Java第09次实验(IO流)-实验报告
0. 字节流与二进制文件
- 使用DataOutputStream与FileOutputStream将Student对象写入二进制文件student.data
- 二进制文件与文本文件的区别
- try...catch...finally注意事项
- 使用try..with...resouces关闭资源
- 使用DataInputStream与FileInputStream从student.data中读取学生信息并组装成对象
我的代码
class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private double grade;
public Student(){
}
public Student(int id, String name, int age, double grade) {
this.id = id;
this.setName(name);
this.setAge(age);
this.setGrade(grade);
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
if (name.length()>10){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("name's length should <=10 "+name.length());
}
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
if (age<=0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("age should >0 "+age);
}
this.age = age;
}
public double getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(double grade) {
if (grade<0 || grade >100){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("grade should be in [0,100] "+grade);
}
this.grade = grade;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", grade=" + grade + "]";
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String fileName="d:\\student.data";
try(DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(fileName)))
{
Student[] stu=new Student[3];
stu[0]=new Student(1,"zhangsan",19,65.0);
stu[1]=new Student(2,"lisi",19,75.0);
stu[2]=new Student(3,"wangwu",20,85.0);
for(Student stu1:stu) {
dos.writeInt(stu1.getId());
dos.writeUTF(stu1.getName());
dos.writeInt(stu1.getAge());
dos.writeDouble(stu1.getGrade());
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("1");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("2");
}
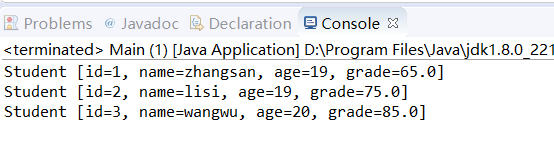
try(DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(fileName)))
{
while(dis!=null) {
int id=dis.readInt();
String name=dis.readUTF();
int age=dis.readInt();
double grade=dis.readDouble();
Student stu=new Student(id,name,age,grade);
System.out.println(stu);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("3");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("4");
}
}
我的总结
在读取文件数据时while循环会报错,加入测试点后发现while循环多读了一次,
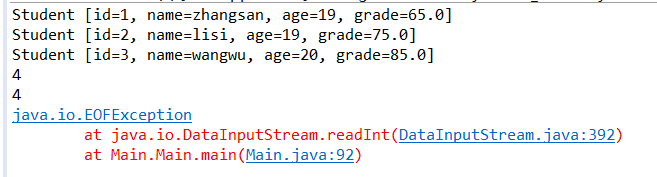
后将while(dis!=null)改成while(dis.available()!=0),问题解决
1. 字符流与文本文件:使用 PrintWriter(写),BufferedReader(读)
任务:
- 使用BufferedReader从编码为UTF-8的文本文件中读出学生信息,并组装成对象然后输出。
- 中文乱码问题(FileReader使用系统默认编码方式读取文件,会产生乱码,可使用InputStreamReader解决)
- String的split方法使用
\\s+可以使用多个空格作为分隔符。 - 进阶:修改Students.txt文件,在正确的数据行中间增加一些错误行(如,每行只有3个数据,或者应该是数字的地方放入其他字符),修改自己的程序,让起可以处理出错的行(报错但可以继续运行)。
- 编写public static ListreadStudents(String fileName);从fileName指定的文本文件中读取所有学生,并将其放入到一个List中
- 使用PrintWriter将Student对象写入文本文件,基础代码见后。注意:缓冲区问题。
- 使用ObjectInputStream/ObjectOutputStream读写学生对象。
我的代码
1.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
String FileName="D:\\TSBrowserDownloads\\Students.txt";
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(FileName),"UTF-8"));
String line = null;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null)
System.out.println(line);
} finally{
if (br!=null){
br.close();
}
}
}
}
我的总结
默认方法打开读取会产生乱码

将模式读取方式改成"UTF-8"后显示正常

2.
