Qt 学习之路 2(49):自定义只读模型
Qt 学习之路 2(49):自定义只读模型
model/view 模型将数据与视图分割开来,也就是说,我们可以为不同的视图,QListView、QTableView和QTreeView提供一个数据模型,这样我们可以从不同角度来展示数据的方方面面。但是,面对变化万千的需求,Qt 预定义的几个模型是远远不能满足需要的。因此,我们还必须自定义模型。
类似QAbstractView类之于自定义视图,QAbstractItemModel 为自定义模型提供了一个足够灵活的接口。它能够支持数据源的层次结构,能够对数据进行增删改操作,还能够支持拖放。不过,有时候一个灵活的类往往显得过于复杂,所以,Qt 又提供了QAbstarctListModel和QAbstractTableModel两个类来简化非层次数据模型的开发。顾名思义,这两个类更适合于结合列表和表格使用。
本节,我们正式开始对自定义模型进行介绍。
在开始自定义模型之前,我们首先需要思考这样一个问题:我们的数据结构适合于哪种视图的显示方式?是列表,还是表格,还是树?如果我们的数据仅仅用于列表或表格的显示,那么QAbstractListModel或者QAbstractTableModel 已经足够,它们为我们实现了很多默认函数。但是,如果我们的数据具有层次结构,并且必须向用户显示这种层次,我们只能选择QAbstractItemModel。不管底层数据结构是怎样的格式,最好都要直接考虑适应于标准的QAbstractItemModel的接口,这样就可以让更多视图能够轻松访问到这个模型。
现在,我们开始自定义一个模型。这个例子修改自《C++ GUI Programming with Qt4, 2nd Edition》。首先描述一下需求。我们想要实现的是一个货币汇率表,就像银行营业厅墙上挂着的那种电子公告牌。当然,你可以选择QTableWidget。的确,直接使用QTableWidget确实很方便。但是,试想一个包含了 100 种货币的汇率表。显然,这是一个二维表,并且对于每一种货币,都需要给出相对于其他 100 种货币的汇率(我们把自己对自己的汇率也包含在内,只不过这个汇率永远是 1.0000)。现在,按照我们的设计,这张表要有 100 x 100 = 10000 个数据项。我们希望减少存储空间,有没有更好的方式?于是我们想,如果我们的数据不是直接向用户显示的数据,而是这种货币相对于美元的汇率,那么其它货币的汇率都可以根据这个汇率计算出来了。比如,我存储人民币相对美元的汇率,日元相对美元的汇率,那么人民币相对日元的汇率只要作一下比就可以得到了。这种数据结构就没有必要存储 10000 个数据项,只要存储 100 个就够了(实际情况中这可能是不现实的,因为两次运算会带来更大的误差,但这不在我们现在的考虑范畴中)。
于是我们设计了CurrencyModel类。它底层使用QMap<QString, double>数据结构进行存储,QString类型的键是货币名字,double类型的值是这种货币相对美元的汇率。(这里提一点,实际应用中,永远不要使用 double 处理金额敏感的数据!因为 double 是不精确的,不过这一点显然不在我们的考虑中。)
首先从头文件开始看起:
{
public:
CurrencyModel(QObject *parent = 0);
void setCurrencyMap(const QMap<QString, double> &map);
int rowCount(const QModelIndex &parent) const;
int columnCount(const QModelIndex &parent) const;
QVariant data(const QModelIndex &index, int role) const;
QVariant headerData(int section, Qt::Orientation orientation, int role) const;
private:
QString currencyAt(int offset) const;
QMap<QString, double> currencyMap;
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
class CurrencyModel : public QAbstractTableModel
{
public:
CurrencyModel(QObject *parent = 0);
void setCurrencyMap(const QMap<QString, double> &map);
int rowCount(const QModelIndex &parent) const;
int columnCount(const QModelIndex &parent) const;
QVariant data(const QModelIndex &index, int role) const;
QVariant headerData(int section, Qt::Orientation orientation, int role) const;
private:
QString currencyAt(int offset) const;
QMap<QString, double> currencyMap;
};
|
