进程间通信-信号-pipe-fifo
一、实验截图
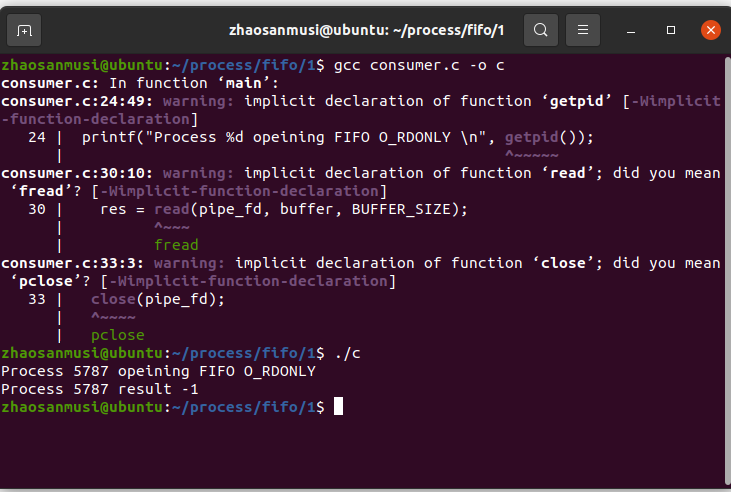
(一)fifo

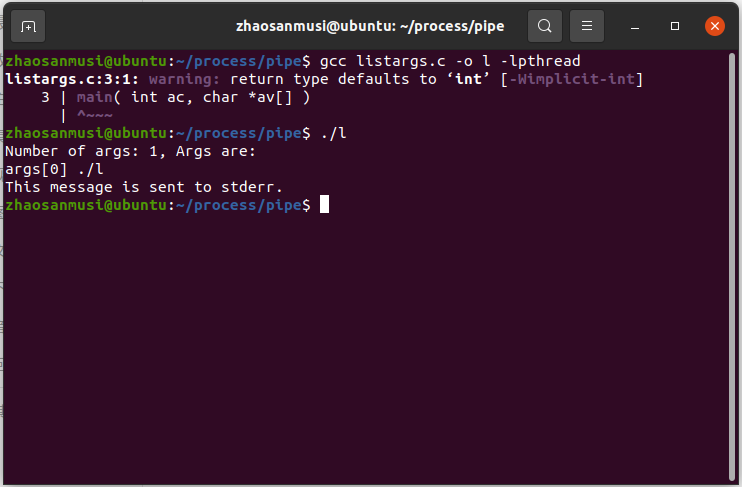
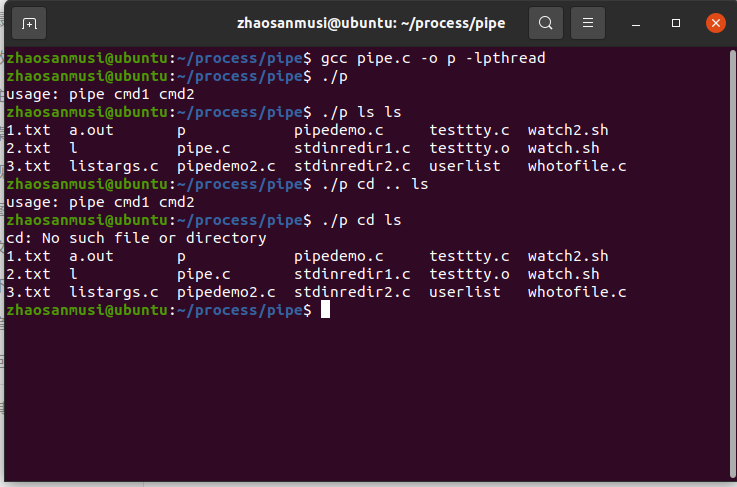
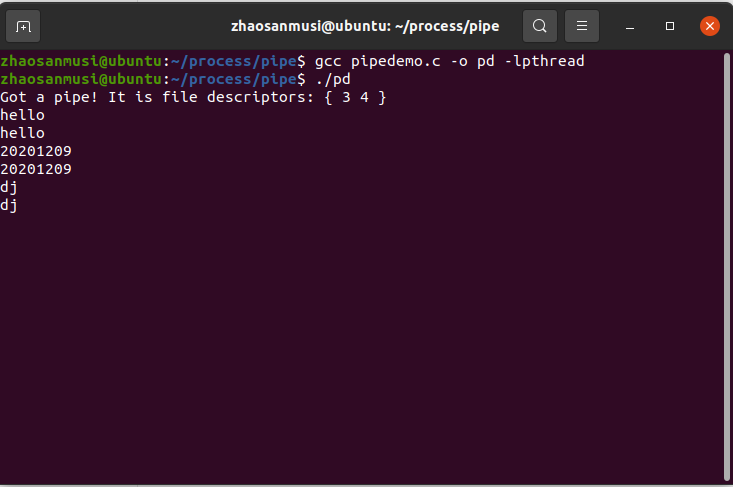
(二)pipe
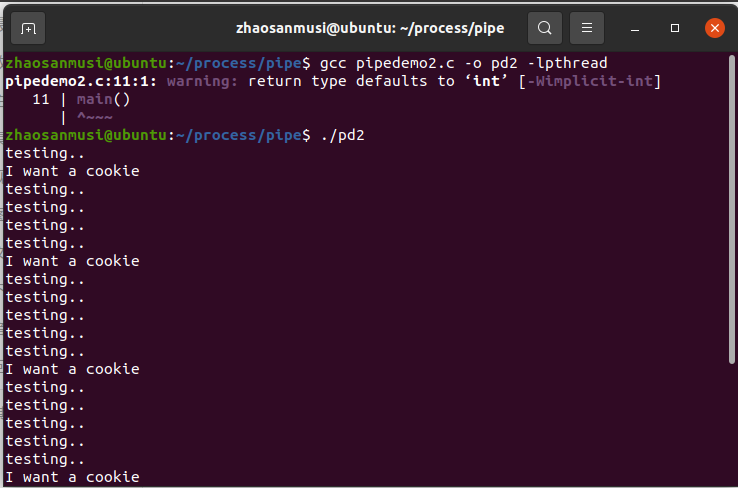
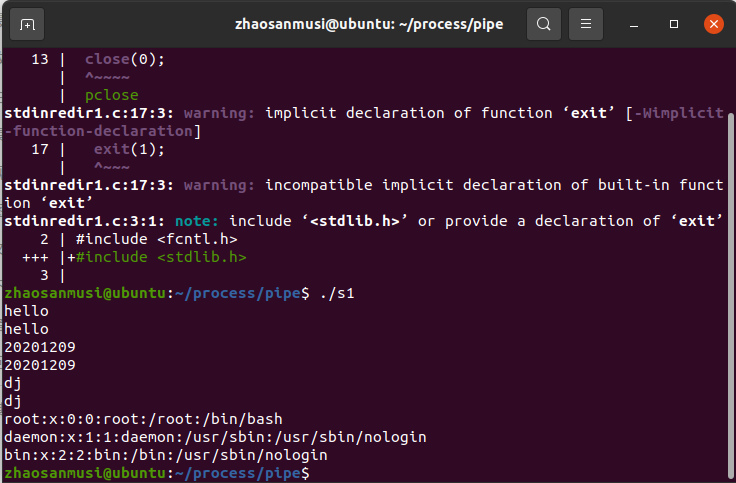

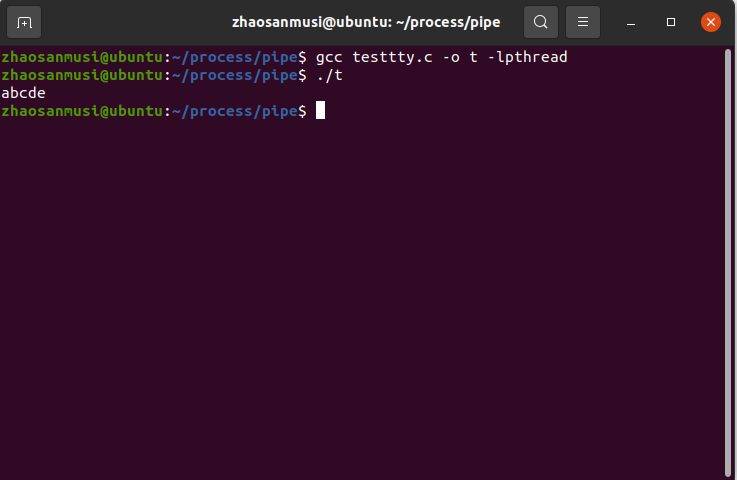
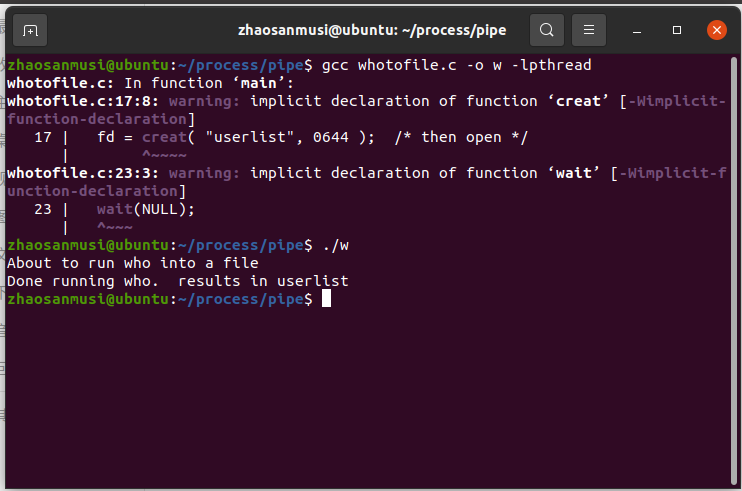
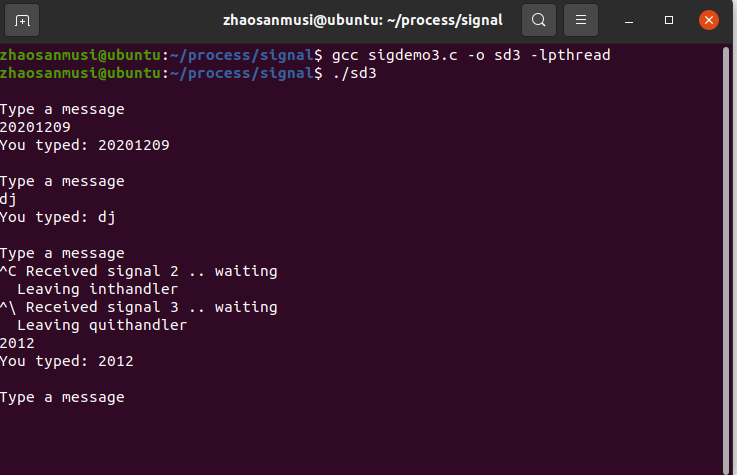
(三)signal
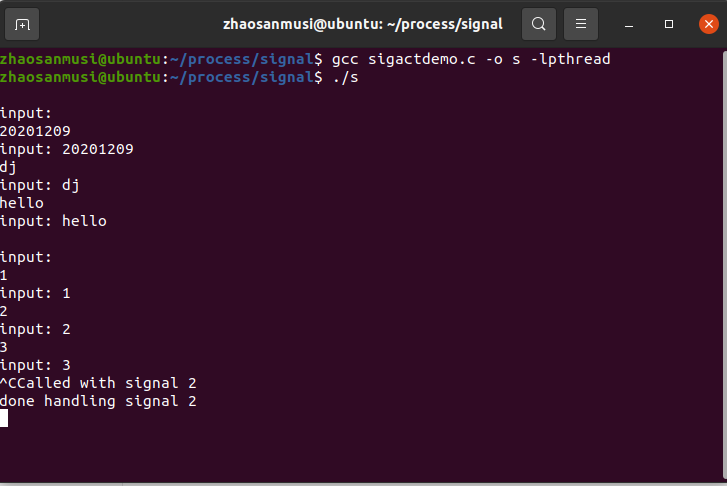
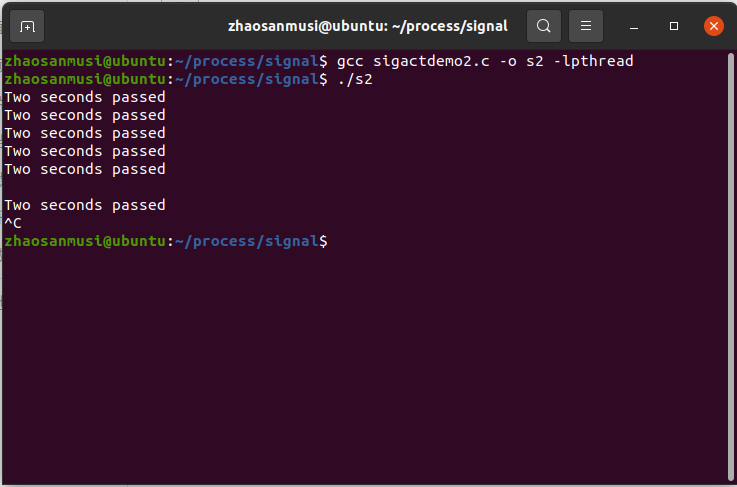
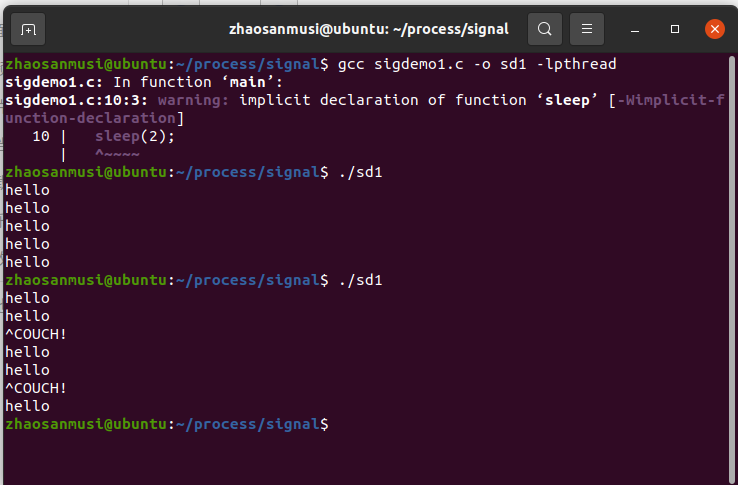
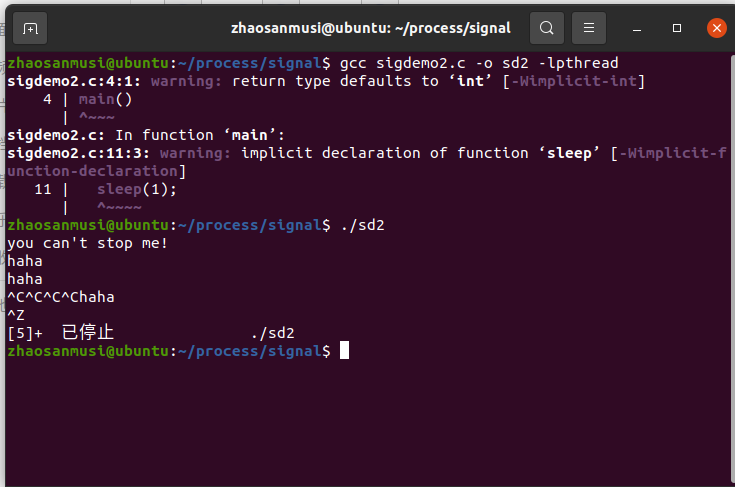
二、实验代码
fifo
//consumer
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#define FIFO_NAME "/tmp/myfifo"
#define BUFFER_SIZE PIPE_BUF
int main()
{
int pipe_fd;
int res;
int open_mode = O_RDONLY;
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE + 1];
int bytes = 0;
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
printf("Process %d opeining FIFO O_RDONLY \n", getpid());
pipe_fd = open(FIFO_NAME, open_mode);
printf("Process %d result %d\n", getpid(), pipe_fd);
if (pipe_fd != -1) {
do {
res = read(pipe_fd, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE);
bytes += res;
} while (res > 0);
close(pipe_fd);
} else {
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Process %d finished, %d bytes read\n", getpid(), bytes);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
//producer
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#define FIFO_NAME "/tmp/myfifo"