public static void ListreadStudents(String fileName){
ArrayList<Student> StudentList=new ArrayList<Student>();
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(fileName),"UTF-8"));
while(br!=null) {
String line=br.readLine();
String[] stu=line.split("\\s+");
int id=Integer.parseInt(stu[0]);
String name=stu[1];
int age=Integer.parseInt(stu[2]);
double grade=Double.parseDouble(stu[3]);
Student Stu=new Student(id,name,age,grade);
StudentList.add(Stu);
}
} finally{
if (br!=null){
br.close();
}
}
}
实验调试
刚开始本来想用和DataInputStream一样直接读,发现BufferedReader只用read和ReadLine方法,得用实验提到的"\\s+"的方法将读到的一整行用分隔符来分开,再用类型转换来读。
3.
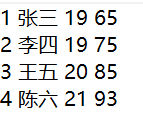
String FileName="D:\\TSBrowserDownloads\\Students.txt";
PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(FileName,true),"UTF-8"));
pw.print("4 陈六 21 93");
pw.close();
我的总结
正确写入文件
4.
String FileName="D:\\TSBrowserDownloads\\student.dat";
try(
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(FileName);
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(fos))
{
Student ts=new Student(5,"asd",14,60);
oos.writeObject(ts);
}
catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
try(
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(FileName);
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis))
{
Student newStudent =(Student)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(newStudent);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
2. 缓冲流(结合使用JUint进行测试)
使用PrintWriter往文件里写入1千万行随机整数,范围在[0,10]。随机数种子设置为100.
然后从文件将每行读取出来转换成整数后相加。然后依次输出“个数 和 平均值(保留5位小数)”。
对比使用BufferedReader与使用Scanner从该文件中读取数据(只读取,不输出),使用哪种方法快?
- 使用junit对比
BufferedReader与Scanner读文件的效率 - 格式化输出:System.out.format。
- 要使用Scanner的hasNextXXX方法来判断是否到文件尾,否则会抛异常。
- Scanner的asNextXXX方法应与相对应的nextXXX方法配合使用,否则容易出。
- 请删除
fail("Not yet implemented");;并且在需要测试的方法上使用@Test进行标注。
写入文件代码
String FILENAME = "test.txt";
double sum=0,aver;
PrintWriter pw=null;
try {
pw = new PrintWriter(FILENAME);
for(int i = 0;i<10000000;i++){//写入1千万行
int r=new Random().nextInt(10);
sum+=r;
pw.println(r);
//System.out.println(r);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
pw.close();
}
aver=sum/10000000;
System.out.format("%.5f", aver);
}
使用JUint的代码
public class test {
@Test
public void test() {
String FILENAME = "test.txt";
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
Scanner scanner=null;
try {
scanner = new Scanner(new File(FILENAME));
while(scanner.hasNextLine()){//只是读出每一行,不做任何处理
scanner.nextLine();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
scanner.close();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("last "+(end-begin));
System.out.println("read using Scanner done");
}
@Test
public void Bufftest() {
String FILENAME = "test.txt";
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(FILENAME)));
while(br.readLine()!=null){};//只是读出,不进行任何处理
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("last "+(end-begin));
System.out.println("read using BufferedReader done");
}
}
我的总结
可以明显对比出缓冲流BufferedReader的方法要比Scanner的方法快很多
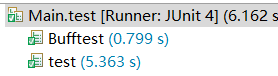
不使用JUint也可以在循环开始前后定义时间变量,最后相减也能得到运行所用时间
第2次实验
3. 字节流之对象流
结合使用ObjectOutputStream、ObjectInputStream与FileInputStream、FileOuputStream实现对Student对象的读写。
编写如下两个方法:
- public static void writeStudent(List stuList)
- public static List readStudents(String fileName)
我的代码
public static void writeStudent(List<Student> stuList)
{
String fileName="D:\\Student.dat";
try ( FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(fileName);
ObjectOutputStream ois=new ObjectOutputStream(fos))
{
ois.writeObject(stuList); }
catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static List<Student> readStudents(String fileName)
{
List<Student> stuList=new ArrayList<>();
try ( FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(fileName);
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis))
{
stuList=(List<Student>)ois.readObject();
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return stuList;
}
5. 文件操作
编写一个程序,可以根据指定目录和文件名,搜索该目录及子目录下的所有文件,如果没有找到指定文件名,则显示无匹配,否则将所有找到的文件名与文件夹名显示出来。
- 编写
public static void findFile(Path dir,String fileName)方法.
