.NET Core on K8S快速入门课程--学习笔记
课程链接:http://video.jessetalk.cn/course/explore
良心课程,大家一起来学习哈!
目录
- 01-介绍K8s是什么
- 02-为什么要学习k8s
- 03-如何学习k8s
- 04-K8S集群基本概念
- 05-安装本地k8s单节点集群
- 06-K8S三大核心组件介绍
- 07-Service的三种类型及Dashboad部署
- 08-kubectl工具命令介绍
- 09-yaml部署文件格式介绍
- 10-部署netcore api到K8S
- 11-k8s高可用集群介绍
- 12-进阶介绍
01-介绍K8s是什么
Docker VS VirtualMachine
- 敏捷地应用创建和部署
- 持续开发,集成和部署
- 开发和运行相分离
- 开发,测试和生产环境的持续
- 云和操作系统版本的可移植性,可以运行在 Ubuntu, RHEL, CoreOS, on-prem, Google Container Engine,和任何其它的运行环境中。
- 松耦合,分布式,弹性,自由的微服务
- 资源隔离:可以预测的应用性能
- 资源使用:高效
Docker 容器集群
镜像 => run => 容器(运行时)
- 同一个容器在同一台Host上能部署几份?
- 如果实现在多台机器上快速部署?
- 不同容器在不同机器上如何交互?如何做负载均衡?
K8S 介绍
一个用于容器集群的自动化部署、扩容以及运维的开源平台
- 快速而有预期地部署你的应用
- 极速地扩展你的应用
- 无缝对接新的应用功能
- 节省资源,优化硬件资源的使用
02-为什么要学习k8s
通过 K8S 降低整个基础设施在架构和运维上的难度
测试环境
- 将多个API打成镜像部署到不同的节点上
- 通过 Node Port 本地可以直接连到 API 进行测试
- Mysql 与 API 可以通过 service 连接
- 一套脚本部署

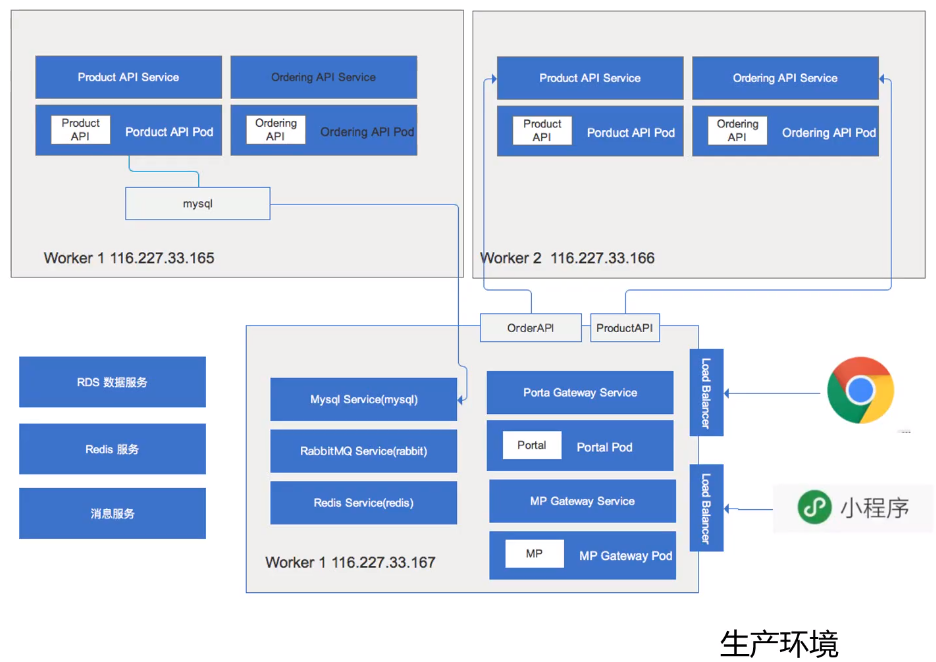
生产环境
- Mysql, Redis, 消息队列使用第三方服务(腾讯云)
- 也可以通过 桥接 将内部 API 与外部服务连接
03-如何学习k8s
掌握学习的方法(刻意练习)
- 先了解全貌和整体
- 对整体结构进入拆分、梳理脉络(思维导图)
- 马上开始行动(比如本地部署一个集群)
- 在动的过程中逐步加深,每一个阶段有阶段性目标
- 及时进行回顾与复盘,与理论相结合
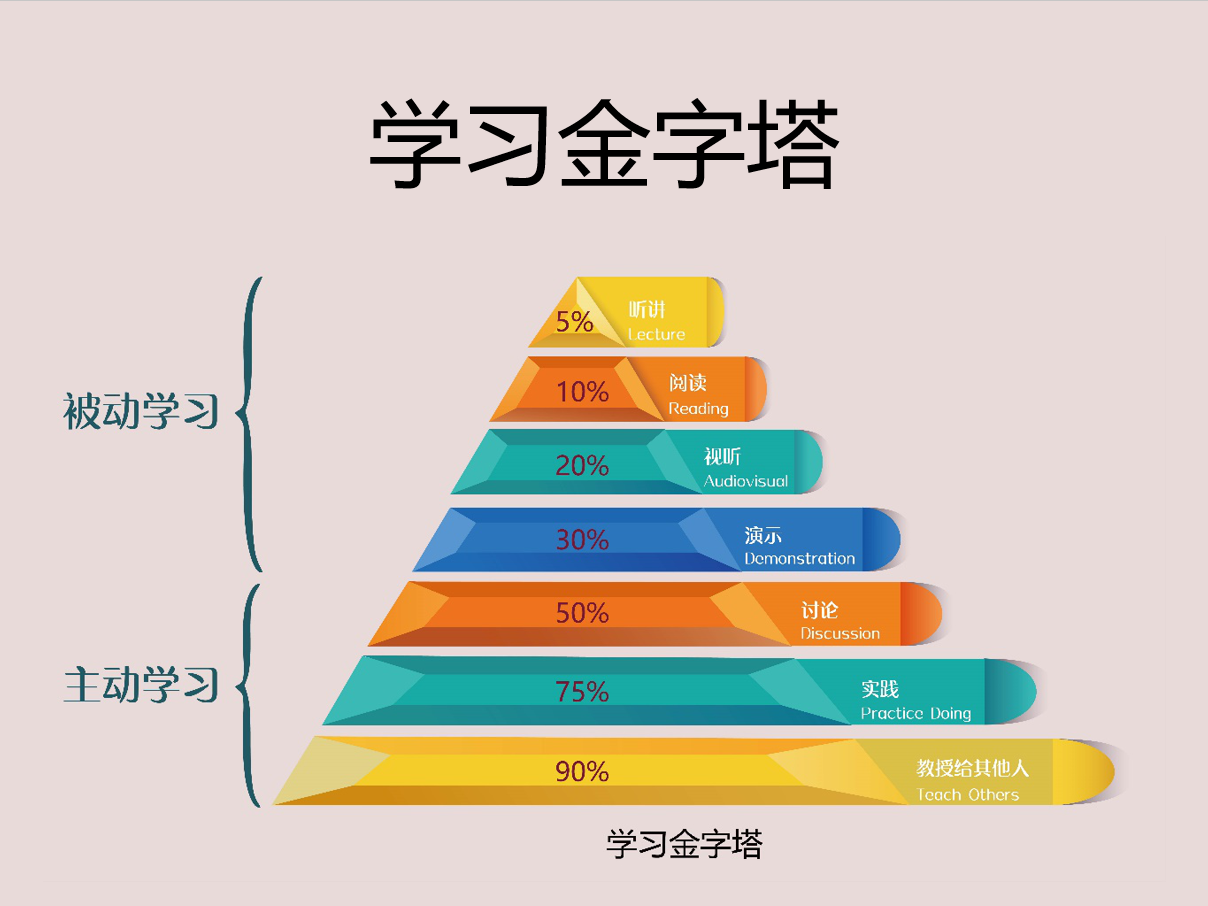
- 输出(学习金字塔)
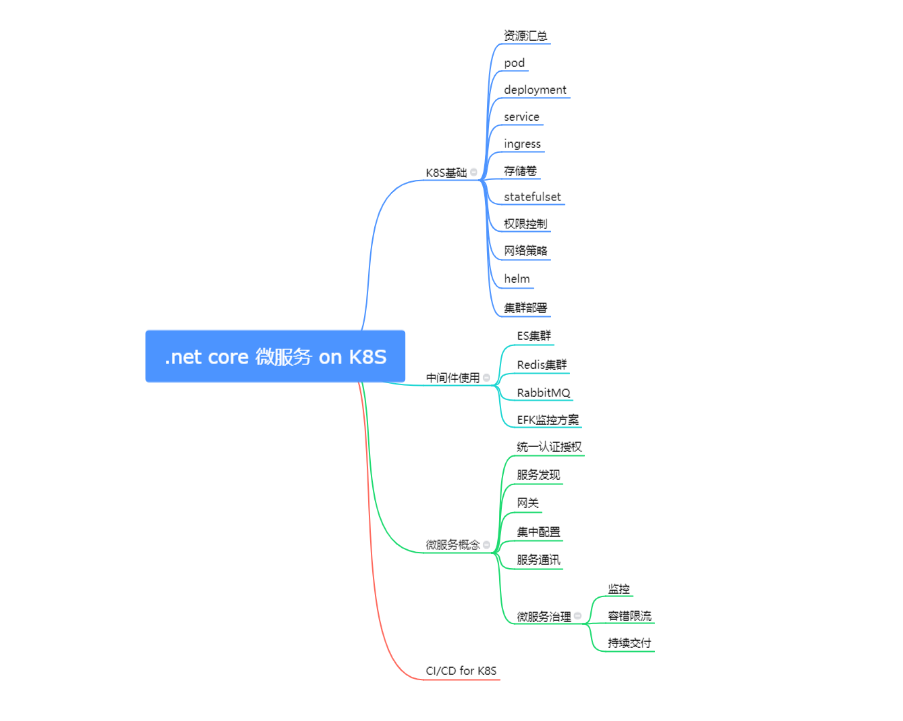
学习K8S的路径
- 了解基本概念及核心组件
- 使用本地单节点集群来学习k8s
- 用kubectl 与本地集群建立连接
- 部署服务到 k8s集群
- 对k8s服务进行扩容、更新
- 进一步学习k8s资源(pod, deployment, service, statefulset, ingress…)
- 设计微服务
- 搭建k8s集群或者使用云服务商的k8s服务
- 添加持续集成、日志搜集、监控和指标度量、跟踪
04-K8S集群基本概念
Agenda
- K8S集群基本概念
- 本地搭建k8s单节点集群
- POD & Service & Deployment
- Service 的三种类型
- Yaml 部署文件语法初体验
- 初始化一个.NET Core API 并push到docker hub
- 把.Net Core API 部署到 K8s
- K8S集群高级概念
K8S集群基本概念
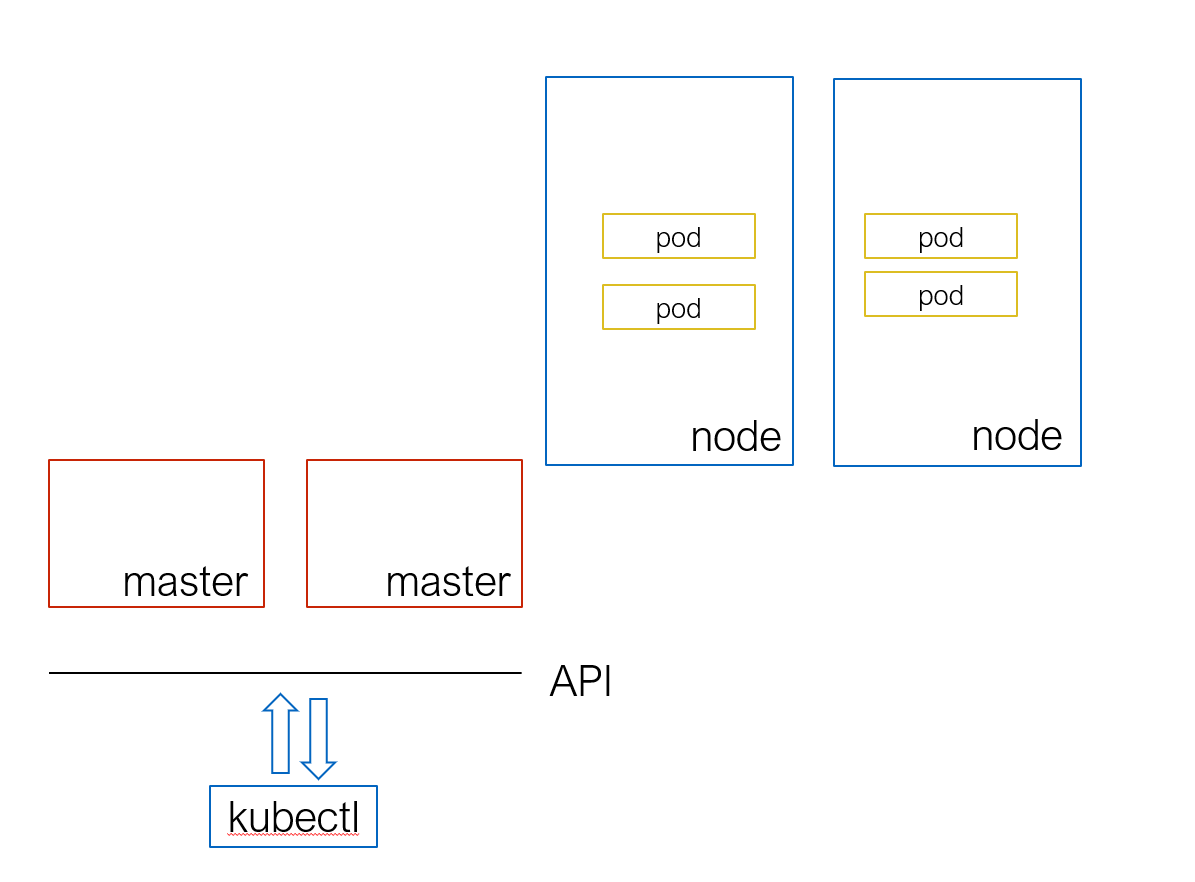
- 集群(多个机器拼在一起,共同处理)
- Node (Master:维护集群状态 and Worker:处理)(高可用时架构不同)
- 资源(内部组件为一个资源,对外暴露 restful 的 WebApi)(例如 Yaml)
- Kubectl (本地客户端,一个命令行工具,连接到 K8S 集群)
05-安装本地k8s单节点集群
安装教程
输入国内镜像地址(https://registry.docker-cn.com),才能更好的拿到谷歌开头的镜像

运行下列脚本可以从阿里云镜像服务下载Kubernetes安装所需Docker镜像,您也可以通过修改 images.properties 文件定义自己安装所需的Docker镜像
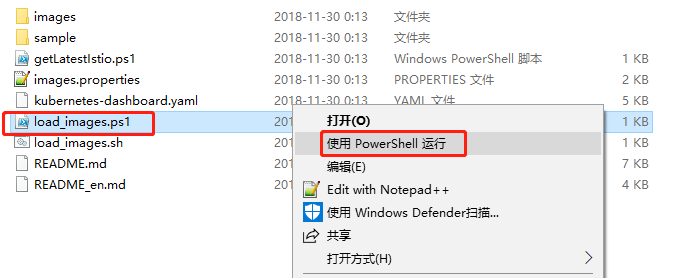
右键 git bash
git clone https://github.com/AliyunContainerService/k8s-for-docker-desktopcd k8s-for-docker-desktop
如果您安装版本为18.09/18.06版本可以直接使用master分支;如果是18.03稳定版请使用对应的代码分支 git checkout 18.03
Windows下加载镜像(./load_images.sh)可能会报错
使用 PowerShell 执行 load_images.ps1 循环拉取 images.properties 的镜像
需要开启VPN
在Docker for Mac中开启 Kubernetes
勾选 Enable Kubernetes 安装,等待消息 Kubernetes is running
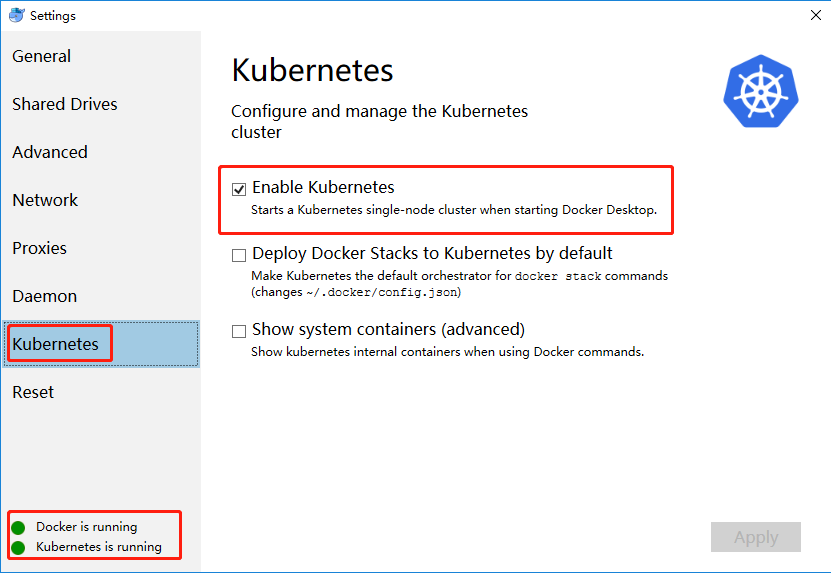
配置信息路径:C:\Users\MINGSON.kube
测试 kubectl 命令,在左下角 Windows 图标右键启动 Window PowerShell(管理员)
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> kubectl get nodesNAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSIONdocker-for-desktop Ready master 1d v1.10.3PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> kubectl get servicesNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGEkubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 1d
06-K8S三大核心组件介绍
POD & Service
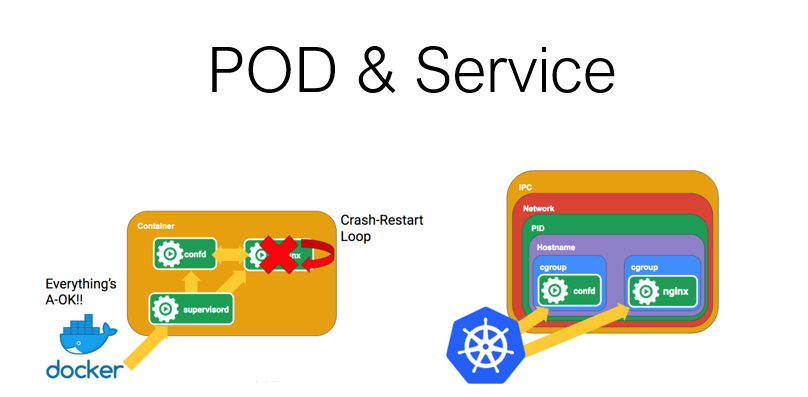
POD: K8S 运行时最小单元逻辑(类似docker里面的容器)
与容器的区别:
docker里面每个容器只有一个主进程挂载,可以使用supervisord同时让两个进程运行起来,可是docker只有一个入口,所以只能把supervisord暴露成入口,这种情况API很难进入到里面每个进程
POD里面可以运行多个容器,同时容器之间的挂载可以共享
docker映射端口后可以直接访问
POD必须挂载一个service(对外暴露POD),之后POD才可以在集群外部被访问
学习资料
deployment
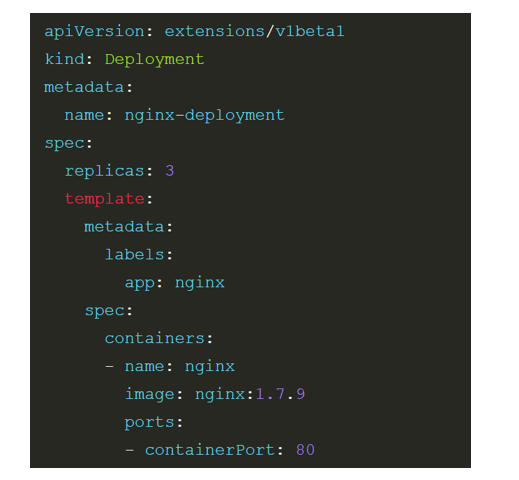
kind:声明k8s资源固定的模板
replicas:POD实例,复本
containers:容器(数组形式,可以定义多个容器)
image:镜像
一个deployment的POD里面可以运行多个容器
