Chap4: question: 19 - 28
19. 二叉树的镜像(递归)
即:交换所有节点的左右子树。从下往上 或 从上往下 都可以。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct BTNode
{
int v; // default positive Integer.
BTNode *pLeft;
BTNode *pRight;
BTNode(int x) : v(x), pLeft(NULL), pRight(NULL) {}
};
/********************************************************/
/***** Basic functions ***********/
BTNode* createBinaryTree(int r)
{
BTNode *pRoot = new BTNode(r);
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
if(u != 0)
pRoot->pLeft = createBinaryTree(u);
if(v != 0)
pRoot->pRight = createBinaryTree(v);
return pRoot;
}
void release(BTNode *root){
if(root == NULL) return;
release(root->pLeft);
release(root->pRight);
delete[] root;
root = NULL;
}
void print(BTNode *root, int level = 1){
if(root == NULL) { cout << "NULL"; return; };
string s;
for(int i = 0; i < level; ++i) s += " ";
cout << root->v << endl << s;
print(root->pLeft, level+1);
cout << endl << s;
print(root->pRight, level+1);
}
/******************************************************************/
void mirrorTree(BTNode *root)
{
if(!root || (!root->pLeft && !root->pRight)) return;
/* 交换左右子树 */
BTNode *pTem = root->pLeft;
root->pLeft = root->pRight;
root->pRight = pTem; mirrorTree(root->pLeft);
mirrorTree(root->pRight);
} int main(){
int TestTime = 3, k = 1;
while(k <= TestTime)
{
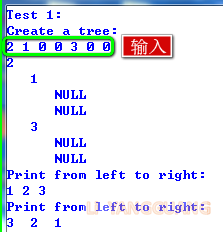
cout << "Test " << k++ << ":" << endl; cout << "Create a tree: " << endl;
BTNode *pRoot = createBinaryTree(8);
print(pRoot);
cout << endl; cout << "The mirror tree: " << endl;
mirrorTree(pRoot);
print(pRoot);
cout << endl; release(pRoot);
}
return 0;
}
20. 顺时针打印矩阵
#include <stdio.h> void printMatrix(int (*A)[], int rows, int columns)
{
if(rows < || columns < ) return;
int r1, r2, c1, c2;
r1 = c1 = , r2 = rows-, c2 = columns-;
while(r1 <= r2 && c1 <= c2) /* 打印结束时, r1 = r2+1, c1 = c2+1; */
{
for(int i = c1; i <= c2 && r1 <= r2; ++i)
printf("%d ", A[r1][i]);
++r1;
for(int i = r1; c1 <= c2 && i <= r2; ++i)
printf("%d ", A[i][c2]); /* 要保证 c1 <= c2 */
--c2;
for(int i = c2; i >= c1 && r1 <= r2; --i)
printf("%d ", A[r2][i]);
--r2;
for(int i = r2; i >= r1 && c1 <= c2; --i)
printf("%d ", A[i][c1]);
++c1;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
int test1[][] = {{, , },
{, , },
{, , }};
printMatrix(test1, , ); int test2[][] = {, , };
printMatrix(test2, , ); /* // first set int (*A)[1], then began called below.
int test3[3][1] = {{1}, {2}, {3}};
printMatrix(test3, 3, 1); int test4[1][1] = {1};
printMatrix(test4, 1, 1);
*/
return ;
}

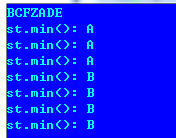
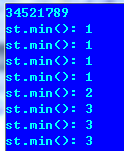
21. 包含 min 函数的栈
要求调用 min,pop,push,时间复杂度都是 O(1)。
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <cassert>
#include <string>
template<typename T> class Stack
{
public:
void push(T value);
void pop();
T min();
private:
std::stack<T> data;
std::stack<T> minData;
};
template<typename T> void Stack<T>::push(T value)
{
data.push(value);
if(minData.empty() || minData.top() >= value)
minData.push(value);
else
minData.push(minData.top());
}
template<typename T> void Stack<T>::pop()
{
assert(data.size() > && minData.size() > );
data.pop();
minData.pop();
}
template<typename T> T Stack<T>::min()
{
return minData.top();
} int main()
{
Stack<char> st;
std::string numbers;
while(std::cin >> numbers)
{
for(size_t i = ; i < numbers.length(); ++i) st.push(numbers[i]);
for(size_t i = ; i < numbers.length(); ++i)
{
std::cout << "st.min(): " << st.min() << std::endl;
st.pop();
}
}
return ;
}
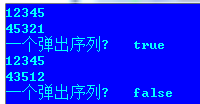
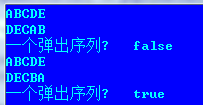
