深入理解MYSQL的MDL元数据锁
前言
好久没更新,主要是因为Inside君最近沉迷于一部动画片——《新葫芦娃兄弟》。终于抽得闲,完成了本篇关于MySQL MDL锁的深入分析与介绍。虽然之前有很多小伙伴分析过,但总感觉少了点什么,故花了点时间翻看了下源码。Inside君或许不是最牛掰的内核开发人员,但自认为应该是业界最会讲故事的码农,希望本篇能做到通俗易懂,因为MDL锁其实并不好理解。如果同学们还有问题,也可以直接看源码文件mdl.cc。
MDL锁与实现
MySQL5.5版本引入了MDL锁(metadata lock),用于解决或者保证DDL操作与DML操作之间的一致性。例如下面的这种情形:
| 会话1 | 会话2 |
| BEGIN; | |
| SELECT * FROM XXX | |
| DROP TABLE XXX | |
| SELECT * FROM XXX |
若没有MDL锁的保护,则事务2可以直接执行DDL操作,并且导致事务1出错,5.1版本即是如此。5.5版本加入MDL锁就在于保护这种情况的发生,由于事务1开启了查询,那么获得了MDL锁,锁的模式为SHARED_READ,事务2要执行DDL,则需获得EXCLUSIVE锁,两者互斥,所以事务2需要等待。
InnoDB层已经有了IS、IX这样的意向锁,有同学觉得可以用来实现上述例子的并发控制。但由于MySQL是Server-Engine架构,所以MDL锁是在Server中实现。另外,MDL锁还能实现其他粒度级别的锁,比如全局锁、库级别的锁、表空间级别的锁,这是InnoDB存储引擎层不能直接实现的锁。
但与InnoDB锁的实现一样,MDL锁也是类似对一颗树的各个对象从上至下进行加锁(对树进行加锁具体见:《MySQL技术内幕:InnoDB存储引擎》)。但是MDL锁对象的层次更多,简单来看有如下的层次:
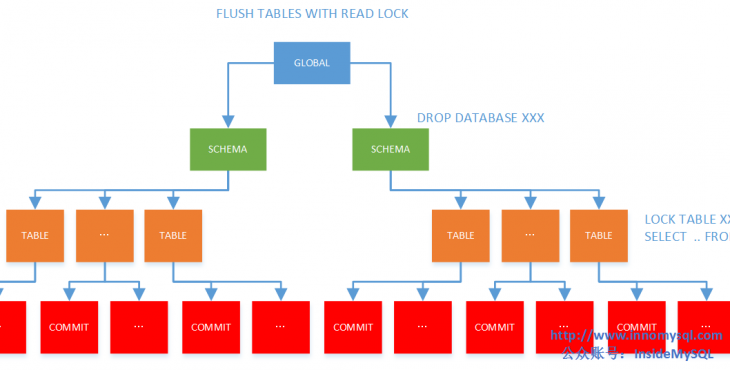
上图中显示了最常见的4种MDL锁的对象,并且注明了常见的SQL语句会触发的锁。与InnoDB层类似的是,某些类型的MDL锁会从上往下一层层进行加锁。比如LOCK TABLE … WRITE这样的SQL语句,其首先会对GLOBAL级别加INTENTION_EXCLUSIVE锁,再对SCHEMA级别加INTENTION_EXCLUSIVE锁,最后对TABLE级别加SHARED_NO_READ_WRITE锁。
这里最令人意外的是还有COMMIT对象层次的锁,其实这主要用于XA事务中。比如分布式事务已经PREPARE成功,但是在XA COMMIT之前有其他会话执行了FLUSH TABLES WITH READ LOCK这样的操作,那么分布式事务的提交就需要等待。
除了上图标注的对象,其实还有TABLESPACE、FUNCTION、PROCEDURE、EVENT等其他对象类型,其实都是为了进行并发控制。只是这些在MySQL数据库中都不常用,故不再赘述(当然也是为了偷懒)。
GLOBAL=0,TABLESPACE,SCHEMA,TABLE,FUNCTION,PROCEDURE,TRIGGER,EVENT,COMMIT,USER_LEVEL_LOCK,LOCKING_SERVICE,NAMESPACE_END
目前MDL有如下锁模式,锁之间的兼容性可见源码mdl.cc:
| 锁模式 | 对应SQL |
| MDL_INTENTION_EXCLUSIVE | GLOBAL对象、SCHEMA对象操作会加此锁 |
| MDL_SHARED | FLUSH TABLES with READ LOCK |
| MDL_SHARED_HIGH_PRIO | 仅对MyISAM存储引擎有效 |
| MDL_SHARED_READ | SELECT查询 |
| MDL_SHARED_WRITE | DML语句 |
| MDL_SHARED_WRITE_LOW_PRIO | 仅对MyISAM存储引擎有效 |
| MDL_SHARED_UPGRADABLE | ALTER TABLE |
| MDL_SHARED_READ_ONLY | LOCK xxx READ |
| MDL_SHARED_NO_WRITE | FLUSH TABLES xxx,yyy,zzz READ |
| MDL_SHARED_NO_READ_WRITE | FLUSH TABLE xxx WRITE |
| MDL_EXCLUSIVE | ALTER TABLE xxx PARTITION BY … |
MDL锁的性能与并发改进
讲到这同学们会发现MDL锁的开销并不比InnoDB层的行锁要小,而且这可能是一个更为密集的并发瓶颈。MySQL 5.6和5.5版本通常通过调整如下两个参数来进行并发调优:
- metadata_locks_cache_size: MDL锁的缓存大小
- metadata_locks_hash_instances:通过分片来提高并发度,与InnoDB AHI类似