07-Service的三种类型及Dashboad部署
- ClusterIP
- NodePort
- LoadBalancer
学习资料
Kubernetes的三种外部访问方式:NodePort、LoadBalancer 和 Ingress
ClusterIP 服务是 Kubernetes 的默认服务。它给你一个集群内的服务,集群内的其它应用都可以访问该服务。集群外部无法访问它。
ClusterIP 服务的 YAML 文件类中 type: ClusterIP(不填写默认也是ClusterIP)
NodePort 服务是引导外部流量到你的服务的最原始方式。NodePort,正如这个名字所示,在所有节点(虚拟机)上开放一个特定端口,任何发送到该端口的流量都被转发到对应服务。
NodePort 服务的 YAML 文件类中 type: NodePort,需要指定一个端口 nodePort: 30036
NodePort 是开发环境中最常用的类型
LoadBalancer 服务是暴露服务到 internet 的标准方式。在 GKE 上,这种方式会启动一个 Network Load Balancer,它将给你一个单独的 IP 地址,转发所有流量到你的服务。
LoadBalancer 主要是云服务商使用
使用 kubectl 连接本地集群,部署 dashboard(脚本中通过 ClusterIP,需要使用代理的模式)
在左下角 Windows 图标右键启动 Window PowerShell(管理员)
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/master/src/deploy/recommended/kubernetes-dashboard.yamlsecret "kubernetes-dashboard-certs" createdserviceaccount "kubernetes-dashboard" createdrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io "kubernetes-dashboard-minimal" createdrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io "kubernetes-dashboard-minimal" createddeployment.apps "kubernetes-dashboard" createdservice "kubernetes-dashboard" created
脚本中的 namespace: kube-system 是一个资源,可以通过 kubectl 命令行获取
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> kubectl get namespaceNAME STATUS AGEdefault Active 1ddocker Active 1dkube-public Active 1dkube-system Active 1dPS C:\WINDOWS\system32> kubectl get deploy -n kube-systemNAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGEkube-dns 1 1 1 1 1dkubernetes-dashboard 1 1 1 1 2mPS C:\WINDOWS\system32> kubectl get service -n kube-systemNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGEkube-dns ClusterIP 10.96.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP 1dkubernetes-dashboard ClusterIP 10.106.79.145 <none> 443/TCP 2m
开启API Server的本地监听端口,之后就可以打开控制台
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> kubectl proxyStarting to serve on 127.0.0.1:8001
跳过
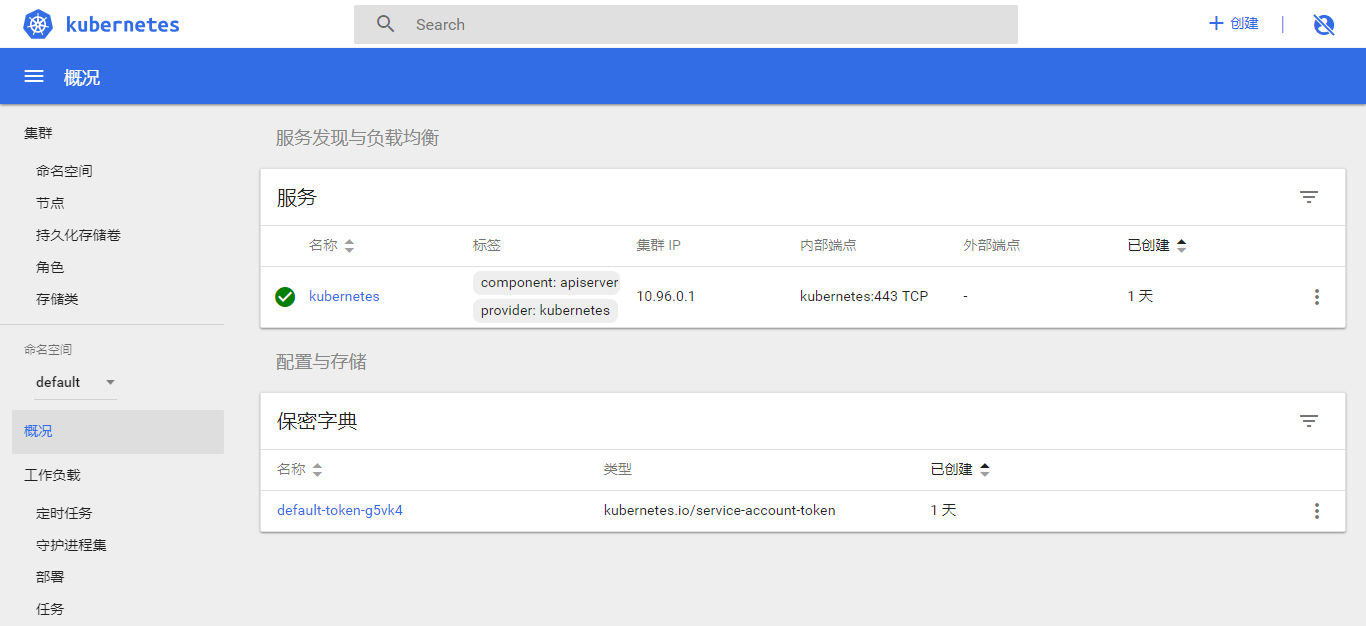
切换命名空间到 kube-system
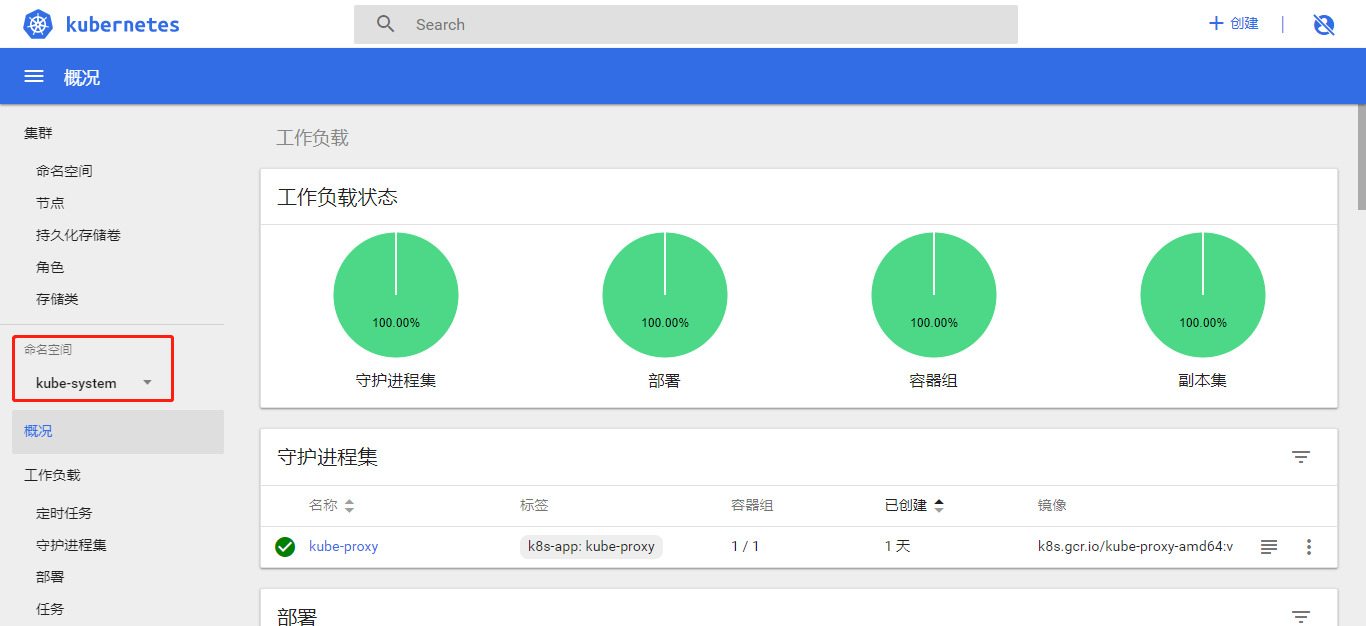
容器组里运行的 dashboard

通过 NodePort 部署
在本地新建一个文件 kubernetes-dashboard.yaml,将脚本(https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/master/src/deploy/recommended/kubernetes-dashboard.yaml)内容保存到本地文件 kubernetes-dashboard.yaml
添加 type: NodePort,nodePort: 30065(端口必须在30000-32767)
# ------------------- Dashboard Service ------------------- #kind: ServiceapiVersion: v1metadata:labels:k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboardname: kubernetes-dashboardnamespace: kube-systemspec:type: NodePortports:- port: 443targetPort: 8443nodePort: 30065selector:k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
删除上面部署的 deploy
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> kubectl get deploy -n kube-systemNAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGEkube-dns 1 1 1 1 1dkubernetes-dashboard 1 1 1 1 52mPS C:\WINDOWS\system32> kubectl delete deploy kubernetes-dashboard -n kube-systemdeployment.extensions "kubernetes-dashboard" deleted
删除服务,使用缩写svc
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> kubectl get svc -n kube-systemNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGEkube-dns ClusterIP 10.96.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP 1dkubernetes-dashboard ClusterIP 10.106.79.145 <none> 443/TCP 53mPS C:\WINDOWS\system32> kubectl delete svc kubernetes-dashboard -n kube-systemservice "kubernetes-dashboard" deleted