#define BUFFER_SIZE PIPE_BUF
#define TEN_MEG (1024 * 1024 * 10)
int main()
{
int pipe_fd;
int res;
int open_mode = O_WRONLY;
int bytes = 0;
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE + 1];
if (access(FIFO_NAME, F_OK) == -1) {
res = mkfifo(FIFO_NAME, 0777);
if (res != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not create fifo %s \n",
FIFO_NAME);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
printf("Process %d opening FIFO O_WRONLY\n", getpid());
pipe_fd = open(FIFO_NAME, open_mode);
printf("Process %d result %d\n", getpid(), pipe_fd);
if (pipe_fd != -1) {
while (bytes < TEN_MEG) {
res = write(pipe_fd, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE);
if (res == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Write error on pipe\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
bytes += res;
}
close(pipe_fd);
} else {
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Process %d finish\n", getpid());
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
//testmf
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int main()
{
int res = mkfifo("/tmp/myfifo", 0777);
if (res == 0) {
printf("FIFO created \n");
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
//tags
!_TAG_FILE_FORMAT 2 /extended format; --format=1 will not append ;" to lines/
!_TAG_FILE_SORTED 1 /0=unsorted, 1=sorted, 2=foldcase/
!_TAG_PROGRAM_AUTHOR Darren Hiebert /dhiebert@users.sourceforge.net/
!_TAG_PROGRAM_NAME Exuberant Ctags //
