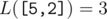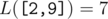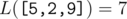Codeforces Round #333 DIV2
D:
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
A function 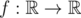 is called Lipschitz continuous if there is a real constant K such that the inequality |f(x) - f(y)| ≤ K·|x - y| holds for all
is called Lipschitz continuous if there is a real constant K such that the inequality |f(x) - f(y)| ≤ K·|x - y| holds for all 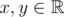 . We'll deal with a more... discrete version of this term.
. We'll deal with a more... discrete version of this term.
For an array 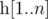 , we define it's Lipschitz constant
, we define it's Lipschitz constant 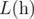 as follows:
as follows:
- if n < 2,
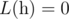
- if n ≥ 2,
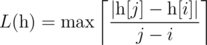 over all 1 ≤ i < j ≤ n
over all 1 ≤ i < j ≤ n
In other words, 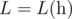 is the smallest non-negative integer such that |h[i] - h[j]| ≤ L·|i - j| holds for all 1 ≤ i, j ≤ n.
is the smallest non-negative integer such that |h[i] - h[j]| ≤ L·|i - j| holds for all 1 ≤ i, j ≤ n.
You are given an array  of size n and q queries of the form [l, r]. For each query, consider the subarray
of size n and q queries of the form [l, r]. For each query, consider the subarray 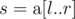 ; determine the sum of Lipschitz constants of all subarrays of
; determine the sum of Lipschitz constants of all subarrays of  .
.
The first line of the input contains two space-separated integers n and q (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000 and 1 ≤ q ≤ 100) — the number of elements in array  and the number of queries respectively.
and the number of queries respectively.
The second line contains n space-separated integers 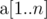 (
(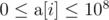 ).
).
The following q lines describe queries. The i-th of those lines contains two space-separated integers li and ri (1 ≤ li < ri ≤ n).
Print the answers to all queries in the order in which they are given in the input. For the i-th query, print one line containing a single integer — the sum of Lipschitz constants of all subarrays of 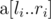 .
.
10 4
1 5 2 9 1 3 4 2 1 7
2 4
3 8
7 10
1 9
17
82
23
210
7 6
5 7 7 4 6 6 2
1 2
2 3
2 6
1 7
4 7
3 5
2
0
22
59
16
8
In the first query of the first sample, the Lipschitz constants of subarrays of  with length at least 2 are:
with length at least 2 are:
The answer to the query is their sum.
思路是;虽然题目说了很多定义,但是基本都是把人弄晕的。
一定是相邻的两个点的最值 ,可以对应在二维坐标上YY 一下。
然后由数组a[I]->得到B[I];
之后就变成统计问题了;
给一个数组B;
比如:3,2,5,7,8,4,9
求 所有子数组最大值得和;
你可以对一个I 求出I 左边范围 比如L,A[L].,A[L+1]...A[I]<A[I];(注意是小于)
右边 I R,A[I+1],A[I+2]..A[R]<=A[I](注意大于等于)
符号要注意 如果都是大于等于就会重复算(我这里错了几百遍
写得很丑
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
typedef long long ll; #define N 123456 int a[N],L[N],R[N];
int b[N],n; int dp[N][]; void init()
{
int k=log(n)/log(2.0);
for (int i=;i<=n;i++)
dp[i][]=b[i]; for (int j=;j<=k;j++)
for (int i=;i+(<<(j-))-<=n;i++)
dp[i][j]=max(dp[i][j-],dp[i+(<<(j-))][j-]);
} int rmq(int l,int r)
{
int k=log(r-l+)/log(2.0);
return max(dp[l][k],dp[r-(<<k)+][k]);
} int main()
{
int q;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&q);
for (int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]); n--;
for (int i=;i<=n;i++)
b[i]=abs(a[i+]-a[i]);
init(); for (int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
int l=,r=i;
L[i]=i;
for (int _=;_<;_++)
{
int mid=(l+r)/;
if (rmq(mid,i-)<b[i])
L[i]=mid,r=mid;
else l=mid+;
} l=i,r=n;
for (int _=;_<;_++)
{
int mid=(l+r)/;
if (rmq(i,mid)<=b[i])
R[i]=mid,l=mid+;
else r=mid;
}
} // for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
// cout<<L[i]<<" "<<R[i]<<endl; while (q--)
{
int l,r;
scanf("%d%d",&l,&r); ll ans=;
r--;
for (int i=l;i<=r;i++)
// ll tmp=(ll) (i-max(l,L[i])+1)*(min(r,R[i])-i+1);
// cout<<tmp<<endl;
ans+=(ll)(i-max(l,L[i])+)*(min(r,R[i])-i+)*b[i]; cout<<ans<<endl;
// printf("%I64d\n",ans);
} return ;
}
C:
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
In Absurdistan, there are n towns (numbered 1 through n) and m bidirectional railways. There is also an absurdly simple road network — for each pair of different towns x and y, there is a bidirectional road between towns x and y if and only if there is no railway between them. Travelling to a different town using one railway or one road always takes exactly one hour.
