python3+ros api
官方文档:https://wiki.mikrotik.com/wiki/Manual:API_Python3
# !/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:lzd import sys, time, binascii, socket, select
import hashlib class ApiRos:
"Routeros api" def __init__(self, sk):
self.sk = sk
self.currenttag = 0 def login(self, username, pwd):
for repl, attrs in self.talk(["/login"]):
chal = binascii.unhexlify((attrs['=ret']).encode('UTF-8'))
md = hashlib.md5()
md.update(b'\x00')
md.update(pwd.encode('UTF-8'))
md.update(chal)
self.talk(["/login", "=name=" + username,
"=response=00" + binascii.hexlify(md.digest()).decode('UTF-8')]) def talk(self, words):
if self.writeSentence(words) == 0: return
r = []
while 1:
i = self.readSentence();
if len(i) == 0: continue
reply = i[0]
attrs = {}
for w in i[1:]:
j = w.find('=', 1)
if (j == -1):
attrs[w] = ''
else:
attrs[w[:j]] = w[j + 1:]
r.append((reply, attrs))
if reply == '!done': return r def writeSentence(self, words):
ret = 0
for w in words:
self.writeWord(w)
ret += 1
self.writeWord('')
return ret def readSentence(self):
r = []
while 1:
w = self.readWord()
if w == '': return r
r.append(w) def writeWord(self, w):
print(("<<< " + w))
self.writeLen(len(w))
self.writeStr(w) def readWord(self):
ret = self.readStr(self.readLen())
print((">>> " + ret))
return ret def writeLen(self, l):
if l < 0x80:
self.writeStr(chr(l))
elif l < 0x4000:
l |= 0x8000
self.writeStr(chr((l >> 8) & 0xFF))
self.writeStr(chr(l & 0xFF))
elif l < 0x200000:
l |= 0xC00000
self.writeStr(chr((l >> 16) & 0xFF))
self.writeStr(chr((l >> 8) & 0xFF))
self.writeStr(chr(l & 0xFF))
elif l < 0x10000000:
l |= 0xE0000000
self.writeStr(chr((l >> 24) & 0xFF))
self.writeStr(chr((l >> 16) & 0xFF))
self.writeStr(chr((l >> 8) & 0xFF))
self.writeStr(chr(l & 0xFF))
else:
self.writeStr(chr(0xF0))
self.writeStr(chr((l >> 24) & 0xFF))
self.writeStr(chr((l >> 16) & 0xFF))
self.writeStr(chr((l >> 8) & 0xFF))
self.writeStr(chr(l & 0xFF)) def readLen(self):
c = ord(self.readStr(1))
if (c & 0x80) == 0x00:
pass
elif (c & 0xC0) == 0x80:
c &= ~0xC0
c <<= 8
c += ord(self.readStr(1))
elif (c & 0xE0) == 0xC0:
c &= ~0xE0
c <<= 8
c += ord(self.readStr(1))
c <<= 8
c += ord(self.readStr(1))
elif (c & 0xF0) == 0xE0:
c &= ~0xF0
c <<= 8
c += ord(self.readStr(1))
c <<= 8
c += ord(self.readStr(1))
c <<= 8
c += ord(self.readStr(1))
elif (c & 0xF8) == 0xF0:
c = ord(self.readStr(1))
c <<= 8
c += ord(self.readStr(1))
c <<= 8
c += ord(self.readStr(1))
c <<= 8
c += ord(self.readStr(1))
return c def writeStr(self, str):
n = 0;
while n < len(str):
r = self.sk.send(bytes(str[n:], 'UTF-8'))
if r == 0: raise RuntimeError("connection closed by remote end")