MySQL 5.7 MDL锁的最大改进之处在于将MDL锁的机制通过lock free算法来实现,从而提高了在多核并发下数据库的整体性能提升。
MDL锁的诊断
MySQL 5.7版本之前并没有提供一个方便的途径来查看MDL锁,github上有一名为mysql-plugin-mdl-info的项目,通过插件的方式来查看,非常有想法的实现,大赞。好在官方也意识到了这个问题,于是在MySQL 5.7中的performance_schea库下新增了一张表metadata_locks,用其来查看MDL锁那是相当的方便:
不过默认PS并没有打开此功能,需要手工将wait/lock/metadata/sql/mdl监控给打开:
SELECT * FROM performance_schema.setup_instruments;
UPDATE performance_schema.setup_consumers SET ENABLED = 'YES' WHERE NAME ='global_instrumentation';
UPDATE performance_schema.setup_instruments SET ENABLED = 'YES' WHERE NAME ='wait/lock/metadata/sql/mdl';
select * from performance_schema.metadata_locks\G
会话1
mysql> lock table xx read;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.21 sec)
会话2:
SELECT * FROM performance_schema.metadata_locks;
mysql> SELECT * FROM performance_schema.metadata_locks\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
OBJECT_TYPE: TABLE
OBJECT_SCHEMA: performance_schema
OBJECT_NAME: metadata_locks
OBJECT_INSTANCE_BEGIN: 240554768
LOCK_TYPE: SHARED_READ
LOCK_DURATION: TRANSACTION
LOCK_STATUS: GRANTED
SOURCE: sql_parse.cc:5927
OWNER_THREAD_ID: 38
OWNER_EVENT_ID: 10
1 row in set (0.00 sec) ERROR:
No query specified
enum enum_mdl_type {
/*
An intention exclusive metadata lock. Used only for scoped locks.
Owner of this type of lock can acquire upgradable exclusive locks on
individual objects.
Compatible with other IX locks, but is incompatible with scoped S and
X locks.
*/
MDL_INTENTION_EXCLUSIVE= 0,
/*
A shared metadata lock.
To be used in cases when we are interested in object metadata only
and there is no intention to access object data (e.g. for stored
routines or during preparing prepared statements).
We also mis-use this type of lock for open HANDLERs, since lock
acquired by this statement has to be compatible with lock acquired
by LOCK TABLES ... WRITE statement, i.e. SNRW (We can't get by by
acquiring S lock at HANDLER ... OPEN time and upgrading it to SR
lock for HANDLER ... READ as it doesn't solve problem with need
to abort DML statements which wait on table level lock while having
open HANDLER in the same connection).