A train and a bus leave town 1 at the same time. They both have the same destination, town n, and don't make any stops on the way (but they can wait in town n). The train can move only along railways and the bus can move only along roads.
You've been asked to plan out routes for the vehicles; each route can use any road/railway multiple times. One of the most important aspects to consider is safety — in order to avoid accidents at railway crossings, the train and the bus must not arrive at the same town (except town n) simultaneously.
Under these constraints, what is the minimum number of hours needed for both vehicles to reach town n (the maximum of arrival times of the bus and the train)? Note, that bus and train are not required to arrive to the town n at the same moment of time, but are allowed to do so.
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n ≤ 400, 0 ≤ m ≤ n(n - 1) / 2) — the number of towns and the number of railways respectively.
Each of the next m lines contains two integers u and v, denoting a railway between towns u and v (1 ≤ u, v ≤ n, u ≠ v).
You may assume that there is at most one railway connecting any two towns.
Output one integer — the smallest possible time of the later vehicle's arrival in town n. If it's impossible for at least one of the vehicles to reach town n, output - 1.
4 2
1 3
3 4
2
4 6
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 3
2 4
3 4
-1
5 5
4 2
3 5
4 5
5 1
1 2
3
In the first sample, the train can take the route 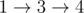 and the bus can take the route
and the bus can take the route  . Note that they can arrive at town 4 at the same time.
. Note that they can arrive at town 4 at the same time.
In the second sample, Absurdistan is ruled by railwaymen. There are no roads, so there's no way for the bus to reach town 4.
太无语了。
没想到,写了一个暴力的BFS 结果TLE了
真心不会读题。。
因为BUS或者 train总有一个 直接连接1-N,所以只要算另一个的最短路就好了O(n^2);
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std; const int inf=<<; bool sb;
queue<int >q;
int dis[];
int mp[][];
int n,m;
int dfs()
{
for(int i=; i<n+; i++)
dis[i]=inf;
q.push();
dis[]=;
while(!q.empty())
{
int u=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int v=; v<=n; v++)
{
if(sb&&!mp[u][v])
{
if(dis[v]==inf)
{
dis[v]=dis[u]+;
q.push(v);
}
}
else if(!sb&&mp[u][v])
{
if(dis[v]==inf)
{
dis[v]=dis[u]+;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
}
return dis[n];
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF)
{
int x,y;
for(int i=; i<m; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
mp[x][y]=;
mp[y][x]=;
if((x==n&&y==)||(x==&&y==n))
sb=true; }
int t=dfs();
t=max(t,);
if(t==inf)
printf("-1\n");
else printf("%d\n",t); }
}
B:
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
When Xellos was doing a practice course in university, he once had to measure the intensity of an effect that slowly approached equilibrium. A good way to determine the equilibrium intensity would be choosing a sufficiently large number of consecutive data points that seems as constant as possible and taking their average. Of course, with the usual sizes of data, it's nothing challenging — but why not make a similar programming contest problem while we're at it?
You're given a sequence of n data points a1, ..., an. There aren't any big jumps between consecutive data points — for each 1 ≤ i < n, it's guaranteed that |ai + 1 - ai| ≤ 1.
A range [l, r] of data points is said to be almost constant if the difference between the largest and the smallest value in that range is at most 1. Formally, let M be the maximum and m the minimum value of ai for l ≤ i ≤ r; the range [l, r] is almost constant if M - m ≤ 1.
Find the length of the longest almost constant range.
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the number of data points.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 100 000).
Print a single number — the maximum length of an almost constant range of the given sequence.
5
1 2 3 3 2
4
11
5 4 5 5 6 7 8 8 8 7 6
5
In the first sample, the longest almost constant range is [2, 5]; its length (the number of data points in it) is 4.
In the second sample, there are three almost constant ranges of length 4: [1, 4], [6, 9] and [7, 10]; the only almost constant range of the maximum length 5 is [6, 10].
好像想复杂了
我是对于:for (int i=1;i<==n;i++)
{
二分Mid 值求出(i,mid)最大值-最小值的大小
}
好吧的确想多了、、、
或者随便set搞搞应该可以
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
#define N 500100 int maxl[N][], minl[N][];
int n, m, a[N]; int min(int a, int b)
{
if (a>b) return b; return a;
} int max(int a, int b)
{
if (a>b) return a; return b;
} void S_table()
{
int l = int(log((double)n)/log(2.0));
for (int j=;j<=l;j++)
{
for (int i=; i + ( << (j-) ) - <=n;++i)
{
maxl[i][j] = max(maxl[i][j-], maxl[i + ( << (j-) )][j-]);
minl[i][j] = min(minl[i][j-], minl[i + ( << (j-) )][j-]);
}
}
} int rmq(int l, int r)
{
int k = int(log((double)(r-l+))/log(2.0));
int a1 = max(maxl[l][k], maxl[r - (<<k) + ][k]);
int a2 = min(minl[l][k], minl[r - (<<k) + ][k]);
return a1-a2;
//printf("Max: %d Min: %d\n", a1, a2);
} int main()
{ cin>>n;
for (int i=;i<=n;++i)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
maxl[i][] = minl[i][] = a[i];
}
S_table(); int ans=;
for (int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
int l=i,r=n;
for (int _=;_<;_++)
{
int mid=(l+r)/;
if (rmq(i,mid)<=) l=mid+,ans=max(ans,mid-i+);
else r=mid;
}
//cout<<ans<<endl;
} cout<<ans<<endl;
return ;
}
A:题水
Codeforces Round #333 DIV2的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #539 div2
Codeforces Round #539 div2 abstract I 离散化三连 sort(pos.begin(), pos.end()); pos.erase(unique(pos.begin ...