22. 根据栈的压入序列,判断一个序列是否是弹出序列。
#include <iostream>
#include <string> bool isPopOrder(const std::string pushS, const std::string popS)
{
size_t outId1 = 0, outId2 = 0, len1 = pushS.length(), len2 = popS.length();
if(len1 != len2) return false;
int *stack = new int[len1];
int tail = 0; // 栈尾
while(outId1 < len1 && outId2 < len2)
{
while(pushS[outId1] != popS[outId2])
{
stack[tail++] = pushS[outId1++]; // 入栈
}
outId1++, outId2++;
while(tail != 0 && popS[outId2] == stack[tail-1])
{
++outId2;
tail--; // 出栈
}
}
delete[] stack;
if(tail == 0) return true; // 栈空
else return false;
} int main()
{
std::string numbers;
std::string popNumbers;
while(std::cin >> numbers >> popNumbers)
{
std::cout << "一个弹出序列? " ; if(isPopOrder(numbers, popNumbers))
std::cout << "true" << std::endl;
else std::cout << "false" << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
23. 从上往下打印二叉树
Go:(Chap2: question: 1 - 10—>6. 重建二叉树—>二叉树的各种遍历)Link: http://www.cnblogs.com/liyangguang1988/p/3667443.html
24. 判断序列是否为二叉搜索树的后序遍历(递归)
note: 二叉搜索树和遍历序列一一对应。
例:后序序列 {3,5,4,6,11,13,12, 10, 8} ,可画出一颗二叉搜索树。
#include <iostream>
/* verify the seq which should be the postOrder of a Binary Search Tree */
bool postOrderOfBST(int sequence[], int len)
{
if(sequence == NULL || len == ) return false;
bool answer = false;
int root = sequence[len-]; /* value of root node */ int leftLength = ;
for(; leftLength < len-; ++leftLength)
{
if(sequence[leftLength] > root) break;
}
/* verify right-subtree, should big than root */
for(int i = leftLength + ; i < len -; ++i)
{
if(sequence[i] < root) return false;
} int rightLength = len - - leftLength;
bool left = true, right = true;
if(leftLength > )
bool left = postOrderOfBST(sequence, leftLength);
if(rightLength)
bool right = postOrderOfBST(sequence+leftLength, rightLength);
return (left && right);
} void printResult(bool v)
{
std::cout << "Is LRD of a BFS? " ;
if(v) std::cout << "true" << std::endl;
else std::cout << "false" << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
std::cout << "Test 1: ";
int test1[] = {, , , , , , , , };
printResult(postOrderOfBST(test1, sizeof(test1) / )) ; std::cout << "Test 2: ";
int test2[] = {, , };
printResult(postOrderOfBST(test2, sizeof(test2) / )); std::cout << "Test 3: ";
int test3[] = {};
printResult(postOrderOfBST(test3, sizeof(test3) / )); return ;
}
25. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径(递归)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct BTNode
{
int v; // default positive Integer.
BTNode *pLeft;
BTNode *pRight;
BTNode(int x) : v(x), pLeft(NULL), pRight(NULL) {}
};
/********************************************************/
/***** Basic functions ***********/
BTNode* createBinaryTree(int r)
{
BTNode *pRoot = new BTNode(r);
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
if(u != )
pRoot->pLeft = createBinaryTree(u);
if(v != )
pRoot->pRight = createBinaryTree(v);
return pRoot;
}
void release(BTNode *root){
if(root == NULL) return;
release(root->pLeft);
release(root->pRight);
delete[] root;
root = NULL;
}
void print(BTNode *root, int level = ){
if(root == NULL) { cout << "NULL"; return; };
string s;
for(int i = ; i < level; ++i) s += "\t";
cout << root->v << endl << s;
print(root->pLeft, level+);
cout << endl << s;
print(root->pRight, level+);
}
/******************************************************************/
void findPath(BTNode *root, int target, vector<int>& path, int curSum)
{
if(root == NULL) return;
curSum += root->v;
path.push_back(root->v);
if(!root->pLeft && !root->pRight && (curSum == target)) // root node is a leaf, get a path.
