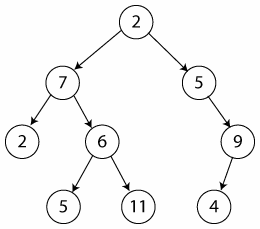 |
- public static Node lowestCommonAncestor(Node root, Node a, Node b) {
- if (root == null) {
- return null;
- }
- if (root.equals(a) || root.equals(b)) {
- // if at least one matched, no need to continue
- // this is the LCA for this root
- return root;
- }
- Node l = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, a, b);
- Node r = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, a, b);
- if (l != null && r != null) {
- return root; // nodes are each on a seaparate branch
- }
- // either one node is on one branch,
- // or none was found in any of the branches
- return l != null ? l : r;
- }
For the node used we will use the following class:
- public class Node {
- public int data;
- public Node right;
- public Node left;
- public Node(int data) {
- this.data = data;
- }
- }
这个问题再follow up一下,就是要找到shortest path in a binary tree between two nodes
- public class Solution {
- public static List<Node> shortestPath(Node root, Node a, Node b) {
- ArrayList<Node> path1 = new ArrayList<Node>();
- ArrayList<Node> path2 = new ArrayList<Node>();
- Node LCA = lowestCommonAncestor(root, a, b);
- helper(LCA.left, a, b, path1, new ArrayList<Node>());
- helper(LCA.right, a, b, path2, new ArrayList<Node>());
- Collections.reverse(path1);
- path1.add(LCA);
- path1.addAll(new ArrayList<Node>(path2));
- return path1;
- }
- public void helper(Node root, Node a, Node b, ArrayList<Node> outpath, ArrayList<Node> temp) {
- if (root == null) return;
- temp.add(root);
- if (root == a || root == b) {
- outpath = new ArrayList<Node>(temp);
- return;
- }
- helper(root.left, a, b, outpath, temp);
- helper(root.right, a, b, outpath, temp);
- temp.remove(temp.size()-1);
- }
- }
别人的Stack做法,未深究 他说First stack is not really needed, a simple list would do - I just like symmetry.
- public static <V> void shortestpath(
- Node<V> root, Node<V> a, Node<V> b,
- Stack<Node<V>> outputPath) {
- if (root == null) {
- return;
- }
- if (root.data.equals(a.data) || root.data.equals(b.data)) {
- outputPath.push(root);
- return;
- }
- shortestpath(root.left, a, b, outputPath);
- shortestpath(root.right, a, b, outputPath);
- outputPath.push(root);
- }
- public static List<Node> shortestPath(Node root, Node a, Node b) {
- Stack<Node> path1 = new Stack<>();
- Stack<Node> path2 = new Stack<>();
- Node lca = lowestCommonAncestor(root, a, b);
- // This is to handle the case where one of the nodes IS the LCA
- Node r = lca.equals(a) ? a : (lca.equals(b) ? b : lca);
- shortestpath(r.left, a, b, path1);
- shortestpath(r.right, a, b, path2);
- path1.push(r);
- // invert the second path
- while (!path2.isEmpty()) {
- path1.push(path2.pop());
- }
- return path1;
- }
Summary: Lowest Common Ancestor in a Binary Tree & Shortest Path In a Binary Tree的更多相关文章
- Range Minimum Query and Lowest Common Ancestor
作者:danielp 出处:http://community.topcoder.com/tc?module=Static&d1=tutorials&d2=lowestCommonAnc ...
- A1143. Lowest Common Ancestor
The lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two nodes U and V in a tree is the deepest node that has both U ...
- PAT A1143 Lowest Common Ancestor (30 分)——二叉搜索树,lca
The lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two nodes U and V in a tree is the deepest node that has both U ...
- 1143 Lowest Common Ancestor
The lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two nodes U and V in a tree is the deepest node that has both U ...
- PAT 甲级 1143 Lowest Common Ancestor
https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805343727501312 The lowest common ance ...
- PAT 1143 Lowest Common Ancestor[难][BST性质]
1143 Lowest Common Ancestor(30 分) The lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two nodes U and V in a tree is ...
- [PAT] 1143 Lowest Common Ancestor(30 分)
1143 Lowest Common Ancestor(30 分)The lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two nodes U and V in a tree is ...
- 1143. Lowest Common Ancestor (30)
The lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two nodes U and V in a tree is the deepest node that has both U ...
- PAT 1143 Lowest Common Ancestor
The lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two nodes U and V in a tree is the deepest node that has both U ...
随机推荐
- rman 中遇到 ORA-01861
RMAN> run{ 2> sql 'alter session set nls_date_format="yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss"'; 3> ...
- ELK系列六:Logstash的Filter模块
Date过滤 input { stdin{ codec => plain } } filter { date { match => ["message", " ...
- docker报错“net/http: TLS handshake timeout”的解决方法
为了永久性保留更改,您可以修改 /etc/docker/daemon.json 文件并添加上 registry-mirrors 键值. { "registry-mirrors": ...
- [压缩]C#下使用SevenZipSharp压缩解压文本
using SevenZip; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.IO; using System.Linq; ...
- CodeForce 832A Sasha and Sticks
A. Sasha and Sticks time limit per test2 seconds memory limit per test256 megabytes inputstandard in ...
- opencv之Mat数据类型
data:Mat对象中的一个指针,指向内存中存放矩阵数据的一块内存 (uchar* data) dims:Mat所代表的矩阵的维度,如 3 * 4 的矩阵为 2 维, 3 * 4 * 5 的为3维 c ...
- NLP常用语料集合
常用语料资源 下面提供一些网上能下载到的中文的好语料,供研究人员学习使用.(1).中科院自动化所的中英文新闻语料库 http://www.datatang.com/data/13484中文新闻分类语料 ...
- MySQL ·InnoDB 文件系统之文件物理结构
从上层的角度来看,InnoDB层的文件,除了redo日志外,基本上具有相当统一的结构,都是固定block大小,普遍使用的btree结构来管理数据.只是针对不同的block的应用场景会分配不同的页类型. ...
- 停机问题(英语:halting problem)是逻辑数学中可计算性理论的一个问题。通俗地说,停机问题就是判断任意一个程序是否能在有限的时间之内结束运行的问题。该问题等价于如下的判定问题:是否存在一个程序P,对于任意输入的程序w,能够判断w会在有限时间内结束或者死循环。
htps://baike.baidu.com/item/停机问题/4131067?fr=aladdin 理发师悖论:村子里有个理发师,这个理发师有条原则是,对于村里所有人,当且仅当这个人不自己理发,理 ...
- 前端开发组件化设计vue,react,angular原则漫谈
前端开发组件化设计vue,react,angular原则漫谈 https://www.toutiao.com/a6346443500179505410/?tt_from=weixin&utm_ ...