这段代码平淡无奇,我们继承了QAbstractTableModel类,然后重写了所要求的几个函数。构造函数同样如此:
: QAbstractTableModel(parent)
{
}
|
1
2
3
4
|
CurrencyModel::CurrencyModel(QObject *parent)
: QAbstractTableModel(parent)
{
}
|
rowCount()和columnCount()用于返回行和列的数目。记得我们保存的是每种货币相对美元的汇率,而需要显示的是它们两两之间的汇率,因此这两个函数都应该返回这个 map 的项数:
{
return currencyMap.count();
}
int CurrencyModel::columnCount(const QModelIndex & parent) const
{
return currencyMap.count();
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
int CurrencyModel::rowCount(const QModelIndex & parent) const
{
return currencyMap.count();
}
int CurrencyModel::columnCount(const QModelIndex & parent) const
{
return currencyMap.count();
}
|
headerData()用于返回列名:
{
if (role != Qt::DisplayRole) {
return QVariant();
}
return currencyAt(section);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
QVariant CurrencyModel::headerData(int section, Qt::Orientation, int role) const
{
if (role != Qt::DisplayRole) {
return QVariant();
}
return currencyAt(section);
}
|
我们在前面的章节中介绍过有关角色的概念。这里我们首先判断这个角色是不是用于显示的,如果是,则调用currencyAt()函数返回第 section 列的名字;如果不是则返回一个空白的QVariant对象。currencyAt()函数定义如下:
{
return (currencyMap.begin() + offset).key();
}
|
1
2
3
4
|
QString CurrencyModel::currencyAt(int offset) const
{
return (currencyMap.begin() + offset).key();
}
|
如果不了解QVariant类,可以简单认为这个类型相当于 Java 里面的 Object,它把 Qt 提供的大部分数据类型封装起来,起到一个类型擦除的作用。比如我们的单元格的数据可以是 string,可以是 int,也可以是一个颜色值,这么多类型怎么使用一个函数返回呢?回忆一下,返回值并不用于区分一个函数。于是,Qt 提供了QVariant类型。你可以把很多类型存放进去,到需要使用的时候使用一系列的 to 函数取出来即可。比如把 int 包装成一个 QVariant,使用的时候要用QVariant::toInt()重新取出来。这非常类似于 union,但是 union 的问题是,无法保持没有默认构造函数的类型,于是 Qt 提供了QVariant作为 union 的一种模拟。
setCurrencyMap()函数则是用于设置底层的实际数据。由于我们不可能将这种数据硬编码,所以我们必须为模型提供一个用于设置的函数:
{
beginResetModel();
currencyMap = map;
endResetModel();
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
void CurrencyModel::setCurrencyMap(const QMap<QString, double> &map)
{
beginResetModel();
currencyMap = map;
endResetModel();
}
|
我们当然可以直接设置 currencyMap,但是我们依然添加了beginResetModel()和endResetModel()两个函数调用。这将告诉关心这个模型的其它类,现在要重置内部数据,大家要做好准备。这是一种契约式的编程方式。
接下来便是最复杂的data()函数:
{
if (!index.isValid()) {
return QVariant();
}
if (role == Qt::TextAlignmentRole) {
return int(Qt::AlignRight | Qt::AlignVCenter);
} else if (role == Qt::DisplayRole) {
QString rowCurrency = currencyAt(index.row());
QString columnCurrency = currencyAt(index.column());
if (currencyMap.value(rowCurrency) == 0.0) {