!_TAG_PROGRAM_URL http://ctags.sourceforge.net /official site/
!_TAG_PROGRAM_VERSION 5.9~svn20110310 //
BUFFER_SIZE consumer.c 10;" d file:
BUFFER_SIZE producer.c 10;" d file:
FIFO_NAME consumer.c 9;" d file:
FIFO_NAME producer.c 9;" d file:
TEN_MEG producer.c 11;" d file:
main consumer.c /^int main()$/;" f
main producer.c /^int main()$/;" f
main testmf.c /^int main()$/;" f
pipe
//listargs
#include <stdio.h>
main( int ac, char *av[] )
{
int i;
printf("Number of args: %d, Args are:\n", ac);
for(i=0;i<ac;i++)
printf("args[%d] %s\n", i, av[i]);
fprintf(stderr,"This message is sent to stderr.\n");
}
//pipe
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define oops(m,x) { perror(m); exit(x); }
int main(int ac, char **av)
{
int thepipe[2],
newfd,
pid;
if ( ac != 3 ){
fprintf(stderr, "usage: pipe cmd1 cmd2\n");
exit(1);
}
if ( pipe( thepipe ) == -1 )
oops("Cannot get a pipe", 1);
if ( (pid = fork()) == -1 )
oops("Cannot fork", 2);
if ( pid > 0 ){
close(thepipe[1]);
if ( dup2(thepipe[0], 0) == -1 )
oops("could not redirect stdin",3);
close(thepipe[0]);
execlp( av[2], av[2], NULL);
oops(av[2], 4);
}
close(thepipe[0]);
if ( dup2(thepipe[1], 1) == -1 )
oops("could not redirect stdout", 4);
close(thepipe[1]);
execlp( av[1], av[1], NULL);
oops(av[1], 5);
}
//pipedemo
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
int len, i, apipe[2];
char buf[BUFSIZ];
if ( pipe ( apipe ) == -1 ){
perror("could not make pipe");
exit(1);
}
