Codeforces Round #370 (Div. 2) A , B , C 水,水,贪心
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
There are n integers b1, b2, ..., bn written in a row. For all i from 1 to n, values ai are defined by the crows performing the following procedure:
- The crow sets ai initially 0.
- The crow then adds bi to ai, subtracts bi + 1, adds the bi + 2 number, and so on until the n'th number. Thus, ai = bi - bi + 1 + bi + 2 - bi + 3....
Memory gives you the values a1, a2, ..., an, and he now wants you to find the initial numbers b1, b2, ..., bn written in the row? Can you do it?
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the number of integers written in the row.
The next line contains n, the i'th of which is ai ( - 109 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — the value of the i'th number.
Print n integers corresponding to the sequence b1, b2, ..., bn. It's guaranteed that the answer is unique and fits in 32-bit integer type.
5
6 -4 8 -2 3
2 4 6 1 3
5
3 -2 -1 5 6
1 -3 4 11 6
In the first sample test, the crows report the numbers 6, - 4, 8, - 2, and 3 when he starts at indices 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 respectively. It is easy to check that the sequence 2 4 6 1 3 satisfies the reports. For example, 6 = 2 - 4 + 6 - 1 + 3, and - 4 = 4 - 6 + 1 - 3.
In the second sample test, the sequence 1, - 3, 4, 11, 6 satisfies the reports. For example, 5 = 11 - 6 and 6 = 6.
思路:a[i]+a[i+1];
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
const int N=1e5+,M=4e6+,inf=1e9+,mod=1e9+;
const ll INF=1e18+;
ll a[N];
int main()
{
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
for(int i=;i<=x;i++)
scanf("%lld",&a[i]);
for(int i=;i<=x;i++)
printf("%lld ",a[i]+a[i+]);
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Memory is performing a walk on the two-dimensional plane, starting at the origin. He is given a string s with his directions for motion:
- An 'L' indicates he should move one unit left.
- An 'R' indicates he should move one unit right.
- A 'U' indicates he should move one unit up.
- A 'D' indicates he should move one unit down.
But now Memory wants to end at the origin. To do this, he has a special trident. This trident can replace any character in s with any of 'L', 'R', 'U', or 'D'. However, because he doesn't want to wear out the trident, he wants to make the minimum number of edits possible. Please tell Memory what is the minimum number of changes he needs to make to produce a string that, when walked, will end at the origin, or if there is no such string.
The first and only line contains the string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 100 000) — the instructions Memory is given.
If there is a string satisfying the conditions, output a single integer — the minimum number of edits required. In case it's not possible to change the sequence in such a way that it will bring Memory to to the origin, output -1.
RRU
-1
UDUR
1
RUUR
2
In the first sample test, Memory is told to walk right, then right, then up. It is easy to see that it is impossible to edit these instructions to form a valid walk.
In the second sample test, Memory is told to walk up, then down, then up, then right. One possible solution is to change s to "LDUR". This string uses 1 edit, which is the minimum possible. It also ends at the origin.
题意:上下左右的走,问最少变几步可以回到原点;
思路:奇数步,显然不能回到,ans=(abs(l-r)+abs(u-d))/ 2;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
const int N=1e5+,M=4e6+,inf=1e9+,mod=1e9+;
const ll INF=1e18+;
char a[N];
int flag[];
int main()
{
int x;
scanf("%s",a);
x=strlen(a);
if(x&)
{
printf("-1\n");
return ;
}
for(int i=;i<x;i++)
{
if(a[i]=='U')
flag[]++;
if(a[i]=='D')
flag[]++;
if(a[i]=='L')
flag[]++;
if(a[i]=='R')
flag[]++;
}
printf("%d\n",(abs(flag[]-flag[])+abs(flag[]-flag[]))/);
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Memory is now interested in the de-evolution of objects, specifically triangles. He starts with an equilateral triangle of side length x, and he wishes to perform operations to obtain an equilateral triangle of side length y.
In a single second, he can modify the length of a single side of the current triangle such that it remains a non-degenerate triangle (triangle of positive area). At any moment of time, the length of each side should be integer.
What is the minimum number of seconds required for Memory to obtain the equilateral triangle of side length y?
The first and only line contains two integers x and y (3 ≤ y < x ≤ 100 000) — the starting and ending equilateral triangle side lengths respectively.
Print a single integer — the minimum number of seconds required for Memory to obtain the equilateral triangle of side length y if he starts with the equilateral triangle of side length x.
6 3
4
8 5
3
22 4
6
In the first sample test, Memory starts with an equilateral triangle of side length 6 and wants one of side length 3. Denote a triangle with sides a, b, and c as (a, b, c). Then, Memory can do 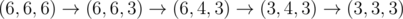 .
.
In the second sample test, Memory can do 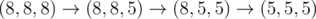 .
.