return "####";
}
double amount = currencyMap.value(columnCurrency)
/ currencyMap.value(rowCurrency);
return QString("%1").arg(amount, 0, 'f', 4);
}
return QVariant();
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
QVariant CurrencyModel::data(const QModelIndex &index, int role) const
{
if (!index.isValid()) {
return QVariant();
}
if (role == Qt::TextAlignmentRole) {
return int(Qt::AlignRight | Qt::AlignVCenter);
} else if (role == Qt::DisplayRole) {
QString rowCurrency = currencyAt(index.row());
QString columnCurrency = currencyAt(index.column());
if (currencyMap.value(rowCurrency) == 0.0) {
return "####";
}
double amount = currencyMap.value(columnCurrency)
/ currencyMap.value(rowCurrency);
return QString("%1").arg(amount, 0, 'f', 4);
}
return QVariant();
}
|
data()函数返回一个单元格的数据。它有两个参数:第一个是QModelIndex,也就是单元格的位置;第二个是role,也就是这个数据的角色。这个函数的返回值是QVariant类型。我们首先判断传入的index是不是合法,如果不合法直接返回一个空白的QVariant。然后如果role是Qt::TextAlignmentRole,也就是文本的对齐方式,返回int(Qt::AlignRight | Qt::AlignVCenter);如果是Qt::DisplayRole,就按照我们前面所说的逻辑进行计算,然后以字符串的格式返回。这时候你就会发现,其实我们在 if…else… 里面返回的不是一种数据类型:if 里面返回的是 int,而 else 里面是QString,这就是QVariant的作用了。
为了看看实际效果,我们可以使用这样的main()函数代码:
{
QApplication a(argc, argv);
QMap<QString, double> data;
data["USD"] = 1.0000;
data["CNY"] = 0.1628;
data["GBP"] = 1.5361;
data["EUR"] = 1.2992;
data["HKD"] = 0.1289;
QTableView view;
CurrencyModel *model = new CurrencyModel(&view);
model->setCurrencyMap(data);
view.setModel(model);
view.resize(400, 300);
view.show();
return a.exec();
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication a(argc, argv);
QMap<QString, double> data;
data["USD"] = 1.0000;
data["CNY"] = 0.1628;
data["GBP"] = 1.5361;
data["EUR"] = 1.2992;
data["HKD"] = 0.1289;
QTableView view;
CurrencyModel *model = new CurrencyModel(&view);
model->setCurrencyMap(data);
view.setModel(model);
view.resize(400, 300);
view.show();
return a.exec();
}
|
这是我们的实际运行效果:
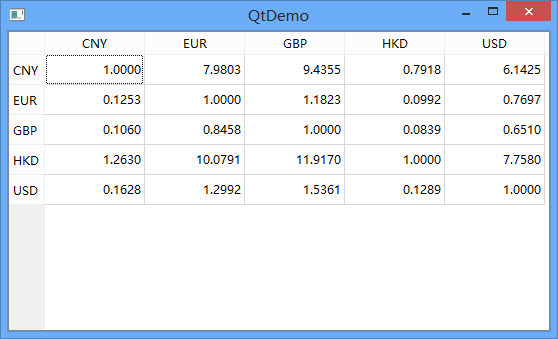
自定义只读模型
Qt 学习之路 2(49):自定义只读模型的更多相关文章
- Qt 学习之路 2(53):自定义拖放数据
Qt 学习之路 2(53):自定义拖放数据 豆子 2013年5月26日 Qt 学习之路 2 13条评论上一章中,我们的例子使用系统提供的拖放对象QMimeData进行拖放数据的存储.比如使用QM ...
- Qt 学习之路 2(50):自定义可编辑模型
Home / Qt 学习之路 2 / Qt 学习之路 2(50):自定义可编辑模型 Qt 学习之路 2(50):自定义可编辑模型 豆子 2013年5月13日 Qt 学习之路 2 13条评论 上一章我们 ...
- Qt 学习之路 2(5):自定义信号槽
Home / Qt 学习之路 2 / Qt 学习之路 2(5):自定义信号槽 Qt 学习之路 2(5):自定义信号槽 豆子 2012年8月24日 Qt 学习之路 2 131条评论 上一节我们详 ...