printf("Got a pipe! It is file descriptors: { %d %d }\n",
apipe[0], apipe[1]);
while ( fgets(buf, BUFSIZ, stdin) ){
len = strlen( buf );
if ( write( apipe[1], buf, len) != len ){
perror("writing to pipe");
break;
}
for ( i = 0 ; i<len ; i++ )
buf[i] = 'X' ;
len = read( apipe[0], buf, BUFSIZ ) ;
if ( len == -1 ){
perror("reading from pipe");
break;
}
if ( write( 1 , buf, len ) != len ){
perror("writing to stdout");
break;
}
}
}
//pipedemo2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define CHILD_MESS "I want a cookie\n"
#define PAR_MESS "testing..\n"
#define oops(m,x) { perror(m); exit(x); }
main()
{
int pipefd[2];
int len;
char buf[BUFSIZ];
int read_len;
if ( pipe( pipefd ) == -1 )
oops("cannot get a pipe", 1);
switch( fork() ){
case -1:
oops("cannot fork", 2);
case 0:
len = strlen(CHILD_MESS);
while ( 1 ){
if (write( pipefd[1], CHILD_MESS, len) != len )
oops("write", 3);
sleep(5);
}
default:
len = strlen( PAR_MESS );
while ( 1 ){
if ( write( pipefd[1], PAR_MESS, len)!=len )
oops("write", 4);
sleep(1);
read_len = read( pipefd[0], buf, BUFSIZ );
if ( read_len <= 0 )
break;
write( 1 , buf, read_len );
}
}
}
//stdinredir1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main()
{
int fd ;
char line[100];
fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );
fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );
fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );
close(0);
fd = open("/etc/passwd", O_RDONLY);
if ( fd != 0 ){
fprintf(stderr,"Could not open data as fd 0\n");
