Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 2) A ,B ,C 暴力,暴力,暴力
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Mike is trying rock climbing but he is awful at it.
There are n holds on the wall, i-th hold is at height ai off the ground. Besides, let the sequence ai increase, that is, ai < ai + 1 for all ifrom 1 to n - 1; we will call such sequence a track. Mike thinks that the track a1, ..., an has difficulty 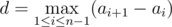 . In other words, difficulty equals the maximum distance between two holds that are adjacent in height.
. In other words, difficulty equals the maximum distance between two holds that are adjacent in height.
Today Mike decided to cover the track with holds hanging on heights a1, ..., an. To make the problem harder, Mike decided to remove one hold, that is, remove one element of the sequence (for example, if we take the sequence (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) and remove the third element from it, we obtain the sequence (1, 2, 4, 5)). However, as Mike is awful at climbing, he wants the final difficulty (i.e. the maximum difference of heights between adjacent holds after removing the hold) to be as small as possible among all possible options of removing a hold. The first and last holds must stay at their positions.
Help Mike determine the minimum difficulty of the track after removing one hold.
The first line contains a single integer n (3 ≤ n ≤ 100) — the number of holds.
The next line contains n space-separated integers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ 1000), where ai is the height where the hold number i hangs. The sequence ai is increasing (i.e. each element except for the first one is strictly larger than the previous one).
Print a single number — the minimum difficulty of the track after removing a single hold.
3
1 4 6
5
5
1 2 3 4 5
2
5
1 2 3 7 8
4
In the first sample you can remove only the second hold, then the sequence looks like (1, 6), the maximum difference of the neighboring elements equals 5.
In the second test after removing every hold the difficulty equals 2.
In the third test you can obtain sequences (1, 3, 7, 8), (1, 2, 7, 8), (1, 2, 3, 8), for which the difficulty is 4, 5 and 5, respectively. Thus, after removing the second element we obtain the optimal answer — 4.
题意:依次只删掉2-(n-1) 的点,找到每次相邻的最大值,再找最大值里的最小值;
思路:暴力,直接贴代码;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
#define eps 1e-14
const int N=2e5+,M=1e6+,inf=1e9+,mod=1e9+;
int a[N];
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
int ans=inf;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
int maxx=;
for(int t=;t<=n;t++)
{
if(i==t)continue;
if(i+==t)
maxx=max(maxx,a[t]-a[t-]);
else
maxx=max(maxx,a[t]-a[t-]); }
ans=min(ans,maxx);
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You got a box with a combination lock. The lock has a display showing n digits. There are two buttons on the box, each button changes digits on the display. You have quickly discovered that the first button adds 1 to all the digits (all digits 9 become digits 0), and the second button shifts all the digits on the display one position to the right (the last digit becomes the first one). For example, if the display is currently showing number 579, then if we push the first button, the display will show 680, and if after that we push the second button, the display will show 068.
You know that the lock will open if the display is showing the smallest possible number that can be obtained by pushing the buttons in some order. The leading zeros are ignored while comparing numbers. Now your task is to find the desired number.
The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000) — the number of digits on the display.
The second line contains n digits — the initial state of the display.
Print a single line containing n digits — the desired state of the display containing the smallest possible number.
3
579
024
4
2014
0142
题意:你可以让每个数+1,再循环让每个数向后移一位,求最小;
思路:暴力,n*n*10;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
#define eps 1e-14
const int N=2e5+,M=1e6+,inf=1e9+,mod=1e9+;
char a[N];
string s[N];
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
scanf("%s",a);
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
a[i+n]=a[i];
a[*n]=;
string minn="";
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
s[i].clear();
for(int t=i;t<i+n;t++)
s[i]+=a[t];
if(minn=="")
minn=s[i];
else if(minn>s[i])
minn=s[i];
for(int t=;t<=;t++)
{
for(int j=;j<n;j++)
{
s[i][j]+=;
if(s[i][j]>'')
s[i][j]-=;
}
if(minn>s[i])
minn=s[i];
}
}
cout<<minn<<endl;
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You are given an n × m rectangular table consisting of lower case English letters. In one operation you can completely remove one column from the table. The remaining parts are combined forming a new table. For example, after removing the second column from the table
abcd
edfg
hijk
we obtain the table:
acd
efg
hjk
A table is called good if its rows are ordered from top to bottom lexicographically, i.e. each row is lexicographically no larger than the following one. Determine the minimum number of operations of removing a column needed to make a given table good.
The first line contains two integers — n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 100).
Next n lines contain m small English letters each — the characters of the table.
Print a single number — the minimum number of columns that you need to remove in order to make the table good.
1 10
codeforces
0
4 4
case
care
test
code
2
5 4
code
forc
esco
defo
rces
4
In the first sample the table is already good.
In the second sample you may remove the first and third column.
In the third sample you have to remove all the columns (note that the table where all rows are empty is considered good by definition).
Let strings s and t have equal length. Then, s is lexicographically larger than t if they are not equal and the character following the largest common prefix of s and t (the prefix may be empty) in s is alphabetically larger than the corresponding character of t.