再次启动代理
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> kubectl proxyStarting to serve on 127.0.0.1:8001
无法访问

切换到文件所在目录部署deploy
PS D:\jessetalk\k8s> kubectl create -f .\kubernetes-dashboard.yamlservice "kubernetes-dashboard" createdError from server (AlreadyExists): error when creating ".\\kubernetes-dashboard.yaml": secrets "kubernetes-dashboard-certs" already existsError from server (AlreadyExists): error when creating ".\\kubernetes-dashboard.yaml": serviceaccounts "kubernetes-dashboard" already existsError from server (AlreadyExists): error when creating ".\\kubernetes-dashboard.yaml": roles.rbac.authorization.k8s.io "kubernetes-dashboard-minimal" already existsError from server (AlreadyExists): error when creating ".\\kubernetes-dashboard.yaml": rolebindings.rbac.authorization.k8s.io "kubernetes-dashboard-minimal" already existsError from server (AlreadyExists): error when creating ".\\kubernetes-dashboard.yaml": deployments.apps "kubernetes-dashboard" already existsPS D:\jessetalk\k8s> kubectl get service -n kube-systemNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGEkube-dns ClusterIP 10.96.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP 1dkubernetes-dashboard NodePort 10.105.60.55 <none> 443:30065/TCP 33s
浏览器访问:https://127.0.0.1:30065/
由于 dashboard 使用 https,所以假的证书无法访问
08-kubectl工具命令介绍
Kubectl 命令详解
不同 namespace 下的资源(pod, deployment, services)是隔离的
09-yaml部署文件格式介绍
下载 k8s-demo:https://github.com/MINGSON666/k8s-demo.git
Yaml 部署文件详解

--查看解释PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> kubectl explain deployment.metadataKIND: DeploymentVERSION: extensions/v1beta1RESOURCE: metadata <Object>DESCRIPTION:Standard object metadata.ObjectMeta is metadata that all persisted resources must have, whichincludes all objects users must create.FIELDS:annotations <map[string]string>Annotations is an unstructured key value map stored with a resource thatmay be set by external tools to store and retrieve arbitrary metadata. Theyare not queryable and should be preserved when modifying objects. Moreinfo: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/annotationsclusterName <string>The name of the cluster which the object belongs to. This is used todistinguish resources with same name and namespace in different clusters.This field is not set anywhere right now and apiserver is going to ignoreit if set in create or update request.creationTimestamp <string>CreationTimestamp is a timestamp representing the server time when thisobject was created. It is not guaranteed to be set in happens-before orderacross separate operations. Clients may not set this value. It isrepresented in RFC3339 form and is in UTC. Populated by the system.Read-only. Null for lists. More info:https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/api-conventions.md#metadatadeletionGracePeriodSeconds <integer>Number of seconds allowed for this object to gracefully terminate before itwill be removed from the system. Only set when deletionTimestamp is alsoset. May only be shortened. Read-only.deletionTimestamp <string>DeletionTimestamp is RFC 3339 date and time at which this resource will bedeleted. This field is set by the server when a graceful deletion isrequested by the user, and