n += r def readStr(self, length):
ret = ''
while len(ret) < length:
s = self.sk.recv(length - len(ret))
if s == '': raise RuntimeError("connection closed by remote end")
ret += s.decode('UTF-8', 'replace')
return ret def main():
s = None
for res in socket.getaddrinfo(sys.argv[1], "8728", socket.AF_UNSPEC, socket.SOCK_STREAM):
af, socktype, proto, canonname, sa = res
try:
s = socket.socket(af, socktype, proto)
except (socket.error, msg):
s = None
continue
try:
s.connect(sa)
except (socket.error, msg):
s.close()
s = None
continue
break
if s is None:
print('could not open socket')
sys.exit(1) apiros = ApiRos(s);
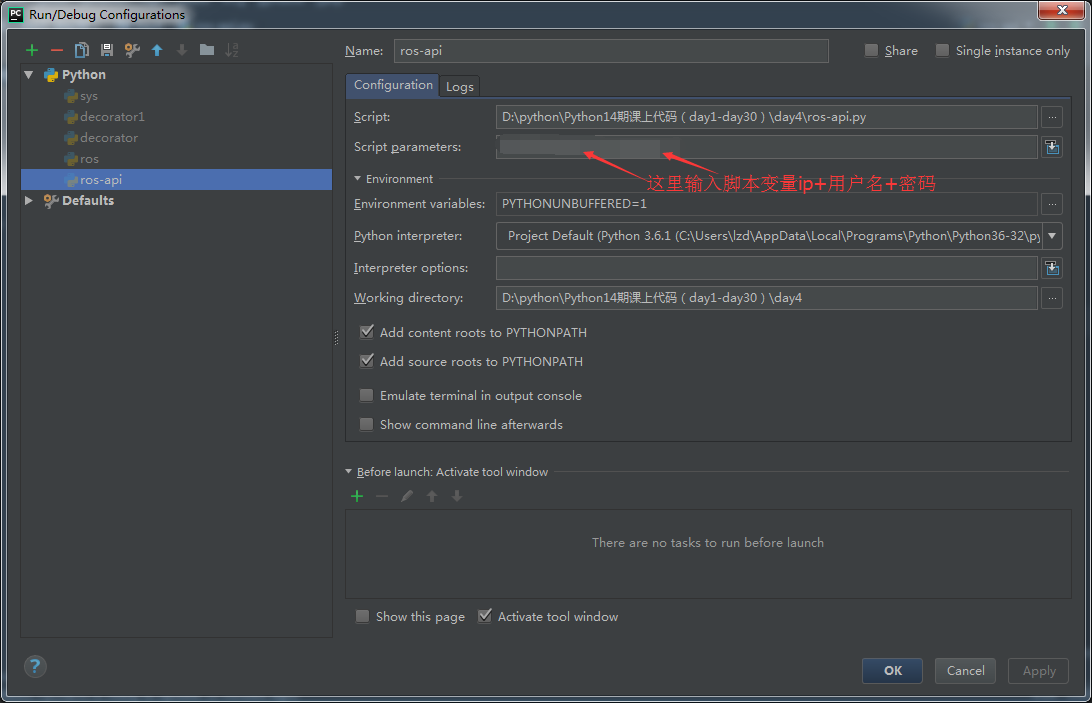
apiros.login(sys.argv[2], sys.argv[3]); #模拟用户自己输入代码进行api控制
tmpcommand=input('请输入你想查询的命令')
inputsentence = []
inputsentence.append(tmpcommand)
apiros.writeSentence(inputsentence)
while 1:
x = apiros.readSentence()
#print(x)
if x == ['!done'] or x==['!re', '=status=finished']:
break
#导出ros配置到ROS本地ghg1.rsc文件
# inputsentence = []
#
# inputsentence.append('/export')
# inputsentence.append('=file=ghg1.rsc')
# apiros.writeSentence(inputsentence)
# while 1:
# x = apiros.readSentence()
# #print(x)
# if x == ['!done'] or x==['!re', '=status=finished']:
# break
#从ros上传文件到ftp的代码
# inputsentence = []
# inputsentence.append('/tool/fetch')
# inputsentence.append('=address=192.168.0.108')
# inputsentence.append('=src-path=ghg1.rsc')
# inputsentence.append('=user=xxxxx')
# inputsentence.append('=mode=ftp')
# inputsentence.append('=password=xxxxx')
# inputsentence.append('=dst-path=123.rsc')
# inputsentence.append('=upload=yes')
# apiros.writeSentence(inputsentence)
# inputsentence = []
# while 1:
# x = apiros.readSentence()
# #print(x)
# if x == ['!done'] or x==['!re', '=status=finished']:
# break
#删除文件代码
# inputsentence = []
# inputsentence.append('/file/remove')
# inputsentence.append('=numbers=ghg1.rsc')
# apiros.writeSentence(inputsentence)
# while 1:
# x = apiros.readSentence()
# print(x)
# if x == ['!done'] or x==['!re', '=status=finished']:
# break
#官方循环代码,等待你输入命令行,可以用来测试代码命令行
# while 1:
# r = select.select([s, sys.stdin], [], [], None)
# if s in r[0]:
# # something to read in socket, read sentence
# x = apiros.readSentence()
#
# if sys.stdin in r[0]:
# # read line from input and strip off newline
# l = sys.stdin.readline()
# print(l)
# l = l[:-1]
# print(l)
#
#
# # if empty line, send sentence and start with new
# # otherwise append to input sentence
# if l == '':
# apiros.writeSentence(inputsentence)
# inputsentence = []
# else:
# inputsentence.append(l) if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
# !/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:lzd import sys, time, binascii, socket, select
import hashlib class ApiRos:
"Routeros api" def __init__(self, sk):
self.sk = sk
self.currenttag = 0 def login(self, username, pwd):
for repl, attrs in self.talk(["/login"]):
chal = binascii.unhexlify((attrs['=ret']).encode('UTF-8'))
md = hashlib.md5()
md.update(b'\x00')
md.update(pwd.encode('UTF-8'))
md.update(chal)
self.talk(["/login", "=name=" + username,
"=response=00" + binascii.hexlify(md.digest()).decode('UTF-8')]) def talk(self, words):
if self.writeSentence(words) == 0: return
r = []
while 1:
i = self.readSentence();
if len(i) == 0: continue
reply = i[0]
attrs = {}
for w in i[1:]:
j = w.find('=', 1)
if (j == -1):
attrs[w] = ''
else:
attrs[w[:j]] = w[j + 1:]
r.append((reply, attrs))
if reply == '!done': return r def writeSentence(self, words):
ret = 0
for w in words:
self.writeWord(w)
ret += 1
self.writeWord('')
return ret def readSentence(self):
r = []
while 1:
w = self.readWord()
if w == '': return r
r.append(w) def writeWord(self, w):
print(("<<< " + w))
self.writeLen(len(w))
self.writeStr(w) def readWord(self):
ret = self.readStr(self.readLen())
print((">>> " + ret))
return ret def writeLen(self, l):
if l < 0x80:
self.writeStr(chr(l))
elif l < 0x4000:
l |= 0x8000
self.writeStr(chr((l >> 8) & 0xFF))
self.writeStr(chr(l & 0xFF))
elif l < 0x200000:
l |= 0xC00000
self.writeStr(chr((l >> 16) & 0xFF))
self.writeStr(chr((l >> 8) & 0xFF))
self.writeStr(chr(l & 0xFF))
elif l < 0x10000000:
l |= 0xE0000000
self.writeStr(chr((l >> 24) & 0xFF))
self.writeStr(chr((l >> 16) & 0xFF))
self.writeStr(chr((l >> 8) & 0xFF))
self.writeStr(chr(l & 0xFF))
else:
self.writeStr(chr(0xF0))
self.writeStr(chr((l >> 24) & 0xFF))
self.writeStr(chr((l >> 16) & 0xFF))
self.writeStr(chr((l >> 8) & 0xFF))
self.writeStr(chr(l & 0xFF)) def readLen(self):
c = ord(self.readStr(1))
if (c & 0x80) == 0x00:
pass
elif (c & 0xC0) == 0x80:
c &= ~0xC0
c <<= 8
c += ord(self.readStr(1))
elif (c & 0xE0) == 0xC0:
c &= ~0xE0
c <<= 8
c += ord(self.readStr(1))
c <<= 8
c += ord(self.readStr(1))
elif (c & 0xF0) == 0xE0:
c &= ~0xF0
c <<= 8
c += ord(self.readStr(1))
c <<= 8
c += ord(self.readStr(1))
c <<= 8
c += ord(self.readStr(1))
elif (c & 0xF8) == 0xF0:
c = ord(self.readStr(1))
c <<= 8
c += ord(self.readStr(1))
c <<= 8
c += ord(self.readStr(1))
c <<= 8
c += ord(self.readStr(1))
return c def writeStr(self, str):
n = 0;
while n < len(str):
r = self.sk.send(bytes(str[n:], 'UTF-8'))
if r == 0: raise RuntimeError("connection closed by remote end")
n += r def readStr(self, length):
ret = ''
while len(ret) < length:
s = self.sk.recv(length - len(ret))