- 【前行】◇第3站◇ Codeforces Round #512 Div2
[第3站]Codeforces Round #512 Div2 第三题莫名卡半天……一堆细节没处理,改一个发现还有一个……然后就炸了,罚了一啪啦时间 Rating又掉了……但是没什么,比上一次好多了: ...
- Codeforces Round#320 Div2 解题报告
Codeforces Round#320 Div2 先做个标题党,骗骗访问量,结束后再来写咯. codeforces 579A Raising Bacteria codeforces 579B Fin ...
- Codeforces Round #564(div2)
Codeforces Round #564(div2) 本来以为是送分场,结果成了送命场. 菜是原罪 A SB题,上来读不懂题就交WA了一发,代码就不粘了 B 简单构造 很明显,\(n*n\)的矩阵可 ...
- Codeforces Round #361 div2
ProblemA(Codeforces Round 689A): 题意: 给一个手势, 问这个手势是否是唯一. 思路: 暴力, 模拟将这个手势上下左右移动一次看是否还在键盘上即可. 代码: #incl ...
- Codeforces Round #626 Div2 D,E
比赛链接: Codeforces Round #626 (Div. 2, based on Moscow Open Olympiad in Informatics) D.Present 题意: 给定大 ...
- CodeForces Round 192 Div2
This is the first time I took part in Codeforces Competition.The only felt is that my IQ was contemp ...
- Codeforces Round #333 (Div. 1) C. Kleofáš and the n-thlon 树状数组优化dp
C. Kleofáš and the n-thlon Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contes ...
- Codeforces Round #333 (Div. 1) B. Lipshitz Sequence 倍增 二分
B. Lipshitz Sequence Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/601/ ...
随机推荐
- GUID (全局唯一标识符)
全局唯一标识符(GUID,Globally Unique Identifier)是一种由算法生成的二进制长度为128位的数字标识符.GUID主要用于在拥有多个节点.多台计算机的网络或系统中. ...
- JQuery Mobile + Cordova 实战一
好的,今天给大家继续讲解 JQM 和 Cordova 的结合吧.Cordova 和 Phonegap 反正是一个东西,大家就当做一个是旧版(Phonegap)的一个是新版(Cordova)的就行.不同 ...
- android sqlite操作(2)
以下只是我个人的浅见,大神请忽略~ 这一篇说一下sqlite的相关操作,其实安卓提供了相当多的操作sqlite的方法,这里我介绍下我常用的方法. (1)创建一个数据库文件,这个很简单 File dbP ...
- 《RHEL6硬盘的分区和swap分区管理》——硬盘分区的大总结
首先介绍下几个简单的命令: free查看当前系统内存的使用情况 查看分区的使用情况:T类型.H显示大小以G,M 查看系统所有硬盘的分区信息:分区的没分区的都显示出来了 开始分区:为什么要加cu 不加 ...
- JSON结构
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式.易于人阅读和编写.同时也易于机器解析和生成.它基于JavaScript Programming Langu ...
- Jquery Slick幻灯片插件
slick 是一个基于 jQuery 的幻灯片插件,具有以下特点: 支持响应式 浏览器支持 CSS3 时,则使用 CSS3 过度/动画 支持移动设备滑动 支持桌面浏览器鼠标拖动 支持循环 支持左右控制 ...
- Java抽象类和抽象方法例子
题目:定义Shape类表示一般二维图形.Shape具有抽象方法area和perimeter,分别计算形状的面积和周长.试定义一些二维形状类(如矩形.三角形.圆形等),这些均为Shape类的子类并计算出 ...
- C#中linq
class IntroToLINQ { static void Main() { // The Three Parts of a LINQ Query: // 1. Data source. ] { ...
- mysql基本知识---20151127-1
2015年11月27日,作为PHPer的我开始全面学习mysql数据库. 基本语法: 1.连接服务器: mysql>mysql -h host -u root -p 回车 输入密码(本地环境可以 ...
- Sublime Text博客插件 --- iblog
iblog是一款 sublime 博客插件,目前只支持cnblog. 项目地址:https://github.com/iskeeter/iblog 功能介绍 新建和更新cnblog的博客 支持mark ...