题意:n个单词,每次可以删除一列,使得n个单词字典序;
思路:暴力;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
#define eps 1e-14
const int N=1e2+,M=1e6+,inf=1e9+,mod=1e9+;
int n,m;
int flag[N];
string a[N];
int check(int x)
{
string st[N];
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
st[i].clear();
for(int t=;t<=x;t++)
if(!flag[t])
st[i]+=a[i][t];
if(i)
{
if(st[i]<st[i-])
return ;
}
}
return ;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
cin>>a[i];
int ans=;
for(int i=;i<m;i++)
{
if(check(i)==)
{
flag[i]=;
ans++;
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 2) A ,B ,C 暴力,暴力,暴力的更多相关文章
- 暴力+构造 Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 2) C. Removing Columns
题目传送门 /* 题意:删除若干行,使得n行字符串成递增排序 暴力+构造:从前往后枚举列,当之前的顺序已经正确时,之后就不用考虑了,这样删列最小 */ /*********************** ...
- 构造+暴力 Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 2) B. Secret Combination
题目传送门 /* 构造+暴力:按照题目意思,只要10次加1就变回原来的数字,暴力枚举所有数字,string大法好! */ /************************************** ...
- Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 2) C. Removing Columns 暴力
C. Removing Columns time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- Codeforces Round #283 Div.2 D Tennis Game --二分
题意: 两个人比赛,给出比赛序列,如果为1,说明这场1赢,为2则2赢,假如谁先赢 t 盘谁就胜这一轮,谁先赢 s 轮则赢得整个比赛.求有多少种 t 和 s 的分配方案并输出t,s. 解法: 因为要知道 ...
- Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 2)
A:暴力弄就好,怎么方便怎么来. B:我们知道最多加10次, 然后每次加1后我们求能移动的最小值,大概O(N)的效率. #include<bits/stdc++.h> using name ...
- codeforces 497c//Distributing Parts// Codeforces Round #283(Div. 1)
题意:有n个区间[ai,bi],然后有n个人落在[ci,di],每个人能用ki次.问一种方式站满n个区间. 两种区间都用先x后y的升序排序.对于当前的区间[ai,bi],将ci值小于当前ai的全部放入 ...
- codeforces 497b// Tennis Game// Codeforces Round #283(Div. 1)
题意:网球有一方赢t球算一场,先赢s场的获胜.数列arr(长度为n)记录了每场的胜利者,问可能的t和s. 首先,合法的场景必须: 1两方赢的场数不一样多. 2赢多的一方最后一场必须赢. 3最后一场必须 ...
- Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 2) B. Secret Combination 暴力水题
B. Secret Combination time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standa ...
- Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 2) A. Minimum Difficulty 暴力水题
A. Minimum Difficulty time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standa ...
随机推荐
- 【BZOJ1977】[BeiJing2010组队]次小生成树 Tree 最小生成树+倍增
[BZOJ1977][BeiJing2010组队]次小生成树 Tree Description 小 C 最近学了很多最小生成树的算法,Prim 算法.Kurskal 算法.消圈算法等等. 正当小 C ...
- 【BZOJ2870】最长道路tree 点分治+树状数组
[BZOJ2870]最长道路tree Description H城很大,有N个路口(从1到N编号),路口之间有N-1边,使得任意两个路口都能互相到达,这些道路的长度我们视作一样.每个路口都有很多车辆来 ...
- passback_params 支付回调的 原样返回字段 自定义字段的存放字段
开放平台文档中心 https://docs.open.alipay.com/204/105465/ passback_params String 否 512 公用回传参数,如果请求时传递了该参数,则返 ...
- [mysql]清除单表大量数据方法(需保留部分数据)
大半夜的在删除线上的日志数据,需要清理的大概有1亿八千万条...任务艰巨. 毕业前没学过数据库,所以对于如何清理大量数据还真一时不知道该怎么办才好.刚开始确实想过对表进行重命名的方式来处理,不过当时因 ...
- Nginx服务监听端口修改启动bug
监听的端口从80 修改到其他端口出现启动不起来问题. 解决方案如下: yum install policycoreutils-python sudo cat /var/log/audit/audit. ...
- 扩展运算符和rest运算符
扩展运算符 扩展运算符用三个点号表示,功能是把数组或类数组对象展开成一系列用逗号隔开的值 一.拆分数组 扩展运算符可以直接把数组拆分成用逗号隔开的值 <template> <sect ...
- 洛谷 P3393 逃离僵尸岛
洛谷 这道题目其实是最短路裸题. 首先看到题目,要求的到"被占点"距离不大于S的点,自然想到了以"被占点"为源点,求一遍最短路,处理出"危险点&quo ...
- LOJ#2230. 「BJOI2014」大融合
LOJ#2230. 「BJOI2014」大融合 题目描述 小强要在$N$个孤立的星球上建立起一套通信系统.这套通信系统就是连接$N$个点的一个树.这个树的边是一条一条添加上去的. 在某个时刻,一条边的 ...
- Android基础入门教程
http://www.kancloud.cn/wizardforcel/w3school-android/100491
- JavaScript Promise异步实现章节的下载显示
Links: JavaScript Promise:简介 1.一章一章顺序地下载显示下载显示 使用Array.reduce()和Promise.resolve()将各章的下载及显示作为整体串联起来. ...