以dir指定的路径为根目录,在其目录与子目录下查找所有和filename
相同的文件名,一旦找到就马上输出到控制台。
我的代码
if (args.length == 0) args = new String[] { ".." };
try
{
File pathName = new File(args[0]);
String[] fileNames = pathName.list();
// enumerate all files in the directory
for (int i = 0; i < fileNames.length; i++)
{
File f = new File(pathName.getPath(), fileNames[i]);
// if the file is again a directory, call the main method recursively
if (f.isDirectory())
{
if(f.getName().contains(fileName)) {
System.out.println(f.getCanonicalPath());
main(new String[] { f.getPath() });
}
}
}
}
catch (IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
我的总结
用了参考代码稍加修改,若文件名字包含fileName,则输出该文件的路径
6. 正则表达式
- 如何判断一个给定的字符串是否是10进制数字格式?尝试编程进行验证。
- 修改HrefMatch.java
- 尝试匹配网页中的数字字符串
- 尝试匹配网页中的图片字符串
1.
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
Pattern pattern=Pattern.compile("^-?[0-9]\\d*(\\.\\d+)?$");
Matcher matcher=null;
while(sc.hasNext())
{
String str=sc.next();
matcher=pattern.matcher(str);
System.out.println(matcher.matches());
}
sc.close();
2.
try
{
// get URL string from command line or use default
String urlString;
if (args.length > 0) urlString = args[0];
else urlString = "http://cec.jmu.edu.cn"; // open reader for URL
InputStreamReader in = new InputStreamReader(new URL(urlString).openStream());
//InputStreamReader in = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("集美大学-计算机工程学院.htm"));
// read contents into string builder
StringBuilder input = new StringBuilder();
int ch;
while ((ch = in.read()) != -1)
input.append((char) ch); // search for all occurrences of pattern
String patternString = "<a\\s+href\\s*=\\s*(\"[^\"]*\"|[^\\s>]*)\\s*>";
String patternImgString = "[+-]?[0-9]+";
//String patternString = "[\u4e00-\u9fa5]"; //匹配文档中的所有中文
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(patternString, Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(input); while (matcher.find())
{
int start = matcher.start();
int end = matcher.end();
String match = input.substring(start, end);
System.out.println(match);
}
}
catch (IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (PatternSyntaxException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}

总结:这次实验内容较多,花费了大量的时间,总的来说IO流是java中很重要的一部分,涉及面很广,还会和今后的网络编程牵扯关系,应该好好学。正值表达式的内容较难理解
Java第09次实验(IO流)-实验报告的更多相关文章
- Java输入、输入、IO流 类层次关系梳理
本文主要关注在Java编程中涉及到的IO相关的类库.方法.以及对各个层次(抽线.接口继承)的流之间的关系进行梳理 相关学习资料 http://baike.baidu.com/view/1007958. ...
- Java基础知识强化之IO流笔记71:NIO之 NIO的(New IO流)介绍
1. I/O 简介 I/O ( 输入/输出 ):指的是计算机与外部世界或者一个程序与计算机的其余部分的之间的接口.它对于任何计算机系统都非常关键,因而所有 I/O 的主体实际上是内置在操作系统中的. ...
- Java基础知识强化之IO流笔记68:Properties和IO流集合使用
1. Properties和IO流集合使用 这里的集合必须是Properties集合: public void load(Reader reader):把文件中的数据读取到集合中 public v ...
- Java基础知识强化之IO流笔记66:Properties的概述 和 使用(作为Map集合使用)
1. Properties的概述 Properties:属性集合类.是一个可以和IO流相结合使用的集合类. 该类主要用于读取以项目的配置文件(以.properties结尾的文件 和 xml文件). ...
- Java笔记(二十六)……IO流上 字节流与字符流
概述 IO流用来处理设备之间的数据传输 Java对数据的操作时通过流的方式 Java用于操作流的对象都在IO包中 流按操作的数据分为:字节流和字符流 流按流向不同分为:输入流和输出流 IO流常用基类 ...