{
for(auto it = path.begin(); it != path.end(); ++it)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << endl;
}
findPath(root->pLeft, target, path, curSum);
findPath(root->pRight, target, path, curSum);
path.pop_back();
} void findPath(BTNode *root, int target)
{
if(root == NULL) return;
vector<int> path;
findPath(root, target, path, );
} int main(){
int TestTime = , k = ;
while(k <= TestTime)
{
int root;
cout << "Test " << k++ << ":" << endl; cout << "Create a tree: " << endl;
cin >> root;
BTNode *pRoot = createBinaryTree(root);
print(pRoot);
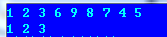
cout << endl; cout << "target : 22" << endl << "findPath :" << endl;
findPath(pRoot, ); release(pRoot);
}
return ;
}
Code
26. 复杂链表的复制
#include <stdio.h>
typedef char Elem;
typedef struct ComplexListNode
{
Elem e;
ComplexListNode *next;
ComplexListNode *sibling;
} ComplexList;
ComplexListNode Node[] = {};
/***************************************************************/
ComplexList* creatComplexList()
{
for(int i = ; i < ; ++i)
Node[i].e = i + 'A';
char u, v;
while((scanf("%c%c", &u, &v) == ) )
{
if(u >= 'A' && u <= 'Z' && v >= 'A' && v <= 'Z')
{
if(Node[u-'A'].next == NULL)
Node[u-'A'].next = &Node[v-'A'];
else if(Node[u-'A'].sibling == NULL)
Node[u-'A'].sibling = &Node[v-'A'];
}
if(getchar() == '\n') break;
}
return &Node[];
} void printComplexList(ComplexList *pHead)
{
ComplexListNode *p = pHead;
while(p != NULL)
{
printf("%c -> ", p->e);
p = p->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
p = pHead;
while(p != NULL)
{
if(p->sibling != NULL)
{
printf("%c -> ", p->e);
printf("%c\t", p->sibling->e);
}
p = p->next;
}
}
/***************************************************************************/
void cloneNodes(ComplexList *pHead)
{
ComplexListNode *p = pHead;
while(p != NULL)
{
ComplexListNode *newNode = new ComplexListNode;
newNode->e = p->e + ;
newNode->next = p->next;
newNode->sibling = NULL;
p->next = newNode;
p = newNode->next;
}
} void connectSibling(ComplexList *pHead)
{
ComplexListNode *pPre = pHead, *p;
while(pPre != NULL && pPre->next != NULL)
{
p = pPre->next;
if(pPre->sibling != NULL)
p->sibling = pPre->sibling->next;
pPre = p->next;
}
} ComplexList* getClonedComplexList(ComplexList *pHead)
{
ComplexListNode *pPre = pHead, *newHead = NULL, *p;
while(pPre != NULL && pPre->next != NULL)
{
if(newHead != NULL)
{
p->next = pPre->next;
p = p->next;
}
else
{
newHead = pPre->next;
p = newHead;
}
pPre->next = pPre->next->next;
pPre = pPre->next;
}
return newHead;
} ComplexList* clone(ComplexList *pHead)
{
cloneNodes(pHead);
connectSibling(pHead);
return getClonedComplexList(pHead);
} int main()
{
ComplexList *pHead = creatComplexList();
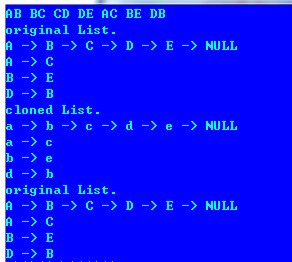
printf("original List.\n");
printComplexList(pHead); ComplexList *newHead = clone(pHead);
printf("cloned List.\n");
printComplexList(newHead); printf("original List.\n");
printComplexList(pHead); return ;
}
程序说明:对一个结点,若 next 和 sibling 同时为 0,先保存 next 指针。
样例输入:AB AC BC BE CD DE DB(回车换行)
27.二叉搜索树生成有序双向链表
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
typedef struct BTNode
{
int v; // In this code, default positive Integer.
BTNode *pLeft;
BTNode *pRight;
BTNode(int x) : v(x), pLeft(NULL), pRight(NULL) {}
} DbList;
/********************************************************/
/***** Basic functions for binary tree ***********/
BTNode* createBinaryTree() // input a preOrder sequence, 0 denote empty node.
