opencv学习笔记(六)---图像梯度
图像梯度的算法有很多方法:sabel算子,scharr算子,laplacian算子,sanny边缘检测(下个随笔)。。。
这些算子的原理可参考:https://blog.csdn.net/poem_qianmo/article/details/25560901
下面是我的一些理解:
sabel算子:
sobel算子主要用于获得数字图像的一阶梯度,常见的应用和物理意义是边缘检测。
函数:
Python: cv2.Sobel(src, ddepth, dx, dy[, dst[, ksize[, scale[, delta[, borderType]]]]]) → dst (参数就不一一说了,常用的就那几个,其他默认即可)
|
Parameters: |
|
|---|
原理
算子使用两个33的矩阵(图1)算子使用两个33的矩阵(图1)去和原始图片作卷积,分别得到横向G(x)和纵向G(y)的梯度值,如果梯度值大于某一个阈值,则认为该点为边缘点
Gx方向的相关模板:
Gy方向的相关模板:
具体计算如下:
图像的每一个像素的横向及纵向灰度值通过以下公式结合,来计算该点灰度的大小:

通常,为了提高效率使用不开平方的近似值:

- #sobels算子
- img = cv.imread("E:/pictures/lena.jpg",cv.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)
- sobelx= cv.Sobel(img,cv.CV_64F,1,0) #cv.CV_64F将像素值转换为double型,不然计算后为负值的像素会被截断为0
- sobelx = cv.convertScaleAbs(sobelx) #转换为uint8类型(x方向)
- sobely = cv.Sobel(img,cv.CV_64F,0,1)
- sobely = cv.convertScaleAbs(sobely)
- sobelxy11 = cv.Sobel(img,cv.CV_64F,1,1) #直接x,y方向一起计算(效果不好,应分开计算,再求权重和)
- sobelxy11 = cv.convertScaleAbs(sobelxy11)
- sobelxy = cv.addWeighted(sobelx,0.5,sobely,0.5,0) #图像权重和
- cv.imshow("orginal",img) #dst = cv.addWidget(src1,alpha,src2,beta,gamma)
- cv.imshow("sobelx",sobelx) #src1 图一 alpha->图一的权重 src2->图二 beta->图二的权重 gamma->修正值
- cv.imshow("sobely",sobely) #dst = src1*alpha+src2*beta+gamma
- cv.imshow("sobelxy",sobelxy)
- cv.imshow("sobelxy11",sobelxy11)
- cv.waitKey()
- cv.destroyAllWindows()
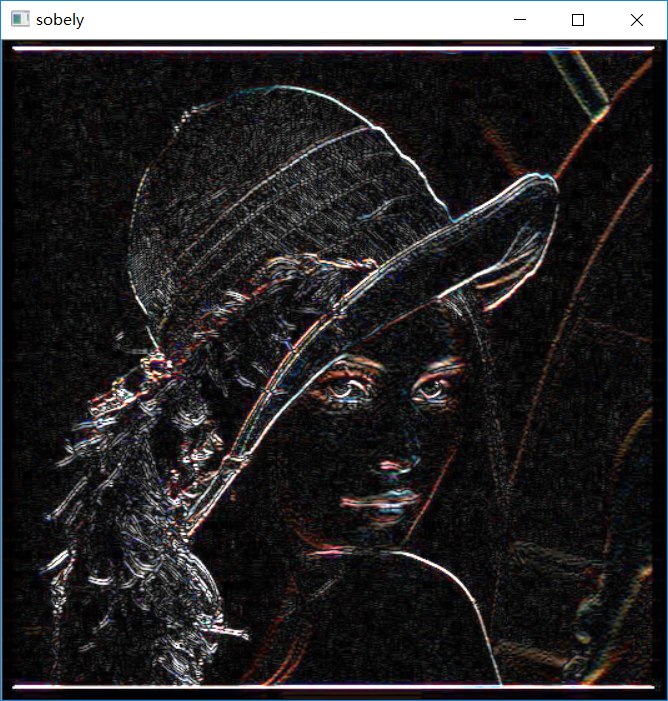