is not directly settable by a client. Theresource is expected to be deleted (no longer visible from resource lists,and not reachable by name) after the time in this field, once thefinalizers list is empty. As long as the finalizers list contains items,deletion is blocked. Once the deletionTimestamp is set, this value may notbe unset or be set further into the future, although it may be shortened orthe resource may be deleted prior to this time. For example, a user mayrequest that a pod is deleted in 30 seconds. The Kubelet will react bysending a graceful termination signal to the containers in the pod. Afterthat 30 seconds, the Kubelet will send a hard termination signal (SIGKILL)to the container and after cleanup, remove the pod from the API. In thepresence of network partitions, this object may still exist after thistimestamp, until an administrator or automated process can determine theresource is fully terminated. If not set, graceful deletion of the objecthas not been requested. Populated by the system when a graceful deletion isrequested. Read-only. More info:https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/api-conventions.md#metadatafinalizers <[]string>Must be empty before the object is deleted from the registry. Each entry isan identifier for the responsible component that will remove the entry fromthe list. If the deletionTimestamp of the object is non-nil, entries inthis list can only be removed.generateName <string>GenerateName is an optional prefix, used by the server, to generate aunique name ONLY IF the Name field has not been provided. If this field isused, the name returned to the client will be different than the namepassed. This value will also be combined with a unique suffix. The providedvalue has the same validation rules as the Name field, and may be truncatedby the length of the suffix required to make the value unique on theserver. If this field is specified and the generated name exists, theserver will NOT return a 409 - instead, it will either return 201 Createdor 500 with Reason ServerTimeout indicating a unique name could not befound in the time allotted, and the client should retry (optionally afterthe time indicated in the Retry-After header). Applied only if Name is notspecified. More info:https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/api-conventions.md#idempotencygeneration <integer>A sequence number representing a specific generation of the desired state.Populated by the system. Read-only.initializers <Object>An initializer is a controller which enforces some system invariant atobject creation time. This field is a list of initializers that have notyet acted on this object. If nil or empty, this object has been completelyinitialized. Otherwise, the object is considered uninitialized and ishidden (in list/watch and get calls) from clients that haven't explicitlyasked to observe uninitialized objects. When an object is created, thesystem will populate this list with the current set of initializers. Onlyprivileged users may set or modify this list. Once it is empty, it may notbe modified further by any user.labels <map[string]string>Map of string keys and values that can be used to organize and categorize(scope and select) objects. May match selectors of replication controllersand services. More