- Qt 学习之路 2(23):自定义事件
Qt 学习之路 2(23):自定义事件 豆子 2012年10月23日 Qt 学习之路 2 21条评论 尽管 Qt 已经提供了很多事件,但对于更加千变万化的需求来说,有限的事件都是不够的.例如, ...
- Qt 学习之路 2(51):布尔表达式树模型
Qt 学习之路 2(51):布尔表达式树模型 豆子 2013年5月15日 Qt 学习之路 2 17条评论 本章将会是自定义模型的最后一部分.原本打算结束这部分内容,不过实在不忍心放弃这个示例.来自于 ...
- Qt 学习之路 2(16):深入 Qt5 信号槽新语法
Qt 学习之路 2(16):深入 Qt5 信号槽新语法 豆子 2012年9月19日 Qt 学习之路 2 53条评论 在前面的章节(信号槽和自定义信号槽)中,我们详细介绍了有关 Qt 5 的信号 ...
- 《Qt 学习之路 2》目录
<Qt 学习之路 2>目录 <Qt 学习之路 2>目录 豆子 2012年8月23日 Qt 学习之路 2 177条评论 <Qt 学习之路 2>目录 序 Qt ...
- Qt 学习之路 2(71):线程简介
Qt 学习之路 2(71):线程简介 豆子 2013年11月18日 Qt 学习之路 2 30条评论 前面我们讨论了有关进程以及进程间通讯的相关问题,现在我们开始讨论线程.事实上,现代的程序中,使用线程 ...
- Qt 学习之路 2(67):访问网络(3)
Qt 学习之路 2(67):访问网络(3) 豆子 2013年11月5日 Qt 学习之路 2 16条评论 上一章我们了解了如何使用我们设计的NetWorker类实现我们所需要的网络操作.本章我们将继续完 ...
随机推荐
- Neo4j的集群架构
Neo4j的集群架构 参考资料: 1.http://lib.csdn.net/article/mysql/5742,其中有集群的集中模式master-slave.sharding.多主模式.cassa ...
- FeiQ项目
一.映射表 UDPMeditor.h中: typedef void (UDPMeditor::*pFunc)(char*,long); struct ProtocolMap { PackdefType ...
- Golang简单写文件操作的四种方法
package main import ( "bufio" //缓存IO "fmt" "io" "io/ioutil" ...
- no newline at the end of file
[no newline at the end of file] 修复这个警告,在文件结尾回车一下就行了. 这么规定的初衷是,为了每一行都要以换行结束. 因为行尾的/表示连接下一行,如果一个文件最后一 ...
- 【CF#338D】GCD Table
[题目描述] 有一张N,M<=10^12的表格,i行j列的元素是gcd(i,j) 读入一个长度不超过10^4,元素不超过10^12的序列a[1..k],问是否在某一行中出现过 [题解] 要保证g ...
- 高性能的城市定位API接口
如果不需要精准的定位,还有一种通过IP地址获取当前城市的方法,采用新浪的api接口. <script src="http://int.dpool.sina.com.cn/iplooku ...
- MAT(Memory Analyzer tool)使用
当线上环境出现OOM/内存泄漏了,怎么办? 让虚拟机在发生内存溢出时 Dump 出当前的内存堆转储快照,配置-XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError, 当出现OOM时,分析dum ...
- Asp.net MVC获取访问系统的客户端计算机的主机名和IP地址
string HostName = string.Empty; string ip = string.Empty; string ipv4 = String.Empty; if (!string.Is ...
- Creating and Using Static Libraries for iPhone using Xcode 4.3
Recently, after developing a collection of applications for iPhone that were intended to be used as ...
- 【实习项目记录】(二) JSON
介绍 JSON JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式. 易于人阅读和编写.同时也易于机器解析和生成. 它基于JavaScript Program ...