用sobel函数同时对想x,y方向检测的效果并不好,一般不用。
scharr算子:
函数:
Python: cv2.Scharr(src, ddepth, dx, dy[, dst[, scale[, delta[, borderType]]]]) → dst
| Parameters: |
|
|---|
scharr算子是对sabel算子的增强,可以看到上图中很多细小的边缘都没检测到,那么scharr算子就是解决这个问题的,它比sabel算子更精确,速度和复杂程度却一样,只是因为用的核不一样
是scharr 的卷积核,他的原理和sabel算子一样。
- #scharr算子 scharr算子是对sabel算子的增强 scharr算子等价于ksize=-1的sabel算子
- img = cv.imread("E:/pictures/lena.jpg",cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
- scharrx= cv.Scharr(img,cv.CV_64F,1,0) #scharrx算子要满足dx>=0&&dy>=0&&dx+dy=1
- scharrx = cv.convertScaleAbs(scharrx)
- scharry = cv.Scharr(img,cv.CV_64F,0,1)
- scharry = cv.convertScaleAbs(scharry)
- scharrxy = cv.addWeighted(scharrx,0.5,scharry,0.5,0)
- #sabel算子和 scharr算子的比较
- sobelx= cv.Sobel(img,cv.CV_64F,1,0)
- sobelx = cv.convertScaleAbs(sobelx)
- sobely = cv.Sobel(img,cv.CV_64F,0,1)
- sobely = cv.convertScaleAbs(sobely)
- sobelxy = cv.addWeighted(sobelx,0.5,sobely,0.5,0)
- cv.imshow("orginal",img)
- cv.imshow("sobelxy",sobelxy)
- cv.imshow("scharrxy",scharrxy)
- cv.waitKey()
- cv.destroyAllWindows()



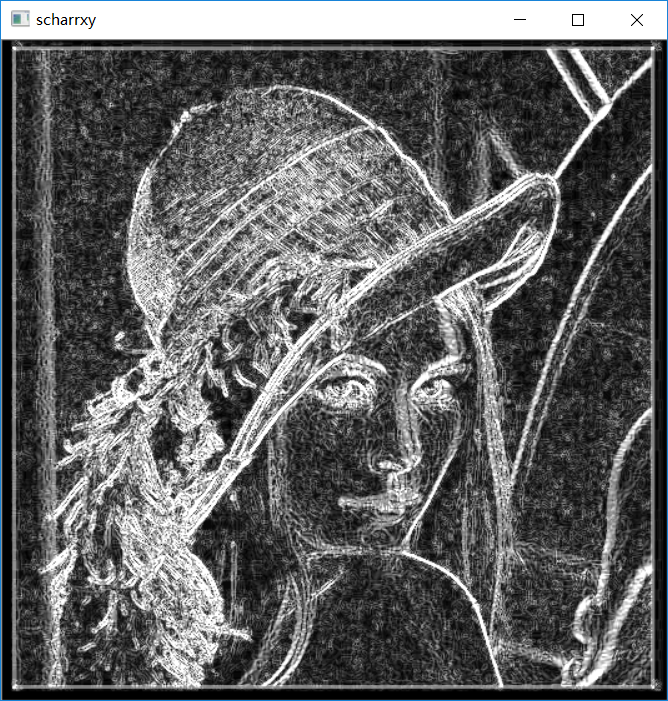
laplacian算子:
Laplace算子和Sobel算子一样,属于空间锐化滤波操作,只不过是用的二阶微分,看官网的一些解释:
The function calculates the Laplacian of the source image by adding up the second x and y derivatives calculated using the Sobel operator:
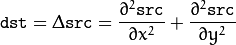
This is done when ksize > 1 . When ksize == 1 , the Laplacian is computed by filtering the image with the following  aperture:
aperture:
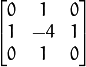
cv.Laplace(src, dst, ksize=3) → None
|
Parameters: |
|
|---|
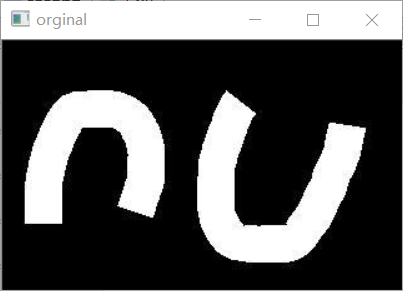
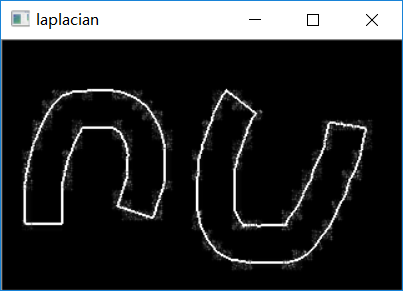
- #拉普拉斯算子
- img = cv.imread("E:/pictures/erode1.jpg",cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
- r = cv.Laplacian(img,cv.CV_64F)
- r = cv.convertScaleAbs(r) #关键代码就这两行,拉普拉斯算子不用再求x,y的权重和,因为这个函数都计算好了
- cv.imshow("orginal",img)
- cv.imshow("laplacian",r)
- cv.waitKey()
- cv.destroyAllWindows()
Canny边缘检测:
Python: cv2.Canny(image, threshold1, threshold2[, edges[, apertureSize[, L2gradient]]]) → edges
threshold1和threshold2是两个阈值,越小检测效果越好
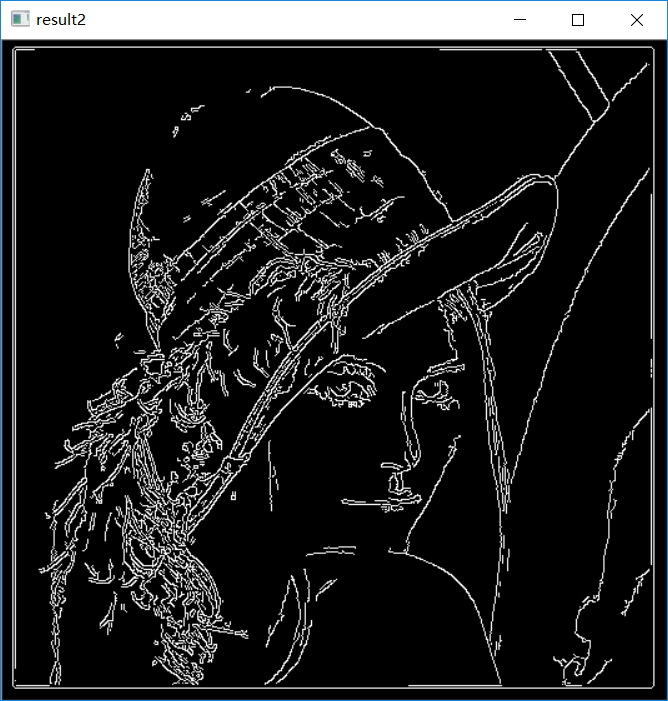
- import cv2 as cv
- import numpy as np
- img = cv.imread("E:/pictures/lena.jpg")
- result1 = cv.Canny(img,50,100)
- result2 = cv.Canny(img,100,200)
- cv.imshow("orginal",img)
- cv.imshow("result1",result1)
- cv.imshow("result2",result2)
- cv.waitKey()
- cv.destroyAllWindows()


opencv学习笔记(六)---图像梯度的更多相关文章
- OpenCV学习笔记(10)——图像梯度
学习图像梯度,图像边界等 梯度简单来说就是求导. OpenCV提供了三种不同的梯度滤波器,或者说高通滤波器:Sobel,Scharr和Lapacian.Sobel,Scharr其实就是求一阶或二阶导. ...
- 【opencv学习笔记六】图像的ROI区域选择与复制
图像的数据量还是比较大的,对整张图片进行处理会影响我们的处理效率,因此常常只对图像中我们需要的部分进行处理,也就是感兴趣区域ROI.今天我们来看一下如何设置图像的感兴趣区域ROI.以及对ROI区域图像 ...
- [OpenCV学习笔记3][图像的加载+修改+显示+保存]
正式进入OpenCV学习了,前面开始的都是一些环境搭建和准备工作,对一些数据结构的认识主要是Mat类的认识: [1.学习目标] 图像的加载:imread() 图像的修改:cvtColor() 图像的显 ...