- Java基础知识强化之IO流笔记22:FileInputStream / FileOutputStream 复制文本文件案例1
1. 使用字节流FileInputStream / FileOutputStream 复制文本文件案例: 分析: (1)数据源:从哪里来 a.txt -- 读取数据 -- FileInpu ...
- Java基础知识强化之IO流笔记17:FileOutputStream构造方法使用
1. 可以参照之前写的笔记: Android(java)学习笔记167:Java中操作文件的类介绍(File + IO流) 2. FileOutputStream(常用的)构造方法: FileOu ...
- Java基础知识强化之IO流笔记16:IO流的概述和分类
1. IO流的分类 流向: (1)输入流:读取数据到内存 (2)输出流:写入数据到硬盘(磁盘) 操作的数据类型: (1)字节流:操作的数据是字节 ...
- Java基础知识强化之IO流笔记01:异常的概述和分类
IO流操作的时候会出现很多问题,java中叫作异常,所以我们先介绍一下异常: 1. 程序的异常:Throwable(Throwable类是java中所有异常或错误的超类) (1)严重问题:Error ...
随机推荐
- Spring Cloud zuul网关服务 一
上一篇进行Netflix Zuul 1.0 与 gateway的对比.今天来介绍一下 zuul的搭建及应用 Zuul 工程创建 工程创建 cloud-gateway-zuul.还是基于之前的工程 po ...
- django测试开发-1.开始Hello django!
用python开发出一个web页面的时候,需要找一个支持python语言的web框架.django框架有丰富的文档和学习资料,也是非常成熟的web开发框架,本篇写一个简单的“hello django! ...
- Tomcat原理与优化随笔
1. 基础组件: Server, Service: Connector(http, https, ajp用于Apache反向代理), Engine Engine: Realm用于安全配置等,如User ...
- dom 创建时间
下面讲述如何在页面生成一个装有日期的盒子 首先写出一个日期的函数进行赋值使用document.createElement创建一个文档节点div,然后将时间函数输出在div之中,利用document.b ...
- Flask源码分析二:路由内部实现原理
前言 Flask是目前为止我最喜欢的一个Python Web框架了,为了更好的掌握其内部实现机制,这两天准备学习下Flask的源码,将由浅入深跟大家分享下,其中Flask版本为1.1.1. 上次了解了 ...
- quartus使用串口IP模块
在quartus平台中使用串口模块的IP,需要使用到platform designer软件来实现. 1.在quartus界面调出IP Catalog界面. 2.在IP catalog中搜索UART,找 ...
- List、Set集合系列之剖析HashSet存储原理(HashMap底层)
目录 List接口 1.1 List接口介绍 1.2 List接口中常用方法 List的子类 2.1 ArrayList集合 2.2 LinkedList集合 Set接口 3.1 Set接口介绍 Se ...
- 《JavaScript设计模式与开发实践》-- 策略模式
详情个人博客:https://shengchangwei.github.io/js-shejimoshi-celue/ 策略模式 1.定义 策略模式:定义一系列的算法,把它们一个个封装起来,并且使它们 ...
- PHP函数preg_match()
部分内容来自:http://www.nowamagic.net/librarys/veda/detail/1054 preg_match — 进行正则表达式匹配. 语法:int preg_match ...
- C Primer Plus (一)
摘要:重读C Primer Plus ,查漏补缺 重读C Primer Plus,记录遗漏的.未掌握的.不清楚的知识点. 一.概览 1.链接器的作用是将这3个目标元素(目标代码.系统的标准启动代码和库 ...