info: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/labelsname <string>Name must be unique within a namespace. Is required when creatingresources, although some resources may allow a client to request thegeneration of an appropriate name automatically. Name is primarily intendedfor creation idempotence and configuration definition. Cannot be updated.More info: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/identifiers#namesnamespace <string>Namespace defines the space within each name must be unique. An emptynamespace is equivalent to the "default" namespace, but "default" is thecanonical representation. Not all objects are required to be scoped to anamespace - the value of this field for those objects will be empty. Mustbe a DNS_LABEL. Cannot be updated. More info:http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/namespacesownerReferences <[]Object>List of objects depended by this object. If ALL objects in the list havebeen deleted, this object will be garbage collected. If this object ismanaged by a controller, then an entry in this list will point to thiscontroller, with the controller field set to true. There cannot be morethan one managing controller.resourceVersion <string>An opaque value that represents the internal version of this object thatcan be used by clients to determine when objects have changed. May be usedfor optimistic concurrency, change detection, and the watch operation on aresource or set of resources. Clients must treat these values as opaque andpassed unmodified back to the server. They may only be valid for aparticular resource or set of resources. Populated by the system.Read-only. Value must be treated as opaque by clients and . More info:https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/api-conventions.md#concurrency-control-and-consistencyselfLink <string>SelfLink is a URL representing this object. Populated by the system.Read-only.uid <string>UID is the unique in time and space value for this object. It is typicallygenerated by the server on successful creation of a resource and is notallowed to change on PUT operations. Populated by the system. Read-only.More info: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/identifiers#uids
学习资料
使用YAML创建一个 Kubernetes Depolyment
#deploy.yamlapiVersion: apps/v1kind: Deploymentmetadata:name: k8s-demonamespace: netcorelabels:name: k8s-demospec:replicas: 2selector:matchLabels:name: k8s-demotemplate:metadata:labels:name: k8s-demospec:containers:- name: k8s-demoimage: jessetalk/k8s-demoports:- containerPort: 80imagePullPolicy: Always---kind: ServiceapiVersion: v1metadata:name: k8s-demonamespace: netcorespec:type: NodePortports:- port: 80targetPort: 80selector:name: k8s-demo
- 通过 name 使 Deployment 和 Service 对应
- imagePullPolicy(策略:总是下载最新的镜像)
#通过 yaml 文件创建服务实例PS D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo> kubectl create namespace netcorenamespace "netcore" createdPS D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo> kubectl get namespaceNAME STATUS AGEdefault Active 1ddocker Active 1dkube-public Active 1dkube-system Active 1dnetcore Active 3mPS D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo> kubectl create -f deploy.yamldeployment.apps "k8s-demo" createdservice "k8s-demo" createdPS D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo> kubectl get deploy -n netcoreNAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGEk8s-demo 2 2 2 2 36sPS D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo> kubectl get svc -n netcoreNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGEk8s-demo NodePort 10.104.253.169 <none> 80:30022/TCP 4m