exit(1);
}
fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );
fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );
fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );
}
//stdinredir2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
//#define CLOSE_DUP
//#define USE_DUP2
main()
{
int fd ;
int newfd;
char line[100];
fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );
fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );
fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );
fd = open("data", O_RDONLY);
#ifdef CLOSE_DUP
close(0);
newfd = dup(fd);
#else
newfd = dup2(fd,0);
#endif
if ( newfd != 0 ){
fprintf(stderr,"Could not duplicate fd to 0\n");
exit(1);
}
close(fd);
fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );
fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );
fgets( line, 100, stdin ); printf("%s", line );
}
//testtty
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
char *buf = "abcde\n";
write(0, buf, 6);
}
//whotofile
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
int pid ;
int fd;
printf("About to run who into a file\n");
if( (pid = fork() ) == -1 ){
perror("fork"); exit(1);
}
if ( pid == 0 ){
close(1); /* close, */
fd = creat( "userlist", 0644 ); /* then open */
execlp( "who", "who", NULL ); /* and run */
perror("execlp");
exit(1);
}
if ( pid != 0 ){
wait(NULL);
printf("Done running who. results in userlist\n");
}
return 0;
}
signal
//sigactdemo
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#define INPUTLEN 100
void inthandler();
int main()
{
struct sigaction newhandler;
sigset_t blocked;
char x[INPUTLEN];
newhandler.sa_handler = inthandler;
newhandler.sa_flags = SA_RESTART|SA_NODEFER
|SA_RESETHAND;
sigemptyset(&blocked);
sigaddset(&blocked, SIGQUIT);
newhandler.sa_mask = blocked;
if (sigaction(SIGINT, &newhandler, NULL) == -1)
perror("sigaction");
else
while (1) {
fgets(x, INPUTLEN, stdin);
printf("input: %s", x);
}
return 0;
}
void inthandler(int s)
{
printf("Called with signal %d\n", s);
sleep(s * 4);
printf("done handling signal %d\n", s);
}
//sigactdemo2
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void sig_alrm( int signo )
{
/*do nothing*/
}
unsigned int mysleep(unsigned int nsecs)
{
struct sigaction newact, oldact;
unsigned int unslept;
newact.sa_handler = sig_alrm;
sigemptyset( &newact.sa_mask );
newact.sa_flags = 0;
sigaction( SIGALRM, &newact, &oldact );
alarm( nsecs );
pause();
unslept = alarm ( 0 );
sigaction( SIGALRM, &oldact, NULL );
return unslept;
}
int main( void )
{
while( 1 )
{
mysleep( 2 );
printf( "Two seconds passed\n" );
}
return 0;
}
//sigdemo1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
void f(int);
int main()
{
int i;
signal( SIGINT, f );
for(i=0; i<5; i++ ){
printf("hello\n");
sleep(2);
}
return 0;
}
void f(int signum)
{
printf("OUCH!\n");
}
//sigdemo2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
main()
{
signal( SIGINT, SIG_IGN );
printf("you can't stop me!\n");