- opencv学习笔记(五)----图像的形态学操作
图像的形态学操作有基本的腐蚀和膨胀操作和其余扩展形态学变换操作(高级操作)-----开运算,闭运算,礼帽(顶帽)操作,黑帽操作...(主要也是为了去噪声,改善图像) 形态学操作都是用于处理二值图像(其 ...
- OpenCV学习笔记(7)——图像阈值
简单阈值,自适应阈值,Otsu's二值化等 1.简单阈值 当像素值高于阈值时,我们给这个像素赋予一个新值,否则给他赋予另一个值.这个函数就是cv2.threshhold().这个函数的第一个参数就是原 ...
- opencv学习笔记(七)---图像金字塔
图像金字塔指的是同一图像不同分辨率的子图的集合,有向下取样金字塔,向上取样金字塔,拉普拉斯金字塔....它是图像多尺度表达的一种,最主要的是用于图像的分割 向下取样金字塔指高分辨率图像向低分辨率图像的 ...
- opencv学习笔记3——图像缩放,翻转和阈值分割
#图像的缩放操作 #cv.resize(src,dsize,dst=None,,fx=None,fy=None,interpolation=None) #src->原图像,dsize->目 ...
- OpenCV学习笔记(3)——图像的基本操作
获取图像的像素值并修改 获取图像的属性(信息) 图像的ROI() 图像通道的拆分及合并 1.获取并修改像素值 先读入图像装入一个图像实体,然后该实体相当于一个多维list,可以直接用数组操作提取像素信 ...
- OpenCV 学习笔记 02 使用opencv处理图像
1 不同色彩空间的转换 opencv 中有数百种关于不同色彩空间的转换方法,但常用的有三种色彩空间:灰度.BRG.HSV(Hue-Saturation-Value) 灰度 - 灰度色彩空间是通过去除彩 ...
随机推荐
- How to Change Master Page @ Run-time
This tip will give complete knowledge of how to change master page, render controls and accessing it ...
- Cannot+use+T4+templates+inside+a+.NET+Core+project,NetCore2.0无法使用T4模板解决方法
Cannot+use+T4+templates+inside+a+.NET+Core+project,NetCore2.0无法使用T4模板解决方法 请见:https://csharp.wekeepco ...
- ubuntu apt-get用法
如何在ubuntu下面直接查找想要安装的软件?比如我想安装tomcat,但是我又不知道ubuntu里面有哪些版本,也不知道都需要装什么,但是我能确认我装的是tomcat,那么我就可以用搜索命令:例如: ...
- tomcat 7 7.0.73 url 参数 大括号 {} 不支持 , 7.0.67支持
7.0.73 url有JSON.stringify一个对象,然后作为参数拼接.结果请求报400错误,但是tomcat 7.0.67版本没有问题,猜测是高级版本对url参数比较严格. 处理方法: ...
- Mesh Filter & Mesh Render
[Mesh Filter] The Mesh Filter takes a mesh from your assets and passes it to the Mesh Renderer for r ...
- linux 目录和用户权限命令
1.linux 修改文件目录所有者 例:要将当前目录下名 title 的文件夹及其子文件的所有者改为geust组的su用户,方法如下: #chown -R su.geust title -R 递归式地 ...
- 当一个SQL语句同时出现了where,group by,having,order by的时候,执行顺序和编写顺序
当一个查询语句同时出现了where,group by,having,order by的时候,执行顺序和编写顺序 1.执行where xx对全表数据做筛选,返回第1个结果集. 2.针对第1个结果集使用g ...
- day58-activiti 13-搭建web项目环境
Eclipse的项目的build目录不可被删除,删除了也会被自动创建. 到项目的输出路径才看得到编译好的Java类.Eclipse的视图下是看不见的,因为类路径下的这个目录build不想让你操作,它给 ...
- 玩转Mysql命令
连接数据库mysql -hlocalhost -uroot -p 在MYsql的跟目录文件下进行 show databses:展示所有数据库 解决方法1:在MySql安装目录下找到my.ini,将[m ...
- mysql外键约束总结
总结三种MySQL外键约束方式 如果表A的主关键字是表B中的字段,则该字段称为表B的外键,表A称为主表,表B称为从表.外键是用来实现参照完整性的,不同的外键约束方式将可以使两张表紧密的结合起来,特别是 ...