学习资料
10-部署netcore api到K8S
下载 k8s-demo:https://github.com/MINGSON666/k8s-demo.git
PS D:\jessetalk\k8s> dotnet new webapi --name k8s-demo欢迎使用 .NET Core!---------------------若要详细了解 NET Core: https://aka.ms/dotnet-docs请使用 “dotnet --help”查看可用的命令或访问: https://aka.ms/dotnet-cli-docs遥测---------.NET Core 工具收集用法数据,以便帮助改善用户体验。数据是匿名的,且不包括命令行参数。数据由 Microsoft 收集并与社区共享。可使用喜欢的 shell 将环境变量 DOTNET_CLI_TELEMETRY_OPTOUT 设置为 “1” 或 “true”,从而选择推出遥测。若要深入了解 .NET Core CLI 工具遥测,请访问 https://aka.ms/dotnet-cli-telemetryASP.NET Core------------已成功安装 ASP.NET Core HTTPS 开发证书。要信任证书,请运行 "dotnet dev-certs https --trust"(仅限 Windows 和 macOS)。要在其他平台上建立信任,请参阅特定于平台的文档。有关配置 HTTPS 的详细信息,请参阅 https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=848054。正在准备...创建此模板将对现有文件进行更改:覆盖 appsettings.Development.json覆盖 appsettings.json覆盖 k8s-demo.csproj覆盖 Controllers/ValuesController.cs覆盖 Program.cs覆盖 Properties/launchSettings.json覆盖 Startup.cs覆盖 wwwroot重新运行命令并传递 --force 以接受并创建。PS D:\jessetalk\k8s> dotnet dev-certs https --trustTrusting the HTTPS development certificate was requested. A confirmation prompt will be displayed if the certificate was not previously trusted. Click yes on the prompt to trust the certificate.A valid HTTPS certificate is already present.PS D:\jessetalk\k8s> dotnet new webapi --name k8s-demo --force已成功创建模板“ASP.NET Core Web API”。正在处理创建后操作...正在 k8s-demo\k8s-demo.csproj 上运行 "dotnet restore"...正在还原 D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo\k8s-demo.csproj 的包...正在生成 MSBuild 文件 D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo\obj\k8s-demo.csproj.nuget.g.props。D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo\k8s-demo.csproj 的还原在 2.72 sec 内完成。还原成功。PS D:\jessetalk\k8s> cd k8s-demo#用 vscode 打开文件PS D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo> code .
修改 ValuesController
// GET api/values/5[HttpGet("{id}")]public ActionResult<string> Get(int id){return id.ToString();}
在 VSCode 中 View =》Terminal 输入 dotnet run 本地跑起来
PS D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo> dotnet run
浏览器地址栏输入:https://localhost:5001/api/values/1 看到结果为1
新建一个 Dockerfile
FROM microsoft/dotnet:2.1-aspnetcore-runtime AS baseWORKDIR /appEXPOSE 80FROM microsoft/dotnet:2.1-sdk AS buildWORKDIR /srcCOPY . .RUN dotnet restoreRUN dotnet build -c Release -o /appFROM build AS publishRUN dotnet publish -c Release -o /appFROM base AS finalWORKDIR /appCOPY --from=publish /app .ENTRYPOINT ["dotnet", "k8s-demo.dll"]
在 VSCode 终端 build
PS D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo> docker build -t jessetalk/k8s-demo .
build 成功
Successfully built e143b4e67d1eSuccessfully tagged jessetalk/k8s-demo:latest
查看一下镜像,有一个 jessetalk/k8s-demo
PS D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo> docker imagesREPOSITORY TAG IMAGE IDCREATED SIZE<none> <none> ff94f468e5772 minutes ago 1.73GBjessetalk/k8s-demo latest e143b4e67d1e24 hours ago 253MB
run ,端口8085映射到80
PS D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo> docker run -d -p 8085:80 --name k8s-demo jessetalk/k8s-demoa441b03ac073fab5139b3a679b35a6e6260fc595916978137acb6a555ed462b5