if s == '': raise RuntimeError("connection closed by remote end")
ret += s.decode('UTF-8', 'replace')
return ret def main():
s = None
for res in socket.getaddrinfo(sys.argv[1], "", socket.AF_UNSPEC, socket.SOCK_STREAM):
af, socktype, proto, canonname, sa = res
try:
s = socket.socket(af, socktype, proto)
except (socket.error, msg):
s = None
continue
try:
s.connect(sa)
except (socket.error, msg):
s.close()
s = None
continue
break
if s is None:
print('could not open socket')
sys.exit(1) apiros = ApiRos(s);
apiros.login(sys.argv[2], sys.argv[3]); #模拟用户自己输入代码进行api控制
tmpcommand=input('请输入你想查询的命令')
inputsentence = []
inputsentence.append(tmpcommand)
apiros.writeSentence(inputsentence)
while 1:
x = apiros.readSentence()
#print(x)
if x == ['!done'] or x==['!re', '=status=finished']:
break
#导出ros配置到ROS本地ghg1.rsc文件
# inputsentence = []
#
# inputsentence.append('/export')
# inputsentence.append('=file=ghg1.rsc')
# apiros.writeSentence(inputsentence)
# while 1:
# x = apiros.readSentence()
# #print(x)
# if x == ['!done'] or x==['!re', '=status=finished']:
# break
#从ros上传文件到ftp的代码
# inputsentence = []
# inputsentence.append('/tool/fetch')
# inputsentence.append('=address=192.168.0.108')
# inputsentence.append('=src-path=ghg1.rsc')
# inputsentence.append('=user=xxxxx')
# inputsentence.append('=mode=ftp')
# inputsentence.append('=password=xxxxx')
# inputsentence.append('=dst-path=123.rsc')
# inputsentence.append('=upload=yes')
# apiros.writeSentence(inputsentence)
# inputsentence = []
# while 1:
# x = apiros.readSentence()
# #print(x)
# if x == ['!done'] or x==['!re', '=status=finished']:
# break
#删除文件代码
# inputsentence = []
# inputsentence.append('/file/remove')
# inputsentence.append('=numbers=ghg1.rsc')
# apiros.writeSentence(inputsentence)
# while 1:
# x = apiros.readSentence()
# print(x)
# if x == ['!done'] or x==['!re', '=status=finished']:
# break
#官方循环代码,等待你输入命令行,可以用来测试代码命令行
# while 1:
# r = select.select([s, sys.stdin], [], [], None)
# if s in r[0]:
# # something to read in socket, read sentence
# x = apiros.readSentence()
#
# if sys.stdin in r[0]:
# # read line from input and strip off newline
# l = sys.stdin.readline()
# print(l)
# l = l[:-1]
# print(l)
#
#
# # if empty line, send sentence and start with new
# # otherwise append to input sentence
# if l == '':
# apiros.writeSentence(inputsentence)
# inputsentence = []
# else:
# inputsentence.append(l) if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
python3+ros api的更多相关文章
- easyradius隆重发布ROS API计费接口,支持ROS 3.3以上版本,实现简单快捷的ROS宽带计费系统云端版
easyradius对接ROS也是使用的是ROS的api接口,即您要开启 /ip /service api服务,不了解api接口的,可以自己百度噢 开启API,就到easyradius配置通讯接口,具 ...