In the third sample test, Memory can do: 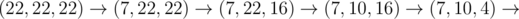
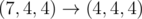 .
.
题意:给你一个边长为x的等边三角形,可以改变一条边使其成为另一个三角形,求最少改变的次数,得到边长为y的等边三角形;
思路:贪心,从y往上最大的改变;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
const int N=1e5+,M=4e6+,inf=1e9+,mod=1e9+;
const ll INF=1e18+;
int a[];
int main()
{
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
for(int i=;i<=;i++)a[i]=y;
int ans=;
while()
{
if(a[]==x&&a[]==x&&a[]==x)
break;
sort(a+,a+);
a[]=min(x,a[]+a[]-);
ans++;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #370 (Div. 2) A , B , C 水,水,贪心的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #370 (Div. 2) C. Memory and De-Evolution 水题
C. Memory and De-Evolution 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/712/problem/C Description Memory is n ...
- Codeforces Round #370 (Div. 2) B. Memory and Trident 水题
B. Memory and Trident 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/712/problem/B Description Memory is perfor ...
- Codeforces Round #370 (Div. 2) A. Memory and Crow 水题
A. Memory and Crow 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/712/problem/A Description There are n integer ...
- Codeforces Round #297 (Div. 2)A. Vitaliy and Pie 水题
Codeforces Round #297 (Div. 2)A. Vitaliy and Pie Time Limit: 2 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MBSubmit: xxx ...
- Codeforces Round #396 (Div. 2) A B C D 水 trick dp 并查集
A. Mahmoud and Longest Uncommon Subsequence time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 ...
- Codeforces Round #370 (Div. 2) E. Memory and Casinos (数学&&概率&&线段树)
题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/712/problem/E 题目大意: 一条直线上有n格,在第i格有pi的可能性向右走一格,1-pi的可能性向左走一格,有2中操 ...
- Codeforces Round #370 (Div. 2) E. Memory and Casinos 线段树
E. Memory and Casinos 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/712/problem/E Description There are n casi ...
- Codeforces Round #370 (Div. 2)C. Memory and De-Evolution 贪心
地址:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/712/C 题目: C. Memory and De-Evolution time limit per test ...
- Codeforces Round #370 (Div. 2)B. Memory and Trident
地址:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/712/B 题目: B. Memory and Trident time limit per test 2 se ...
- Codeforces Round #370 (Div. 2) D. Memory and Scores 动态规划
D. Memory and Scores 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/712/problem/D Description Memory and his fr ...
随机推荐
- zookeeper安装步骤
zookeeper安装步骤 百度搜索:zookeeper 进入后点击下载: 进入到下载的页面 英文: 中文: 进入版本列表: 进入后复制该链接, 在linux执行wget下载: wget https: ...
- Linux 装JDK
1.查看当前系统有没有装jdk java -version 2.看看有没有安装包 rpm -qa | grep java 3.卸载OpenJDK $>rpm -e --nodeps tzdata ...
- jquery 操作动态添加的元素
动态添加的元素,无法侦听到事件,写法如下: 使用函数.on 格式为: $(父元素).on('event','selector',function(){ //do something }) 例如 < ...
- 解决Vue的表格中,expand只有某些行需要展开的问题。
element UI里的表格里,type="expand"的话,所有行都有展开的选项,然而实际中有些行根据判断不需要展开,而element目前对这个问题还不是很友好,现在有个可以通 ...
- PHP的文件下载
1.通过header头部下载文件 header("Content-length: ".filesize($filename)); //指定文件下载的大小 header(' ...
- Python3.6全栈开发实例[014]
14.好声音选秀大赛评委在打分的时,可以进行输入. 假设,有10个评委.让10个评委进行打分, 要求, 分数必须大于5分, 小于10分. count = 1 while count <= 10: ...
- Oracle学习笔记—Oracle左连接、右连接、全外连接以及(+)号用法(转载)
转载自: Oracle左连接.右连接.全外连接以及(+)号用法 对于外连接,Oracle中可以使用“(+)”来表示. 关于使用(+)的一些注意事项: (+)操作符只能出现在WHERE子句中,并且不能与 ...
- Network Basic Knowledge
@1: 应用层的常用协议以及对应的端口号: DNS 53/tcp/udp SMTP 25/tcp POP3 110/tcp HTTP 80/tcp HTTPS 443/udp TELNET 23/tc ...
- 深度学习2--安装opencv3.1
1\opencv的安装参考视频 2\ 以下内容来自:http://blog.csdn.net/l18930738887/article/details/54696148 本人因为被坑过,所以建议各位最 ...
- 搭建backup服务器基本流程
守护进程实现,将daemon配置在backup服务器,因为这样其他服务器就能通过服务推即可. 服务端配置流程: 前提两台服务41为backup服务 31是其他服务器即客户端 在41服务器中配置 ...