查看结果
PS D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo> docker psCONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMESa441b03ac073 jessetalk/k8s-demo "dotnet k8s-demo.dll" 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 0.0.0.0:8085->80/tcp k8s-demof8af1ff029a4 jessetalk/k8s-demo "dotnet k8s-demo.dll" 2 hours ago Up 2 hours k8s_k8s-demo_k8s-demo-7d9787fcb9-lnnrp_netcore_0e765fb2-f70c-11e8-8043-00155d0b9215_4c9fffde727a3 jessetalk/k8s-demo "dotnet k8s-demo.dll" 2 hours ago Up 2 hours k8s_k8s-demo_k8s-demo-7d9787fcb9-jz2hs_default_73dadea3-f70b-11e8-8043-00155d0b9215_4518f280971f9 jessetalk/k8s-demo "dotnet k8s-demo.dll" 2 hours ago Up 2 hours k8s_k8s-demo_k8s-demo-7d9787fcb9-m8slt_default_73e5e434-f70b-11e8-8043-00155d0b9215_4c28b5b43b967 jessetalk/k8s-demo "dotnet k8s-demo.dll" 2 hours ago Up 2 hours k8s_k8s-demo_k8s-demo-7d9787fcb9-2j8hx_netcore_0e6fbfca-f70c-11e8-8043-00155d0b9215_4
浏览器访问:http://localhost:8085/api/values
得到返回值:["value1","value2"]
登陆 docker
PS D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo> docker login --username mingsonzhengPassword:Login Succeeded
推送镜像(推送前先修改为自己的用户名)
PS D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo> docker tag jessetalk/k8s-demo mingsonzheng/k8s-demoPS D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo> docker push mingsonzheng/k8s-demoThe push refers to repository [docker.io/mingsonzheng/k8s-demo]3629f42d7187: Pushed0bb37faafa32: Pushedb29986f25fdb: Pushedb116468880ac: Pushed57bda236ae67: Pushedef68f6734aa4: Pushedlatest: digest: sha256:b3dab95b049d2308e2cd94af35dbfeb9c955011a63c1f1caf49faab6ae9d36ff size: 1579
推送完成后可以看到自动创建的仓库 k8s-demo
快速部署 k8s-demo
PS D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo> kubectl create -f deploy.yamlservice "k8s-demo" createdPS D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo> kubectl get svc -n netcoreNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGEk8s-demo NodePort 10.101.30.110 <none> 80:30585/TCP 1m
根据端口号访问本地 k8s 服务:
http://127.0.0.1:30585/api/values
http://127.0.0.1:30585/api/values/1
http://127.0.0.1:30585/api/values/2
通过 dashboard 查看
PS D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo> kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/master/src/deploy/recommended/kubernetes-dashboard.yamlsecret "kubernetes-dashboard-certs" createdserviceaccount "kubernetes-dashboard" createdrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io "kubernetes-dashboard-minimal" createdrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io "kubernetes-dashboard-minimal" createddeployment.apps "kubernetes-dashboard" createdservice "kubernetes-dashboard" created
启动代理
PS D:\jessetalk\k8s\k8s-demo> kubectl proxyStarting to serve on 127.0.0.1:8001
切换命名空间 netcore,可以看到部署的 k8s-demo

点击容器组,选择一个容器组,点击日志按钮查看日志
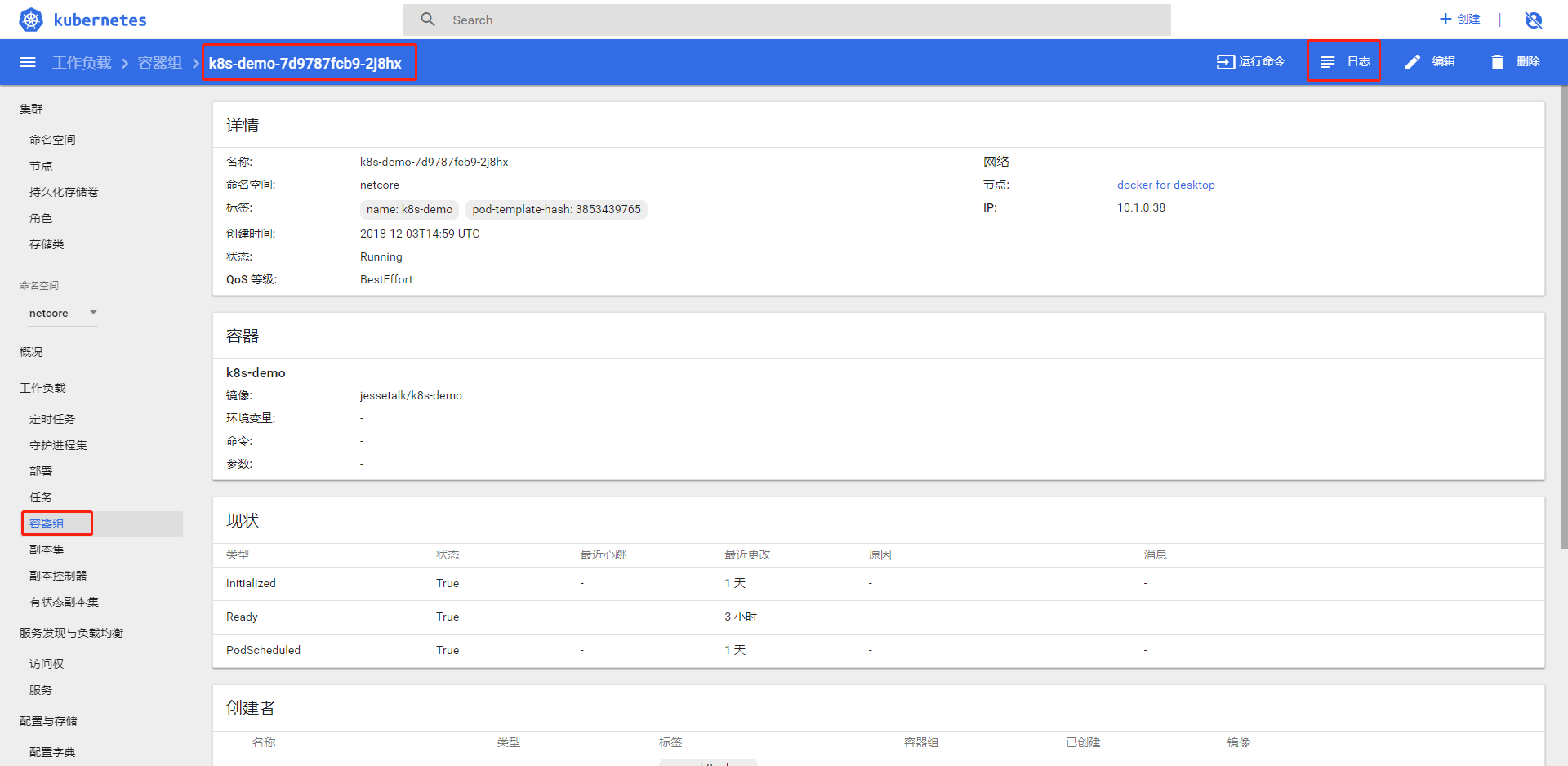
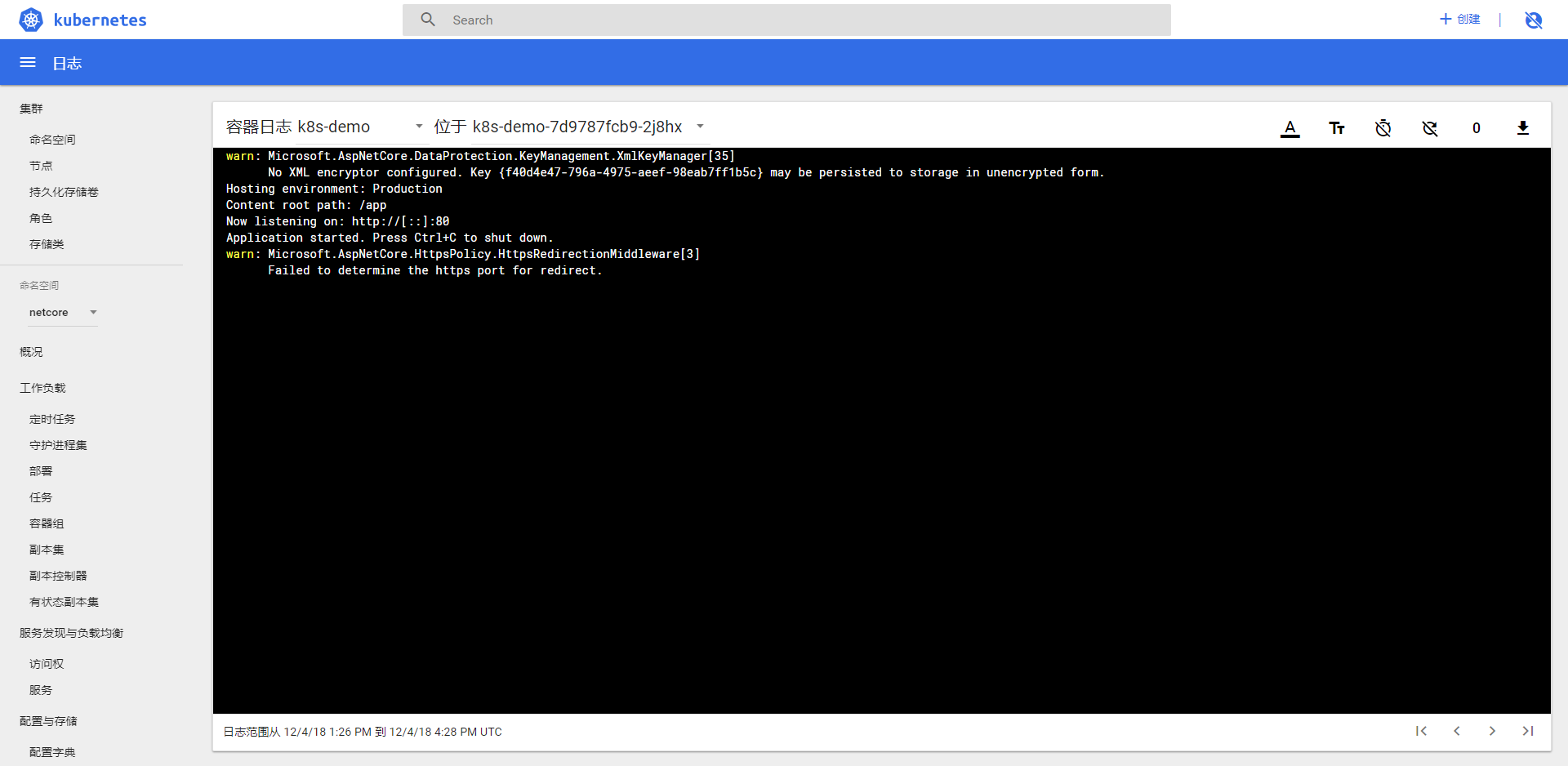
点击运行命令进入 docker 的命令行
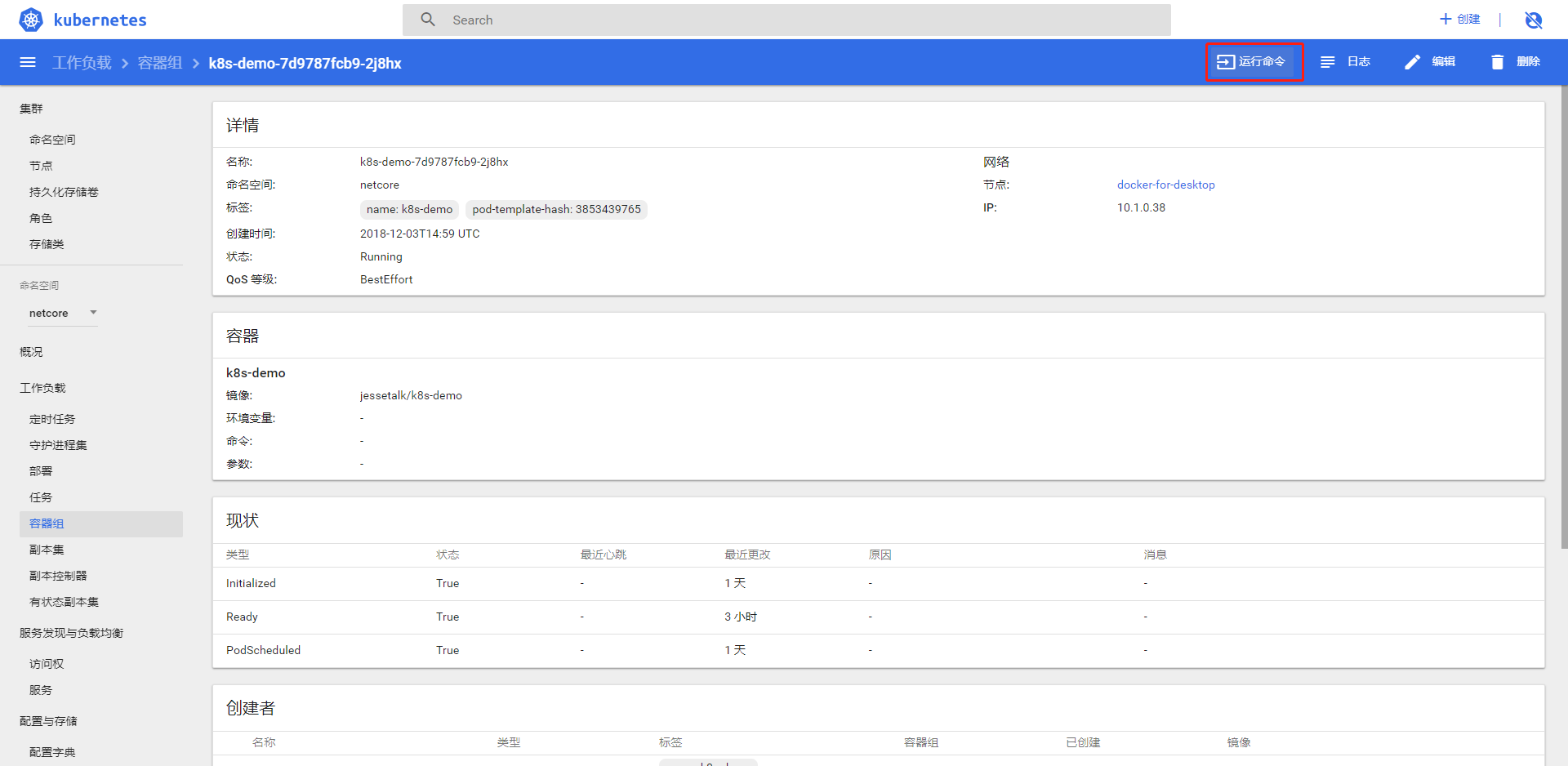
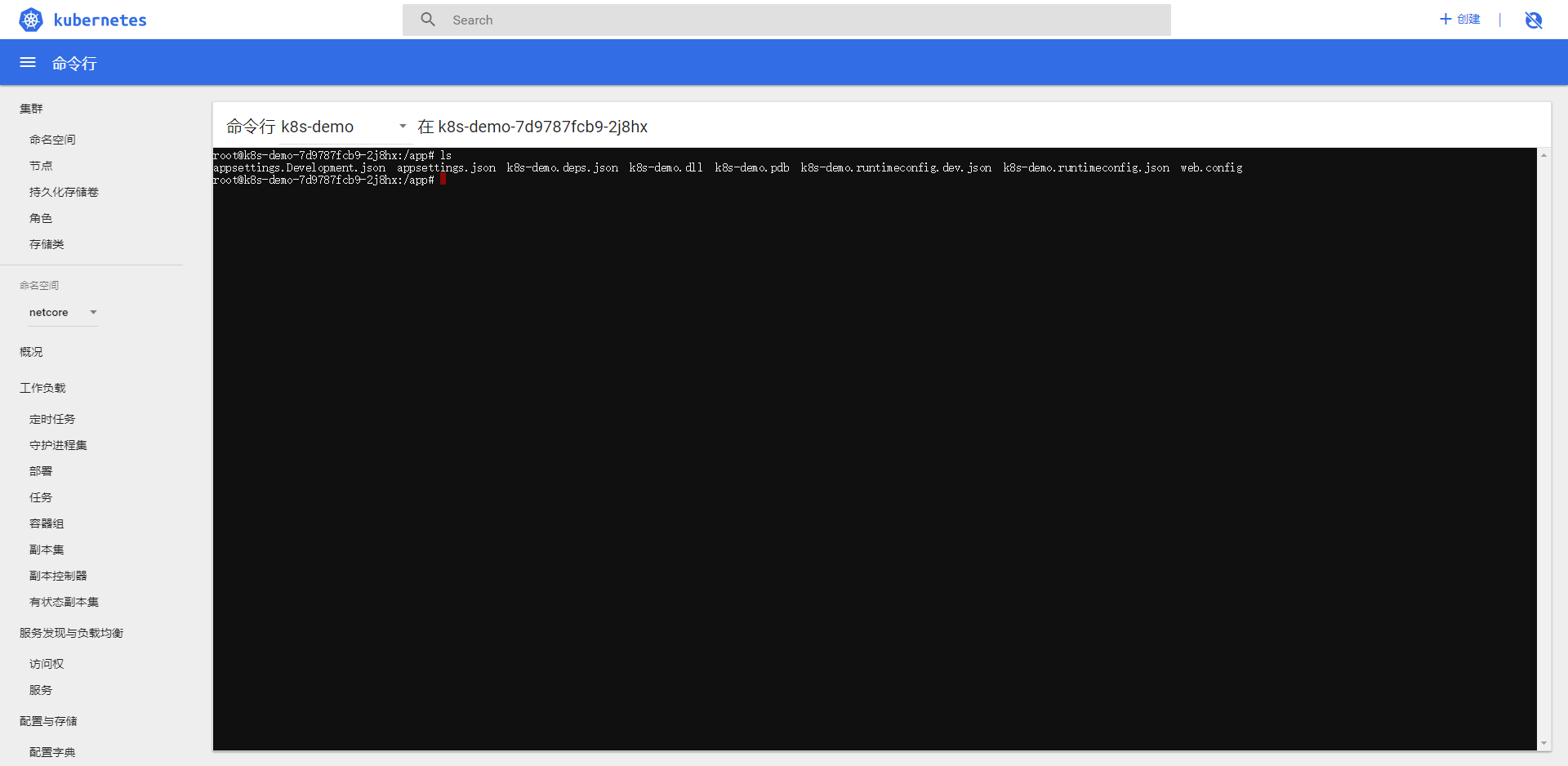
11-k8s高可用集群介绍
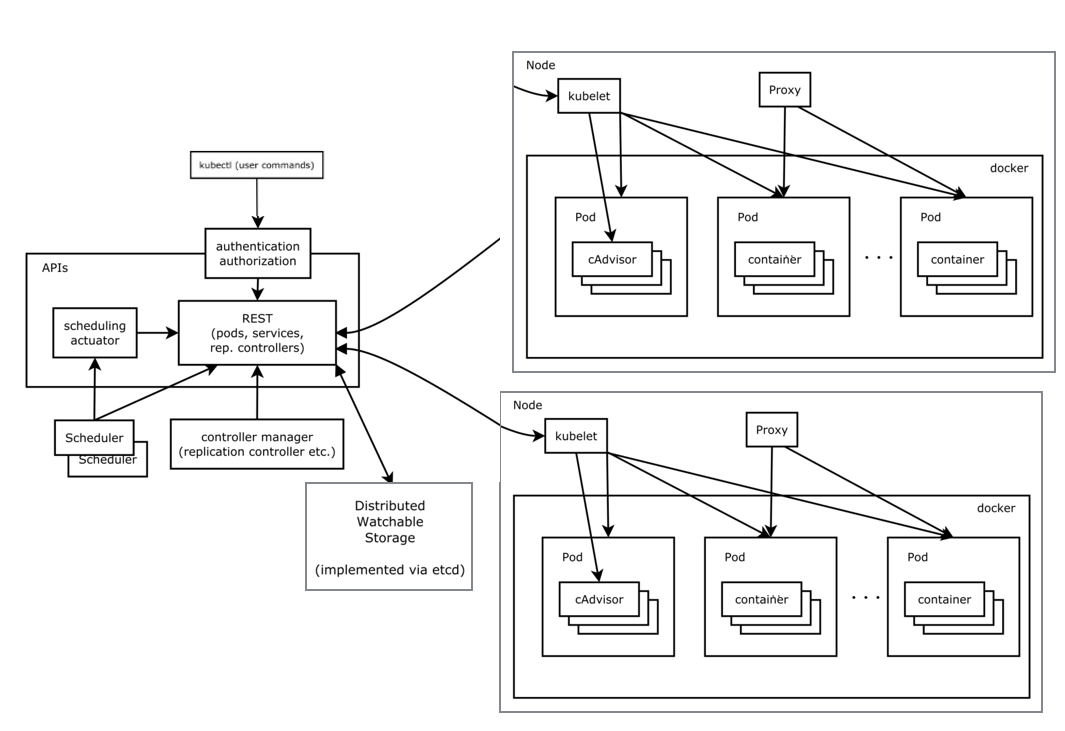
- 一个集群分为多个 Node (worker节点),左侧为 master 节点
- 每个节点上安装一个 kubelet ,与 docker 交互,负责每个 Pod 的创建、删除等
- 外部 service 访问通过 Proxy
- k8s 所有资源,数据存储在分布式数据库 etcd
- Scheduler 负责资源调度,根据 Node 负载情况选择 Node 分配任务
k8s 核心组件
- etcd 保存了整个集群的状态;