- python3 + zabbix api 的使用
喜欢需要理由吗?需要吗?当然需要,zabbix的那么多功能足以让你喜欢她,现在还有zabbix API,zabbix真让我疯了,太牛逼了,太让人喜欢了.有zabbix API我们可以做很多,自己开发w ...
- python3+ros+telnet+telnetlib
利用python3的telnetlib模块 远程登录ros,输入帐号密码,然后执行命令,并导出结果到txt文本: 不过实际操作这种方式不行,因为telnet导出来的文本文件,带颜色编码,根本无法看哦. ...
- python3 kubernetes api 使用
一.安装 github:https://github.com/kubernetes-client/python 安装 pip install kubernetes 二.认证 1.kubeconfig文 ...
- python3 ansible api 命令和playbook
一.api代码 # coding: utf-8 import os import sys from collections import namedtuple from ansible.parsing ...
- python3封装Api接口
注:本篇的代码和语法基于Python3.5环境,下面将用到Python 的Flask框架 封装接口主要讲静态接口(无参数传入).动态接口(有参数传入,不同参数返回的信息不同).针对动态接口有三种传参方 ...
- python3 tornado api + angular8 + nginx 跨域问题
问题: 上一个博客部署好了api之后,前端开始吊发现了跨域的问题. 接口地址: http://111.231.201.164/api/houses 服务器上使用的是nginx转发 数据: 前端ang ...
- python3 jenkins api操作
一.安装依赖包 pip install python-jenkins 二.常用操作 0.调用jenkins(以下用的server都是这里的环境) import jenkins server = jen ...
- python3 mysql API
1. 安装引入 2. 对象简介 3. 代码封装 1. 安装引入 1)安装: pip install PyMySQL 2)Pycharm 中引入 pymysql:
随机推荐
- JNI简单步骤01
1.环境变量 1.1.相应的环境变量中,加入如下内容:(Windows) (1).ClASSPATH中输入 : ".;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.7.0_07\jr ...
- freemarker报 java.io.FileNotFoundException:及TemplateLoader使用
使用过freemarker的肯定其见过如下情况: java.io.FileNotFoundException: Template xxx.ftl not found. 模板找不到.可能你会认为我明明指 ...
- SSL和SSH的区别
SSL是一种国际标准的加密及身份认证通信协议,您用的浏览器就支持此协议.SSL(Secure Sockets Layer)最初是由美国Netscape公司研究出来的,后来成为了Internet网上安全 ...
- poj1330lca入门题
直接套模板,dfs的时候注意起点 #include<map> #include<set> #include<cmath> #include<queue> ...
- Ubuntu 18.04 下 emscripten SDK 的安装
Ubuntu 18.04 下 emscripten SDK 的安装http://kripken.github.io/emscripten-site/docs/getting_started/downl ...
- mooseFS学习篇
官方网站:http://www.moosefs.org/ About MooseFS MooseFS is a fault tolerant, network distributed file sys ...
- 连接mysql报错:error 2003 (hy000):can't connect to mysql server on 'localhost' (10061)
一.mysql 的bin目录下有个MySQLInstanceConfig.exe,运行就可以进行创建数据库实例,创建实例时也可以生成windows 服务,把服务设置成自动启动就可以了 二.安装在D盘的 ...
- Openstack Mitaka 负载均衡 LoadBalancerv2
最近研究了一下Openstack负载均衡,yum源和源码级别的安装都尝试成功了.网上有很多文章都是LoadBalancerv1,这个已经被放弃了.所以写一下自己是如何使用LoadBalancerv ...
- 剑指offer--30.二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
正常情况下,因为二叉搜索树,左子树所有结点比根小,右子树所有结点比根大,所以循环一遍就能结束 ----------------------------------------------------- ...
- Every derived table must have its own alias
完整错误信息如下: Every derived table must have its own alias 三月 28, 2017 10:20:46 上午 org.apache.catalina.co ...