To avoid deadlock which may occur when SNRW lock is being upgraded to
X lock for table on which there is an active S lock which is owned by
thread which waits in its turn for table-level lock owned by thread
performing upgrade we have to use thr_abort_locks_for_thread()
facility in such situation.
This problem does not arise for locks on stored routines as we don't
use SNRW locks for them. It also does not arise when S locks are used
during PREPARE calls as table-level locks are not acquired in this
case.
*/
MDL_SHARED,
/*
A high priority shared metadata lock.
Used for cases when there is no intention to access object data (i.e.
data in the table).
"High priority" means that, unlike other shared locks, it is granted
ignoring pending requests for exclusive locks. Intended for use in
cases when we only need to access metadata and not data, e.g. when
filling an INFORMATION_SCHEMA table.
Since SH lock is compatible with SNRW lock, the connection that
holds SH lock lock should not try to acquire any kind of table-level
or row-level lock, as this can lead to a deadlock. Moreover, after
acquiring SH lock, the connection should not wait for any other
resource, as it might cause starvation for X locks and a potential
deadlock during upgrade of SNW or SNRW to X lock (e.g. if the
upgrading connection holds the resource that is being waited for).
*/
MDL_SHARED_HIGH_PRIO,
/*
A shared metadata lock for cases when there is an intention to read data
from table.
A connection holding this kind of lock can read table metadata and read
table data (after acquiring appropriate table and row-level locks).
This means that one can only acquire TL_READ, TL_READ_NO_INSERT, and
similar table-level locks on table if one holds SR MDL lock on it.
To be used for tables in SELECTs, subqueries, and LOCK TABLE ... READ
statements.
*/
MDL_SHARED_READ,
/*
A shared metadata lock for cases when there is an intention to modify
(and not just read) data in the table.
A connection holding SW lock can read table metadata and modify or read
table data (after acquiring appropriate table and row-level locks).
To be used for tables to be modified by INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
statements, but not LOCK TABLE ... WRITE or DDL). Also taken by
SELECT ... FOR UPDATE.
*/
MDL_SHARED_WRITE,
/*
A version of MDL_SHARED_WRITE lock which has lower priority than
MDL_SHARED_READ_ONLY locks. Used by DML statements modifying
tables and using the LOW_PRIORITY clause.
*/
MDL_SHARED_WRITE_LOW_PRIO,
/*
An upgradable shared metadata lock which allows concurrent updates and
reads of table data.
A connection holding this kind of lock can read table metadata and read
table data. It should not modify data as this lock is compatible with
SRO locks.
Can be upgraded to SNW, SNRW and X locks. Once SU lock is upgraded to X
or SNRW lock data modification can happen freely.
To be used for the first phase of ALTER TABLE.
*/
MDL_SHARED_UPGRADABLE,
/*
A shared metadata lock for cases when we need to read data from table
and block all concurrent modifications to it (for both data and metadata).
Used by LOCK TABLES READ statement.
*/
MDL_SHARED_READ_ONLY,
/*
An upgradable shared metadata lock which blocks all attempts to update
table data, allowing reads.
A connection holding this kind of lock can read table metadata and read
table data.
Can be upgraded to X metadata lock.
Note, that since this type of lock is not compatible with SNRW or SW
lock types, acquiring appropriate engine-level locks for reading
(TL_READ* for MyISAM, shared row locks in InnoDB) should be
contention-free.
To be used for the first phase of ALTER TABLE, when copying data between
tables, to allow concurrent SELECTs from the table, but not UPDATEs.
*/
MDL_SHARED_NO_WRITE,
/*
An upgradable shared metadata lock which allows other connections
to access table metadata, but not data.
It blocks all attempts to read or update table data, while allowing
INFORMATION_SCHEMA and SHOW queries.
A connection holding this kind of lock can read table metadata modify and
read table data.
Can be upgraded to X metadata lock.
To be used for LOCK TABLES WRITE statement.
Not compatible with any other lock type except S and SH.