while( 1 )
{
sleep(1);
printf("haha\n");
}
}
//sigdemo3
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define INPUTLEN 100
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
void inthandler(int);
void quithandler(int);
char input[INPUTLEN];
int nchars;
signal(SIGINT, inthandler);//^C
signal(SIGQUIT, quithandler);//^\
do {
printf("\nType a message\n");
nchars = read(0, input, (INPUTLEN - 1));
if (nchars == -1)
perror("read returned an error");
else {
input[nchars] = '\0';
printf("You typed: %s", input);
}
}
while (strncmp(input, "quit", 4) != 0);
return 0;
}
void inthandler(int s)
{
printf(" Received signal %d .. waiting\n", s);
sleep(2);
printf(" Leaving inthandler \n");
}
void quithandler(int s)
{
printf(" Received signal %d .. waiting\n", s);
sleep(3);
printf(" Leaving quithandler \n");
}
进程间通信-信号-pipe-fifo的更多相关文章
- Linux中的pipe(管道)与named pipe(FIFO 命名管道)
catalogue . pipe匿名管道 . named pipe(FIFO)有名管道 1. pipe匿名管道 管道是Linux中很重要的一种通信方式,是把一个程序的输出直接连接到另一个程序的输入,常 ...
- [15]APUE:pipe / FIFO
管道 pipe 一.概述 管道(pipe / FIFO)是一种文件,属于 pipefs 文件系统类型,可以使用 read.write.close 等系统调用进行操作 其本质是内核维护了一块缓冲区与管道 ...
- Linux进程间通信——信号集函数
一.什么是信号 用过Windows的我们都知道,当我们无法正常结束一个程序时,可以用任务管理器强制结束这个进程,但这其实是怎么实现的呢?同样的功能在Linux上是通过生成信号和捕获信号来实现的,运行中 ...
- 详解linux进程间通信-信号
前言:之前说看<C++ Primer >暂时搁浅一下,迷上公司大神写的代码,想要明白,主要是socket.进程间通信! 知道进程间通信:信号.信号量.管道.消息队列.共享内存(共享存储), ...
- 进程间通信之数据传输--FIFO
One of the fundamental features that makes Linux and other Unices useful is the “pipe”. Pipes allow ...