- api server 提供了资源操作的唯一入口,并提供认证、授权、访问控制、API注册和发现等机制;
- controller manager 负责维护集群的状态,比如故障检测、自动扩展、滚动更新等;
- scheduler 负责资源的调度,按照预定的调度策略将Pod调度到相应的机器上;
- kubelet 负责维护容器的生命周期,同时也负责Volume(CVI)和网络(CNI)的管理;
- container runtime 负责镜像管理以及Pod和容器的真正运行(CRI);
- kube-proxy 负责为Service提供cluster内部的服务发现和负载均衡;
k8s 调度过程
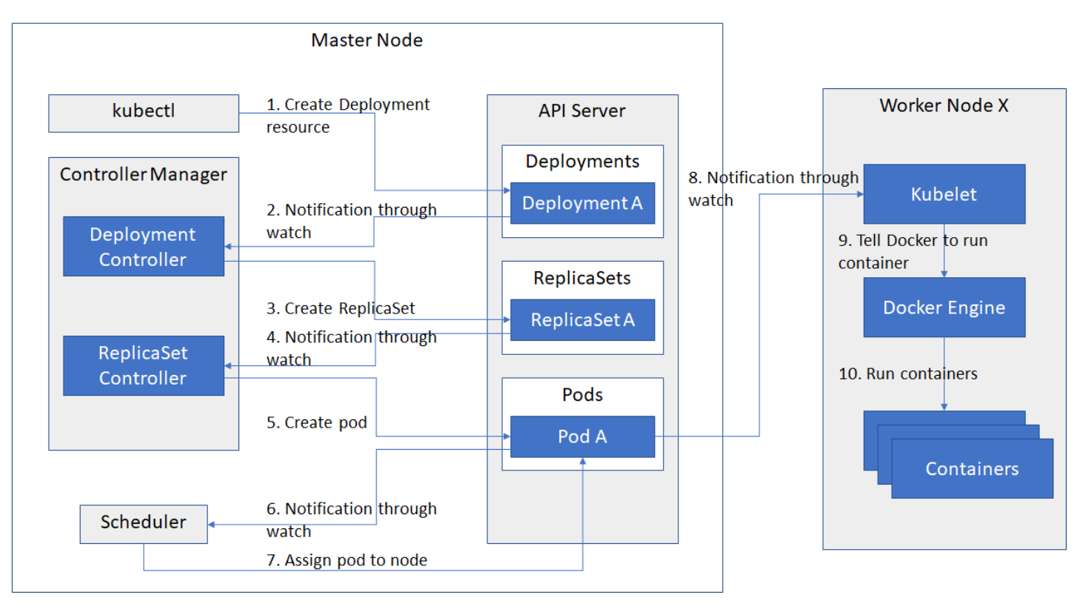
- API Server 异步请求
- ReplicaSets 副本管理
- 所有数据保存在 etcd
- 如果 MasterNode 出现问题,整个集群会挂掉
k8s 高可用集群
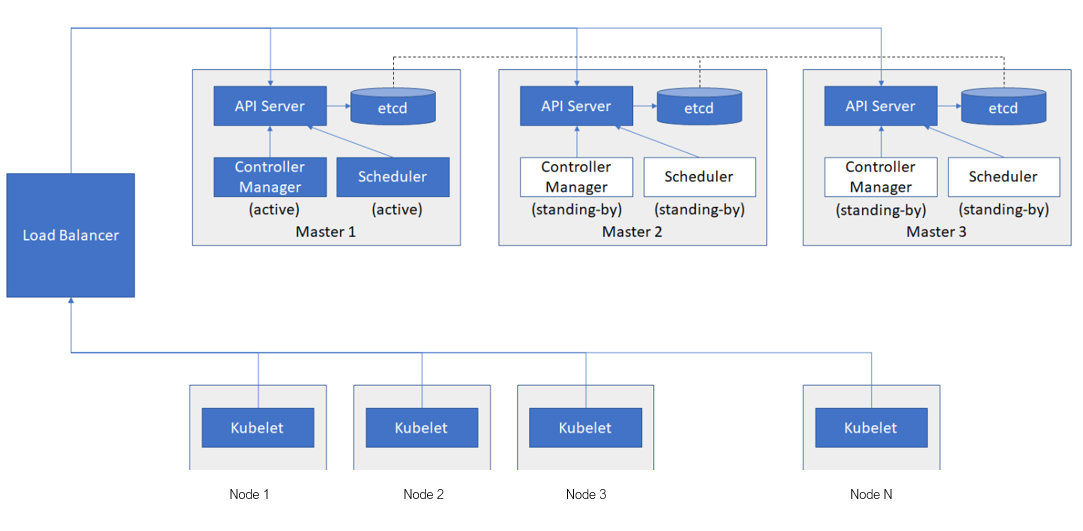
- 一般需要3台 MasterNode,Node 最多25台(与 IP 地址限制有关)
- etcd 数据库会进行数据同步,通过选举算法选举 leader
12-进阶介绍



本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。
欢迎转载、使用、重新发布,但务必保留文章署名 郑子铭 (包含链接: http://www.cnblogs.com/MingsonZheng/ ),不得用于商业目的,基于本文修改后的作品务必以相同的许可发布。
如有任何疑问,请与我联系 (MingsonZheng@outlook.com) 。
.NET Core on K8S快速入门课程--学习笔记的更多相关文章
- .NET Core on K8S快速入门课程学习笔记
课程链接:http://video.jessetalk.cn/course/explore 良心课程,大家一起来学习哈! 目录 01-介绍K8s是什么 02-为什么要学习k8s 03-如何学习k8s ...
- 【笔记目录2】【jessetalk 】ASP.NET Core快速入门_学习笔记汇总
当前标签: ASP.NET Core快速入门 共2页: 上一页 1 2 任务27:Middleware管道介绍 GASA 2019-02-12 20:07 阅读:15 评论:0 任务26:dotne ...
- 【笔记目录1】【jessetalk 】ASP.NET Core快速入门_学习笔记汇总
当前标签: ASP.NET Core快速入门 共2页: 1 2 下一页 任务50:Identity MVC:DbContextSeed初始化 GASA 2019-03-02 14:09 阅读:16 ...
- ASP.NET Core快速入门_学习笔记汇总
第2章 配置管理 任务12:Bind读取配置到C#实例 任务13:在Core Mvc中使用Options 任务14:配置的热更新 任务15:配置框架设计浅析 第3章 依赖注入 任务16:介绍- 任务1 ...
- SpringMVC插件安装、环境配置及快速入门_学习笔记
SpringMVC 是现在广泛应用的框架结构,我也只是一个初学者,一遍学习一遍梳理整合,如有错误,希望大神指点,别误人. MVC :Model-View-Control 框架性质的C 层要完成的主要工 ...
- 零基础快速入门web学习路线(含视频教程)
下面小编专门为广大web学习爱好者汇总了一条完整的自学线路:零基础快速入门web学习路线(含视频教程)(绝对纯干货)适合初学者的最新WEB前端学习路线汇总! 在当下来说web前端开发工程师可谓是高福利 ...
- 菜鸟系列k8s——k8s快速入门(1)
k8s快速入门 1.快速创建k8s集群 参考网站:https://kubernetes.io/docs/tutorials/kubernetes-basics 点击教程菜单 1. Create a C ...
- Webpack新手入门教程(学习笔记)
p.p1 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; text-align: center; font: 30.0px Helvetica; color: #000000 } ...
- 一个数学不好的菜鸡的快速沃尔什变换(FWT)学习笔记
一个数学不好的菜鸡的快速沃尔什变换(FWT)学习笔记 曾经某个下午我以为我会了FWT,结果现在一丁点也想不起来了--看来"学"完新东西不经常做题不写博客,就白学了 = = 我没啥智 ...
随机推荐
- C# QRBarCode
1. install-package barcode -v 4.0.2.2; 2. using IronBarCode; class Program { static void Main(string ...
- Delphi - 创建SuperDll 持续更新
Delphi SuperDll 作为一名5年的Delpher,一直认为Delphi是桌面应用的王者,我相信其他的Delpher也这么认为. 但是,慢慢的我发现普通方式的Delphi开发会造成代码的严重 ...
- Z从壹开始前后端分离【 .NET Core2.2/3.0 +Vue2.0 】框架之九 || 依赖注入IoC学习 + AOP界面编程初探
本文梯子 本文3.0版本文章 更新 代码已上传Github+Gitee,文末有地址 零.今天完成的绿色部分 一.依赖注入的理解和思考 二.常见的IoC框架有哪些 1.Autofac+原生 2.三种注入 ...
- 学习Python前言
先介绍下自己: 我是小芒果,在一家互联网公司上班 目前担任的是测试工程师职 自工作开始至今,已经3年之载 一路过来倒也轻松 期间学过几次python没一次能坚持下来 随着行业的饱和 测试技术的要求 以 ...
- JAVA 设置模块间的依赖关系
项目目录概况 Demo01项目 Test01.java package com.sam.demo01; public class Test01 { public void ShowTest01() { ...
- KB奇遇记(3):糟糕的IT现状
2015年8月3号,终于告别了过去来到了KB. 公司给安排的住房是一间套房里的小房间,小的简直连坐的地方都没有了,中间一个大床将房间隔了两边,显得特别狭小.由于是刚来,我也不好要求太多.但就这个小房间 ...
- golang的析构函数
runtime.SetFinalizer 使用这个函数可以给一个对象设置一个析构函数,如果这个对象没有引用了,那么就会调用这个析构函数,然后会把这个对象给释放掉
- sleep() 和 wait() 有什么区别:
①原理不同. sleep()方法是Thread类的静态方法,是线程用来控制自身流程的,它会使此线程暂停执行一段时间,而把执行机会让给其他线程,等到计时时间一到,此线程会自动苏醒.而wait() ...
- AtCoder - 2282 (思维+构造)
题意 https://vjudge.net/problem/AtCoder-2282 告诉你sx,sy,tx,ty,问从s走到t,再从t走到s,再从s走到t,再从t回到s的最短路,每次只能上下左右选一 ...
- Java 种15种锁的介绍:公平锁,可重入锁,独享锁,互斥锁等等…
Java 中15种锁的介绍 1,在读很多并发文章中,会提及各种各样的锁,如公平锁,乐观锁,下面是对各种锁的总结归纳: 公平锁/非公平锁 可重入锁/不可重入锁 独享锁/共享锁 互斥锁/读写锁 乐观锁/悲 ...