*/
MDL_SHARED_NO_READ_WRITE,
/*
An exclusive metadata lock.
A connection holding this lock can modify both table's metadata and data.
No other type of metadata lock can be granted while this lock is held.
To be used for CREATE/DROP/RENAME TABLE statements and for execution of
certain phases of other DDL statements.
*/
MDL_EXCLUSIVE,
/* This should be the last !!! */
MDL_TYPE_END};
/** Duration of metadata lock. */
enum enum_mdl_duration {
/**
Locks with statement duration are automatically released at the end
of statement or transaction.
*/
MDL_STATEMENT= 0,
/**
Locks with transaction duration are automatically released at the end
of transaction.
*/
MDL_TRANSACTION,
/**
Locks with explicit duration survive the end of statement and transaction.
They have to be released explicitly by calling MDL_context::release_lock().
*/
MDL_EXPLICIT,
/* This should be the last ! */
MDL_DURATION_END };
/** Maximal length of key for metadata locking subsystem. */
#define MAX_MDLKEY_LENGTH (1 + NAME_LEN + 1 + NAME_LEN + 1)
/**
Metadata lock object key.
A lock is requested or granted based on a fully qualified name and type.
E.g. They key for a table consists of <0 (=table)> + <database> + <table name>.
Elsewhere in the comments this triple will be referred to simply as "key"
or "name".
*/
struct MDL_key
{
public:
#ifdef HAVE_PSI_INTERFACE
static void init_psi_keys();
#endif
/**
Object namespaces.
Sic: when adding a new member to this enum make sure to
update m_namespace_to_wait_state_name array in mdl.cc!
Different types of objects exist in different namespaces
- GLOBAL is used for the global read lock.
- TABLESPACE is for tablespaces.
- SCHEMA is for schemas (aka databases).
- TABLE is for tables and views.
- FUNCTION is for stored functions.
- PROCEDURE is for stored procedures.
- TRIGGER is for triggers.
- EVENT is for event scheduler events.
- COMMIT is for enabling the global read lock to block commits.
- USER_LEVEL_LOCK is for user-level locks.
- LOCKING_SERVICE is for the name plugin RW-lock service
Note that although there isn't metadata locking on triggers,
it's necessary to have a separate namespace for them since
MDL_key is also used outside of the MDL subsystem.
Also note that requests waiting for user-level locks get special
treatment - waiting is aborted if connection to client is lost.
*/
enum enum_mdl_namespace { GLOBAL=0,
TABLESPACE,
SCHEMA,
TABLE,
FUNCTION,
PROCEDURE,
TRIGGER,
EVENT,
COMMIT,
USER_LEVEL_LOCK,
LOCKING_SERVICE,
/* This should be the last ! */
NAMESPACE_END
};
。。。
if (!MY_TEST(table_options & TL_OPTION_ALIAS))
{
MDL_REQUEST_INIT(& ptr->mdl_request,
MDL_key::TABLE, ptr->db, ptr->table_name, mdl_type,
MDL_TRANSACTION);
TABLE_LIST *ptr;
MySQL 5.7对于MDL的最后一个改进在mysqldump,有同学能知道是在哪嘛?第一个答对的同学可获Inside君签名的《MySQL内核:InnoDB存储引擎 卷1》书籍一本。
深入理解MYSQL的MDL元数据锁的更多相关文章
- 深入理解MDL元数据锁
前言: 当你在MySQL中执行一条SQL时,语句并没有在你预期的时间内执行完成,这时候我们通常会登陆到MySQL数据库上查看是不是出了什么问题,通常会使用的一个命令就是 show processli ...
- (转载)深入理解MDL元数据锁
作者:MySQL技术本文为作者原创,转载请注明出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/kunjian/p/11993708.html 前言: 当你在MySQL中执行一条SQL时,语句并没 ...
- 深入理解MySQL的并发控制、锁和事务【转】
本文主要是针对MySQL/InnoDB的并发控制和加锁技术做一个比较深入的剖析,并且对其中涉及到的重要的概念,如多版本并发控制(MVCC),脏读(dirty read),幻读(phantom read ...