- linux多进/线程编程(4)——进程间通信之pipe和fifo
前言: Linux环境下,进程地址空间相互独立,每个进程各自有不同的用户地址空间.任何一个进程的全局变量在另一个进程中都看不到,所以进程和进程之间不能相互访问,要交换数据必须通过内核,在内核中开辟一块 ...
- Linux 进程间通信之管道(pipe),(fifo)
无名管道(pipe) 管道可用于具有亲缘关系进程间的通信,有名管道克服了管道没有名字的限制,因此,除具有管道所具有的功能外,它还允许无亲缘关系进程间的通信: 定义函数: int pipe(int f ...
- Linux进程间通信 -- 管道(pipe)
前言 进程是一个独立的资源管理单元,不同进程间的资源是独立的,不能在一个进程中访问另一个进程的用户空间和内存空间.但是,进程不是孤立的,不同进程之间需要信息的交互和状态的传递,因此需要进程间数据 ...
- python进程间通信--信号Signal
信号signal 是python进程间通信多种机制中的其中一种机制.可以对操作系统进程的控制,当进程中发生某种原因而中断时,可以异步处理这个异常. 信号通过注册的方式‘挂’在一个进程中,并且不会阻塞该 ...
- Linux进程间通信—信号
三.信号(Signal) 信号是Unix系统中使用的最古老的进程间通信的方法之一.操作系统通过信号来通知某一进程发生了某一种预定好的事件:接收到信号的进程可以选择不同的方式处理该信号,一是可以采用默认 ...
随机推荐
- canvas 学习笔记
1.利用上下文对象进行绘制画笔 var canvas=canvas.getContext('2d') 2.绘制路径 canvas.rect(30,30,300,300) 3.填充 canvas.fil ...
- LogAgent —— etcd+kafka+zookeeper+go实现实时读取日志发送到kafka,并实现热加载配置读取的日志路径
工具包目录结构: .├── conf│ ├── logAgent.ini│ └── logAgentConfig.go├── etcd│ └── etcd.go├── kafka│ └ ...
- jmeter接口之json提取器应用
在接口测试中有一个这样的场景:业务接口需要用到登录token:下个接口需要用到前个接口返回值作为参数,该怎么实现? 首先先看下登录.业务接口,本文用的jmeter版本为5.4.1 一.json提取器设 ...
- Java编写1到100质数之和
int sum = 0; int k = 2; // 找出1-100的质数之和 for (int i = 2; i <= 100; i++) { // i值为2,质数为除去1和自身整除的数 j初 ...
- Blender中服装网格重新拓扑实录
最近了解到游戏行业服装的一些处理流程.简单来说: 用MD等做衣服的软件,将服装做出来: 导出2种模型:缝合好的服装模型(叫它3d)以及没有变形的平铺板片模型(叫它2d),建议导出单层的,都要带着UV, ...
- C# 生成二维码方法(QRCoder)
前言 二维码很多地方都有使用到.如果是静态的二维码还是比较好处理的,通过在线工具就可以直接生成一张二维码图片,比如:草料二维码. 但有的时候是需要动态生成的(根据动态数据生成),这个使用在线就工具就无 ...
- 记录multipartFile表单类型转化为file
导入依赖 <dependency> <groupId>commons-io</groupId> <artifactId>commons-io</a ...
- python的开发工具pycharm的安装
如何下载 如何安装 如何配置环境 (mac和win版本) Pycharm的安装与配置以及汉化 一.pycharm的安装与配置(一定要去pycharm的官网去下载哦!) 1.最受欢迎的开发工具pycha ...
- geoserver的自动化部署
年后接到一个任务,需求是这样的: 搭建一个geoserver服务器,将公司内部的mbtile数据(EPSG:3857)发布出去 服务的输出格式为MBTiles with vector tiles的矢量 ...
- Vue + Element table的@select方法获取当table中的id值都相同时,获取他们索引
先说下问题情况,原本通过双重forEach方法方法,遍历可以获取到被勾选中的索引. let arr = []val.forEach((val, index) => { this.TableDat ...