{
BTNode *pRoot = NULL;
int r;
cin >> r;
if(r != ) // equal to if(!r) return;
{
pRoot = new BTNode(r);
pRoot->pLeft = createBinaryTree();
pRoot->pRight = createBinaryTree(); }
return pRoot;
} void printBinaryTree(BTNode *root, int level = ){
if(root == NULL) { cout << "NULL"; return; };
string s;
for(int i = ; i < level; ++i) s += " ";
cout << root->v << endl << s;
printBinaryTree(root->pLeft, level+);
cout << endl << s;
printBinaryTree(root->pRight, level+);
} // void releaseBinaryTree(BTNode *root){
// if(root == NULL) return;
// releaseBinaryTree(root->pLeft);
// releaseBinaryTree(root->pRight);
// delete[] root;
// root = NULL;
// }
/******************************************************************/
/****************** basic function for double linked list. *******/
void printDbList(DbList *pHead)
{
if(pHead == NULL) return;
DbList *p = pHead;
cout << "Print from left to right:" << endl;
while(p->pRight != NULL) { cout << p->v << " "; p = p->pRight;}
cout << p->v << endl; cout << "Print from left to right:" << endl;
while(p != NULL) { printf("%-3d", p->v); p = p->pLeft;}
cout << endl;
}
void releaseDbList(DbList *pHead)
{
if(pHead == NULL) return;
releaseDbList(pHead->pRight);
delete[] pHead;
}
/******************************************************************/
/***** binary search tree translate to double linked list ******/
void convert(BTNode *root, BTNode **tail)
{
if(root == NULL) return; if(root->pLeft != NULL)
convert(root->pLeft, tail);
root->pLeft = *tail;
if(*tail)
(*tail)->pRight = root;
*tail = root; if(root->pRight != NULL)
convert(root->pRight, tail);
}; BTNode* treeToDList(BTNode *root)
{
if(root == NULL) return NULL;
BTNode *tail = NULL;
convert(root, &tail);
BTNode *pHead = tail;
while(pHead != NULL && pHead->pLeft != NULL)
pHead = pHead->pLeft;
return pHead;
} int main(){
int TestTime = , k = ;
while(k <= TestTime)
{
cout << "Test " << k++ << ":" << endl; cout << "Create a tree: " << endl;
BTNode *pRoot = createBinaryTree();
printBinaryTree(pRoot);
cout << endl; DbList *DbListHead = treeToDList(pRoot); // pRoot translate to Double linked list. printDbList(DbListHead);
cout << endl; releaseDbList(DbListHead);
}
return ;
}
note: 按先序输入,0表示结束。
样例输入:
a. 10 6 4 0 0 8 0 0 14 12 0 0 16 00
b. 0 (生成空树)
c. 1
d. 2 1 0 0 3 0 0
28.字符串的全排列
Go: ( 3. 字符的排列组合 )
相关例题:八皇后问题(可扩展为 n 皇后问题)
题目:8 x 8国际象棋上,摆8 个皇后,求她们任两个不同行、不同列且不在同一对角线上的摆法个数。
#include <stdio.h>
int solutionNumber = 0; void print(int data[], int length)
{
for(int i = 0; i < length; ++i)
printf("(%d, %d) ", i+1, data[i]+1);
printf("\n");
}
bool judge(int data[], int length)
{
for(int i = 0; i < length; ++i)
{
for(int j = i +1; j < length; ++j)
{
if((j - i) == (data[j] - data[i]) || (j - i) == data[i] - data[j])
return false; // not the solution
} }
return true;
}
void swap(int &a, int &b) // do not forget the reference.
{
int tem = a;
a = b;
b = tem;
} void permutation(int data[], int length, int begin)
{
if(begin == length-1)
{
if(judge(data, length))
{
// print(data, length);
++solutionNumber;
}
return;
}
for(int start = begin; start < length; ++start)
{
swap(data[start], data[begin]);
permutation(data, length, begin+1);
swap(data[start], data[begin]);
}
} int main()
{
int columnIndex[] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15}; /* 不在同行同列 */
permutation(columnIndex, 8, 0); /* 判断是否可以不在同一对角线 */
printf("Number of Solution: %d\n", solutionNumber);
return 0;
}
Chap4: question: 19 - 28的更多相关文章
- ubuntu下设置jupyter notebook 2017年07月29日 19:28:34 小旋锋 阅读数:8329 标签: ubuntu 更多 个人分类: python 二三事 来源:http://blog.csdn.net/suzyu12345/article/details/51037905 Ipython Notebook现在已经改名为Ipython jupyter,是最知名最好用的
ubuntu下设置jupyter notebook 来源:http://blog.csdn.net/suzyu12345/article/details/51037905 Ipython No ...
- 根据pid获得路径 2006-10-25 19:28
这是编写kill process时用到的 BOOL GetProcessModule(DWORD dwPID, DWORD dwModuleID, LPMODULEENTRY32 lpMe32, DW ...