- 一步步搞懂MySQL元数据锁(MDL)
某日,路上收到用户咨询,为了清除空间,想删除某200多G大表数据,且已经确认此表不再有业务访问,于是执行了一条命令'delete from bigtable',但好长时间也没删完,经过咨询后,获知dr ...
- Mysql加锁过程详解(7)-初步理解MySQL的gap锁
Mysql加锁过程详解(1)-基本知识 Mysql加锁过程详解(2)-关于mysql 幻读理解 Mysql加锁过程详解(3)-关于mysql 幻读理解 Mysql加锁过程详解(4)-select fo ...
- 深入理解 MySQL ——锁、事务与并发控制
本文首发于vivo互联网技术微信公众号 mp.weixin.qq.com/s/JFSDqI5ya… 作者:张硕 本文对 MySQL 数据库中有关锁.事务及并发控制的知识及其原理做了系统化的介绍和总结, ...
- [转帖]2019-03-26 发布 深入理解 MySQL ——锁、事务与并发控制
深入理解 MySQL ——锁.事务与并发控制 https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000018658828 太长了 没看完.. 数据库 并发 mysql 639 次阅读 ...
- [转帖]深入理解 MySQL—锁、事务与并发控制
深入理解 MySQL—锁.事务与并发控制 http://www.itpub.net/2019/04/28/1723/ 跟oracle也类似 其实所有的数据库都有相同的机制.. 学习了机制才能够更好的工 ...
- 深入理解MySQL系列之锁
按锁思想分类 悲观锁 优点:适合在写多读少的并发环境中使用,虽然无法维持非常高的性能,但是在乐观锁无法提更好的性能前提下,可以做到数据的安全性 缺点:加锁会增加系统开销,虽然能保证数据的安全,但数据处 ...
随机推荐
- SpringMVC + Spring + MyBatis 学习笔记:在类和方法上都使用RequestMapping如何访问
系统:WIN8.1 数据库:Oracle 11GR2 开发工具:MyEclipse 8.6 框架:Spring3.2.9.SpringMVC3.2.9.MyBatis3.2.8 先看代码: @Requ ...
- Fedora20 和ubuntu 14.04 chrome标签中文乱码
作为两个流行的桌面发行版本,Fedora和ubuntu最新版本都存在chrome标签中文乱码问题. 下面是解决办法,都来自百度贴吧. 1.ubuntu 系列: 解决办法就是: 编辑/etc/fonts ...
- STL源码剖析读书笔记--第6章&第7章--算法与仿函数
老实说,这两章内容还蛮多的,但是其实在应用中一点点了解比较好.所以我决定这两张在以后使用过程中零零散散地总结,这个时候就说些基本概念好了.实际上,这两个STL组件都及其重要,我不详述一方面是自己偷懒, ...
- 【开源项目之路】jquery的build问题
在刚开始clone了jquery到本地build的时候,就遇到了问题. “ENORESTARGET No tag found that was able to satisfy ...” 提示为bowe ...
- 通过ajax提交form表单
$.ajax({ url : 'deliveryWarrant/update.do', data : $('#myform').serialize(), type : "POST" ...
- SQL Server文本和图像函数
文本和图像函数 1.查找特定字符串PATINDEX 语法与字符串的patindex一样. 2.获取文本指针TEXTPTR SQLServer在存储文本类型(ntext.text)和图像数据类型(ima ...
- 【转】log4j详解及简易搭建
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/mailingfeng/archive/2011/07/28/2119937.html log4j是一个非常强大的log记录软件. 首先当然是得 ...
- esb异常20160322_1948
异常1. Failed to find entry point for component, the following resolvers tried but failed: [ 2016-03-2 ...
- [iOS微博项目 - 3.4] - 获取用户信息
github: https://github.com/hellovoidworld/HVWWeibo A.获取用户信息 1.需求 获取用户信息并储存 把用户昵称显示在“首页”界面导航栏的标题上 ...
- POJ3345
http://poj.org/problem?id=3345 大意: 大意是说现在有n个城市来给你投票,你需要至少拿到m个城市的赞成票.想要获得第i个城市的赞成需要花费w[i],有个条件就是某些城市是 ...