- JavaSE_ IO流 总目录(19~22)
JavaSE学习总结第19天_IO流119.01 集合的特点和数据结构总结19.02 如何选择使用哪种集合19.03 集合常见功能和遍历方式总结19.04 异常的概述和分类19.05 JVM默认处理异 ...
- JavaSE学习总结第19天_IO流1
19.01 集合的特点和数据结构总结 HashSet.HashMap.Hashtable判断元素唯一性的方式: 通过对象的hashCode和equals方法来完成元素唯一性 如果对象的hashC ...
- 1Z0-050
QUESTION 13 View the Exhibit.Examine the following command that is executed for the TRANSPORT table ...
- A.Kaw矩阵代数初步学习笔记 5. System of Equations
“矩阵代数初步”(Introduction to MATRIX ALGEBRA)课程由Prof. A.K.Kaw(University of South Florida)设计并讲授. PDF格式学习笔 ...
- .NET运用AJAX 总结及其实例
1.AJAX简介 (1.没有AJAX会怎么样?普通的ASP.Net每次执行服务端方法的时候都要刷新当前页面,比如实现显示服务器的时间.每次都要刷新页面的坏处:页面刷新打断用户操作.速度慢.增加服务器的 ...
- 转:switch内部的变量定义问题(goto类似)
自我总结:(之前查过goto和switch的资料但是一直没有搞懂,直到今天看到这个讨论才懂了) 1 int a; 是个描述,而不是个命令,只是说明我需要空间,编译器会保证在相应的作用域之中这 ...
- HTML+CSS+JAVASCRIPT 总结
1. HTML 1: <!doctype html> 2: <!-- This is a test html for html, css, javascript --> 3: ...
随机推荐
- 在Eclipse上建立hbase 0.98.3/0.96.2源代码阅读环境
2.1. 切换到源代码目录,执行: mvn 黄色部分作用为设置代理.由于本人的编译环境在公司内网,所以需要设置代理 2.2. 生成eclipse项目环境: mvn eclipse:eclipse -D ...
- 【转】Nginx+Tomcat+Memcached集群
Tomcat集群session同步方案有以下几种方式: 使用tomcat自带的cluster方式,多个tomcat间自动实时复制session信息,配置起来很简单.但这个方案的效率比较低,在大并发下表 ...
- 团队开发——冲刺1.f
冲刺阶段一(第六天) 1.昨天做了什么? 为解决自己电脑的问题,查找关于C#的资料,后期做准备. 2.今天准备做什么? 把最初版与交予代码书写的同学,进行整合:测试程序. 3.遇到什么困难? 第一次整 ...
- UIkit框架之UIwebview
1.继承链:UIview:UIResponder:NSObject 2.使用loadHTMLString:baseURL:方法来加载本地的HTML文件,或者使用 loadRequest:方法来加载网络 ...
- windows核心编程---第六章 线程的调度
每个线程都有一个CONTEXT结构,保存在线程内核对象中.大约每隔20ms windows就会查看所有当前存在的线程内核对象.并在可调度的线程内核对象中选择一个,将其保存在CONTEXT结构的值载入c ...
- source insight 相对路径
source insight项目 在移动到另外一个地方时,会因为之前是绝对路径而导致,项目中的文件都不可用,需要重新把这些文件添加一遍. 这是个令人讨厌的事情. 解决办法为创建项目时设定为绝对路径.方 ...
- notifyDataSetInvalidated()跟notifyDataSetChanged()的区别
public void notifyDataSetChanged(): 通过一个外部的方法控制,如果适配器的内容改变了,那么就会强制调用getView来刷新每个Item的内容.这个方法内部实现了在每个 ...
- python数据结构与算法——图的基本实现及迭代器
本文参考自<复杂性思考>一书的第二章,并给出这一章节里我的习题解答. (这书不到120页纸,要卖50块!!,一开始以为很厚的样子,拿回来一看,尼玛.....代码很少,给点提示,然后让读者自 ...
- iOS 的基本框架
在iOS中框架是一个目录,包含了共享资源库,用于访问该资源库中储存的代码的头文件,以及图像.声音文件等其他资源.共享资源库定义应用程序可以调用的函数和方法. iOS为应用程序开发提供了许多可使用 ...
- JDK源码解读之toUnsignedString
我们知道,所有整数都是通过二进制编码的形式存储在内存中的.比如32位的整数,最高位是符号位,0代表正数,1代表负数. 那么怎么才能够将整数的二进制编码形式打印出来呢?Integer类提供了一个公有静态 ...